Who is a periodontist?
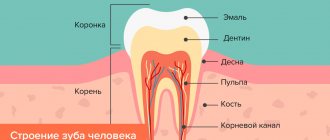
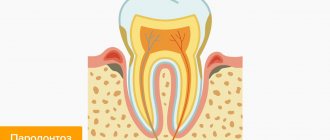
A periodontist is a doctor who treats periodontal diseases. The term “periodontium” includes a complex of tissues surrounding the teeth and performing a retaining, nutritional and protective function in relation to them. It includes:
- gums - soft tissue that covers the roots of the teeth;
- periodontium - the layer between the cement of the tooth and the wall of the alveolar socket - consists mainly of collagen fibers that hold the tooth in the alveolus.
- alveolar process - the bone bed on which the teeth are located;
- tooth root cement
In what cases is it necessary to contact a periodontist?
Lateral flap
Thus, healthy tissues are shifted onto the exposed roots.
How the flap is applied to the gum
However, if the disorder appears throughout the entire jaw, then there is no point in applying a flap. At the same time, a noticeable effect is achievable within a few weeks. And if prevention is carried out and the gums are not subjected to stress in the future, the patient is unlikely to encounter this problem again.
It is installed on the cortical plate of the alveolar process. There it helps tissues recover. After the treatment is completed, the membrane must be removed. There are also those that dissolve in the alkaline environment of the mouth.
What does a bioimplant look like? A visit to the office is carried out in the following cases:
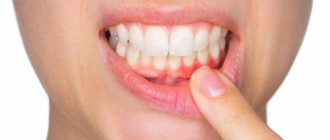
- when eating hot food or brushing your teeth in the morning, there is heavy bleeding from the gums;
- formation of abscesses on the surface of the gums;
- chewing food is accompanied by pain and discomfort;
- there is visual swelling of the surface of the gums;
- persistent bad breath that is impossible to get rid of;
- change in gum color. They become unnaturally red or, conversely, white;
- the spaces between the teeth expand;
- teeth become exposed due to the gums receding.
Major periodontal diseases
The most common periodontal diseases are: gum inflammation (gingivitis), acute and chronic periodontitis, periodontal disease, periodontoma (oncological processes in tissues), idiopathic pathologies (diseases of unknown origin) and peri-implantitis. Let's look at the main ones in more detail.
Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis)
Gingivitis is a gum disease characterized by an inflammatory-destructive process without disruption of the periodontal joints.
It develops due to the accumulation of microbial plaque on the teeth or poor oral hygiene. This disease is typical mainly for smokers, people who are unable to seek dental care on time or suffer from chronic diseases. In adolescents and children, it can occur in the absence of proper hygiene - accumulated bacteria are a source of gum inflammation. Signs of gingivitis: redness, swelling and bleeding of the gums. In advanced cases, looseness of the gums is observed - this indicates infection and destruction of the integrity of the soft tissues.
Fortunately, this disease provides effective and comprehensive treatment and restoration of the aesthetic appearance of the gums. The main thing is to contact your treating periodontist in a timely manner to diagnose and choose a method to solve the problem. Otherwise, the inflammatory process will worsen and cause complications.
Acute and chronic periodontitis
Periodontitis is a disease characterized by inflammation and progressive destruction of tooth-fixing ligaments and tissues (periodontal, cementum and alveolar process).
It occurs as a result of infection entering the root space through the damaged surface of the gums. This can happen after the gums are damaged by a toothbrush or floss. In advanced cases of caries and gingivitis, gaps (pockets) appear between the tooth and gum, in which food debris accumulate, creating a favorable environment for the development of bacteria. The products of their vital activity are lactic acid and decomposing amino acids, which lead to inflammation.
Periodontitis manifests itself as bleeding gums, the formation of “pockets,” pain when chewing, itchy gums and loose teeth. There are acute and chronic forms.
Due to the fact that the inflammatory process during periodontitis progresses rapidly and ultimately leads to tooth loss, you should contact a periodontist immediately! It is important to understand that if the acute form becomes chronic, the disease is difficult to cure, proceeds very slowly with alternating periods of exacerbation and remission, and is fraught with serious complications for human health in general.
Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease
Treatment of periodontal disease is carried out in 2 stages. On the 1st, symptomatic therapy is carried out.
- Remineralization (for the purpose of treating hyperesthesia) – deep fluoridation, sodium and potassium chloride films, hydroxyapatite, fluoride varnish.
- Filling wedge-shaped defects and enamel erosions.
- If required, selective grinding is performed.
