8118
People of different age groups turn to dentists with the problem of missing teeth. Their deficiency not only affects the overall aesthetics of the face, but also leads to the development of anatomical and functional pathologies of the dental system, and changes in the psycho-emotional state.
Removable dentures will help correct all these problems, or slow down the progress of irreversible changes in the tissues of the oral cavity.
Indications
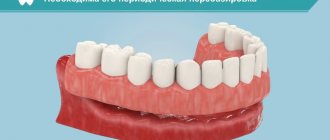
A removable denture is a design that restores the chewing and aesthetic functions of the dentition in the absence of conditions for fixed prosthetics. The patient can put on and take off this product at any time without the help of specialists.
Such prosthetics are performed in the following cases:
- the absence of one or more units in a row;
- complete edentia;
- simultaneous extraction of two or more teeth;
- before installing a fixed prosthesis as a temporary device;
- dental defects;
- looseness of the remaining units;
- severe form of periodontal disease;
- if you are allergic to the material of a fixed product;
- refusal of the patient himself (this may be caused by his fear of the implantation procedure, financial difficulties, etc.).
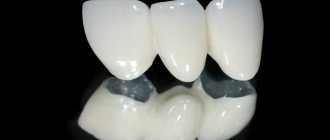
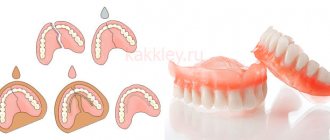
Prosthetics using removable structures includes a number of techniques. So, with complete edentia, specialists install a complete denture - this is the basis on which artificial chewing organs are placed.
It is supported by the palate of the upper jaw and the alveolar processes of both jaws. Stabilization of the product is ensured by the so-called “suction effect”, when a discharged area is formed between the mucous membrane and the prosthesis itself.
Typically, plastic or nylon is used to make its base, and porcelain or plastic is used for artificial units.
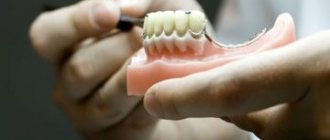
If one or more adjacent teeth are lost, a partial denture is placed. It consists of a base made of acrylic or nylon, simulating gum, and artificial teeth.
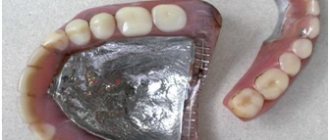
Its fastening occurs using clasps - metal support-retaining elements . They wrap around the natural unit, thereby stabilizing the position of the denture in the mouth. Partial structures come in two types - clasp or plate.
In situations where, for certain anatomical or medical reasons, the placement of bridge systems and removable products is impossible , a conditionally removable type of prosthesis is installed . This device can only be removed in a dental office.
Important! For many patients who want to restore the integrity of their dentition, prosthetics with removable types of structures is the only acceptable method of orthopedic treatment.
It successfully combines three important indicators - quality, effectiveness, cost.
Technique for making removable dentures
Poor chewing of food due to missing teeth can impair the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. In some cases, the only way to restore chewing function, which is extremely important for maintaining health, and to regain a beautiful smile, is to make removable dentures. technology protects the jaws from further destruction. The manufacture of removable dentures is carried out in cases where natural teeth for some reason could not be preserved. Removable prosthetic structures are attached to the jaw due to the ability to stick to it. They have the shape of curved plates on which artificial teeth are installed. The shape and color of the teeth are selected according to the individual needs and wishes of the patient. The color of a removable denture is as close to natural as possible. How are removable dentures made today? The technology of making dentures has now reached a level that far exceeds that of the recent past. Modern production of dentures is based on the use of new technologies and materials. Thanks to the successes that dentistry has achieved to date , removable dentures have high strength characteristics, aesthetic properties and hygienic qualities. Removable prosthetic structures have no age restrictions, and their manufacture takes into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s jaws, thereby minimizing discomfort when using them. Of course, dentures should not cause discomfort in the mouth. For this reason, dentists advise not to remove them for the first time after installation, so you can monitor the human body’s reaction to them and make adjustments if necessary.
Clinical stages
Clinical preparation for prosthetics is of great importance, since how comfortable the patient will feel in the future will depend on the quality of its implementation.
