Causes
Factors leading to mesial occlusion are divided into congenital and acquired.
The problem can manifest itself in a child in the womb due to various disorders. Acquired causes of pathology include bad habits and poor nutrition.
Among the provoking factors should be highlighted:
- hereditary predisposition;
- impaired fetal formation due to excessive consumption of medications during pregnancy;
- birth injuries;
- diseases of the maxillofacial apparatus that were not eliminated in time;
- insufficient development of the lower jaw;
- shortened frenulum of the tongue;
- rickets;
- premature loss of dental elements or rapid wear of enamel;
- violation of the sequence of loss of milk and eruption of permanent teeth;
- constant mouth breathing, which is a consequence of diseases of the ENT organs (adenoid, deformation of the nasal bridge);
- incorrect position of the child’s body during rest;
- bad habits.
Several factors can cause a mesial bite. Identifying the cause of the problem is the key to successfully combating pathology.
Reasons for the development of mesial occlusion
- The formation of progeny is most often influenced by heredity. Even if the curvature was observed in only one parent, the risk of its development in the child increases greatly.
- Often mesial occlusion is a congenital anomaly that forms at one of the stages of pregnancy.
- The protrusion of the lower jaw is facilitated by enlarged tonsils and adenoids, as well as mouth breathing.
- Frequent biting of the upper lip, excessive pressure on the chin, excessive and uneven wear of baby and molars, or loss of the front teeth also contribute to the appearance of mesial occlusion.
- The size of the upper jaw is also affected by the absence or untimely loss of teeth.
- Short frenulum of the tongue and cleft palatine.
- Mesial occlusion can form due to tumors on the jaws, osteomyelitis, rickets and trauma.
Classification
The disease is divided into several types, depending on the size of the gap and the location of the bone structures relative to each other.
- Macrognathia. The defect occurs due to abnormal development of the upper jaw or significant mobility of both bones of the facial skull.
- Micrognathia. The disease manifests itself due to underdevelopment of the structures of the upper or lower jaw.
- Prognathia. The defect is caused by excessive protrusion of one of the bones.
- Retrogression. Malocclusions are formed due to the mobility of the jaw structures.
Depending on the degree of violation of jaw closure and the angle of the lower jaw, 3 degrees of mesial occlusion are distinguished:
- 1st degree – the distance between the chewing surfaces of the lower and upper front teeth does not exceed 2 mm. In this case, a deviation of the position of the side elements by 5 mm from the norm is noted. The angle of bone mobility is 131 degrees.
- 2nd degree – the size of the sagittal fissure does not exceed 10 mm. The angle of movement is 133 degrees.
- 3rd degree – the size of the sagittal fissure is from 12 mm. The anteroposterior position of the lateral elements is disrupted (up to 20mm). The angle of movement is 145 degrees.
Diagnosis of progeny
Only an experienced orthodontist can correctly recognize the type of malocclusion. This pathology can be true or false, and have 3 degrees of manifestations, which differ in the size of the sagittal gap between the front teeth and the different angle of the lower jaw. This complex orthodontic pathology has 5 varieties, characterized by enlargement, underdevelopment and displacement of various parts of the jaws.
The doctor must take into account the medical history, examine the patient’s face in various projections, take anthropometric indicators, study the ratio of facial sizes on diagnostic models, conduct the necessary functional tests, and visually assess the occlusion of the oral cavity. The position of the lower jaw and options for placement of the articular heads are also studied in detail. The specialist determines what form of progeny is observed in the patient - true or false.
True progeny is said to occur when excessive development of the lower jaw occurs (usually due to a genetic predisposition).
With false progeny, bite deformation occurs due to incorrect position of the lower jaw, more often in the presence of any chronic changes in the nasopharynx, as well as in impaired nasal breathing.
With the combined form of progeny, a simultaneous combination of symptoms of the true and false forms of the disease occurs.
To correctly determine the degree of mesial occlusion in orthodontics, radiography, teleradiography, orthopantomography, and tomography are used. For diagnosis, bite ridges are used, special diagnostic models of bites are made, and electromyography of various muscles of the face and head (temporal, chewing, etc.) is performed. When functional problems are identified in this pathology, consultations with an otolaryngologist, speech therapist, or neurologist are often prescribed.
How to deal with pathology
Correcting a mesial malocclusion usually takes a long time. It is important to start treatment as early as possible, preferably in childhood. Most experts recommend correcting any malocclusion before age 12. At this time, therapy is carried out in the most painless ways and has the most favorable prognosis.
