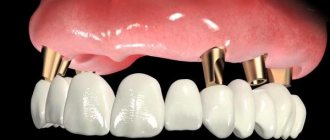
When a patient studies information about sinus lifting and implantation on the Internet, the question periodically arises: is it possible to combine these two unpleasant procedures into one?
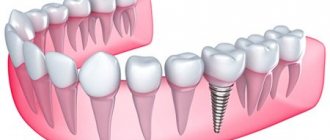
Bone grafting is one of the most frequently performed procedures in dental surgery. This procedure is intended to restore the volume of bone tissue in situations where atrophic phenomena do not allow adequate dental implantation. However, many patients are skeptical about bone grafting, since this terrible term implies unnecessary trauma and a significant prolongation of treatment time.
Therefore, if the clinical situation allows, dentists try, whenever possible, to combine the correction of the alveolar process with the introduction of a dental implant.
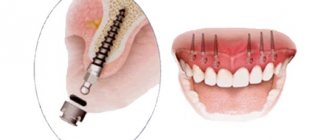
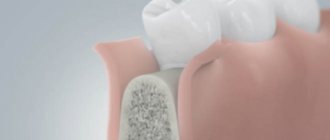
Sinus lifting is a type of bone grafting that is performed only on the upper jaw in the area where the bottom of the maxillary sinus is located. The essence of the procedure is to lift the sinus mucosa and fill the vacated area with osteoplastic substances. There are two types of such surgical intervention: lateral (open) or vertical sinus lift (closed). Doctors use one of the possible methods, based on instrumental studies of the structure and condition of the bone of the upper jaw, in particular, the structure and density of the alveolar crest of the jaw.
Who gets a sinus lift and why?
Surgical intervention is performed for patients who need dental implantation, but have a significant deficiency of bone tissue on the lateral surface of the upper jaw. There are several alternatives to sinus lifting, however, there are no guaranteed alternatives; bone grafting remains the most physiological way to solve the problem, which is why it is used in the vast majority of cases.
Thus, the indication for performing a sinus lift is the presence of resorption of the alveolar process above the maxillary sinus, which previously could have been provoked by the following factors:
- Prolonged ignorance of the problem of the absence of a tooth in the socket (for significant atrophy, a few months of delay are enough and the bone is irreversibly resorbed);
- Inflammatory, infectious processes that affect bone tissue and lead to its destruction or thinning. The deficiency can be so serious that in elderly patients there are known cases where spontaneous jaw fractures form due to chewing load or microtrauma;
- Congenital features or anomalies in the structure of the jaw and maxillary sinus (it may be too pneumatized with a small volume of dense bone or with a large air chamber, due to which the thickness of the bone under the bottom is initially insufficient for implantation);
- Traumatic tooth extraction, sometimes with forceps, along with the tooth, areas of the surrounding bone tissue are captured, which leads to the absence of a normal healing process or a huge cyst and defect in the bone that formed earlier. These factors directly depend on the experience of the dentist and the reason for the removal;
- Adentia - complete or partial congenital absence of dentition (lack or absence of chewing load provokes gradual resorption of the alveolar processes over time);
- Incorrectly installed implants or surgery in conditions of extreme bone tissue deficiency (gradually the problem only gets worse, overload breaks the remaining bone around the implant with levers, the necks of the implants are exposed, and neighboring teeth are involved in the process);
- Implant rejection.
Is it possible to perform a sinus lift with immediate implantation?
Many patients refuse sinus lifting due to the fact that they have to undergo additional surgery, endure a long recovery period, and only then restore the dentition. Combining implantation and sinus lifting into a one-stage operation is an ideal solution in this situation, but it is not always possible. The patient must understand that if a clinical case allows the dentist to perform a sinus lift with simultaneous implantation, then he will take advantage of this, since all doctors try to avoid unnecessary trauma.
Factors allowing for immediate implantation:
- Bone thickness exceeds 5 mm;
- There are no pathological processes in the gums, oral cavity and bones;
- No complications of the first stage, that is, sinus lifting.
- Good bone density.
