Geographic tongue is a pathological condition that is characterized by dystrophic and inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane of the tongue. The causes of occurrence include various factors that negatively affect tissue nutrition. As a result, areas of desquamation (peeling with flaking) and thickening alternate, and the tongue becomes like a geographical map. The disease itself does not cause significant harm to human health, which cannot be said about its root cause, and therefore requires treatment. Let us consider this issue in more detail.
Definition of disease - what is geographic language
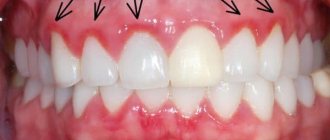
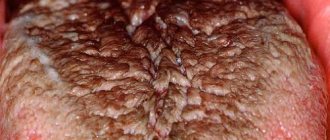
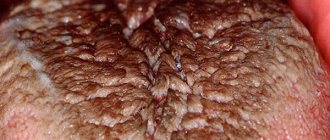
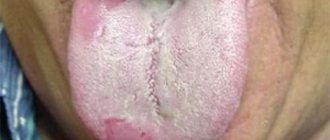
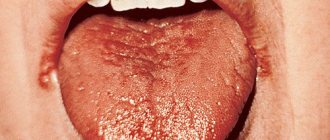
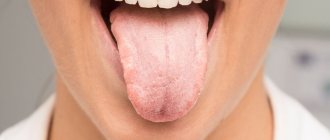
Geographic tongue or desquamative glossitis is an inflammatory-dystrophic disease of the tongue mucosa, which manifests itself in the form of zonal desquamation of the epithelium of a rich red hue. Areas of exfoliating epithelium are surrounded by a white rim.
When characteristic symptoms appear, it is not the tongue itself that needs to be treated, but the root causes of its changes.
Most often, lesions affect the lateral surfaces and back of the tongue and are always associated with keratinization of the epithelium and dystrophic changes in the papillae of the tongue. Some researchers attribute it to neurodystrophic pathologies, others to acute inflammatory processes. Some scientists do not consider geographic tongue a disease at all. This lesion occurs quite often. This link will tell you about the reasons for the appearance of a yellow coating on the tongue.
It is not necessary to treat the geographic tongue itself - it is important to determine the cause of the development of the pathological process (usually it lies in other organs and systems of the body) and take action.
Therapeutic measures
The diagnosis is made based on visual examination and patient complaints.
To date, there is no traditional treatment regimen for the condition in which geographic tongue is observed. The general method of therapy is determined by the specific cause that caused the disease, be it vitamin deficiency, diseases of internal organs, viruses, etc.
Traditional therapeutic measures for identifying this disease are:
- Taking combined vitamin preparations for several weeks to strengthen the immune system and saturate the body with useful substances.
- Perform regular rinses of the mouth with medicinal solutions (only as prescribed by a doctor).
- Performing applications with anesthetics.
- Identification of all areas of teeth affected by caries and their treatment.
- Taking antihistamines if the disease was caused by an allergy.
- Concomitant systemic treatment of those diseases that provoked inflammation, and the patient’s tongue began to peel off.
Symptoms of the disease and signs of a raised tongue
The lateral surfaces and back of the tongue are mainly affected - here areas of desquamation of the surface layer of the epithelium appear. As a result, spots of a white-gray or bright pink hue are formed; they have a round, irregular shape, visually similar to a geographical map.
There are usually no complaints with geographic tongue - pathology is detected during examination of the oral cavity.
If the patient eats irritating foods or does not maintain hygiene, the following symptoms may occur:
- itching;
- discomfort;
- burning;
- tingling;
- change in sensitivity.
The geographic tongue reacts sharply to salty, spicy, sweet foods with burning and itching. In other cases, there may be no symptoms at all.
Oral diseases
Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, including the tongue, do not always reflect the development of pathologies of internal organs - sometimes we are talking about independent diseases. If a burning sensation or the presence of a foreign body appears in the mouth, the tongue turns red and swells (the swelling tends to progress over time), salivation increases, taste sensations change (they may become dull or completely disappear), speech and eating become difficult, the patient feels pain in the tongue - these are symptoms of the development of glossitis, that is, inflammation of the tongue. This disease can take various forms, but the symptoms listed above are inherent in almost all of them.