Symptoms
Among the facial signs of mesial occlusion are:
- protrusion of the lower lip and chin forward;
- sinking of the upper lip;
- concave facial profile.
On the part of the dental system with mesial occlusion, the following symptoms are noted:
- the location of the lower incisors in front of the teeth of the upper jaw;
- clicking and crunching of jaw bones when chewing food;
- inclination of the teeth of the lower jaw;
- the presence of excessively large elements in the oral cavity.
Patients with a defect note signs of functional impairment:
- sharp pain in the jaw when talking and eating;
- inflammation of the gums and damage to tooth enamel due to excessive crowding;
- violation of diction;
- problems with biting and chewing food;
- early loss of teeth due to unevenly distributed load on them.
Effective methods of treating distal occlusion in children and adults.
Let's talk here about the consequences of malocclusion in case of refusal of its treatment.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/ot-chego-obrazuetsya-i-kak-lechitsya-perekrestnyiy.html we will talk about ways to correct crossbite in a child.
General overview
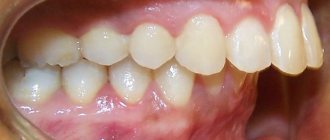
The anomaly is a malocclusion pathology in which the lower teeth overlap the upper anterior teeth, and the relationship of the chewing teeth is disturbed. In this case, the sagittal fissure may or may not be present.
Progenic occlusion has many other names: mesial occlusion, reverse or anterior (from the Latin Anterior - front) bite, progeny, lower macrognathia, upper micrognathia. This abundance of terms is explained by the lack of a common view among specialists on the etiology and features of the anomaly.
Functional disorders in progenic occlusion are numerous and are mainly caused by negative disturbances in the functioning of the masticatory muscles.
There are facial and intraoral manifestations of progeny. The first include:
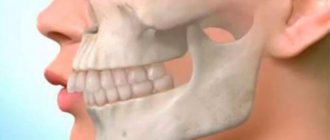
- The lower jaw is enlarged and protrudes sharply forward.
- The middle facial area (from the bridge of the nose to the upper lip) is sunken and has a flat appearance.
- The front lower part is elongated.
- The upper lip is shortened or gives the impression of being so.
- The lower lip is thickened and protruded forward.
- The nasolabial folds are deepened.
- The labiomental groove is smoothed.
The severity of the above signs depends on age, the degree and nature of morphological disorders, the presence of transversal (lateral) and vertical anomalies.
Intraoral signs of a progenic malocclusion include:
- reverse overlap (mandibular incisors are in front of the maxillary ones);
- the sagittal fissure has dimensions from 2 to 15 mm;
- the relationship between the lateral segments of the jaws along the sagittal and transverse sides is disrupted;
- there is an abnormal position of individual teeth and their groups, there are tremata and diastemas, crowding of teeth, tortoanomaly (deviation in height), dystopia (displacement) of the fangs.
What orthognathic bite defects require correction. Read here how to straighten your teeth at home.
At this address https://dentist-pro.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/etapy-planirovaniya-lecheniya.html we will consider the tactics of planning orthodontic treatment.
Consequences
People who have suffered from malocclusion since childhood gradually get used to the defect and stop noticing the unpleasant symptoms associated with it.
However, the problem should not be left without medical help. Progeny, in addition to an aesthetic defect, ultimately becomes the cause of functional disorders in the body.
The abnormal structure of the jaw interferes with normal chewing of food, which in turn provokes:
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract . Large pieces of food, moving through the digestive organs, cause injury to the mucous membranes. Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract are accompanied by problematic swallowing of food.
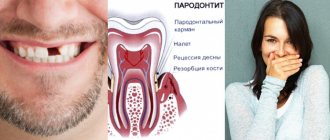
- Severe abrasion of the enamel of teeth located on the upper jaw. This condition occurs due to the fact that the main load when chewing food is distributed on the elements of the upper row. Damage to enamel increases the risk of developing dental diseases and inflammation of periodontal tissue.
- Damage to the temporomandibular joint , located in front of the auricle. The condition is accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms - headaches, enlarged lymph nodes, a feeling of constant ringing in the ears, dizziness.
Pathology or physiology?
Although there is no clear correlation between the external signs of progeny and a person’s age, you can still focus on its manifestations during the first examination and even simple observation from the outside.
Manifestations
- The appearance of the teeth is unaesthetic.
- Diction is broken (“pseudo-English accent”).
- The body of the lower jaw is significantly longer than the upper jaw; it protrudes noticeably forward, which is especially noticeable when looking at a person’s face in profile.
- While eating, a person himself feels painful or simply unpleasant phenomena that accompany biting and chewing food.