This procedure consists of several stages:
- Anamnesis analysis - a specialist interviews a person about his health, finds out his living conditions and occupation. It is also important for the doctor to find out whether he has had experience wearing a prosthesis, and whether there were any inconveniences during its use.
- Instrumental examination of the oral cavity. The dentist identifies the characteristics of the muscular system, mucous and bone tissue of the prosthetic bed, determines the degree of their atrophy (according to Schroeder, Keller and Oxman).
In special cases, he refers the patient for additional examination - testing motor and speech function, myography and mastication to study the characteristics of chewing and swallowing, radiography and tomography of the temporal mandibular joints. - Preparation of the oral cavity. Dental cleaning, filling of carious cavities and removal of impacted units are carried out (if not removed, then as they appear, the fixation of the structure will weaken. This may lead to its breakage and gradual loosening of the supporting units).
- Selection of the type of removable device and material. Based on the number of missing teeth, the location of the defect, and the condition of the oral cavity, the specialist selects the type of structure and material for its manufacture.
- Receiving an impression. Using alginate or silicone mass, an impression is made of both jaws with the obligatory design of the end of the impression.
What are Akri Free removable dentures and indications for their installation.
Let's discuss here the price of the new Sandwich generation of dental prostheses.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/protezirovanie/semnyie-p/byugelnyie/na-nizhnyuyu-chelyust.html all the most important things about clasp dentures with locks on the lower jaw.
Manufacturing stages
Dentists and dental technicians are involved in the process of making dentures. They do this in stages:
- The dentist takes an impression of the teeth and jaw to create a future design. They must be removed from both parts. This must be done to ensure that the shape of the prosthesis is convenient and comfortable for the patient.
- A scale model is created from plaster.
- Plaster models are adjusted to each other using professional tools. In this case, the dental technician must accurately take into account the position of the patient’s teeth.
- Prostheses are made using special devices.
- The finished structure is carefully polished and made to fit the patient’s jaw.
- The dentist provides the patient with a finished prosthesis for fitting. If there is severe discomfort, the structure may be sent for correction.
The removable denture is prepared within a short time. During the manufacturing period, the dentist offers the patient to wear a temporary structure.
Laboratory steps
The main stage of manufacturing a removable denture takes place in the laboratory , and here the professionalism and well-coordinated work of the orthodontist and technician play an important role in achieving the final result. Together they solve one important problem - returning to a person the beauty of his smile.
After the impression arrives at the laboratory, the main process of manufacturing the structure begins:
- Using a plaster impression, the technician casts models of both jaws (individual sections or the whole), from which the prosthesis will later be made.
- After the models have hardened, they are fixed so that the interval between them completely repeats the intermaxillary space of a person at rest, i.e., corresponds to his central occlusion.
For this purpose, occlusal ridges are made from wax. The technician directs them to the orthodontist to determine the occlusion by placing the appliance in the patient's mouth. - Having received them back and using an impression tray, the technician attaches the model to the articulator and casts a model of the future product from plaster. An articulator is a special device that allows you to fix samples at the required distance from each other and simulate the closure of the jaws.
- Afterwards, the ridges are removed and artificial chewing organs are installed in their place.
- In this condition, the sample is sent for fitting. It is necessary to check the correctness of the bite and the correspondence of the shade of artificial units to the color of real teeth (if any).
- The model returns to the technician again, where he, taking into account all the changes, forms the final version of the prosthesis.
It often happens that over time, due to atrophy, the condition of the mucous membrane changes, the jaw bone decreases, which inevitably leads to a deterioration in the fixation of the prosthesis. It sticks loosely and “walks” across the sky.
Then a small amount of the material that was used in its manufacture is added to it, and the shape is also changed. This procedure is called relining (correction) of the prosthesis.
Learn more about laboratory manufacturing of structures in the video.
Results and discussion
A comparison of the strength indicators during static bending of thermoplastic materials with the traditional acrylic material Ftorax for the bases of removable dentures allows us to conclude that the Ftorax material, even after cyclic loading, has bending strength indicators that are on average 2 times higher than those of the thermoplastic material Acry F711, and its indicator the elastic modulus is almost 3 times higher than that of the polyamide material Flexi N 512 (Fig. 1, a, b)
.
Figure 1. Fig.