The second stage involves improving blood microcirculation in periodontal tissues in order to eliminate hypoxia and normalize metabolism. Antisclerotic (mevacor) and vasotropic (trental) drugs, vitamin E, etc. are used.
If periodontal disease is complicated by inflammation, its treatment is carried out like periodontitis, but taking into account the characteristics of periodontal disease.
Root cyst
It is a benign tumor that occurs at the tooth root due to infection. A small tumor (up to 7-8 mm) is difficult to detect because it does not bother the patient. As the cyst grows, the following symptoms of the disease appear:
- nagging pain that increases with pressure;
- swelling, redness, suppuration of the gums around the defective tooth, its loosening;
- general weakness, high body temperature, headaches, enlarged lymph nodes.
What does a periodontist do with a cyst? First, it is treated with conservative methods (when the cyst is small, the dental tissue is destroyed not below the level of the gums), then surgically (removing the apex of the root or the entire tooth, if it cannot be saved).
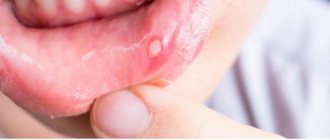
Stomatitis
This is an inflammation of the oral mucosa due to injury, infections (viral, fungal, bacterial), and allergies. Accompanied by increased salivation, the appearance of white plaque, ulcers, blisters and erosions.
They treat the oral mucosa using medications for topical use (ointments, gels, rinses) and drugs for the treatment of the underlying disease (allergies, infections).
Peri-implantitis
Peri-implantitis is inflammation of the bone tissue around the implant. It is characterized by inflammation and swelling of the gums, shaky implant design and pain in the implantation area. There are a number of reasons why this disease develops:
- physiological implant rejection;
- incorrect installation of the abutment (part of the structure to which the crown is attached) by the surgeon;
- non-compliance by the patient with recommendations for caring for the implant and oral cavity;
- contraindications to surgery not identified in advance;
- bad habits of the patient.
Peri-implantitis begins with an inflammatory process at the site of the operation. There is redness, swelling and bleeding of the gums, pain when exposed to the implant, and mobility of the implanted structure. Ignoring the initial symptoms will lead to a deterioration in the patient’s general condition, thinning, destruction and deformation of the bone tissue, ultimately resulting in complete rejection of the implant.
Considering the risks of this disease and its consequences, it is necessary to adhere to all the rules of the preoperative period and conduct all necessary examinations and examinations. Also follow your doctor's recommendations after surgery. If you suspect peri-implantitis, you should immediately consult a dentist for diagnosis and treatment. If the disease is detected in the initial stages, it is possible to preserve the implant or reinstall it.
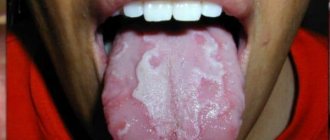
Glossitis
Glossitis is an inflammation of the tongue. It is caused by the same factors as stomatitis: infectious, traumatic or allergic.
Glossitis can also be a manifestation of systemic diseases or stomatitis.
Signs of pathology are hyperemia of the tongue, the formation of various patterns and formations on it, a change or loss of taste sensations. Treatment is similar to that for stomatitis.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis (candidiasis) or oral thrush is a fungal infection of the mucous membranes. It occurs when there is an overgrowth of fungi of the genus Candida. Normally, they are present in every person, but when immunity decreases, they become more active.
Candidiasis most often develops in childhood. It manifests itself as an abundant cheesy coating on the gums, the inside of the lips and cheeks, and the tongue. Treated with antimycotic drugs and immunostimulants.
Cheilitis
Cheilitis is an inflammation of the lips. The process involves the lips themselves, as well as the mucous membrane on the inside and the skin around the mouth.
Patients with this disease experience swelling of the lips, redness and peeling, and ulceration. Patients often complain of pain and burning when talking and eating.
Treatment for cheilitis varies depending on its form. But in most cases, the provoking factors are eliminated and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed. Sometimes they resort to immunomodulatory and local hormonal drugs.
What diseases does it treat?
After the diagnosis has been completely completed, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment:
- Using ultrasound, remove plaque that has accumulated near the gums. You can also use a sandblasting tool or laser. Note that the laser can also be used to eliminate caries. Read more information about laser caries treatment here.
- Surgical intervention in particularly difficult cases.
- Secure especially loose teeth. Read more about how to save teeth during periodontal disease below.
- Cleaning periodontal pockets.
- Disinfection and elimination of the inflammatory process.
The specialist selects an individual program for each patient individually. It depends on what kind of disease it is and at what stage it is.
Gingivitis
This form of the disease is very common in patients who seek help. It precedes the onset of periodontitis. With catarrhal gingivitis, an inflammatory process occurs in the gum tissue and areas between the teeth.