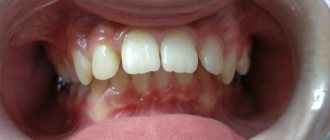
- The upper arch of the upper front teeth is completely or partially hidden behind those located on the lower arch. This is especially true for incisors and canines.
- There is no contact between the teeth of the upper and lower arches; between them, with the jaws closed, there is a noticeable gap, sometimes up to 10 mm.
Norm
But there are types of progenic bite that can be considered normal. According to the classification of experts, progeny can be a normal physiological phenomenon in cases where:
- The load on both jaws, if present, is the same.
- The jaws work fully, there is no prevailing pressure on the chewing surfaces of the upper and lower teeth.
- The gums of both jaws do not bleed or become inflamed.
- The advancement of the teeth of the lower jaw forward compared to the teeth of the upper jaw is insignificant, and their relative position does not affect the functioning of the entire dentofacial apparatus. In such cases, the anamnesis indicates “micrognathia of the upper jaw” and “macrognathia of the lower jaw.”
Such progeny is normal and does not require corrective treatment. Since it does not affect the health of all components of the oral cavity, and along with it - all other systems of the body.
In men and women
The difference in attitude towards such a facial defect manifests itself differently in men and women. In men, such a defect may be called a “manly chin.”
It’s a different matter for women: a progenic bite coarsens the face, especially in profile, and makes a woman really worry, considering such a cosmetic defect unacceptable. And in addition to the aesthetic component, the characteristics of the female body make such a defect have a negative impact on the general state of health.
Diagnostics
To diagnose a type of mesial malocclusion and successfully eliminate it, the help of an orthodontist is required. During the initial examination, the specialist notes facial signs of problems and dental pathology.
The doctor then performs linear and angular measurements of the bone structures. The orthodontist determines the severity of the defect using a bite block.
Among the additional studies prescribed for malocclusion pathology, the following should be highlighted:
- panoramic photograph of the jaw;
- X-ray;
- radiology diagnostics.
Functional disorders of bone structures are determined through myography.
The video provides information on diagnosing mesial malocclusion.
What is this type of violation?
Mesial occlusion is an anomaly in the development of the lower jaw, which manifests itself in its advancement forward relative to the upper dentition, with the lower incisors overlapping the upper ones.
This violation has other names:
- progeny;
- lower prognathia;
- mesiocclusion;
- anterial.
It is much less common than other teeth closure anomalies. In pediatric practice it is detected more often than in adults. This defect is difficult to correct.
Correction methods
The chosen treatment method for abnormal bite depends on the age of the patient. This is explained by the structural features of bone structures in children and adults.
In general, there are several effective ways to combat the defect:
- Myogymnastics . The technique is prescribed for the treatment of mesial malocclusion in children under 6 years of age. Special exercises are aimed at strengthening the muscles of the oral cavity and head, which are responsible for the chewing process. Myogymnastics is recommended as part of complex therapy.
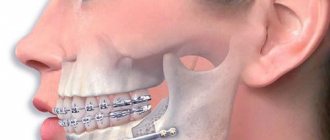
- Orthodontic systems. Bite correction is carried out through the use of fixing devices - plates, mouthguards or braces. In certain areas of the jaw, orthodontic therapy can be supplemented with surgery.
- Operational method. The operation is prescribed both on individual elements of the dentition and on the moving bone. The technique gives better results compared to the listed treatment methods.
- A complex approach. The doctor prescribes a consistent set of procedures to correct malocclusions.
This includes correcting nutrition, giving up bad habits, wearing orthodontic appliances, and performing special gymnastic exercises. In severe cases, complex therapy is supplemented with surgery. - Orthopedic method. In some cases, to solve the problem it is impossible to do without restoration of individual elements of the dentition.
Treatment in children
Until the age of 10, children are prescribed a standard treatment regimen, which includes:
- wearing orthodontic appliances;
- trimming the lingual frenulum;
- myogymnastics;
- use of vestibular plates;
- massage of the alveolar processes of the jaw.
The bone structures of children are susceptible to various corrective manipulations, so their treatment of mesial occlusion is easier and faster.
To correct anomalies in children, the following devices are used:
- trainers;
- mouthguards;
- Wunderer activator;
- Bruckle's apparatus;
- caps with a retainer on the jaw;
- Persin device;
- Frenkil stimulator.
When a child has permanent teeth, corrective plates and appliances are replaced with braces. Installation of such systems is an expensive procedure, but it gives noticeable results 1.5-2 years after treatment.
