Features of dental prosthetics for periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is diagnosed in an average of 1-8% of patients. At the same time, many make this diagnosis for themselves, confusing periodontitis and periodontal disease.
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process. With it, the gums become loose and recede, exposing the necks of the teeth. Often the disease is accompanied by purulent discharge.
Periodontal disease is a chronic non-inflammatory disease. It affects the gums, periodontium, dental cementum and alveolar processes. If left untreated, periodontal disease can lead to bone loss and tooth loss over time.
Why does periodontal disease occur? Medicine has not yet found a clear answer to this question. Experts are of the opinion that periodontal disease is a consequence of poor heredity, diabetes, glandular dysfunction, and diseases of internal organs. However, these are only indirect reasons that influence the development of many diseases, not only periodontal disease.
It is currently impossible to cure periodontal disease completely. In this respect, the disease is somewhat similar to psoriasis. The only thing that medicine can achieve in relation to these diseases is stabilization of the condition and stable remission.
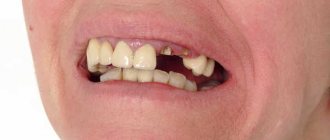
Periodontal disease in the initial stages is treated with therapeutic methods, and in later stages - with surgical methods. If the patient has started the disease, and it has “reached” the fourth, most complex, stage, then dentists are often forced to remove teeth and replace them with dentures.
The insidiousness of periodontal disease is that its initial stages do not make themselves felt in any way - nothing hurts the person. Therefore, many patients come to the dentist with advanced stages of the disease that cannot be completely cured. And the most unpleasant thing is the generalized form of the disease: the entire dentition is affected at once.
How is implantation performed?
When visiting an implantologist for the first time, the doctor’s main goal will be to find out what condition the patient’s gums and jaw bone tissue are in, and whether bone grafting or gum transplantation is required.
If there is a need for these operations, then implantation will be delayed for a period of several months to a year, depending on the complexity of the situation. If positive results are achieved, the doctor will proceed to dental implantation, which consists of the following stages:
- Implantation of titanium screws (implants) into the jaw simultaneously with tooth extraction. Before implanting the rods, a thorough curettage (cleaning) of the dental sockets is carried out.
- Installation of abutment and healing abutment. Depending on the type of implantation, this may be on the day of implantation or 3-6 months after surgery.
- After 10 days, a temporary prosthesis (crown) is installed using previously taken impressions.
- A few months later, a permanent prosthesis will be installed.
Implantation technologies for periodontitis and periodontal disease
Considering the high risk of infection in case of periodontal tissue disease, it is advisable to perform as few surgical operations as possible. In this case, preference is given to express implantation technologies with immediate loading.
In patients for whom removal of all teeth is indicated, implantation is performed using the All-on-4 protocol. In this case, 4 implants are used to fix the prosthesis, 2 of which are screwed at an angle into the lateral parts of the jaw. For better prosthesis stability, the alternative All-on-6 protocol is preferred in many cases. Read more about technologies.
Prosthetics on implants for periodontal diseases: forecasts
According to research, patients with periodontitis, periodontal disease, who do not develop the disease, regularly visit the dentist and take a responsible approach to daily oral hygiene, have almost the same chances of successful implantation as healthy patients.
If you want to create an attractive snow-white smile with the help of implants, you also need to take care of the health of the entire oral cavity, including your gums. With chronic periodontal disease, you need to put in more effort to ensure that the implant lasts for many years.
Do you have any questions? Make an appointment with one of the NovaDent clinic specialists. During your free consultation, your dentist will conduct a thorough examination of your oral cavity and talk about denture options for your case.
What types of prosthetics are possible for periodontal disease?
Before installing dentures, dentists must carry out comprehensive treatment of the disease in order to achieve its remission. If bone loss is not stopped, any prosthesis will quickly become unusable.
Zirconium dioxide crowns
fixed onto ground natural teeth.
Metal ceramics and porcelain are not used for periodontal disease. Dentists prefer to install zirconium crowns - they prevent the accumulation of bacteria and inhibit the development of the disease. Zirconium dioxide crowns are quite expensive, so they are most often installed in the smile area.
Bridges
fixed to abutment teeth or crowns.
Such dentures create excessive pressure on the “support teeth” and jawbone. Therefore, such prosthetics for periodontal disease are a rare occurrence. In addition, bridges can be installed only if the teeth are not loose and the bone tissue is completely preserved or its atrophy is minimal. That is, a bridge is a possible solution only for the initial stages of periodontal disease. When the disease begins to progress again - and this, unfortunately, is inevitable, the supporting teeth will begin to move due to excessive load and the bridge will either have to be changed or a new solution to the problem must be sought.
Removable dentures
fixed with clasps and occlusal pads.