Every adult knows that teeth need to be brushed twice a day. But, in addition, it is necessary to take care of the areas between them. This requires flossing once a day. It is easier for bacteria to destroy soft gum tissue than hard tooth tissue. In this regard, microorganisms penetrate the gums and lead to an inflammatory process. Gradually, the disease develops into the next stage – periodontitis.
The main reason is improper oral care.
Periodontitis
Deep tissue damage occurs. Treatment of this stage requires much more time and effort. Damage can affect several teeth or the entire gum.
First of all, it is necessary to remove tartar and plaque. Comprehensive treatment is needed to eliminate the cause of the disease. After this, the periodontist rinses the periodontal pockets, applies compresses, and also recommends special solutions for treating the oral cavity.
Periodontal disease
The most difficult disease. Changes occur in the gums that can no longer be cured. At this stage, you cannot carry out independent treatment. At this stage, the gums turn pale, but no longer bleed or hurt. Most of the tooth is visible. It is approximately three-quarters open and only one-fourth is in the gum. In this regard, a person who bites off hard food may be left without teeth. More information about the treatment of exposed tooth roots in this article.
The more advanced the stage, the more time is needed to eliminate it: 1) At a mild stage, when swelling of the gums appears, their redness appears and periodontal inflammation begins, it is necessary to consult a doctor. First a visual inspection is carried out. Next, the specialist will recommend what tests you need to take.
The periodontist prescribes treatment. It consists of rinsing and using medications. After a certain time, you should visit the doctor again and determine the effectiveness of the technique:
- When bleeding gums and severe swelling occur, a more serious approach and comprehensive treatment is needed. It may be necessary to rinse and use antibiotics.
- In particularly severe cases, surgical intervention is required. You should make an incision in the gum and clean the teeth from the stone. After this, the tissues are sutured.
Timely treatment will help solve the problem once and for all. It is necessary to undergo regular dental examinations to avoid the development of the disease.
Symptoms that require you to visit a doctor
The appearance of signs of the diseases mentioned earlier should be a reason to contact a periodontist. Self-medication is unacceptable, since without examination and examination by a specialist it is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe suitable therapy. Moreover, the symptoms of different pathologies can be similar.
So, don’t put off visiting your doctor if:
- signs of inflammation and bleeding gums appeared;
- there is pain in the gums, and when pressure is applied to them, fluid is released;
- teeth began to loosen, and the periodontal tissues began to recede and sag, forming periodontal pockets;
- bad breath has appeared, which persists after brushing and rinsing your teeth.
Gingivitis is a gum disease in adults
Gingivitis is the most common gum disease, but also the least dangerous of the other two. This name comes from the Latin word gingivitis, which translates as “inflammation of the gums.” Of course, modern dentistry highlights more specific features and symptoms of this disease.
Despite the fact that gingivitis is much easier to treat than periodontitis and periodontal disease, the lack of timely treatment can subsequently be costly for the patient, both in terms of treatment costs and in terms of overall health. The main causes of gingivitis lie, first of all, in improper hygiene or its complete absence.
This disease can also occur due to mechanical or thermal injuries to the gums, a weakened immune system, and improperly performed dental prosthetics. Gingivitis is a shallow inflammation of the gum line around one or more teeth, but this is just general information. There are several forms of gingivitis that need to be briefly mentioned.
Catarrhal
The most common form of gingivitis, it is characterized by redness of the gums around one or more teeth. Often accompanied by bleeding gums, mild itching, pain when eating and performing hygiene.
Hypertrophic
With this form of gingivitis, significant compaction and growth of gum tissue is observed, up to the keratinization of individual areas. The color of soft tissue becomes dark red. With this form, treatment of the gums between the teeth is often required.
We suggest you read: What is the name of a dental prosthetist?
Ulcerative
One of the most severe forms, in which large areas of the gums are affected and a characteristic gray coating appears. In an advanced stage, it can be accompanied by purulent inflammation, death of soft tissue areas and bad breath.
How to prepare for your appointment
Before going to the periodontist, you need to prepare in advance. You should consult a doctor not only if a number of symptoms appear, but also undergo an examination every 6 months as a preventive measure against dental diseases. But you should know that before this you need to carry out certain procedures:
- You need to brush your teeth with toothpaste. Clean the areas between them with dental floss. After this, rinse your teeth with a herbal decoction.
- You should not go to the doctor without eating first. This is due to the fact that medications taken on an empty stomach lead to a sharp compression of blood vessels. The patient may even experience loss of consciousness.
