From this article you will learn:
- why does flux (abscess) occur?
- abscess on the gum: treatment, antibiotics,
- opening of a gum abscess: video.
Flux on the gum is a swelling of the gums associated with the development of purulent inflammation. Dentists do not use the term gumboil or abscess (only patients say so), but use terms such as “gingival abscess” or “periostitis”.
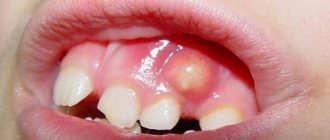
Flux on the gum: photo
Flux - reasons for the formation of a purulent lump on the gum and methods of treatment
Flux rightfully takes its place among the most unpleasant and painful pathological phenomena encountered in dental practice. The periodontal tissue and periosteum become inflamed, which leads to the rapid development of periostitis - this is what gumboil is called in medical terminology. Among the obvious signs of the disease are severe swelling of the gum tissue, their redness and the formation of a purulent lump. Often, against the background of a pathological process, the temperature rises and general health worsens. Later in this article we will talk about what gumboil is and how to treat it.
Pain
The most important sign of gumboil is severe pain. It is characterized by:
- aching, sharp or throbbing sensations;
- increased when biting;
- uncertain localization: both the causative tooth and the gums around it or the entire jaw may hurt;
- irradiation: often the pain “radiates” to the ears, temples, back of the head, forehead, neck;
- gradual increase: every day the discomfort becomes stronger.
Important! Pain during periostitis is practically not relieved by painkillers. Slight relief of symptoms is possible only in the first days of the development of the disease.
The medical name for flux is abscess or periostitis.
What is a pathological process
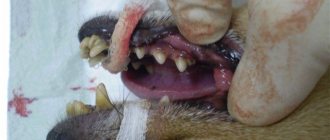
The development of inflammation of the periosteum most often occurs due to tissue infection through the root canals and periapical area. As a result, the patient gradually develops severe swelling of the mucous membrane in the area of inflammation. The gums turn red, increase in volume, a characteristic lump and painful sensations appear, and the cheek swells. You can see how this looks in practice by looking at the photo below.
This is what gumboil looks like
An infection can trigger the process, for example, from a carious cavity through the pulp chamber and tissue adjacent to the root. Flux of odontogenic etiology usually results from the active activity of staphylococci, streptococci and other pathogenic microorganisms1. The situation requires immediate medical attention, because otherwise the patient risks experiencing severe piercing pain and even more serious complications.
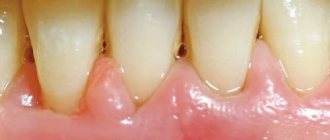
Gingival hyperemia
Externally, an abscess appears as a pouch on the gum on the inside or outside. Pus can shine through, causing the surface to turn white.
In this case, the mucous membrane turns red and swells. Touching her is unpleasant and painful.
Additional Information! In some cases, spontaneous opening of the flux occurs. The pus drains through the fistulous tracts. Temporarily the patient's well-being improves. However, after a while the symptoms return. This condition is the most dangerous, as the disease becomes chronic.
The main symptom is severe pain.
Causes provoking purulent inflammation
When answering the question of what causes flux, you should immediately note that the etiology of the development of the disease is infectious in nature. Thus, a kind of swelling on the gum appears as a result of infection and further inflammation of the tissue. However, experts in the field of dentistry highlight a whole list of factors that can provoke a pathological process. Here are the main ones:
- carious lesion: one of the most common reasons for the appearance of a purulent lump on the mucous membrane is caries, namely its deep form. Pathogenic microorganisms destroy hard tooth tissues and penetrate closer to the pulp through root canals. If the process is left unattended, pulpitis will soon develop. The bacteria will continue to spread and begin to “invade” the root tissues. All this will lead to the risk of inflammation of the periosteum and the development of gumboil,
Pulpitis may be the cause of gumboil - infection in a chronic form: regular exacerbations of inflammatory processes in the sinuses and ENT organs can also lead to illness,
- tooth trauma: damage will open a direct path for bacteria to penetrate into the deeper structures of the tooth and jaw as a whole,
- periodontitis (marginal form): inflammation develops in the tissues of the marginal gums, which leads to the formation of pathological pockets, and this is a direct road to periodontal infection,
- stomatitis: when the integrity of the mucous membrane is compromised, there is a risk of streptococci penetrating into the tissue, which, in turn, often lead to the development of purulent inflammation,
- cyst: the formation of a neoplasm is accompanied by the release of purulent exudate in the perihilar sac, which as a result can provoke inflammatory processes in the periosteal tissues,
- poor-quality treatment: mistakes made by the doctor during root canal treatment and filling can cause irritation of the root tissues and further spread of infection.