A removable denture for periodontal disease should have minimal impact on soft tissues and mucous membranes. Therefore, dentists often install a splinting clasp prosthesis for patients with periodontal disease, which restores lost teeth, tightly fixes natural teeth and evenly distributes the chewing load. This design can be used even if all the teeth are loose - in this case, the doctor connects them and secures all the elements of the row together. The clasp splinting prosthesis is fixed on the supports with clasps - ring-shaped and claw-shaped hooks.
Is it possible to place implants with periodontitis?
Periodontitis is a common inflammatory disease of periodontal tissue, accompanied by resorption of the jaw bone. It is the main cause of early loss of permanent teeth. It differs from periodontal disease in its infectious nature.
Develops due to:
- poor oral hygiene;
- advanced caries, gingivitis;
- improper prosthetics;
- malfunctions of the digestive system.
It occurs in acute or chronic form. The first is characterized by:
- accumulation of plaque on the enamel surface;
- bleeding from the gums;
- pain, itching;
- purulent exudate in gum pockets;
- tooth mobility;
- bad breath.
In chronic cases, there is bleeding and instability of dental units.
There are three stages of the disease:
- Mild - the depth of periodontal pockets is less than 4 mm, bone resorption in the area of the interradicular septum is up to ⅓ of the root length, tooth mobility is grade I-II.
- Medium - pockets up to 6 mm, loss of bone mass by ½ of the root length, degree I-II instability.
- Severe - the size of the pockets is more than 6 mm, the resorption of the partitions is more than half the length of the roots, degree III mobility.
Periodontitis and implantation are quite compatible. Moreover, this is the only effective method of restoring lost teeth, but only if the source of infection is stopped. Therefore, before the procedure, complex treatment is carried out, restoration of periodontal ligaments, and strengthening of soft tissues. In patients with a chronic form of the disease of mild and moderate stages, only the missing units of the dentition are restored. In severe and acute cases, all teeth are removed and implants are placed.
Contraindications:
- the inflammatory process has not been eliminated;
- complete atrophy of jaw tissue due to the impossibility of bone grafting;
- general diseases that are included in the list of restrictions for implantation;
- poor oral hygiene, bad habits.
Complete dentures
If a patient with periodontal disease has lost all his teeth, then the above prosthetic options will not suit him. In case of complete edentia, removable dentures are sometimes used with support on the mucous membrane, which are “sucked” to the jaw. But this is perhaps the worst solution to the problem.
- Such a prosthesis constantly “pleases” its owner by shifting and falling out. This happens due to the fact that the mucous membrane with periodontal disease in different areas has different volume and height, that is, there is no talk of any tight fixation of the prosthesis.
- The entire load goes not to the bone tissue, but to the mucous membrane. Because of this, blood flow in the gums is disrupted - and this is half a step before inflammation.
- Complete removable dentures require careful care to avoid the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria in the mouth.
All this does not help the patient with periodontal disease, but only worsens his mood and the condition of the oral cavity.
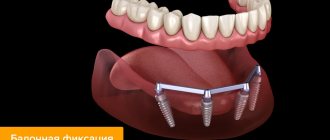
Installation of implant-supported dentures for periodontal disease
Implantation for periodontal disease usually proceeds as follows:
- the doctor agrees with the patient on the treatment method;
- removes all diseased teeth;
- performs plastic surgery of bone and soft tissues;
- performs one-stage or basal implantation.
The choice of implants for periodontal disease is very important. Dentists use implant systems with maximum survival rates and primary stability. Often these are artificial roots that have a smooth antibacterial coating - it reduces the risk of developing peri-implantitis. Another requirement for implants when working with a patient with periodontal disease is that they must be installed in the basal layer of bone, the likelihood of inflammation of which tends to zero.
But no matter how high-quality an implant the dentist installs, its service life depends on the patient. If he does not regularly undergo periodontal therapy and the disease leads to relapse, the risk of implant failure will increase significantly.
Features of care
The service life of dentures depends on how well the patient takes care of the oral cavity. And for people with periodontal disease, care is the main requirement; if it is not enough, relapse and rejection of the prosthesis is possible.
First of all, you need to thoroughly clean your teeth. If a regular brush is unable to remove all food debris from the mouth, you should use an irrigator. Such a device delivers a pressure stream of water, thereby cleaning the interdental spaces. In the absence of food residues in the oral cavity, bacterial attack is significantly reduced.
Dental floss is also a good way to clean interdental spaces, but its use can be inconvenient if bridges are installed in the oral cavity. But for the spaces between living teeth it is indispensable.
When choosing an irrigator or a thread, it is better to opt for the latter, since it is easier to use and at the same time prevents dental ailments.
Which dentures to choose for periodontal disease?
Only a dentist can accurately answer this question - the choice depends entirely on the clinical case.