- If you have an allergic reaction to certain medications, you must first notify your doctor. You also need to talk about pregnancy or lactation period.
- It is not recommended to drink alcoholic beverages before visiting the doctor. They are completely eliminated from the body only after 96 hours. Alcohol reduces the effect of medications.
How is an appointment with a periodontist?
First, the doctor will examine your mouth.
If the detected pathology is expressed by slight inflammation and bad breath, he will prescribe anti-inflammatory treatment and give hygiene recommendations. In cases where the situation is more serious, the doctor will rinse the periodontal pockets with an antiseptic solution, remove existing subgingival deposits (if any), choosing the most appropriate method, and prescribe subsequent treatment.
If the gum condition requires surgical intervention, it will be prescribed and carried out after a thorough diagnosis.
Folk remedies for the prevention of gum disease
Do you have a problem with your gums? What to do? Of course, go to an experienced specialist! But you should remember that treating gums at home is impossible. After all, the wrong approach will lead not only to complications, but also to tooth loss. Only prevention is possible. Only a doctor can identify gum problems and prescribe appropriate treatment.
It is generally accepted that any herbs relieve gum inflammation and eliminate pain. But dentists say that oak bark infusions have a bad effect on the structure of the dental bone, forming microcracks. At the same time, a solution of salt and soda will quickly relieve pain and swelling of the gums. The first component has antiseptic abilities and fights infections.
Infusions of chamomile, sage, and St. John's wort also help get rid of harmful oral bacteria without destroying the tooth. You need to take 3 tbsp. spoons of each component, mix and add hot water. Bring to a boil in a steam bath, let it brew for 40 minutes. Strain and rinse twice a day. And propolis and tar can be rubbed directly into the gums or added to rinsing infusions.
How does he diagnose?
The main way to diagnose periodontal disease is to examine the dental cavity. The doctor uses endodontic instruments to assess the condition of the gums and teeth and decide on the need for fluoroscopy.
Normal and pathological state of periodontium
| Parameter | Norm | Pathology | Possible illness |
| Gum color. | Pale pink (pink coral). | Bright red. Grey. Dark burgundy red. | Gingivitis. Ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis. Periodontitis. |
| Gum texture. | Similar to the peel of a lemon, there are depressions and roughness. | Smooth surface without changing color or contours. | Gingivitis. |
| Condition of interdental papillae. | Pointed shape, dense consistency. The dental necks are completely covered, the spaces between the teeth are filled. | Hyperemia, swelling, bleeding, itching, hyperplasia (overgrowth). | Gingivitis, periodontitis. |
| Condition of the gum margin. | It is located 2 mm above the enamel-cementum border. | The distance from the enamel-cementum border to the gum edge is less than 2 mm. | Gum recession. |
| Presence of gum pockets. | The depth of the groove between the tooth and the gum does not exceed 2.5 mm, there is no bleeding. | The pocket depth is more than 2.5 mm; bleeding occurs when probing. When you press the probe on the edge of the gum, exudate appears. | Periodontitis. |
| Mobility of teeth. | No tooth movement in all directions. | The presence of mobility of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd or 4th degree according to the classification of D. A. Entin. | Pathological mobility of teeth. |
Radiography
Periodontal disease on x-ray
X-ray examination at the early stage of periodontitis and periodontal disease is not informative. In severe forms, it allows you to determine the condition and structure of bone tissue, the presence of resorption, osteoporosis, osteolysis, destruction, osteosclerosis. Osteoporosis appears in the image as increased transparency of the bones.
Based on the X-ray examination, a conclusion is made about the initial, moderate or severe degree of changes in bone tissue.
- The initial stage of periodontal disease - the apices and end plates of the ridges disappear, the height of the septa is preserved.
- Moderate degree - interalveolar ridges are destroyed by more than ⅓, bone tissue is absent at the level of the buccal part and the approximal third of the roots.
- Severe degree - destruction of the interalveolar septa by more than ½ of the height. Exposure of roots more than ½ of the length.
Physiotherapy for gingivitis
Gingivitis responds well to physical and laser therapy. Electrophoresis uses heparin, lidase, potassium iodide, enzymes, vitamins B1, B2, PP, C. The laser is used to excise overgrown areas of the gums with cauterization (electrocoagulation). Ultraviolet irradiation and UHF therapy work well.
What tests should I take?
If you decide to see a periodontist, take the following tests:
that will be necessary for the doctor:
- General and biochemical blood test.
- Immunogram. Checking the state of the immune system through a venous blood test.
- Leukocyte vitality analysis. The study of cell activity, thereby checking the viability of leukocytes.