1a. Changes after cycling and exposure of base material samples to water. Modulus of elasticity (E, MPa) during bending. Figure 1. Fig. 1b. Changes after cycling and exposure of base material samples to water. Bending strength (flex, MPa); The x-axis shows initial indicators and after 6 and 12 months of exposure to water after cyclic loads. The test results showed that after 6 and 12 months of exposure in water after exposure to cyclic loads, the initial elastic modulus during static bending ( p
<0.05). However, there is a noticeable tendency towards an increase in rigidity after 1000 loading cycles for the acrylic material Ftorax, and for the tested thermoplastics the opposite tendency is noticeable - a decrease in the elastic modulus, i.e. Thermoplastics after repeated loading become more pliable and deform more under the same load.
The bending strength after 6 and 12 months of aging in water and after exposure to repeated cyclic loads significantly decreased by 22% for the Ftorax material ( p
=0.027), and for thermoplastics this indicator practically did not change (
p
=0.62).
The effect of repeated loads on samples of polymer base materials can be illustrated by changes in deformation rates under the influence of cyclic bending loading. In Fig. 2
Rice. 2. The influence of repeated cyclic loading on the deflection value (ॉtotal, mm) of base material samples. the deflection indicators of sample-strips of base materials under cyclic loading in the 1st and 1000th cycles are presented.
As can be seen from the presented histogram, after cyclic loading the deflection value of the samples increases ( p
<0.05), while for samples of the Ftorax material this increase is significantly less than for samples from the thermoplastic base materials Acry F711 and Flexi N 512. Deformation of samples of all tested materials under repeated loading after exposure to water for 6 and 12 months has not changed significantly.
The sample strips of the base materials were subjected to a force that created an equal stress in all samples—30 MPa. During the tests, the magnitude of the force was recorded at the initial moment of loading and after 1 s, after which the force changed, decreasing by the amount खF, N, due to relaxation processes in each material (Fig. 3)
.
Rice.
3. Change in the bending force of samples of base materials for 1 s during cycling. By comparing the values of खF for the 1st loading cycle with the last, 1000th, cycle, one can to some extent judge the rate of relaxation processes in each of the compared polymer materials. The rate of these processes in the Ftorax material at the beginning of cycling is low and increases at the end of cyclic loading, which significantly distinguishes this base material from the thermoplastic materials Acry F711 and Flexi N 512. For thermoplastic materials this rate decreases, as evidenced by the drop in values by the 1000th cycle . Keeping samples of the Ftorax material in water in a thermostat does not change the nature of the change in the खF index, which also significantly distinguishes this material from the thermoplastic Acry F711 and Flexi N 512.
The differences in the rate of relaxation of the acrylic polymer-monomer material Ftorax from that of thermoplastic base materials are confirmed by the values of residual deformation (ॉres., mm), which sharply increases by the 1000th cycle in thermoplastics (Fig. 4)
.
Rice. 4. The magnitude of residual deformation (res., mm) of polymer base materials at the beginning of cycling, on the 1st cycle and at the end, on the 1000th cycle.
Production time
The duration of production of removable structures depends on the location and extent of the defect, its type and characteristics of the patient’s oral cavity.
Approximate production time for removable dentures:
- single – 10-12 days;
- bridge-like – 12-14 days;
- partial or complete removable – 10 days;
- clasp with clasps – 14 days;
- a similar product with a locking fastening – 3 weeks;
- removable plate with implant support – 3 weeks.
Important! The indicated production times are calculated from the day the impression is taken until the final placement of the system in the mouth by the orthopedic surgeon.
Laboratory stages of creation
Making a spoon for the patient
An orthopedic spoon can be made using a direct or indirect method.
It is created on the patient's jaw from special wax.
- With the indirect method, the spoon is made from a plaster cast, which is removed from the patient’s jaw. Using an impression, dental technicians create a plastic, different tray in the laboratory.
- The direct method is considered practical and gives an idea of the moving soft tissues of the patient's jaw.
A standard dental tray made of metal exceeds the size of the jaw, and excess product can deform moving soft tissues, this can cause difficulties in the manufacture of the structure, and the data will not be accurate. A removable prosthesis made using indirect technology may require subsequent correction.
Such an orthopedic spoon can be made in a quarter of an hour. It is considered ready if it is correctly installed on the jaw and does not change position under mechanical influence.