Implant-supported dentures are the most functional and aesthetic way to solve the problem. It should be understood that the risk of artificial roots being rejected is quite high.
In case of advanced periodontal disease, when all remaining teeth are removed, implantation followed by prosthetics is most often performed. But only after completing the therapeutic course of treatment, which puts periodontal disease into remission.
If the patient still has natural teeth, dentists recommend installing a removable denture. It leaves the edge of the gum open, allows you to control the development of inflammation and provides the dentist with easy access to the affected gums.
Recovery methods
After all the necessary treatment measures have been carried out and with the approval of the doctor, the method of prosthetics is selected.
The best option depends on the condition of the jaw, the health of the gums and the number of units lost. The final decision is made by the attending physician.
Dental implantation
Implantation allows you to restore the integrity of the jaw row and maintain the normal state of the jaw bone, avoiding atrophic changes.
During the procedure, a titanium rod is implanted into the gum tissue, simulating a root. An artificial crown is installed on it, completely replicating the real one.
Implants are more often used when it is necessary to restore a single lost element. Before the procedure, it is necessary to get rid of periodontal disease; with loose, inflamed gums, there is a high probability of rejection of the artificial root.
Contraindications also include diabetes mellitus, some chronic diseases of internal organs, immunity problems, pregnancy and lactation.
Before implantation, you must undergo a series of tests. The list includes:
- blood biochemistry;
- tests for infections and STDs;
- coagulogram;
- blood glucose level test;
- general urine analysis;
- stool analysis.
To assess the condition of the bone tissue and jaw structure, the patient is sent for a computed tomography and orthopantogram, and a panoramic image of the jaw is taken.
Clasp dentures
A clasp denture is a removable structure, the peculiarity of which is a power frame - a metal arch on which a nylon or plastic base with artificial teeth is installed.
A prosthesis is placed only if the patient has healthy, strong teeth on both sides of the jaws , and the prosthesis is fixed to them.
Unlike the “standard” removable system, the arch prosthesis leaves the palate open, so the patient experiences virtually no discomfort while talking and eating.
At the same time , the normal chewing load is maintained, which makes it possible to slow down the atrophic processes in the tissues of the jaw and gums.
The service life of the structure reaches five years. Afterwards, the patient must return to the orthopedic dentist to make a new prosthesis.
It is necessary to remove the denture every few months for thorough cleaning. You can do this yourself, without the help of a specialist.
Splinting bridges
Splinting bridges are non-removable prosthetics. The procedure requires the presence of healthy units that serve as support. A cavity is created in them, into which a fiberglass tape is placed, which fastens real crowns with an artificial implant.
This method is convenient when it is necessary to correct a single defect; the procedure can be performed in one visit . The supporting teeth are practically not injured, and there is no weakening. Thanks to the uniform distribution of the load, the artificial tooth fully participates in the process of chewing food.
The method has some disadvantages. Thus, there is a possibility of re-exacerbation of chronic periodontal disease. This can lead to the destruction of the supporting units, which will compromise the integrity of the splint structure.
The method is temporary, and in the future it will be necessary to use other prosthetic options.
Permanent splinting
Splinting is a technique that involves linking several moving teeth into a single block using fixing elements.
This method makes it possible to redistribute the pressure exerted on the connecting ligaments of problem units. The method is more often used to strengthen shaky units.
The number of teeth used in splinting depends on the overall clinical picture. Aramid threads, fiberglass tapes or metal arches are used for fixation.
Fastening occurs using a composite filling material. The coupling can be carried out both inside “their” teeth and outside - along the enamel.
Veneers
Veneers are more often used for aesthetic row correction. They belong to microprostheses and are a kind of lining that is attached to the front surface of the tooth.
The procedure involves slight grinding of the enamel - about one mm needs to be removed.
Different materials are used to create veneers:
- composite;
- porcelain;
- ceramics.
The appearance and strength of the lining depends on the selected material. Porcelain lumineers are considered the most optimal option - thin plates that can be installed practically without turning and on artificial crowns.
The procedure for installing veneers has a number of limitations. Thus, onlays are not used for bruxism, malocclusion or the absence of a large number of teeth.
In the video, the specialist will supplement the information presented in the article.
Periodontal disease and prosthetics of the smile area
Periodontal disease is merciless to all teeth - including the front ones. As we said, if the disease is started, it will “evict” all the teeth from the jaw, without exception. Is it possible to restore the aesthetics of a smile in this case? In modern dentistry, it is possible.
The following types of prosthetic replacement of anterior teeth for periodontal disease are possible:
✔
if natural teeth are preserved, use zirconium dioxide crowns and veneers. True, installation of the latter is possible only in the early stages of the disease;
✔
if all the teeth have fallen out or had to be removed, use removable dentures or implant-supported dentures. The first option is budget-friendly, the second will allow you to get a good functional and aesthetic result.