On a note! Poor root canal treatment is one of the common reasons why gumboil occurs. However, modern patients can insure themselves against medical errors by choosing clinics where complex dental procedures are performed under a microscope. Optical technology in the work of a specialist is the key to quality, safety, dense filling of the narrowest and most curved root canals, maximum preservation of healthy tissue, durable fillings and beautiful restorations. If you have become a victim of medical errors, then a microscope significantly increases the chances of saving a diseased tooth, as it allows you to carefully re-treat canals, close perforations, and even remove fragments of instruments left inside.
If we are talking about how flux begins, then it is worth noting that at first the formation of purulent masses does not occur. Only after a few days does suppuration begin, which is accompanied by swelling and the appearance of throbbing pain. If you continue to ignore the problem, literally within a day your general condition and well-being will sharply worsen. How dangerous is gumboil if left untreated? The likely consequences are very dire - all this can lead to the appearance of phlegmon, the development of an abscess and even sepsis.
How does an abscess manifest?
Effective antibiotics
Today, an extensive list of medications used for tooth flux is produced. They are produced in the following forms:
- Tablets or capsules. Such drugs are easy to dose and take. The shell quickly dissolves in gastric juice, and the active substance enters the bloodstream. The antibiotic in this form of release can be taken for flux in both adults and children.
- Ointments and creams. Apply directly to the periosteum area. Only the early stage of the disease is treated with such drugs; they effectively reduce the pain that accompanies periostitis and have an anti-inflammatory effect. The ointment must be used several times a day.
- Solutions for injections. Such antibiotics are used in dentistry for inflammation of the periosteum in an advanced stage. The injection is given intravenously or intramuscularly. The active substance instantly enters the circulatory system and reaches the source of infection.
Separately, we can distinguish a form of antibacterial drugs such as syrups. They are used to treat children; syrups are used extremely rarely in dentistry.
The best antibiotics in tablet form
Most often, antibiotics in the form of tablets are used to treat flux; they can quickly cure the disease. The list of the most effective drugs includes:
- Lincomycin. Dentists recommend it more often than all other remedies. This drug is recognized as the most powerful and is characterized by a wide spectrum of action. For flux, lincomycin is taken at a dosage of 500 mg per day, the capsule is washed down with clean water. In some situations, after using the drug, the appearance of side effects is noted: hypertension, attacks of nausea, dizziness. For patients suffering from severe disorders in the functioning of the liver and kidneys, Lincomycin is replaced with another drug.
- Tsiprolet. An antibiotic from the fluoroquinolone group, which is effective against most microorganisms that cause flux. Bacteria are not able to adapt to the influence of Tsiprolet, which determines its effectiveness.
It is a direct analogue of Tsiprolet. Produced in dosages of 250, 500 and 750 mg. Ciprofloxacin should not be used during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or under the age of 18 years. It is better to take these tablets on an empty stomach.
Ciprofloxacin.- Amoxicillin. A type of semi-synthetic penicillin. It is prohibited to use it if you have an individual sensitivity to the substance, as well as infectious mononucleosis. The dosage of Amoxicillin is selected according to an individual scheme for each patient. In exceptional cases, after using Amoxicillin, urticaria, signs of conjunctivitis or a runny nose appear during flux. In such a situation, you will have to interrupt therapy and select another drug.
- Ampiox. The product contains ampicillin and oxacillin, thanks to which it has a complex effect. The duration of therapy is about 7 days. Sometimes there is an allergic reaction to the medication, in which case it is worth replacing it with another antibiotic.
One of the most popular drugs for periostitis. Its popularity is due to the minimal list of side effects. Biseptol is not indicated for flux during pregnancy, as well as for diagnosing severe diseases of the liver, kidneys and blood. Approved for the treatment of adults and children. The specific dosage is selected according to the person’s body weight. In rare cases, Biseptol leads to allergic manifestations, headaches or attacks of nausea.