Along with orthodontic therapy, children are recommended to have classes with a speech therapist to correct speech defects.
For mesial occlusion, gymnastics for the muscles of the face and jaw are effective. The main condition for conducting myogymnastics is regularity of exercises, a gradual increase in load, and cessation of exercises when fatigue appears.
In teenagers, the problem is dealt with by installing braces. Less often, doctors prescribe complex treatment, for example, when there is a need to remove or restore several elements of the dentition.
Treatment in adults
After installation of orthodontic structures, adults often feel pain and discomfort in the teeth, muscles and joints of the jaws.
After 18-19 years, bone structures are practically impossible to correct. For this reason, the choice of ways to combat the problem is limited.
Treatment is carried out according to two schemes:
- Conservative technique , which includes wearing removable or non-removable corrective structures.
- Surgical operation (from the removal of several elements of the dentition to the dissection of bone tissue for the purpose of their further movement to a normal anatomical position).
Therapy with braces in adults lasts about 2 years. These designs give noticeable results. Braces are prescribed to eliminate various malocclusion pathologies, including progeny.
A modern technique for correcting bite defects is the edgewise technique. The meaning of the procedure is to install orthodontic structures with rings and locks on the supporting units. Braces with rounded arches are attached to the front incisors.
Surgical intervention is performed in 3 stages:
- Preparatory period (diagnostic measures, consultation with an anesthesiologist, modeling of the jaws in 3D images).
- Operation.
- Rehabilitation period.
During the operation, the surgeon cuts the jaw bones and moves them into the desired position using screws. The final stage of osteotomy is the application of a splint.
Is it necessary to get rid of the gap between the front teeth, and which method is more effective?
In this publication we will tell you in what cases it is advisable to prescribe myogymnastics.
Follow the link https://zubovv.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/chto-lechit-vrach-spisok-uslug.html if you are interested in what a pediatric orthodontist treats.
Mesial bite in a child
In order to correct an anomaly in very young children, it is necessary first to find the cause of its development and, if it is not congenital, try to eliminate it. For example, you can correct a child’s mesial bite by weaning him off bad habits or by purchasing an orthodontic pacifier and bottle. In preschool age, daily myogymnastics in the form of the following exercises is also effective:
- Use the tip of your tongue to apply pressure on the upper front teeth from the inside until the muscles become fatigued (about 3-5 minutes).
- Hold your lower lip between your upper teeth and then release it.
- Open, then slowly close the mouth, shifting the lower jaw back and placing the front teeth in marginal closure. Hold time is from 4 to 8 seconds.
If the curvature is associated with uneven abrasion of baby teeth, they should be aligned by “sharpening” the others or restoring the ground ones with crowns. As for the short frenulum of the tongue, it can be “lengthened” surgically while still in the maternity hospital.
More serious curvatures during the period of primary and mixed dentition are eliminated using combined treatment. Vestibular plates, bite formers, Brückl appliances, Frenkl and Klammt activators and other similar devices help to change the position of the dentition, as well as minimize the pressure exerted on them from the cheeks and lips. However, additional structures are needed to normalize the size and position of the jaws.
To eliminate defects of the lower jaw bone, face arches and a chin sling with a rubber rod are used. With their help, a certain pressure is applied to the lower jaw, due to which it is deformed and takes the correct position. When the upper jaw is underdeveloped, a palatal expander is used, but its effect is directed only on the dentition and, accordingly, on the alveolar processes from which the teeth grow. But, unfortunately, he cannot change the size of the entire jaw - this will require surgical intervention.
Prevention
To avoid bite defects, you should follow the following preventive rules:
- Continue breastfeeding your baby for as long as possible;
- periodically check the condition of your teeth not only with the dentist, but also with the orthodontist;
- monitor the development of baby teeth in children;
- give preference to a balanced diet;
- control the child’s body position during sleep;
- unlearn bad habits - biting nails, putting your hand under your jaw.
It is important to remember that the earlier treatment is started, the greater the chance of successfully getting rid of the problem. Even in the absence of malocclusion, children and adults are recommended to use it taking into account age-related characteristics.
Correction of anomaly
Bite correction is designed to stimulate an increase in the upper arch and slow down the rapid development of a mobile jaw.
You can stimulate jaw growth or slow down its active growth with the help of orthodontic devices that need to be used on a regular basis.
In a milky bite
At night, to correct lower prognathia, use a special extraoral dressing , which can be purchased at a pharmacy.
The bandage prevents hypertrophy of the lower jaw, keeping it in a backward position. The cost of the device ranges from 300 to 1500 rubles.
