Failure to comply with oral hygiene rules can cause serious pathologies, including tooth loss. Inflammation of the gums requires immediate treatment, and the longer a trip to the doctor is delayed, the more radical, more expensive and longer the recovery process will take. If at the stage of gingivitis you can get by with folk remedies, then advanced periodontal disease already requires surgical intervention.
What is gingivitis
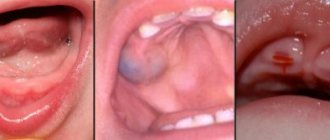
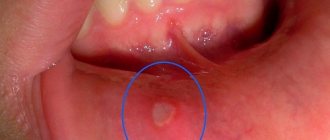
Gingivitis is the very initial stage of the inflammatory process. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms: redness (sometimes blue discoloration) and slight swelling of the gums, temporary bleeding (mainly due to mechanical damage), the formation of slight plaque and tartar, including under the gums.
An example of gingivitis
The main reasons for the development of gingivitis are poor-quality or irregular dental care, hormonal imbalances (the problem often occurs during pregnancy and in adolescents), diseases affecting the immune system, genetic predisposition, trauma and vitamin deficiency.
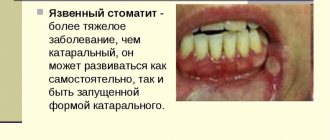
How to distinguish a sore throat from stomatitis and how they are similar
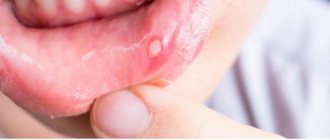
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of any of the components of the oral cavity:
If the inflammation affects the tongue, it is called glossitis; if it affects the gums, it is called gingivitis.
Mouth ulcers are another form of stomatitis. Stomatitis of bacterial origin often leads to sinusitis and sore throat.
Whatever part of the mouth is affected by stomatitis, it is usually a short-lived condition. It can be painful, but rarely causes serious problems. While complications after tonsillitis can be in the form of glomerulonephritis, scarlet fever, rheumatic fever and peritonsillar abscess.
How to distinguish a sore throat from stomatitis on the tonsils? First of all, they have different causes.
Inflammation with stomatitis can be caused by:
- poor oral hygiene; lack of protein foods; poorly fitting dentures; damage to the mouth from hot food or drinks; consumption of poisonous plants; conditions that affect the entire body, such as medications, allergic reactions, radiation therapy, or infection; severe iron deficiency anemia (lack of iron can lead to ineffective “repair” and regeneration of epithelial cells, especially in the oral cavity and lips); deficiency of vitamin B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B6 (pyridoxine), B9 (folate) or B12 (cyanocobalamin).
A sore throat is mainly caused by a virus and is often preceded by a cold, runny nose, cough and eye pain. Fewer cases (one in seven) are caused by bacteria. The most common type of bacteria that causes a sore throat is streptococcus.
What is periodontitis
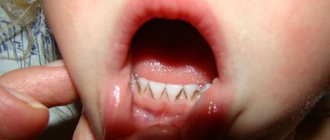
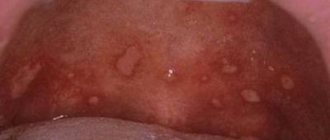
Periodontitis is the stage that follows gingivitis. Characterized by the spread of inflammation to the tissue around the tooth. There is swelling, redness and bleeding of the gums, which is constant. Gum pockets form - the soft mucous membrane peels off from the surface of the tooth and food debris and microbes accumulate in the resulting cavity. With periodontitis, there is a very unpleasant odor from the mouth.
An example of periodontitis
Periodontitis occurs as a consequence of untreated gingivitis. And since the inflammation spreads to the tissues around the tooth, the ligaments that hold it in the socket are affected. That is why periodontitis is one of the main causes of early loss of even healthy teeth.
Gum prevention
A good therapeutic, preventive and strengthening effect on the gums is provided by daily self-massage, which is done after brushing your teeth.
Apply a small amount of toothpaste to your index finger and thumb. The massage begins from the center of the jaw, gradually moving the fingers to the sides. The upper jaw should be massaged from top to bottom (from the gums to the teeth), and the lower jaw - from bottom to top.
In the morning the massage is done clockwise, in the evening - in the opposite direction. The pressure on the mucous membrane should be painless, and stronger in the morning than in the evening.
The duration of this massage is 5-7 minutes. After the massage, you should rinse your mouth with infusion of chamomile, oregano or sage for 2-3 minutes.
What is periodontal disease
If gingivitis and periodontitis are similar in symptoms, then periodontal disease proceeds in a completely different way. This disease can occur independently or be the final stage of gingivitis or periodontitis, when metabolic processes in the gingival tissues are disrupted and the mucous membrane simply atrophies, that is, it decreases in volume. Periodontitis is very common in older people, whose tissue blood supply deteriorates due to age.