Biseptol.- Doxycycline. One of the most powerful drugs, so the daily dose does not exceed 100 mg. Doxycycline is prohibited for use during pregnancy, porphyria, myasthenia gravis, leukopenia, and severe liver failure. For flux, Doxycycline is taken once a day or divided into two doses.
Included in the group of fluoroquinolones. Its use allows you to quickly stop the spread of the inflammatory process and eliminate the cause of the disease. Suitable for the treatment of mild and severe forms of periostitis. For flux, Cifran should be taken twice a day. During therapy, it is recommended to refrain from visiting the beach, as the components of the drug increase skin sensitivity. Cifran is indicated for use for at least two weeks.
Digital- Azithromycin. A modern medicine from the macrolide group. Its advantage is its gentle effect on the body. The list of contraindications and possible side effects is minimal. Azithromycin is approved for use during pregnancy and is suitable for treating people allergic to penicillin.
- Flemoxin Solutab. The active ingredient of this drug is amoxicillin. The main feature of the drug is its rapid absorption into the blood. The components are quickly transported to the epicenter of the infection and suppress inflammation. Flemoxin is widely used in pediatrics.
Anti-gum gum tablets are only available upon presentation of a prescription from a doctor. Their uncontrolled use leads to negative consequences.
Injectable drugs
To find out which antibiotic is best to prescribe to a patient with tooth flux, the doctor determines the severity of the disease and the patient’s condition. In severe situations, it is recommended to administer the medicine intravenously or intramuscularly; with the help of injections, a positive result can be quickly achieved.
Among the most popular medications are:
A complex drug containing amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Allows you to suppress the activity of most known pathogenic microorganisms. Amoxiclav copes with the task better than cephalosporins and penicillins. Allowed for children and the elderly. The use of Amoxiclav is prohibited in case of severe liver diseases, lymphocytic leukemia, as well as individual intolerance to the active substance. Amoxiclav is not used to treat flux in expectant mothers, as it can harm the baby.
Amoxiclav.- Ampiox. The combined medicine has a wide spectrum of action and contains ampicillin and oxacillin. Does not affect the gastrointestinal tract and has a minimal list of contraindications.
- Ampicillin. Effective against streptococcus and staphylococcus. It has average bioavailability, so it has been used less frequently lately. Today, Ampicillin is being replaced by more effective analogues with a wide spectrum of action.
Antibiotics in the form of injections used for flux of the cheeks and gums require correct dosing. They can cause muscle weakness, gastrointestinal disturbances, headaches and some other side effects.
Antibacterial ointments
Flux on the gums can be treated with antibiotics in the form of ointments and gels. The best drugs:
- Levomekol. Allows you to quickly stop the growth of bacteria and restore damaged cells. Used for lesions of the gums and cheeks. The ointment is injected into the cavity of the abscess after it is opened and left for some time.
- Vishnevsky ointment. Suppresses bacterial activity and has an anti-inflammatory effect. The ointment contains a natural antibiotic - xeroform. This drug can be used only in the initial stages of the development of the disease - before an abscess has formed. The composition is spread on a gauze pad and applied to the cheek in the area of inflammation.
- Metrogil Denta. Produced in gel form. The drug contains chlorhexidine and metronidazole. The medication quickly relieves swelling and pain in the area of inflamed tissue, and prevents the formation of an abscess.
In dentistry, antibiotics in the form of ointments are used for gumboils only as an auxiliary medicine. Their use is usually combined with tablet drugs, which increases the effectiveness of treatment several times.
You can take antibiotics for tooth flux only after consulting a doctor. Self-medication is fraught with irreparable consequences, so when the first signs of a problem appear, immediately contact the clinic.
Characteristic symptoms
Before moving on to the question of what to do with a swollen cheek and how to cure gumboil in general, you need to consider the accompanying symptoms. The intensity of pathological manifestations largely depends on the patient’s age, the state of his immune system and the structural features of the jaw apparatus. So, for example, the disease develops much faster in a child than in an adult. The same goes for a weakened immune system. If we are talking about exactly how a tooth hurts during gumboil, then it is quite difficult to give an unambiguous description of the symptom - the pain can take on a different character, but over time it becomes aching and constant, with periodic pulsation.