READ ALSO: Why does the tongue turn white and what does it mean?
Causes of occurrence in adults and children
The development of geographic language is caused by various factors. The first and most common is a violation of the metabolism of B vitamins:
- B1 deficiency negatively affects the functioning of the heart, blood vessels, and gastrointestinal tract;
- if there is not enough vitamin B2 , inflammation of the lips and tongue may develop;
- B6 is responsible for the condition of the skin - if it is not enough, the epidermis peels off, cracks, and long-term non-healing wounds may appear;
- Vitamin B12 deficiency is the cause of the development of pernicious anemia (a disorder of hematopoietic processes).
Also, the reason for the appearance of a geographic language may lie in:
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract - stomach, duodenum. Diseases – ulcer, gastroduodenitis, malabsorption syndrome.
- Liver pathologies (especially hepatitis).
- Diseases of the pancreas are all types of pancreatitis, tumors, diabetes mellitus of the first and second types.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system - disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal glands.
- Autoimmune pathologies – lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes.
- Severe forms of viral infections - mononuclesis, ARVI, esudative diathesis, other diseases of the oral cavity.
Pancreatitis is not a harmless disease. When the pancreas is inflamed, enzymes trigger the processes of its self-digestion. This releases toxins that can damage various organs and systems of the body.
Treatment methods
You can cure a child in various ways. Pharmacy and folk remedies will help you recover.
Medication
If a geographic tongue appears, specialists prescribe:
- rinse the mouth with a solution of 1% citral . Mix 25 drops of solution and 100 g of warm boiled water. The resulting medicine is used to rinse the mouth in the morning and evening for five days. The product relieves burning and itching, eliminates swelling. Discomfort in the oral cavity disappears;
- Vitamin E oil solution . Sold in a pharmacy. The product is applied to a cotton pad and applied to the tongue for ten minutes, then the medicine is removed. The procedure is carried out twice a day;
- analgin . Prescribed for severe pain. You need to take it one tablet if necessary, but no more than three tablets per day;
- taking vitamins . You need to take vitamin complexes, or vitamins B and E separately, two capsules a day;
- calcium pantothenate . The drug is taken one tablet twice a day. The medicine fights the disease and eliminates unpleasant symptoms.
The duration of taking the drug is two weeks. Usually this time is enough to eliminate the disease. It goes away as suddenly as it appears.
Folk remedies
It is recommended to rinse the mouth with herbal solutions. To do this, mix one tablespoon of St. John's wort and a glass of boiling water. The medicine is infused for an hour, then filtered. You should rinse your mouth with the prepared solution at least four times a day.
chamomile to treat oral cavity . To do this, mix two teaspoons of herbs and a glass of boiling water.
The medicine must be infused for thirty minutes, then strained and cooled. Rinse the mouth with the prepared product three times a day.
Apply fresh carrot juice to the tongue three times a day. If you don't have carrots, you can use fresh potato juice.
Propolis is used to treat the tongue . They lubricate the affected area three times a day. Recovery will begin quickly, the child will get better.
Recommendations for the treatment of varicocele in adolescents can be found on our website.
Treatment
Specific treatment for the disease is not provided - it is necessary to diagnose the chronic pathologies that caused its appearance and take appropriate measures. Make sure there is no deficiency of B vitamins, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, or endocrine system. Bad habits can have a negative impact on your general condition. Find out how to properly treat green plaque on your tongue here.
Smokers develop geographic tongue more often than people who do not suffer from this habit. Smoking generally negatively affects the condition of the oral mucosa.
Components of complex therapy:
- Alkaline rinses and compresses with anesthetics help quite well in the initial stages of the development of the disease. Also use special medications that eliminate excessive sensitivity and itching of the surface of the tongue.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity – dental treatment, professional cleaning, stone removal. Visit your dentist regularly - even if you think nothing is bothering you, this does not mean there is no problem.
- Diet – all irritants that additionally provoke the development of inflammatory processes in the oral mucosa should be removed from the diet. These are mainly spicy, salty, too hot and cold dishes.
- Vitamin therapy – vitamin therapy provides good results as part of complex treatment.
