December 16, 2020 Last revised: September 12, 2020 Dental diseases
We will talk about canines - powerful single-rooted teeth with serial number 3, located in pairs in the upper and lower jaws between the front incisors and premolars. The term “eye teeth” appeared in parallel as a common one, primarily among dentists themselves. There is even a diagnosis of “eye tooth”, and it is made by doctors when the child’s fangs begin to grow, accompanied by a distinct pain syndrome.
Because the roots of these teeth are located in close proximity to the facial and optic nerves, this growth may be accompanied by pain in the eyeballs. And the removal of such a tooth is also fraught with unpleasant sensations in the eye area. True, rumors that you can go blind after surgery related to these teeth have no basis.
Among non-specialists, the name “eye teeth” is used due to the fact that if you mentally continue the axis of such a tooth upward, it will pass right along the corner of the eye, which can be seen by stretching your lips and exposing your fangs in a grin.
Features of appearance and growth
The first to appear in infants are the lower paired symmetrical incisors, No. 1. Then the top ones with the same number. Then the second pairs of incisors are cut, first the lower one, and then the upper one, under No. 2. Logically, the next ones should be the heroes of our story - the “eye teeth”, the fangs, which are assigned No. 3. But no! Leaving an empty space, the primary molars emerge. And only after they erupt, a little hell can begin for moms and dads associated with the growth of baby canines, with their unusually long root, which is why they are born later than teeth number 4 and 5.
These teeth in children usually begin to grow before the age of 24 months. Rarely - up to one and a half years. The child begins to cry, pulls his hands to his mouth only to immediately pull them away, rubs his eyes, and when he tries to see what’s wrong with his little eye, he also starts screaming. Even bright sunlight can become a painful irritant while walking a child in a stroller. To avoid this, you should use a light-protective canopy over the canopy. Parents should be aware of these symptoms in order to recognize the appearance of these age-related teeth early.
How children's eye teeth develop
Their growth is directly related to physiological changes in the child’s body. With normal development, it is at this age that the transition from mother's breast milk to more solid and heavier food begins, in the digestion of which the fangs can play a leading role. It lies in the fact that the need has arisen for biting off more or less solid food, even tearing off pieces from it, which the fangs are evolutionarily designed to cope with. This is also facilitated by their shape - a thickened cone, which has two cutting edges that meet at an acute angle in the upper part of the crown, and a powerful thickened root. The canines of the upper jaw also have more powerful roots than those of the lower ones, because a greater load falls on them than on the lower ones. Somewhere around 25%.
Unlike incisors, in most cases the upper canines erupt before the lower ones, although there may be exceptions to this rule: in 20% of cases the lower ones erupt earlier.
Symptoms of canine growth
Symptoms of canine growth: they are in every way similar to the eruption of other teeth. But - to a superlative degree. This and
- Gingivitis, which has a non-infectious nature of inflammatory processes
- Increased body temperature, up to 38⁰
- Swelling of the gums, its pronounced edema
- Non-infectious rhinitis associated with the activity of the salivary glands
- Hypersalivation not associated with dysfunction of the central nervous system.
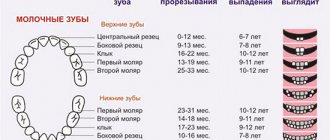
For parents of children whose baby teeth have begun to emerge, it would be a good idea to know both the order in which the teeth are numbered in the child’s mouth and the order in which they grow, starting at 6 months of age. To do this, have a kind of instruction manual on how to behave and how to help children overcome this crisis moment in dental development.
Teething order
Dairy
Incisors. The baby's first teeth appear. The lower ones grow first.
2 central and 2 lateral, a total of 4 each in the upper and lower jaws. Numbering – 1st and 2nd teeth.
Fangs. Tooth number 3. But due to its long and massive root, it will grow later than 4 molars. Molars “peck” through the gum tissue around the end of 20 months. And only after this the most painful ones - the eye ones - begin to grow painfully.
And only after two years will the last ones grow, growing after the fourth.
Thus, there are no premolars in the row of primary teeth at all. Only with the growth of skeletal bones and age-related growth of soft tissues in the mouth does space appear for premolars and, in general, for a full row of teeth inherent in an adult.
There is a so-called formula for teething baby teeth, which is relevant up to 2 years of a baby’s life. To determine the number of baby teeth, you need to subtract “four” from the age taken in months. Example:
The child is one year old, that is, 12 months old. Subtract 4. It turns out that according to this formula, a one-year-old baby should have 8 teeth.
The formula is valid for up to 2 years, after which deviations are possible that are not pathological.