Thus, the main symptomatic manifestations characteristic of periostitis include the following phenomena and conditions:
- pulsation occurs against the background of the beginning of the formation of purulent masses,
- a pronounced lump filled with pus appears on the gum,
- a person loses the ability to open his mouth normally if swelling has formed in the corner of the lower jaw,
- the patient begins to experience severe discomfort while eating and talking,
- swelling of the mucous membrane appears in the area of purulent infiltration,
- painful sensations occur due to mechanical impact on inflamed tissues,
- the general condition worsens, the temperature rises, the patient experiences weakness and dizziness.
A dull, nagging pain in the tooth that can become pulsating.
It should be noted that with the serous form of the disease, the clinical manifestations are less pronounced, which cannot be said about purulent flux. In any case, if characteristic symptoms appear, you should immediately see a dentist.
Folk remedies
Due to the fact that flux without treatment can lead to major complications, doctors do not advise self-medication.
But if it is not possible to get an appointment with a doctor in a timely manner, then you can safely use various traditional medicine.
Circumstances have so developed that people with swollen cheeks have been pondering for many years how to treat gum gum gum disease at home.
Healers have already tried various well-known methods in practice. Therefore, now we can confidently say that folk remedies for dental treatment can be safely used.
The best way to eliminate swelling and pain is to use various mouth rinses using medicinal herbs.
To treat flux, you can use the following tips:
- To eliminate the pain, you need to moisten a tampon in onion juice and apply it to the inflamed gum. Onions quickly destroy unfavorable microflora;
- A piece of ice eliminates swelling and inflammation well if applied to the sore gum;
- Cabbage leaf, rue and calamus are well suited for the treatment of gumboil, because they eliminate pain and swelling from the cheek. To do this, simply apply a cabbage leaf to the gum;
- Honey propolis can relieve pain if you chew it throughout the day. In addition, you can smear your gums with alcohol tincture. However, it is important to remember that some people are allergic to various bee products.
It is important to use natural herbs before bedtime when the pain is so severe that it prevents the person from sleeping. If during self-medication the patient feels nausea, dizziness or fever, then such treatment should be stopped. After all, an infection from the mouth can quickly spread throughout the circulatory system and cause serious illnesses such as sepsis.
It is important to remember that you cannot do warm compresses and baths that involve heating, because this is fraught with serious complications. There is also no need to take antibiotics, as dysbiosis may occur.
What forms of pathology are there?
Next, we will look at how to get rid of a painful lump on the gum and what helps in treating the pathology, but first we will dwell on the generally accepted classification of the disease. So, experts distinguish between acute and chronic periostitis. In the first case, the patient suffers from severe clinical manifestations - high fever, acute pain. When the flux develops into a chronic form, the pain becomes aching, and the temperature does not rise above 38.5 degrees. Also in dentistry, there are several types of periostitis:
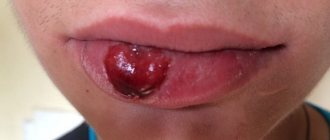
- purulent type is the most common form, nicknamed gumboil in everyday life. An inflamed cavity with purulent exudate forms in the thickness of the soft tissue. The pathology develops rapidly and leads to the formation of a fistula,
The photo shows purulent periostitis - serous form - occurs in approximately 38% of cases and most often results from jaw trauma2. Symptoms include swelling of the periosteum and accumulation of fluid in the tissues,
- diffuse periostitis is a rather complex type of pathology, in which the boundaries of the inflamed focus spread in all directions, and treatment requires the participation of a maxillofacial surgeon.
The photo shows diffuse periostitis
The doctor chooses the treatment tactics, and he does this based on the type of lesion, the degree and depth of its spread, as well as other characteristics of the clinical picture. In this matter, it makes sense to completely trust a professional, and especially not to rely on self-medication.