Functional print border
The plaster model is treated with cold water and used for a wax base. A plate of material is heated with a burner on one side, and the opposite side is applied to a plaster cast. For the upper jaw, the procedure is different: first, the plate is applied to the deepest part of the palate, and then to the alveolar process and teeth on the palate side.
During the crimping process of the plate, the thickness of the wax layer should be maintained over its entire area, and the layer should not be stretched or deformed. While maintaining the thickness of the plate, the wax will adhere tightly to the plaster model over the entire surface. When the technician is convinced that all stages of the work have been completed correctly and the plate follows the relief of the plaster cast, he removes the excess layer of wax, respecting the boundaries that were marked in advance.
Occlusal ridges are made from the same wax plate. Half of the product is cut off, heated on both sides, and then rolled up, giving it a rounded shape resembling a roller. After this, part of the product is cut off so that the width of the remaining object is identical to the width of the missing dentition. The created element is installed strictly in the center of the alveolar process, after which it is glued using special fastening compounds.
The cross-section of the roller should resemble a trapezoid in shape. To do this, the occlusal surface is given a flat shape and made 1-2 millimeters higher than the adjacent teeth. In the anterior section, the width of the roller should be 6-8 millimeters, and in the side, up to 12. The side edges are given a shape that ensures a smooth transition from the roller to the base.
After cooling, the wax base is removed from the model, the edges are rounded with a hot spatula, avoiding contact of melted wax on the inner surface, and its thickness is checked again.
Creation of artificial teeth on a structure
When the dental technician receives all the necessary information and plaster models of the patient's jaw from the orthopedist, he inserts them into the articulator and begins the process of forming the teeth. It is necessary to prepare plaster models. They can be made from a clasp at this stage of work, if they have not been created.
After analyzing the situation, the technician decides how the teeth will be positioned: on a bridge or on artificial gums. Lateral teeth are always placed on artificial gums.
When the design of the dentition is completed, the technician checks the relationship between the antagonist teeth and models the remaining parts of the model. Then he checks the thickness of the wax base in areas, boundaries, tightness of fit to the plaster cast, and other points. If the result does not require any modifications, the technician removes the wax from the teeth and completes the work by engraving the teeth and shaping the relief.
The final stage of design creation
The completed prosthesis is checked directly in the patient's oral cavity and checked for defects. If they are identified, then either they are eliminated on site, or the product is sent to the laboratory. In any case, the final formation of teeth in shape, thickness and size is also carried out there.
Features of the production
The method of securing such a prosthesis in the mouth depends on the complexity and extent of the defect, as well as on the condition of the oral cavity and gums. The doctor must take into account all the restrictions and wishes of the patient himself.
On the upper jaw
Due to the fact that the upper jaw has a larger surface area than the lower jaw, the prosthesis is attached to it faster and more reliably. The method of fixation depends on its type:
- a complete denture has 2 points of support: the gum and the palate. With complete edentia, the structure is held in place by adhesion and suction to the gums.
- Partially removable. The structure is held in place by clasps that tightly grip the supporting units. But this method of fixation is not aesthetically pleasing, since the fastening is visible when talking or smiling.
Attachments (micro-locks) do not affect aesthetics and are completely invisible. Special crowns with a built-in half of the micro-lock are put on the supporting units.Its other half is built into the prosthesis. When putting on the structure, the halves of the attachments are connected and securely snapped into place.
- Conditionally removable – fixed to the jaw using implants.
There are 3 types of fixation of conditionally removable structures:
- locking – 2-4 implants are implanted into the jaw. Ball-shaped micro-locks are screwed into them. On the inside of the device itself there are recesses into which the matrices are inserted. To secure the prosthesis, it is necessary to combine the head of the micro-lock with the matrix.
- beam – implants are also implanted into the jawbone, and a metal beam is laid between them.
A slot is made in the prosthesis, commensurate with the size of the beam, into which the matrix is placed. When putting on the device, it tightly grips the beam and securely fixes it. - intracanal – used if your teeth (or their remains) remain on the jaw.
They are cut down to the root and the canals are filled. Implants are later implanted into them, and they are placed so that a metal head with a built-in matrix protrudes above each root. It, as in the previous version, captures the prosthesis and fixes its position.