An example of periodontal disease
With periodontal disease there is no swelling, redness or bleeding of the gums. On the contrary, soft mucous membranes become whitish and noticeably decrease in volume, which is why the necks and even the roots of the teeth are exposed. The disease “periodontal disease” is in fact extremely rare, but even dentists are confused about the names and often pass off “periodontitis” as “periodontal disease,” which completely confuses patients.
Gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease: differences
Nature of inflammation
With gingivitis, inflammation is localized exclusively on the gums, and in the area of the gingival papillae. With periodontitis, destruction of all periodontal tissues is observed (this is a complex of tissues that hold the tooth in the socket). With periodontal disease, there is no gum inflammation at all.
Formation of periodontal pockets
Periodontal pockets are a characteristic sign of periodontitis; they are absent in gingivitis and periodontal disease. Plaque, stone, and food debris accumulate inside the peculiar pockets - they all rot and provoke inflammatory processes.
Tooth mobility
Along with the formation of periodontal pockets, tooth mobility is another specific sign of periodontitis. When the ligaments that are responsible for fixing the tooth in the socket are destroyed, the teeth become loose and in most cases they have to be removed.
Exposure of the neck and root of the teeth
This symptom is more characteristic of periodontal disease, however, periodontitis can expose the roots of the teeth if the gum pockets are too deep.
Consequences of the disease
Gingivitis has virtually no unpleasant consequences (but only the development of periodontitis), while periodontitis itself leads to tooth loss. Periodontal disease can also cause early tooth loss (due to the destruction of the roots, which are exposed and susceptible to increased attack by bacteria), but to a greater extent the disease affects the deterioration of the aesthetics of the smile. Therefore, if gum inflammation is ranked by degree of danger, the list will look like this (in ascending order): gingivitis, periodontal disease and periodontitis.
Types of gum disease
Timely consultation with a doctor and correct diagnosis will allow you to make the correct diagnosis and promptly begin treatment. Remember that gum problems need to be addressed - even healthy teeth can be lost due to untreated inflammation of the soft mucous membranes.
Inflammation of the gums - treatment in the clinic
Today, periodontics has many methods for diagnosing and treating gum inflammation. Modern digital X-ray equipment gives a complete picture of the condition of the periodontal pocket and the extent of bone tissue destruction. And based on the entire diagnostic picture, the doctor concludes how to treat gum inflammation will be more effective.
Injections for gum inflammation
If antibiotics for gum inflammation are often prescribed and their use is justified, then injections of such drugs into the gums are absolutely not permissible. Local injections can instantly destroy a huge accumulation of microbes. At first glance, this is good, because the symptoms of periodontitis disappear quickly. However, the large-scale death of all bacteria leads to a massive release of toxins, which cause multiple foci of necrosis in the tissues. Inflammation from the gums will go away, but along with it, periodontal tissues will be significantly damaged and the teeth will become irreversibly mobile.
Surgical treatment of gum inflammation
In particularly advanced cases, for example, such as necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, therapeutic methods of treatment are not always effective. Then the doctor decides to perform a surgical intervention with gum resection and installation of a drainage system to drain the pus out. After surgery, the patient is prescribed drug therapy to prevent infection:
- Flemoclav;
- Flemoxin;
- Gentamicin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Tsifran;
- Lincomycin;
- Amicocin;
- Amoxiclav.
Together with antibiotics, the doctor may decide to prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in complex treatment to relieve swelling and inflammation and antiseptics for rinsing. To lubricate the sutures and relieve pain, Metrogil denta ointment with a cooling effect is prescribed.
Inflammation of the gums - laser treatment
In the modern medical world, laser treatment is increasingly prescribed when ulcerative gingivitis is diagnosed. This allows you to significantly reduce the period of tissue recovery and regeneration. The finest laser beam, hitting the infected areas, has a detrimental effect on microbial colonies and eliminates pathological lesions on the gums without pain or bleeding.
Gum pathologies are not uncommon. The point here is not always just a matter of neglecting hygiene rules. Unfavorable environmental conditions, poor quality nutrition, advanced chronic diseases - all this can become the starting point for the formation of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. Only timely treatment will avoid serious consequences.
Video about gum diseases
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
gum disease
Consulting specialist
Malysheva Larisa Andreevna
Doctor rating: 9.3 out of 10 (3) Specialization: Therapist, orthopedist Experience: 25 years
Comments
[…] fixed in the bone. But those who are faced with gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease often run the risk of acquiring dental defects, so [...]
Periodontium: secrets of its structure and 5 main functions it performs (08/28/2018 at 09:00) Reply to comment
[…] forms of periodontal disease in which teeth can become mobile. […]
5 common mistakes when installing a dental bridge, what you should pay attention to (09/03/2018 at 09:02) Reply to comment