How to treat flux in dentistry - surgical methods
Treatment of flux in dentistry involves three different options for solving the problem. The choice of a specific technique will depend on the degree of damage and the individual characteristics of the clinical picture. Let's look at these methods in more detail:
- extraction of the causative tooth: carried out in cases where the pathological process has damaged the internal structures of the tooth too much, when other manipulations are powerless. Also, removal is often prescribed when it comes to baby teeth, which have very little time left before they are replaced. In such a situation, the loss of one unit will not in any way affect the further formation of the dentofacial apparatus. The same applies to wisdom teeth, which most often grow incorrectly, which leads to the onset of purulent processes and displacement of the remaining teeth,
This is how a tooth is removed - periostotomy: the doctor makes an incision in the area of the inflamed lesion, dissecting the periosteum if necessary. This is necessary to open the exit for the release of purulent exudate. After cleansing the cavity, a drainage is installed to drain the pus. And only when the inflammation subsides will it be possible to treat the tooth, which, accordingly, cannot be removed,
“In my case, fortunately, everything worked out. I didn’t have to remove the tooth, which I was incredibly happy about. On the first day, I felt that something had changed in my mouth, as if some other sensation had appeared. On the second day, my cheek became swollen and my gums on one side became swollen. I immediately went to the dentist. The doctor simply opened the gumboil and cleaned the gums of pus. He prescribed rinses, antibiotics and some other medications, and only then, at another appointment, they treated the tooth itself.”
Katerina K., Moscow, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
- combined treatment: carried out in severe cases when tooth extraction is not enough, and after its removal it is necessary to incise the gum and dissect the periosteum to release the pus.
The photo shows a periostotomy.
The decision whether to leave the affected tooth or remove it is made by the treating specialist.
As for how long it takes for the swelling to go away after opening the infiltrate, everything here is also purely individual. Typically, severe symptoms disappear quite quickly, literally the next day, but for some time the patient may experience minor pain and discomfort. It is important to follow all the specialist’s instructions, conscientiously take prescribed antibiotics and maintain oral hygiene in general.
What is tooth flux and what are its symptoms?
Flux is an inflammatory process in the periosteum of the jaw, accompanied by the formation of an abscess with a localized accumulation of pus. More often, an adult suffers from the disease, because with age, problems with the condition of the teeth may appear. But sometimes flux can also occur in children . Regardless of age, the clinical picture will be the same for everyone.
Flux is accompanied by swelling on the cheek. The area near the source of infection may swell. Depending on the location, the nasolabial fold, eye, and chin can also swell. Severe throbbing pain radiating to the temples and eyes is the second obligatory companion of acute inflammation. These are the most common symptoms of incipient periostitis. Other common signs that accompany the disease:
- malaise, weakness;
- temperature rise to 38 degrees;
- headache;
- swelling of the affected and surrounding areas;
- redness of the oral mucosa;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the area of inflammation.
Another early symptom that accompanies dental flux is pain when pressed. When chewing, exactly that area will hurt, in the area of which a swollen, compacted ball with pus can then come out. In photos and videos on the Internet you can see what tooth flux is and its visible, visual signs that cannot be confused with other oral diseases.
What can you do at home?
Treatment at home can be not only ineffective, but even dangerous. To avoid unwanted consequences, you should first consult with your dentist. The pathology does not go away on its own; in any case, medical intervention is required. And only after treatment can you resort to traditional medicine to speed up the recovery process and alleviate your condition.
Soda compress to relieve pain and swelling
This is one of the most effective ways to quickly relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. A teaspoon of sodium carbonate should be mixed with 4-5 drops of water and brought to a paste. Next, wrap the resulting substance in gauze and apply it to the swollen area for half an hour. After the time has passed, you need to rinse your mouth with a weak solution. The procedure can be repeated three times a day, and this therapy lasts about a week.
Linden decoction as an antiseptic
The decoction has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect. This is also one of the most effective means of rinsing your mouth with flux. To prepare it, pour 4 spoons of linden blossom into 500 ml of boiling water and cook for 25 minutes over low heat. Next, the broth is cooled, filtered and used 3-4 times a day after meals. The duration of the course is 10 days.
Linden decoction is a good antiseptic
Alcohol tincture of calendula
You can prepare the product yourself or buy a ready-made solution at the pharmacy. Two tablespoons of dried marigolds should be poured with 200 ml of vodka, mixed thoroughly and stored in a cool place, protected from direct sunlight. The product is infused for a week, after which the tincture can be used for rinsing. To do this, dilute a tablespoon of the finished substance in a glass of water at room temperature. You can repeat the procedure 4 times a day. The course lasts on average about 10 days.