Of great importance in the treatment of a progenic defect in the primary occlusion is normalizing nasal breathing (it is physiologically correct). The longer the child has a breathing pathology, the more complex the bite defect.
It is extremely important to eliminate existing negative habits: sucking fingers and upper lip, pushing the lower jaw forward, sucking the cheeks between the teeth, inserting the tongue between the teeth. These actions can lead to the development of progeny.
In a mixed bite
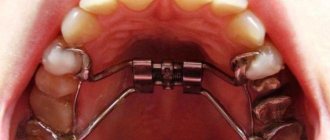
Today in orthodontics, a large number of intraoral devices have been developed to correct bites and uneven teeth. One of the most common designs is the Bruckle apparatus.
It is a removable plate attached to the lower jaw using clasps. The latter are attached to the chewing teeth.
The sliding screw expands the lower arch and also eliminates crowding of the dentition. The cost of the device (with installation) is from 4500 to 6000 rubles.
Kappa Bynina is a single-jaw stationary device . Used for false forced progeny. The mouthguard moves the upper incisors forward and the lower jaw backwards.
Before using the device, it is necessary to grind off the unerased cusps of primary dental units and perform myogymnastics.
The device is activated when the side sections of the mouth guard are ground off. The cost of the structure (with installation) is 6,000–8,000 rubles.
The Frenkel apparatus consists of a metal frame made of medical wire, cheek shields and lip pads. This device is more convenient than vestibular plates.
When using this device, treatment takes much less time. The cost of the device (with installation) is 7,000–18,000 rubles.
In permanent bite
The formation of a permanent bite occurs up to 15 years. During this period, correction of a child’s permanent progenic bite is carried out using braces, plates, and aligners.
The use of a brace system is one of the most effective methods used to correct the bite.
The bracket arches are made of an alloy of titanium and nickel. Initially, the structure takes the form of a pathological location of the teeth, gradually tending to its original configuration.
She pulls her teeth and forces them into the correct position. The duration of wearing braces is from 1 to two years. The cost of the device (with installation) is 5,000–20,000 rubles.
In childhood, the most effective way to straighten teeth is to install orthodontic plates. The device consists of special palatal strips and brackets that secure the structure to the teeth.
The plates are removable and partially fixed. Thanks to the screw lock, the plastic strips are adjusted. Wearing period is from 1 year to several years. The price of the device (with installation) is 1500–15000 rubles.
A dental aligner (aligner) is a transparent removable device that exerts a mechanical effect on the dentition.
It is an alternative to the braces system. Suitable for correcting simple bites. The cost of the structure (with installation) is 700–2500 rubles.
Important! You should buy devices to eliminate malocclusion only on the recommendation of an orthodontist. The final cost of treatment is influenced by the service provided by a specialist, the production and installation of a dental device.
Correction of progeny has characteristic features. It is recommended for children under the age of 14–15 years.
Children with a congenital defect require examination by an orthodontist on a regular basis: from the age of 2 until molars appear instead of baby teeth.
In the video, see the principle of operation of a face mask in the treatment of progenic bite.
Reviews
Patients consider braces to be the optimal treatment method for medial occlusion (in terms of cost and effect).
After their use, there are no complications, as after surgery, and they are much more effective than mouthguards, trainers or plates.
Leave feedback on the treatment of malocclusion pathologies in the comments to the article and tell us what rules should be followed during therapy.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: bite correction, malocclusion, bite
Did you like the article? stay tuned
No comments yet
What if the enlarged lower jaw is to blame?
You can reduce its size in different ways:
- removing the lower premolars - paired “fours” or “fives”, and closing the resulting gaps during orthodontic treatment;
- moving back the entire dentition, if possible, and if it is not possible, removing wisdom teeth or separating the lower teeth.
If the problem is related to the temporal bone, then the orthodontist often has to “push back” the protruding lower jaw together with an osteopath, a specialist in manual therapy. And the block on primary fangs is eliminated by grinding their sharp ends.
Is it possible to correct mesial bite with braces? It is possible, but only in case of pathology caused by shortening of the upper or lengthening of the lower row due to dental anomalies. In practice, such clinical cases do not occur so often.
Danger and consequences
If you do not correct the mesial bite in adults in a timely manner, you can get the most unpleasant consequences, which include:
- High risk of developing periodontal disease.
- There is even a risk of developing various diseases of the temporomandibular joint.
- The shape of the face may be somewhat distorted in relation to the general physiological system.
- The occurrence of quite serious problems during prosthetics or dental implantation.
But timely intervention by specialists will help avoid such difficulties.