Important! The last option for attaching the device to the upper jaw is, according to experts, the most successful, since there is no atrophy of bone tissue, and the life of the prosthesis itself is extended.
In complete absence
Restoring all teeth with complete edentia involves the use of a complete denture, or rather one of its options:
- conditionally removable;
- plastic;
- nylon;
- clasp on implants.
In the case of using a plastic structure , its fastening occurs due to suction. It does not adhere securely to the gums, is not aesthetically pleasing, and cannot withstand significant chewing loads.
The nylon device is much superior to the previous version It has a similar fastening method, is very elastic, and has good aesthetics. But its significant disadvantage is insufficient reliability and incomplete restoration of chewing function.
Dentures on implants have 2 types of fastening - beam and lock. Their principle of operation is similar to attaching a conditionally removable system to the upper jaw.
a clasp denture in the mouth involves implanting supports into the jawbone. The fastening system can be of three types:
- clasp;
- attachment;
- on telescopic crowns.
Important! According to dentists, the most durable, comfortable to use and aesthetically pleasing are conditionally removable and clasp dentures.
Removable denture technology
When a person does not have a single tooth left in one or both jaws, the orthopedic dentist has only two options: to perform expensive partial dental implantation, and then create a permanent structure on the installed implants, or to restore the dentition using completely removable structures, which are created from individual impressions for both the lower and upper jaws.
When used correctly and carefully, removable dentures made from modern materials will serve for a long time as a safe and effective replacement for natural teeth. The advantages of completely removable prosthetics are as follows:
- individual choice of teeth according to shape, size and color;
- excellent aesthetic properties of the prosthetic structure, achieved through the use of modern orthodontics and the latest technologies;
- ease of care for artificial teeth;
- long service life of removable dentures when used carefully, which is achieved through the use of modern wear-resistant materials;
- convenience for effectively maintaining the health of the oral cavity and gums;
- no need to constantly remove dentures while sleeping;
- affordable price.
As for the disadvantages of a completely removable orthopedic design, the following are worth mentioning:
- a fairly long period of adaptation, during which a person long feels the unfamiliarity and foreignness of the prosthetic structure;
- there is a risk of finding yourself in an awkward situation when a removable prosthetic structure accidentally falls out of your mouth at the most inopportune moment;
- constant difficulty chewing solid food;
- the need to use gels to provide a suction effect when finding a prosthetic structure;
- changes in the load on the gums, which can lead to problems in the oral cavity;
- the need to constantly remove the orthopedic structure, clean and treat it with special means.
Not only orthopedic dentists, but also dental technicians are involved in the manufacture of removable dentures. The first ones prepare for the creation of a dental structure and install it on the patient. And the latter make removable dentures in special laboratories. This process requires high qualifications and experience. Dental technicians select materials, create the required relief that matches the relief of the patient’s natural teeth, and give artificial teeth the necessary shape and color so that they do not differ in appearance from natural teeth. The production of prosthetic structures by a dental technician is partly akin to science, partly to art. And the profession of a dental technician has a certain similarity with the profession of a sculptor or artist.
Evaluation of results
The evaluation of the results of prosthetics is carried out according to two main criteria:
- Subjective.
- Objective.
The first group includes indicators for analyzing the patient’s condition after placement of the prosthesis. Namely:
- how comfortable he perceives the presence of the structure in his mouth;
- How was the adaptation period?
- what difficulties does he face?
- Are you happy with the result?
The condition is studied at different periods - after fitting the prosthesis, after its application and a month after final fixation.
The second group of criteria includes the following areas of verification:
- correspondence of the crown shape to the anatomical parameters of natural units;
- occlusal and articulatory correspondence of both jaws;
- color match of artificial units with the shade of natural teeth (if any);
- correctness and tightness of the marginal fit of the structure to hard dental tissues;
- degree of restoration of jaw functionality;
- quality of polishing of the prosthesis.
Many experts supplement this list with another indicator, which indicates the number of complaints received from an orthopedic dentist over a certain period of time and the degree of defectiveness of the prosthesis.
Production time
There are many options for prosthetics. The timing depends on what technology the doctor will use. Basically, this takes 3-6 months if the procedure is carried out in 2 stages - waiting for the structure to engraft to the bone tissue.
Only after good healing is achieved, an incision is made above the implant in the mucous part to install the abutment into it. Ultimately, crowns will be fixed onto it.