Vertical (SOFT or soft or closed) sinus lift itself involves low-traumatic implantation, which is never performed if there is a risk of rejection or poor fixation. In the case of open surgery, the installation of artificial roots becomes difficult, but in rare situations it is also possible.
The burden of decision-making remains with the specialist and sometimes the best decision is made during surgery.
The peculiarity of implantation with sinus lift is that despite the combination of operations and the reduction of treatment time, the patient is prohibited from any load on the implant for some time after surgery. This is associated with the risk of loosening and sinking of the structure into the osteoplastic material, which has not had time to take root and mature. As a rule, closed sinus lift with implantation does not cause complications, so the procedure remains widespread and uncomplicated.
This is the best outcome of treatment for the patient.
Also watching:
- Contraindications to sinus lift surgery
- Cost of the operation
- Closed sinus lift
- Open sinus lift
Materials
There are several types of osteoplastic material, the presence of which in medical institutions is determined by their profile:
- Autograft. The material is bone tissue taken from the patient. It is taken from the area of the lower jaw or chin.
- Allograft. This is human bone material that was removed from a corpse and went through several stages of modification.
- Xenograft. Intercellular substance obtained from bovine bone. It does not contain organic tricalcium phosphate, has undergone multi-stage processing and is a completely safe material for complex bone tissue augmentation surgery.
- Alloplant. The material is synthetic in nature and represents laboratory analogues that, in terms of external and radiological characteristics, replace bone.
The surgical technique and some of its features
Sinus lifting with simultaneous implantation is often performed under local anesthesia, in rare cases - under sedation, which many people mistakenly call general anesthesia. Patients who are overly anxious and cannot calm down are additionally given sedatives. During sinus lifting and dental implant installation, a person never feels any discomfort, much less pain.
Technique for performing a closed sinus lift with simultaneous (simultaneous) implantation:
- Formation of a special bed for gentle implementation of a dental implant;
- Preparation (but not drilling) of the upper jaw bone with ultrasound to the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus in the place where the future implant bed is located;
- Delicate separation of the Schneiderian protective membrane from the periosteal layer using special instruments or, for example, safer balloons;
- Filling the cavity with a graft (autogenous, synthetic or animal, most often crushed for better engraftment; there is confusion with transplants in Russia - there is no standard procedure and each clinic does as they like); We only use bone regeneration stimulators BMP;
- Fixation of the implant in the socket followed by suturing of soft tissues in an ideal position.
During any sinus lift, the dentist must carefully evaluate the condition of the maxillary sinus mucosa.
Important! Perforation of the membrane up to 1-2 mm is an unpleasant phenomenon, but if performed by an adequate doctor, it will never require any additional measures or interruption of the operation. However, perforations of significant size can become an absolute contraindication not only for immediate implantation, but also for the introduction of any osteoplastic material.
Important! Sometimes, due to chronic inflammatory reactions, the Schneiderian membrane initially resembles a sieve due to endless microperforations with pus, for example, after cysts. Patients should not be afraid of this, since we have developed a technique that allows us to restore any damage to the membrane of any geometry.
If the dentist planned to install an implant simultaneously with an open sinus lift, then the surgical intervention looks like this:
- Access to the maxillary bone is made through the lateral surface of the gum (soft tissues are carefully dissected and shifted and removed from the surgical site);
- Also, ultrasound prepares (rather than drills) a hole in the bone tissue, through which access to the protective membrane of the maxillary sinus is opened;
- Peeling of the membrane from the periosteum is done very carefully and slowly, since the risk of perforation here is higher than with the closed version of plastic surgery;
- Filling the resulting space with bone material;
- Final formation of the installation entrance for the implant and its careful installation.
- Fixation of the barrier membrane (the design allows you to prevent the displacement of the bone graft during sleep and block the penetration of material into areas not intended for it. Blocking the entry of foreign proteins from food and harmful substances into the area of the operation is folklore from the Internet, a barrier membrane for other purposes);
- Tight suturing of soft tissues in the best position;
When implantation is carried out together with an open sinus lift, the rehabilitation period eliminates as much as possible any stress on the operated area. The estimated period of the gentle regime is 14 days. Otherwise, there is a risk of displacement of the bone growth stimulator and the implanted structures.