If necessary, hyposensitization is performed. It is prescribed if the disease is causing concern, or the attending physician has given appropriate recommendations. This material will tell you about the causes of inflammation under the tongue.
Signs of diseases according to the characteristics of the tongue
If a person is healthy, all his organs and systems are functioning normally, then the tongue will be pale pink in color with a smooth surface, covered with a thin film of transparent salivary secretion, with clearly visible papillae, a smooth and straight central fold (we recommend reading: bright pink tongue in a person : causes and treatment). Any changes in color, the appearance of plaque or any marks indicate problems and malfunctions in the body.
It should be borne in mind that the condition of the tongue can be influenced by the foods a person eats. Before performing a tongue diagnosis, it is recommended that you refrain from eating and drinking at least 2 hours before the examination. You can clearly see examples and comments in the photo accompanying the article.
Plaque color
Very often, the development of pathology is indicated by a plaque that appears on the tongue. In order to determine which organ has failed and at what stage of development the disease is, you should pay attention to the color of the plaque. It can be of almost any shade - from white or bright red to yellow, blue and even purple: (we recommend reading: white-yellow coating on the tongue: causes and methods of treatment)
- yellow – liver failure, gastrointestinal diseases, smoking,
- blue – indicates kidney failure,
- blue/violet – heart or lung disease,
- black – acidosis, chromogenic fungal infection,
- bright red – pathologies of the cardiovascular system, blood diseases,
- gray – chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract,
- burgundy - speaks of diseases of infectious origin in acute form,
- reddish – inflammatory processes or infectious diseases,
- white – dehydration, acute respiratory viral infections, colds, fungal infection.
When making a diagnosis, it is also important to take into account the intensity and brightness of the color of the plaque on the surface of the tongue.
If it is very pale, almost colorless, then this may indicate that the person has poor nutrition, suffers from vitamin deficiency or anemia. A plaque of a very dark, rich color indicates that the body has a chronic pathology, the treatment of which must be started immediately.
Tongue shape
In the process of identifying pathologies of organs and systems, the shape of the tongue is no less important than the color of plaque. To determine what disease is developing in the body, the specialist who conducts the diagnosis must pay close attention to this characteristic. The signs listed below may indicate a pathological process. Description:
- changes in relief – deficiency of B vitamins,
- uneven, curved midline – scoliosis or other pathologies of the spinal column,
- enlarged, swollen organ – gastrointestinal pathologies,
- excessively thin – impaired metabolism, dysfunction of the circulatory system,
- bulges in the anterior zone – diseases of the bronchopulmonary system,
- an enlarged tip of a tongue that is too long indicates heart failure,
- thickened organ – pathologies of the digestive system, liver failure.
Presence of stains
Spots often appear on the surface of the tongue. They can be of different shapes, colors and sizes and located in different areas of the organ. In some cases, only one spot forms, but there may be several. Depending on these characteristics, as well as the general condition of the tongue during the examination, it is possible not only to clarify the diagnosis, but also to determine the cause that caused the spots to appear.
| Color | Description Features | Probable diagnosis |
| White | Small spots on the edges and root of the tongue. In advanced cases, spread over the entire surface | Thrush |
| The area of the stain is peeling | Lichen planus | |
| The spot is located under the tongue |
| |
| Single formation of round shape | Gastric acid-base balance disorders | |
| Red | Spots of various shapes on the sides and tip | Injury |
| The mark becomes covered with keratinized particles | Predisposition to the formation of cancerous tumors. You should immediately seek advice from an oncologist | |
| Many points on the back of the tongue |
| |
| The spot is surrounded by yellow-gray bubbles | Erythema | |
| Combined with an almost complete absence of salivary secretion | Brain diseases | |
| Bubbles filled with liquid are located on the tip and sides of the tongue | Herpes | |
| Yellow | — |
|
| Brown | — |
|
| Violet | Occurs in rare cases | Blood stagnation |
| Pink | — | Inadequate absorption of nutrients from food. |
| Black | The result of modification of the papillae on the surface of the tongue |
|
| Blue | — |
|
Roughness
The surface of a healthy person’s tongue looks “velvety” due to pronounced taste buds (papillae). If this muscular organ becomes noticeably rough and uneven, then this phenomenon should also be considered from the standpoint of linguodiagnostics. What can the roughness of the surface of the tongue indicate:
- state of dehydration,
- dysfunction of the salivary glands (we recommend reading: what is the location of the salivary glands in the human body?),
- overdose of vitamins A and D,
- overdose of medications (including antibiotics, atropine group drugs),
- rough and swollen – biliary dyskinesia, gastroduodenitis,
- in combination with dryness – complicated diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcer, appendicitis, intestinal infection, peritonitis),
- in combination with dryness and the appearance of cracks - diabetes, thyroid disease.