- The Rotter test is needed to determine the level of saturation with vitamin C. This analysis is carried out with an injection needle, with its help a special reagent solution is applied to the back of the tongue. If the spot disappears in more than 15 seconds, it means there is not enough ascorbic acid in the body. Lack of vitamin leads to tooth loss.
- Assessment of proteolysis activity is required to study the degradation of proteins into enzymes.
- Smears and imprints of the oral mucosa.
- Microbiological research methods.
Treatment and cleaning of teeth by a periodontist
To tidy up the oral cavity, the periodontist begins with the procedure of removing plaque and tartar, since these deposits are the location of pathogenic microbes. For this purpose, dentistry uses both mechanical and ultrasonic and other modern cleansing methods. If the inflammation of the gum area is in the initial stage, professional teeth cleaning is enough to stop the pathological process. But only on the condition that the patient conscientiously follows at home all the recommendations received at the doctor’s appointment.
With the development of the following stages of gingivitis, after removing deposits and dead periodontal tissue, the doctor administers injectable anti-inflammatory drugs to the patient and, if necessary, prescribes a home course of antibiotics.
When a patient develops periodontitis, the periodontist washes the resulting periodontal pockets with antiseptic solutions, and then eliminates tooth mobility using methods such as flap surgery, splinting and open curettage. These serious interventions require local anesthesia and subsequent periodontal restoration with the help of physiotherapy or antibacterial therapy in the event of the formation of abscesses and other suppurations.
Open curettage
In case of periodontal disease, tooth saving tactics are developed on the basis of x-ray examination and laboratory tests. In addition to the treatment methods used for periodontitis, at this severe, often irreversible stage of gum disease, treatment methods are used to stop the atrophy of the periodontal tissues. To activate their blood supply, patients are prescribed physiotherapy, laser, ultrasound, and medications. If the degenerative process is in an advanced stage, the tissue is increased surgically for subsequent prosthetics.
The result achieved after clinical manipulations by a periodontist is consolidated at home with the help of oral medications, herbal rinses, medicinal ointments and gels. In each specific case, the periodontist develops an individual treatment course, taking into account the characteristics of the patient and the pattern of disease development.
Recommendations for effectively strengthening gums
If a person with weakened gums wants to tidy them up and help them recover, he will need to reconsider his lifestyle and habits.
The health of the entire oral cavity directly depends on the quality of food consumed, since it is the oral cavity that performs the primary function of digesting food.
We suggest you read: Tea tree oil for treating gums
Foods that promote gum health:
- Citrus fruit. They are rich in vitamin C, and it has a positive effect on the condition of blood vessels and mucous membranes. By consuming a sufficient amount of this vitamin in food, you help reduce tissue fragility - they become more resistant to various negative influences.
- All kinds of greens. Parsley, celery, dill reduce bleeding gums. Due to the high potassium content, greens have a positive effect on the tone of blood vessels throughout the oral cavity.
- Cheese and dairy products are a natural way to whiten tooth enamel. Calcium, which is contained in large quantities in their composition, helps strengthen tooth and gum tissue.
- Fish products. Due to the presence of phosphorus in its composition, fish products strengthen weakened gums in case of periodontal disease.
- Onion and garlic. Due to their high content of zinc, onions and garlic not only successfully strengthen the skin, but are also powerful antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents.
- Nuts prevent the formation of tartar.
- Red wine in small quantities strengthens gums and reduces inflammation in the mouth.
At this time, a woman should closely monitor the composition of the products she consumes. Pregnant women are recommended to take the necessary vitamin complex to fully replenish minerals and vitamins.
Certain vitamin supplements may not be suitable for some people, so you should consult your doctor before taking them.
Gum massage
In addition to proper nutrition, simple rules must be followed to restore weakened gums.
So, you can grow your gums a little at home thanks to massage. It can be done during every brushing of your teeth. Another advantage is that the procedure does not take much time.
For example, paying attention to your gums for 5 minutes twice a day can significantly improve their appearance and contribute to their recovery.
Simple instructions for performing gum massage:
- The procedure can be performed using therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes and gels.
- The massage should be performed directly in front of the mirror after thoroughly brushing your teeth, when most of the plaque has already been removed.
- Currently, there are many methods of massage influence on the gums, but the main movements are performed starting from the center of the jaw to the left and right to its edges. Gentle movements should be directed from top to bottom, directly from the base of the gum, at the root of the tooth to its edges, and closer to the tooth itself.
- The strength of the massage effect on the gum tissue needs to be controlled by the person himself, but this should not cause pain or increased bleeding.
- You can perform the massage either with your own hands or with the help of special brushes, or using a toothbrush specially designated for this purpose.