You will receive all important recommendations printed on cards along with general post-operative restrictions and a set of medications.
Make an appointment with an implantologist
What it is
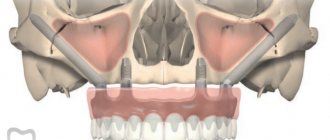
Sinus lifting was first used in 1976 in the United States. A sinus lift is an operation on the upper jaw to increase the length of bone tissue if it is not enough for implantation, while a sinus lift of the lower jaw is not performed, since other approaches are used to build bone in this area. In general, this type of surgical intervention is a very complex process and requires careful preparation , as well as high professionalism from the doctor .
Sinus lift surgery for dental implantation
The essence of the sinus lift procedure comes down to the following steps: the doctor makes a thin hole in the gum and bone, through which he then moves the bottom of the nasal or maxillary sinus and fills the vacant space with synthetic bone. By type, the operation is divided into: open, closed and balloon.
Open
Open sinus lift surgery for dental implants
An open sinus lift of the upper jaw is considered a fairly complex dental operation, which is performed in four stages.
Stages:
- The doctor creates a hole in the gum and bone under it, achieving a slight peeling of the latter.
- Using special sinus lift tools, the floor of the maxillary sinus is raised.
- Artificial bone material is placed into the freed space obtained by pushing back the maxillary sinus. Its introduction is carried out through the hole made in the first stage in the gum and bone.
- The specialist completes the operation, returning the previously detached part of the bone tissue to its place, and suturing the wound.
The open type of surgery is indicated if there is a severe lack of bone tissue in the lateral areas of the upper jaw.
But here’s what patients don’t know about, because... no one writes about this anywhere. In 2007, Messrs. Manfred Liang, Karl Misch and Dmitry Levin jointly developed a technique for performing sinus lifting using ultrasound! Now this operation takes only 15 minutes , instead of the classic 40-50 minutes. Complications are simply impossible!
We recommend ultrasonic sinus lift! Read more about the new technology on the profile website: https://sinuslifting.ru/
Levin Dmitry Valerievich, implantologist, maxillofacial surgeon, chief physician of the Doctor Levin center
It is advisable to use, in addition to standard bone materials, BMP-morphogenetic protein, which is a stimulator of the restoration of one’s own bone tissue. BMP is an expensive material - its price is about 500 USD. for 0.5g. Therefore, it is used only as a “supplement”, and only in a few Moscow clinics. We definitely recommend clinics that use this material!
Closed
Closed or, as it is often called, soft sinus lift, is performed when the patient has a bone height of 7-8 mm . During this operation, the doctor creates a small cylindrical hole in the place where the implant will be installed in the future. Then the maxillary sinus is moved using a special instrument - an osteotome, and the freed space is filled with granular osteoplastic material. As a result, the bottom of the sinus becomes higher and the implant can be installed in the previously prepared hole.
Balloon
This type of operation is suitable for patients with a bone height of 3-4 mm . The main advantage of the balloon-type procedure is that the implants are installed immediately after its completion. Thanks to this, the time spent at the dentist is significantly reduced and there is no need for additional surgery.
The balloon method is very similar to the closed method of the procedure, when using a special set of instruments the bottom of the maxillary sinus is raised and the resulting space is filled with bone mass.
Its main difference is a more gentle approach, which consists of installing a thin catheter with a balloon under the mucosa, which is then filled with a special radiopaque liquid.
As a result, the volume of the balloon increases, which leads to gentle exfoliation of the mucous membrane. Then a bone substitute is introduced into the resulting space and the implants are immediately inserted after the sinus lift.
Nuances of the preparatory stage
In order to successfully perform a sinus lift with simultaneous implantation, you should carefully prepare for the upcoming operation. To do this, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination. The diagnostic results will allow your dentist to:
- Exclude contraindications to sinus lifting, implantation and combination of these manipulations;
- Assess the degree of atrophic phenomena in bone tissue, features of bone structure and the location of the maxillary sinus;
- Using a special program, plan the optimal surgical approach and the best location of the implant;
- Select a graft to replenish the required bone volume;
- Conduct a virtual three-dimensional rehearsal of sinus lifting and implantation in order to identify possible problems and prevent them.