Permanent teeth
The peculiarities of the physiology of the oral cavity are such that the first permanent teeth (and these are molars, they are also called “sixth teeth”) come out at the age of 6-7 years. Their placement in the dentition is immediately behind the second primary molars.
Falling out primary central incisors are replaced by permanent ones at 6-7 years (lower) and at 7-8 years - upper.
The lateral incisors are replaced by adult incisors, respectively, the lower ones - at 7-8 years, the upper ones - at 8-9.
Primary molars are replaced by first premolars at approximately 10 years of age.
Second premolars replace lost second primary molars in the jaw. Their appearance in the upper jaw occurs at 10-12 years, in the lower jaw - usually a year later.
Permanent eye teeth, that is, permanent fangs: grow in place of the falling out milk teeth. Lower ones at 9-10 years old, upper ones at 11-12.
The last and immediately permanent teeth have no milk analogues; the third molars, known to everyone as “wisdom teeth,” will emerge.
Where are they located
They are located on the upper and lower jaws. These are paired canines that are adjacent to the lateral molars on one side, and to the small ones on the other. In the embryo, eye teeth begin to form in the second month of intrauterine development. Like the others, they are formed from the dental epithelial plate, however, they penetrate deeper into the bone tissue than others.
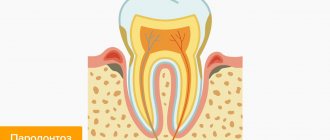
The canine structure is no different from other teeth. If we consider the anatomical structure, the teeth are divided into 3 parts. The part that is above the gum is called the crown. The neck begins from it, it is covered by the gums and ends with the root, which, in fact, holds the tooth in the jaw.
The root can be single or have shoots. Since we are talking about a fang, it must be said that it has one root without branches. It itself consists of several tissues, but mainly dentin. In the root part, the dentin is covered by cement, and the crown is covered by enamel. Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and is necessary for the tooth to protect itself.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Snz23zi6Bko
The nutrition of these teeth, like all others, is provided by the pulp - it is located inside the tooth and consists of blood and lymphatic vessels, as well as nerve cells. A nerve runs through the center and is located in the dental canal.
We suggest you read: Is it possible to remove teeth for a nursing mother?
The anatomy is clearly shown in the video below:
Special cases of eruption of eye teeth
It happens that the nerve of the growing canine is located abnormally close to the ocular and facial nerves. Then there may be profuse lacrimation, which parents may mistake for an allergic reaction to something. You can distinguish such lacrimation from an allergy by carefully examining the surface of the mucous membranes of the eye: if there is no swelling of the conjunctiva, an allergy can be excluded. Otherwise, use Fenistil in drops, carefully monitoring the reaction.
When baby teeth first appear and when a baby eye tooth is replaced with a permanent one at the age of 9-12 years, the following problems are possible.
Edentia
This is a developmental defect that involves the absence of one or more teeth or even their rudiments. It happens with problems with heredity or diseases of the endocrine system.
If there are rudiments of teeth, gum eruption and treatment that stimulates tooth growth are practiced. In the absence of tooth germs, at the age of growth of permanent teeth, implants are indicated.
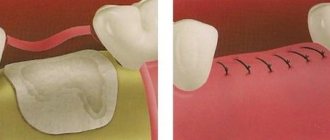
Retention
With this pathology, there is a tooth germ in the gum, but it does not erupt either due to dense gums, or because the growing tooth rests against a milk tooth that has not fallen out.
Characterized by swelling and fever. Treatment is dissection of too dense gums or removal of a baby tooth that is interfering with the growth of a permanent one.
Early eruption
If we are talking about a baby eye tooth, then we talk about periods earlier than 16 months. If about permanent ones, then such a tooth can try to break into the light for up to 9 years. Risks of retention. May indicate undetected tumors or endocrine system problems.
Late eruption
If the primary canine is absent upon reaching 20 months of age, and the permanent one has not appeared even after 12 years. This problem can most often indicate a lack of calcium, or rickets and its long-term consequences.
How to relieve symptoms
If a child's eye teeth are erupting, causing significant discomfort, parents can try a variety of methods to relieve the symptoms. Before using them, it is recommended to consult a doctor who can objectively assess the symptoms and competently select medications or advise safe and effective methods.
It is important to remember that one of the main requirements of this period is impeccable oral hygiene: teeth are brushed by parents using a silicone finger tip. But some children at this age are already able to clean themselves. Of course, it will not be as high quality as we would like, but even superficial hygiene can protect against the development of many dental pathologies. It is advisable to give the child water every time after meals to wash away food debris and restore acidity in the mouth.