The time frame to make dentures can be uncertain . This is due to the emergence of various factors. A significant impact is caused by a deficiency of bone mass, which does not allow the installation of implants on it. This problem occurs very often. To solve this problem, artificial bone tissue augmentation is used.
The one-stage installation method is carried out for up to 5 days. In this case, compression or basal implants are used. They are mounted in deep tissues of a dense structure. In such cases, artificial roots are stable enough to carry out prosthetics within a few days.
Operational period
As statistics show, the optimal period of operation of a removable denture made of plastic is from 3 to 5 years, a partial denture made of thermoplastic and metal is about 8 years, and a nylon denture is 7 years.
Longer wear should be discussed with your doctor on an individual basis. There are special signs that serve as a reason to replace the design with a new model:
- deterioration of the oral cavity;
- the age of the patient;
- the appearance of pain;
- change in occlusion due to changes in the condition of the hard and soft tissues of the mouth;
- wear of artificial teeth, leading to changes in appearance;
- frequent product breakdowns.
The service life of prostheses is influenced by the material from which they are made, the manufacturing method and the “human factor”, including the likelihood of a technician’s error and violations in its operation.
Structural features of Quadrotti dentures and product disadvantages.
This material is dedicated to Butterfly dentures.
Here https://zubovv.ru/protezirovanie/semnyie-p/neylonovyie/kak-privyiknut.html we will tell you how to properly get used to removable dentures.
Removable dentures using injection molding IVOCAP
What is the difference?
Continuing the topic of manufacturing removable dentures using injection molding, I would like to dwell on dentures manufactured using the IVOCAP system.
Nowadays, many people are carried away by the manufacture of thermo-molded removable dentures, having forgotten that for many years the IVOCAP system has been in the arsenal of dental technicians.
The IVOCAP system allows you to obtain high-precision removable dentures with an ideal fit to the mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed, precise occlusal relationships and bases without residual monomer.
Massive interest in thermo-molded prostheses, in my opinion, is associated with many problems plaguing prostheses made by packing plastic dough into a collapsible cuvette.
Many dental technicians and orthopedic dentists, having tried in their practice dentures made by thermomolding, were delighted with the quality of such dentures. However, not many people decided to analyze the reasons for quality. The thermomolding system is very different from the system of packaging plastic dough into a collapsible cuvette, and it is these differences that give the quality that dentists are so pleased with.
What makes them happy?
- Exact fit of the prosthesis to the prosthetic bed.
- Precise occlusal relationship of the dentition without overestimating or distorting the bite.
- The absence of residual monomer and, as a consequence, rare cases of allergies to such prostheses.
- Many people are happy about the flexibility of prostheses, but I would not be happy about it.
- Fracture strength and impact resistance of dentures.
Well, these are all wonderful properties of removable dentures, but they could have been achieved decades ago using the IVOCAP system, minus, of course, the high flexibility.
The IVOCAP system allows the production of high-quality dentures and is most suitable for the production of complete dentures, in contrast to thermomolding systems.
What is the advantage of prostheses made using the IVOCAP system over prostheses made by thermomolding?
Let me start with the fact that acrylic dentures can be repositioned quite simply and even in the oral cavity.
Acrylic plastic is very well polished and chemically bonds with acrylic teeth, thus the aesthetics of acrylic dentures is much higher than that of thermo-cast ones (there are no black halos around the teeth, and they remain shiny for a long time).
What many dentists love about thermo-molded dentures: flexibility – this is lost when making complete dentures due to the bulk of complete dentures.
As for the fracture strength and impact resistance of acrylic prostheses, they are, of course, inferior to many types of thermomolding materials, but not all, and, in addition, they have special reinforced base plastics that have some increased flexibility.
Considering that the only objective indication for the manufacture of a complete removable denture from thermomolded plastics is an allergy to acrylic, it becomes obvious that in most cases for complete dentures it is worth using the IVOCAP injection molding system.
How does it work?
Let's look at the step-by-step production of two complete removable dentures using the IVOCAP injection molding system. After trying on the placement of teeth on wax bases, we make the final modeling of the bases. We do not provide any processing permits.
The wax base should look the way we would like to see the finished prosthesis. We pour the wax base onto the working model (Fig. 1-8).