Smooth surface
If atrophy of taste buds occurs, their number is significantly reduced, or these receptors disappear altogether, then the surface of the tongue becomes very smooth and shiny, this phenomenon is called “varnished tongue” (we recommend reading: how and how to treat “varnished tongue”?). This symptom can be caused by the body's inability to absorb vitamin B2, chronic colitis, or stomach cancer.
READ ALSO: initial stage of tongue cancer with photos
When the tongue becomes covered with a dark, brown-black coating, which lies on the surface of the tongue in a dense layer and is very difficult to remove, and cracks appear (“chessboard”), then we are talking about a pathology such as pellagra (that is, a lack of vitamin B and nicotinic acid). In the later stages of development, one of the symptoms of the disease becomes “cardinal tongue” - the organ becomes bright red, and its surface becomes “varnished”.
READ ALSO: tongue burns and burns: methods of treatment
Other language features
If the tongue hurts, goes numb, or other unpleasant sensations appear, then this indicates a disease of the organ itself or the oral cavity. The appearance of plaque and other surface changes usually indicate the development of general diseases in the body and are not associated with the state of oral health. An experienced diagnostician will pay attention to the following features of the condition of the tongue:
READ ALSO: pimple on the tip of the tongue: what could it be?
- the papillae at the tip become bright red – diseases of the pelvic organs,
- small ulcers appeared on the surface - increased acidity (we recommend reading: increased acidity in the mouth: causes and treatment),
- the appearance of thick dense plaques - candidiasis,
- bright spots – pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract,
- tongue tremors – thyroid diseases, neurotic disorders,
- burning sensation – cervical osteochondrosis, vegetoneurosis, stress,
- the appearance of tooth marks - disturbances in the digestive process,
- the tongue is curved or deviated to the side - cerebrovascular accident, cerebellar dysfunction, hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke.
Complications
Since geographic tongue is not a serious disease, it does not require specific treatment. However, since its appearance often indicates the presence of infections or chronic systemic diseases in the body, you need to undergo a comprehensive health examination and take action based on the diagnostic results.
If you have been diagnosed with geographic tongue, the first thing to do is check your immune and digestive systems.
In older people, geographic tongue often causes the development of cancerophobia - the fear that the affected areas are the result of cancer (malignant tumors of the tongue). When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor; you may also need to consult a psychologist. And don’t worry - geographic language refers to benign conditions that are not prone to degeneration into malignant tumors.
Diagnostic methods
General diagnosis of geographic tongue in an adult is based on the following:
- Collecting the patient's medical history. At the same time, the doctor must ask about recent viral or infectious diseases, as well as the presence of chronic pathologies.
- Blood and urine tests.
- A general examination of the oral cavity, during which the condition of the mucous membrane of the tongue will be clear.
- Allergy test and data collection for vitamin deficiency.
As an additional collection of information to make a diagnosis, the patient may need to consult an endocrinologist, dentist and gastroenterologist.
Prevention
Basic measures to prevent diseases of the tongue mucosa:
- prevention of vitamin deficiencies - eat foods high in B vitamins (whole grain bread, cereals, leafy greens, peas, fish, dairy products), take courses of multivitamin pharmaceutical preparations;
- try to give up bad habits , minimize the consumption of coffee, sugar, alcohol;
- Diagnose and treat somatic diseases in a timely manner;
- devote enough time to oral hygiene - you need to carry out dental treatment in a timely manner, do professional cleaning, and remove stone.
Even simple caries, if left untreated, can become a source of serious health problems. Therefore, have regular check-ups with your dentist and follow his recommendations. Find out about the diagnosis and treatment of superficial, initial caries in this article.