The main methods to alleviate the condition when eye teeth appear are as follows:
- For redness and inflammation of the gums, special dental gels with substances that reduce the sensitivity of the mucous membranes are used. For severe pain, preference is given to gels containing lidocaine hydrochloride. Such drugs can be purchased at a pharmacy without a doctor's prescription. When using for the first time, caution must be exercised in case of possible allergic reactions to the components of the gel.
- To alleviate the condition, massage the gums. You can massage with your finger or using a silicone finger tip. This method has no side effects, and if it alleviates the child’s condition, then it can be used many times a day, massaging the gums for two to three minutes.
- When the temperature rises, you can give antipyretics based on ibuprofen or paracetamol in age-specific dosages. Both medicines in the form of syrup and suppositories are allowed. Typically, the temperature decreases within 20-40 minutes.
- To reduce inflammation, you can use teethers that are pre-cooled in the refrigerator. These silicone products with water inside are harmless when used correctly and as long as they are washed and kept clean.
- For physiological rhinitis (when the snot is not green and does not flow too much), light vasoconstrictor drugs are used. It is important to remember that their long-term use is prohibited. It is best to limit the instillation to bedtime to make it easier to fall asleep.
Permanent fangs
At the age of 7 to 9 years, baby fangs begin to change into “adult”, permanent ones, which a person will have for the rest of his life, under conditions of appropriate care and the genetic predisposition of the teeth to longevity. Fangs very rarely suffer from caries or any other pathologies.
Undesirability of deletion
The inconsistency of rumors about possible blindness after removal of fangs, especially the upper ones, is written above. An exception is the pathology of the development of the canine and its root, when the optic nerve can come into contact with the nerves of the canine root. Then careless extraction, disrupting the canal of the optic nerve, can cause one-sided blindness on the half of the face where the extraction took place. To avoid this, be sure to take an x-ray of the roots and jaw. The resolution of X-ray machines in dental clinics makes it possible to examine and recognize pathology so that subsequent surgery can proceed without complications. And a consultation with an orthodontist and an orthopedic dentist is required to look for opportunities to save the tooth.
Fangs play a big role in pronouncing individual sounds, so removing either the upper or lower eye teeth can lead to a decrease in the quality of diction.
When the dentition is deprived of fangs, whose main function is tearing and tearing solid food, their “duties” begin to be performed by the incisors and, to a lesser extent, premolars (teeth No. 4 and 5). This means that the load on these teeth increases.
Growing pains
At 9-12 years of age, the growth of eye teeth can cause temporary inconvenience and discomfort. And at the age of one and a half years, as the first baby fang moves apart the gum in its desire to grow outward into the oral cavity, this can cause serious suffering to the child. Crying at night, whims - this is a short list of what the parents of a baby have to endure, with whom some kind of meaningful dialogue has just begun to develop, who seems to have already learned to react “correctly”, from an adult point of view, to the environment - and here The relationship between an owl slides down to the level of a baby.
Moreover, disoriented by the confusion of day and night into which their child has been driven, parents may mistake the symptoms of eye teeth growing into something else. In eye disease, as often happens. Therefore, contacting a pediatrician should take place as early as possible.
In complicated cases, the child will be prescribed medications that significantly reduce swelling of the gums and relieve pain. These, after a medical examination and prescriptions, can be pain-relieving gels “Metrogil Denta”, “Kalgel”, “Kamistad”.
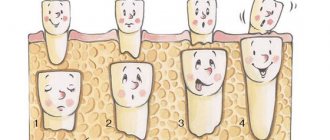
In adolescence, it is time to replace a baby tooth with a permanent one. It often happens that a well-fitting baby tooth does not want to leave its place and prevents the “adult” tooth from taking its place between the incisors and premolars. In such a situation, the canine may grow incorrectly, with a displacement inward, towards the tongue, or outward, towards the cheek, which will distort the bite and will not contribute to normal chewing of food.
How to help your baby?
The baby does not need to experience all the pain of teething. Now there are many tools that will help quickly facilitate this process. Pediatricians often prescribe drops (for example, Dantinorm Baby). They last longer, have no side effects and improve the overall condition of the baby.
But gels and ointments cope better with pain relief. They most often contain lidocaine. It relieves pain almost immediately. But these drugs are quickly washed off by saliva, so their effect lasts for a maximum of half an hour.
Children often suffer from a runny nose.
Among the gels, Kamistad, Kalgel, Dentinox are most often used. Their main advantage is speed of action. They have a pronounced analgesic effect, which manifests itself within a few minutes after use. But this effect passes just as quickly.