Periodontal treatment
In some cases it is carried out differently, however, there are general rules:
- In case of mild symptoms, a preliminary consultation with a dentist is required. The doctor, examining the reddened areas, gives the patient recommendations. In some cases, there is a need for testing. Sometimes it is enough to get by with preventive methods associated with regular rinsing with medications. In case of deterioration, a second visit to the dentist is mandatory;
- The disease may be accompanied by swelling. In this case, immediate intervention by a doctor is needed to rinse the pocket cavities. In the future, he will give advice on the rules of oral hygiene;
- In some severe cases, surgical intervention using anesthesia is required. An incision is made in the gum, followed by washing the inside of the gum, from where all the stones are removed. The wound is then sutured.
As a rule, a trip to the dentist is made when the disease is advanced. To get rid of future worries, it is better to follow a number of recommendations:
- Preventative dental care should not be done from time to time, but throughout your entire existence. Brushing your teeth should be done regularly, after eating. If this is not possible, you can rinse your mouth with warm water. It is good to floss the space between the teeth regularly;
- Constantly monitor the condition of your toothbrush. So that it does not injure the gums, its edges should be semicircular, the pile should be flexible and soft. Duration of use is no more than one quarter. After this time, it must be replaced. Further use is impossible because it is a carrier of bacteria that return to the oral cavity.
- After your next meal, it is recommended to use dental floss. This technique is very good at removing food debris that is located in the gaps between the teeth.
Modern medicine has risen to a very high level. Narrowly focused specialists deal specifically with their problems. Therefore, a timely visit to the doctor will allow you to prevent a bad disease in time and ensure a snow-white smile throughout your life.
Expert advice: how to cure gums
Competent treatment begins with a visit to a specialist, who, after assessing the situation, decides how to help his patient.
As a rule, they are prescribed:
- Mechanical cleaning. Removing dental plaque, removing stones and microbial film is carried out using a special device. Today, the desired result is achieved using three main techniques: laser, ultrasonic and sandblasting. The specialist chooses which one is more appropriate to use.
- Therapy aimed at relieving inflammation. Approximately twice a day, the patient will have to independently treat the gums with antibacterial ointments and creams. This treatment allows you to quickly relieve inflammation and slow down the spread of infection further. If the situation is advanced, the patient may be prescribed antibiotics.
- Physiotherapy. In severe cases, vacuum massage and electrophoresis will help speed up recovery. They accelerate blood circulation and promote rapid regeneration of gum tissue.
- Surgical intervention. This method is considered the most radical and is used only when absolutely necessary. During the operation, the patient's teeth can be removed and the purulent area can be completely excised. Rehabilitation after this takes quite a long period of time.
After this, a follow-up visit to the doctor is mandatory, who will make a verdict - to complete the treatment or continue it for a few more weeks.
How to choose a good periodontist?
The best recommendations for any doctor are good reviews from patients who have been treated by him. You must also pay attention:
- on his length and experience;
- the level of the medical institution, dentistry where he works;
- equipping the dental office with modern equipment.
Of no small importance is the doctor’s communication skills, willingness to tell you the details and nuances of treatment, participation and genuine interest in the condition of your teeth.
How, after consulting a periodontist, can you determine that this specialist is incompetent?
- If you have been recommended “injections of antibiotics into the gums” as one of the treatment methods, injections of the antibiotic Lincomycin into the gums create a terrifying concentration of antibiotic directly at the source of inflammation, which leads to the immediate destruction of a large number of pathogenic microorganisms, which in turn is accompanied by the release of a huge amount of the amount of toxins and inflammatory mediators.
These substances in high concentrations lead to the appearance of foci of necrosis (death) in the periodontium of the teeth (the periodontium is the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, with the help of which the tooth is attached to the bone). Necrotic areas of the periodontium become sclerotic and are gradually replaced by micro-scars, which at the first stage leads to a temporary decrease in tooth mobility.However, such teeth are not able to normally perceive and distribute chewing pressure on the bone, which leads to the gradual loosening of such teeth, and to a greater extent than it was before treatment. That is why this treatment method is not used in Europe, the USA, Israel, or Japan. But these countries are known for the quality of medical care.
- If you have been recommended ointment forms of preparations for applications to the gums, the ointments practically do not stick to the moist mucosa and are instantly swallowed with saliva. In addition, the active substances from ointments cannot penetrate deeply through the oral mucosa, and act only on the most superficial layer of the mucosal epithelium, which is not enough.