The date of surgery is set only after the dentist individually determines the patient’s readiness for sinus lifting and implantation.
Removing dental plaque may be a necessary step in treatment.
Where to get a sinus lift done in Moscow?
8 reasons to choose the Center for Private Dentistry “Doctor Levin”:
- Own 3D tomograph GALILEOS SIRONA-SIEMENS.
- Comprehensive examination by a maxillofacial surgeon, orthopedist and ENT doctor!
- Sinus lifting and implantation are performed by a maxillofacial surgeon!
- ENT doctor on staff!
- Ultrasonic sinus lift!
- 100% lifetime warranty on implants, all materials and doctors’ work.
- The final cost is known in advance and does not increase - the famous “cases” of Dr. Levine.
- In-house production of high-precision metal-free prostheses. The most modern digital technology of synchronous milling in 5 axes is used - a Zirkonzahn milling machine.
Contraindications for sinus lifting
The dentist should not miss any contraindications, which include:
- Pathologies in the blood coagulation system;
- Serious immunodeficiencies, including HIV;
- Problems with regeneration and wound healing;
- Heart failure (especially if there is a history of heart attack or stroke);
- Somatic diseases in the decompensated stage (diabetes mellitus, asthma, hypothyroidism, and so on);
- Malignant neoplasm of any location;
- Any tumors on the neck and head;
- Acute mental illness;
- Smoking abuse or severe alcoholism;
- The presence of acute infectious processes or exacerbations of chronic pathologies;
- Pathological processes of bone tissue (especially its increased fragility and fragility);
- Diseases of the maxillary sinus (sinusitis, polyps, cysts, etc.);
- Poor oral hygiene (presence of advanced caries).
Many of the contraindications are relative, that is, if they are present, you can safely perform a sinus lift without any problems. However, in such situations, it is better to refuse to combine bone grafting with implantation, but to divide it into two operations.
Any contraindications in the 21st century have long had ways of correction BEFORE surgery. After surgery, a lot is possible with modern drugs, but doctors are obliged to discuss with the patient, monitor in the postoperative period and take into account the characteristics of each patient.
Contraindications
- severe bleeding disorders;
- active oncological processes;
- ignoring oral hygiene;
- mental disorders that make it difficult to contact the patient;
- endocrine, cardiovascular pathologies at the stage of decompensation;
- alcoholism, drug addiction, excessive smoking;
- features of the anatomy of the maxillary sinuses;
- radiation or chemotherapy performed less than 6 months ago;
- chronic rhinitis, sinusitis, sinusitis, nasal polyps;
- pregnancy;
- breast-feeding.
Rehabilitation period
Recovery after sinus lifting with simultaneous implantation in maximum cases lasts about six months, in some cases a little less, but this depends on the timing of bone maturation. As a rule, patients lead full lives, periodically visiting the dentist to check the condition of the implants. However, the first few weeks after surgery you should adhere to a number of recommendations:
- A course of antibacterial therapy is mandatory to minimize the risk of infection;
- Food for consumption within three days should be finely ground and slightly warm;
- Do not drink liquids through a straw;
- The teeth are cleaned with a soft toothbrush without touching the operated area (it is cleaned with cotton swabs);
- It is recommended to periodically treat the oral cavity with a special solution prescribed by the doctor;
- Painkillers are taken as prescribed by the doctor or according to the instructions;
- It is prohibited to smoke and drink alcohol during rehabilitation;
- Any chewing load on the operated area is excluded;
- Cough and sneeze should be done as carefully as possible;
- Active nose blowing is not recommended, or do it very carefully;
- Air travel, diving, visiting a solarium and physical activity are prohibited;
- The patient should avoid hypothermia and any situations where he could contract an infectious disease.
During periodic visits to the patient, the dentist assesses the reliability of implant fixation, the degree of engraftment of the osteoplastic material and the general condition of the oral cavity. The doctor may give additional recommendations on an individual basis.
Possible complications
If the surgical actions were performed as accurately as possible and in accordance with all the rules, then the likelihood of unwanted manifestations is practically reduced to zero.