Calendula tincture will relieve pain
Sage decoction against inflammatory processes
A self-prepared decoction of sage with the addition of mint or lemon balm is another effective remedy that provides antibacterial treatment of oral tissues and also helps reduce the intensity of the secretion of purulent masses. To prepare it, you need to pour 2 teaspoons of mint and sage into 400 ml of boiling water and cook for half an hour. The resulting broth should be cooled, filtered and used for rinsing up to 6 times a day for a week.
Other traditional medicine methods
Other effective ways to relieve swelling include rinsing with chamomile decoction. To prepare the remedy, you need to take a tablespoon of crushed and dried flowers, pour a glass of boiling water and leave for 20-30 minutes. Next, the broth is filtered and used warm. The use of folk remedies is justified only if this point has been agreed upon in advance with the attending physician. In addition, home treatment can only act as supportive therapy, but not as the main method of combating the disease.
Chamomile infusion is great for rinsing
Is it possible to treat flux at home?
Treatment of gumboil on the cheek at home is possible only at the initial stage, before pus has formed, since folk remedies can only cope with the infection - eliminate the source of infection and stop the development. The purulent form requires surgical intervention by a doctor; it is impossible to remove pus from the periosteum without a specialist, and it is impossible to eliminate the infection when it suppurates.
The most correct decision for the patient would be to consult a dentist and use folk remedies after consulting a doctor and in conjunction with prescribed drug therapy. However, if the patient categorically does not want to go to a specialist and decides to treat flux at home, he should follow some rules.
- Heat increases the spread of inflammatory processes, so you can’t warm up your cheek and gums!
- Any pressure on the source of inflammation can aggravate the condition of the periosteum and lead, for example, to suppuration, so you should not sleep or lie on your cheek with swelling!
- It is not recommended to take a hot shower or bath, eat hot food and drinks, or rinse your mouth with hot solutions.
- Individual intolerance to foods should be taken into account when preparing tinctures and decoctions.
Attention!
If pus, growths or other signs of deterioration appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Possible complications
It is difficult to give an unambiguous answer as to how long it takes for the flux to pass through and for the swelling to go away from the cheek. Provided that the treatment is carried out correctly and the patient follows all instructions, acute manifestations subside almost immediately, however, swelling and soreness may gradually subside over several days. A course of antibiotics usually lasts 1-2 weeks, after which we can talk about a complete recovery. If the treatment involved tooth extraction, the recovery process will take longer. If, after visiting the dentist, the patient experiences acute pain that only intensifies, he needs to urgently go to the doctor - a complication is likely developing. Everything can be fixed if you react in time.
The photo shows phlegmon
Things are more complicated for those who have put off visiting a specialist for too long. Attempts to cure the disease on your own and a banal fear of dental treatment can lead to very serious consequences. The risk of complications also arises if the patient does not follow the doctor’s instructions after treatment. Among the most severe consequences, experts identify abscess, phlegmon, inflammation of bone tissue and even sepsis.
Prevention - expert advice
We figured out what to do if your cheek is swollen, and how to remove acute pathological manifestations before visiting a doctor. But it is much easier to prevent any disease than to treat it later. To prevent a purulent lump from appearing on your gum, you must follow the recommendations below:
- get into the habit of brushing your teeth at least twice a day, and even better - after every meal,
- if it is not possible to clean every time after a meal, you should thoroughly rinse your mouth with plain water or a special antiseptic, and also use dental floss,
- it makes sense to purchase an irrigator - a portable device that supplies a high-pressure stream of water and air to more effectively clean hard-to-reach places,
- you need to monitor the condition of the gum tissues, prevent their damage and bleeding,
- If you notice the first signs of caries, you should immediately see a doctor.
Don’t forget to visit your dentist’s office every six months to undergo preventive examinations and professional cleaning procedures to remove plaque and deposits. To protect yourself from dental problems, you will have to reconsider your usual diet - limit the consumption of sweets, starchy foods and carbonated drinks with dyes. Eat more fruits and vegetables, as well as foods high in calcium and fluoride.