- If the doctor has not discussed oral hygiene, the only reason for the development of gum inflammation (gingivitis and periodontitis) is unsatisfactory oral hygiene, as a result of which soft microbial plaque and hard supra and subgingival dental deposits accumulate on the teeth and in the dentogingival sulcus. . If the doctor did not emphasize this, did not insist and did not teach the use of dental floss, then this is a bad prognostic symptom.
- If a periodontist, without a certificate in dental surgery, plans to independently perform curettage of periodontal pockets or flap surgery on you, unfortunately, the collapse in the domestic healthcare system has reached such a level that no one is afraid of anything anymore.
The point is that complex tooth-preserving surgical operations for periodontitis are undertaken by doctors without a certificate in “surgical dentistry” and the corresponding skills and experience. Remember that such operations should only be performed by a dental surgeon or periodontist who has a certificate in “dental surgery.” These operations are very complex, accompanied by the grafting of synthetic bone, contour plastic surgery of the inflamed gingival margin, they are lengthy (2-3 hours a fragment is made in the area of 6-8 teeth), and no dentist-therapist will simply be able to perform such an operation efficiently. But complications after such an operation are guaranteed. - State dental clinics - unfortunately, it is worth stating the following: it is almost impossible to receive qualified periodontal care in state dental clinics. This is due both to the unprofessional staffing and the fact that clinics do not invest money in developing the knowledge and skills of doctors, and accordingly do not send them to good and expensive training courses.
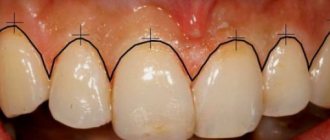
For what reasons can tooth roots become exposed?
Gum recession is dangerous because during its development there is a risk of losing several teeth at once. The disease exposes the roots of the teeth. If the root part of one of them is exposed, the pathology can spread to the entire row.
We suggest you read: Stomatitis and thrush are the same thing
| Group | Cause | Short description |
| Physiological | Aging | Once a person reaches the age of 50 years or older, the periodontium and periodontium are subject to severe wear and tear, which leads to exposure of the roots of wisdom teeth, canines, and incisors. |
| Individual structural features | Sometimes the reasons for exposing the neck are:
| |
| Symptomatic | Infections and inflammations of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity | Epithelial tissues have sagged due to decreased resistance to internal and external influences due to the development of gingivitis, cysts, abscess, periodontal disease, and periodontitis. |
| Irregular hygiene | A large number of dense formations on the enamel provokes the descent of soft tissues, and the neck (and root part) is exposed. | |
| Traumatic | Orthodontic intervention | When force is applied to the gums during the treatment of dental diseases, a phenomenon such as recession can develop after:
|
| Injury |
| |
| Household mechanical damage | Because of what the soft tissue peeled off and exposed the cervical or root part:
| |
| Improper hygiene | The use of hard brushes, damage caused by floss, toothpicks, brushes to clean the interdental space. |
Many people are interested in the name of the disease in which the roots of the teeth are exposed. This phenomenon in dentistry is called “gum recession,” but it is more of a symptom than an independent disease. It is most often found in the area of the lower front teeth.
Most often, the cause of this phenomenon is periodontitis - inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues that are chronic in nature. Such pathological processes are usually the result of poor oral hygiene. Thus, plaque and food debris that accumulate on the surface of the teeth and in their spaces gradually affect the soft tissues and provoke the development of inflammation. This explains why the gums become weak and loose and begin to recede, exposing the necks of the teeth and leading to their loosening.
Periodontitis can cause pathology
Another cause is periodontal disease - unlike periodontitis, it is not an inflammatory disease, but a systemic one. But at the same time, the gums still shrink in size, only not because of the accumulation of a large amount of plaque, but because of the atrophy of this tissue and metabolic disorders.
Prevention
No one will take care of our health for us. Therefore, the burden of responsibility lies only with us. It is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity. In order to avoid the occurrence of inflammatory processes, it is necessary to brush your teeth in a timely and proper manner.
In addition, it is necessary to visit the dentist at least once every six months. Even if there are no problems with your teeth, at your appointment you will be offered professional cleaning of soft and hard deposits. You also need to watch your diet. Nutrition should contain a complex of all necessary microelements and vitamins.
Periodontist: what he treats and what he does during the appointment
A dentist who treats periodontal disease is called a periodontist. Periodontium is the tissue that surrounds the tooth. They require careful care and can cause a lot of problems for the owner.
Oral health is very important for the functioning of the entire body. When problems arise in this area, disturbances occur in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the cardiovascular system. In this regard, a person should monitor his oral health from an early age. If caries appears, you should contact a dentist, and if you have periodontal diseases, you should contact a periodontist.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Income Tax Refund for Dental Treatment: Tax Deduction for Dental Services || Documents for personal income tax refund for dental treatment
How to become a periodontist?