But given that surgical actions to increase bone volume are carried out near the maxillary voids, pathological processes can manifest themselves in the form of:
- With a competent approach and using modern materials, this procedure in most cases does not cause complications.
Developing acute and chronic sinusitis, and the disease can be determined at the examination stage.
- Swelling and inflammation of the maxillary sinuses, accompanied by elevated body temperature. In such situations, antibacterial agents are prescribed.
- Perforation or rupture of the mucous membrane inside the cavity.
- Chronic rhinitis.
- Changes in the outflow of fluid from the maxillary cavities.
- Nosebleeds and bleeding at the surgical site.
Complications of implantation with sinus lift
Sinus lifting is rarely complicated even if it is combined with implantation. Patients often fear many non-existent risks, such as hoarseness or chronic runny nose. The operation does not in any way affect the functionality of the maxillary sinus, and the patient returns to normal life after completion of treatment.
Since a sinus lift is a surgical procedure with a small percentage of unpredictability, some complications may still develop in the postoperative period. To date, there is data on the following postoperative conditions:
- Infection of the operated area;
- Perforation of the maxillary sinus;
- Inflammation of the maxillary sinus;
- Bleeding after surgery;
- Loosening of the implant due to overload;
- Progression of atrophy and implant exposure in osteoplastic material.
The extensive experience and high qualifications of the maxillofacial surgeon allow them to be avoided; I strongly advise against performing such operations by a dental surgeon. All patients need to do is strictly follow all recommendations during the recovery period and everything will be fine.
Postoperative period
In order for the recovery period after surgery to be as effective as possible, you must follow the doctor’s instructions. First of all, in the postoperative period you need to take medications strictly according to the schedule.
This course necessarily includes antibacterial medications; in some situations, enhanced medications may be prescribed to avoid the risk of infectious processes.
As additional therapy for bone restoration, painkillers, antiseptics, and healing ointments are used to speed up tissue regeneration.
Basic recommendations regarding oral care after bone grafting include:
- Cleaning the operated area with an antiseptic solution. The procedure should be done after each meal with a cotton swab dipped in antiseptic.
- Brushing your teeth for 7 days only with a brush with soft bristles, do not touch the wound.
- Applying a healing ointment if it was prescribed by a doctor.
- If bleeding occurs, pinch the wound with a clean finger or apply a moistened tea bag.
If any suspicious manifestations appear after restoration of the bone mass, you should contact a qualified specialist.
Seams
When performing a sinus lift, 3 main types are used:
- In most cases, swelling at the site of bone enlargement lasts 7-10 days
Single seams (monotypic). The associated nodule is located near the buccal surface of the alveolar process. This option allows you to easily remove stitches in the future and is a preventive measure in case of accidental injury to the tongue. It is often used when suturing with rigid threads.
- Support seam. It is used when there are prohibitions for surgical intervention to build bone tissue. The doctor makes cuttings only on the vestibular or lingual flap.
- The seam is continuous. It is suitable for moving all flaps in an apical direction, in the area of several teeth. As a final result, the flap is fixed along the entire length. From the inner edge, the steps are repeated, but only with the lingual flap. The knot is tied at the site of the original seam.
How long does the swelling last?
Swelling, the size and duration of which depends on the individual characteristics of the body, can be insignificant and pass quickly, or can persist for 2 weeks.
In most cases, swelling at the site of increased bone tissue lasts 7-10 days. Its maximum severity is observed on the third day after surgical procedures.
If after 14 days the swelling at the site of bone augmentation has not gone down, then you need to consult a specialist.
What can and cannot be done after surgery?
The operated patient can:
- Eat only warm and soft food, which is recommended to be chewed on the other side.
- Make baths using antiseptics, for example, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine.
- Brush your teeth, but only without using toothpaste and on the second day after surgery.
The doctor also recommends sleeping with your head elevated and applying cold compresses to relieve swelling.
Restrictions include a ban on:
- eating hard, hot and spicy foods;
- playing any kind of sport;
- visiting the swimming pool, sauna, solarium;
- air travel;
- diving;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- using a straw while eating.
The patient should know that sleeping on the side on which the manipulation to restore bone tissue was performed is also prohibited.