In accordance with Russian standards, periodontology is not identified as an independent specialty. Therefore, if you decide to improve in this direction, you will have to go through several stages. First, you will have to obtain a higher education in the specialty “Dentistry”. This program is offered by leading Moscow universities, for example, Perm State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov and RNRMU named after. N.I. Pirogov. Then you should continue your residency training. The specialty you need is “therapeutic dentistry.” It is successfully taught at MGMSU named after. A.I. Evdokimov. At the same university there is the only department of periodontology in Moscow, which allows you to obtain the necessary knowledge.
To work as a periodontist, you need to obtain additional education. This can be done in special courses that are conducted by both private and public institutions (including the already mentioned medical and dental university). Knowledge in the field of dental surgery will also be extremely useful for the doctor.
Advice from a periodontist
It so happens that many people go to the doctor when the disease has already manifested itself and is causing concern. Every trip to the clinic is a reason for excitement.
To reduce stress and suffering due to problems with the oral cavity, periodontists advise following a few simple recommendations as a preventative measure:
- The basis of healthy periodontal disease is daily oral hygiene. This means that you need to take care of your teeth and gums every day, throughout your life.
- Teeth should be brushed morning and evening. During the day, after each meal, rinse your mouth. Carefully remove food debris stuck between the teeth with a toothpick or special floss.
- The toothbrush should have rounded edges and soft bristles. This will allow you to brush your teeth without damaging your gums.
- The service life of a toothbrush is from 2 to 4 months. It is important to change it on time.
- You need to choose your toothpaste carefully. It is not only a means of removing plaque, but also a powerful tool for the prevention of oral diseases. Many pastes contain special additives and are intended for those with gum problems. To choose the best option, it is better to consult your periodontist.
Keeping your gums healthy is not difficult if you approach it seriously and responsibly. Moreover, there are specialists - periodontists, whom you can always turn to for advice and help. They will get rid of problems and provide treatment at the highest professional level.
Hygienist: assistance in the initial stages
Prevention of diseases of teeth and gums is the main thing that a person concerned about the condition of the oral cavity should remember. The maximum benefit at this stage will come from communication with a hygienist. It does not cure, but prevents; Its tasks include cleaning from dental plaque, stones and bacteria.
Causes and treatment of gum exostosis
But it is these harmful objects that cause the development of gum disease. In addition, you should contact a hygienist for minor problems. For example, slight itching in the gums when chewing hard food, or slight bleeding when brushing hard, or the presence of an unpleasant odor in the mouth.
In advanced cases, a fistula may form, which will lead to loosening and loss of the tooth.
In most cases, at this stage, professional teeth cleaning by a hygienist is sufficient, and gum problems will disappear on their own. Another important function that this specialist performs is informational. Including telling patients about the rules of oral care.
How to properly brush your teeth, floss and massage your gums to improve blood circulation? An experienced hygienist will give detailed answers to these and other questions.
conclusions
- A periodontist is a specialist who monitors the condition of gum tissue and tooth ligaments. He examines the periodontium, conducts diagnostic studies, finds the cause of the disease and begins treatment.
- contact a specialist at the first problem with your gums, if the neck of the tooth becomes visible, an unpleasant smell, taste and pain appear.
- Before going to see a doctor , it is necessary to prepare the oral cavity in a certain way, and also inform the periodontist about any allergies to medications.
- The periodontist will help in the treatment of gingivitis, periodontitis, and periodontal disease. You may also be interested in treating chronic periodontal disease.
Sources
- https://dentoland.com/lechenie/parodontolog-kto-eto.html
- https://DentConsult.ru/desna/parodontolog.html
- https://MikDent.ru/stomatolog/o-zubax/vrach-parodontolog-v-stomatologii.html
- https://stomatdoc.ru/parodontolog-kto-eto.html
- https://DesnaZub.ru/lechenie/chto-lechit-parodontolog
- https://prozubpastu.ru/lechenie/chem-zanimaetsya-parodontolog-chem-on-otlichaetsya-ot-stomatologa-terapevta
- https://PlastikaPlus.ru/desny/vrach-parodontolog.html
- https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5b06c1308309051cd7102ac5/chto-lechit-parodontolog-5bc483b735b68100aa4166e8
- https://StomaGet.ru/o-zubah/vrach-stomatolog-parodontolog
- https://24stoma.ru/parodontolog.html
- https://ZubZdorov.online/bolezni/parodontologiya/parodontoz/lechenie-par/parodontolog-eto.html
[collapse]