Rice. 1. Fig. 2. Fig. 3. Fig. 4. Fig. 5. Fig. 6. Fig. 7. Fig. 8.
We separate the model from the articulator plaster platform and prepare the necessary accessories for the IVOCAP system (Fig. 9-10).
Rice. 9. Fig. 10.
We install an analogue cannula in the first half of the cuvette. Cover the bottom of the cuvette with a paper gasket.
We mix 2nd class gypsum in a vacuum mixer and pour it into the first half of the cuvette, then place the model with the wax composition of the prosthesis soaked in water (Fig. 11-12).
Rice. 11. Fig. 12.
We level the plaster surface and create smooth transitions to the model.
After the plaster has cured, we replace the cannula analogue with a cartridge connector with a cannula and install the gating system (Fig. 13).
Rice. 13.
We wet the first half of the cuvette with a special release agent. Again, mix the 2nd class plaster in a vacuum mixer and apply a thin layer of plaster to the surface of the prosthesis using a sponge, paying special attention to the interdental spaces (Fig. 14).
Rice. 14.
We assemble the cuvette and fill its second part with plaster.
After the plaster has cured, place the cuvette in hot water to remove the wax.
Having opened the cuvette and removed the wax, we carefully treat the model and teeth with a steam jet. After cleaning the teeth and plaster molds, apply an insulating varnish to the plaster (Fig. 15-17).
Rice. 15. Fig. 16. Fig. 17.
After the varnish has dried, the cuvette is assembled and installed in a special clamping device. Using a hydraulic press, we clamp the cuvette in this device.
In a special cartridge, which contains a precisely measured amount of polymer powder and monomer liquid at the factory, the base plastic is mixed in a vibrating mixer (Fig. 18-20).
Rice. 18. Fig. 19. Fig. 20.
The cartridge is placed in a cuvette, and plastic, using a piston, fills the cuvette under a pressure of 6 atmospheres (Fig. 21).
Rice. 21.
The cuvettes are placed in a polymerization bath (Fig. 22) with water heated to 95-98 degrees for 35 minutes.
Rice. 22.
After this period, the cuvettes are still placed under pressure in cold water for 10 minutes (Fig. 23).
Rice. 23.
After completion of the polymerization process and cooling, the cuvettes are unpacked (Fig. 24).
Rice. 24.
The dentures, without being separated from the models, are freed from plaster and, after washing and cleaning with a steam jet, they are returned to the articulator for adjustment to the bite (Fig. 25-27).
Rice. 25. Fig. 26. Fig. 27.
Dentures adjusted to the bites are freed from models, processed and polished (Fig. 28-30).
Rice. 28. Fig. 29. Fig. thirty.
The result of the work
Prostheses made in this way have a high precision fit to the prosthetic bed, the absence of residual monomer (due to the precise factory dosage of ingredients and their homogenization in a vibrating mixer). Such dentures do not have overbite. The base plastic has a high density and the absence of micropores, which makes such prostheses durable and strong.
Even with prolonged use, dentures do not absorb odor or change color.
The ability to quickly and accurately reline without large material costs allows you to use such prostheses for many years (Fig. 31).
Rice. 31.
Care
Daily proper care of the prosthetic structure, compliance with the rules of storage and operation, will increase the duration of wearing and make use more comfortable.
In this direction, orthodontists advise:
- The removable product should be cleaned outside the mouth twice a day with a classic brush and toothpaste or soap.
- To process plastic parts of a prosthesis, you should use a brush with medium-hard bristles; for nylon parts, special devices and products for orthopedic products should be used; and for metal parts, a brush with hard bristles.
- To remove solid deposits, use only products that are sold in specialized stores and pharmacies.
- Do not wash the structure with boiling water - its shape may change.
- To avoid accidental breakage of the product, solid food should be removed from the diet and food should be bitten into small pieces. You should also not consume hot food or drinks.
- After the adaptation period, the device can be removed before going to bed.
- It should be stored in a closed container, first wrapped in a moistened napkin.
- Do not allow it to fall onto a hard surface.
Possible breakdowns and repairs
Almost half of all orthopedic systems become unusable before the time specified in the guarantee, and in 10% of all cases this is observed in the first year of wear.
Common types of breakdowns are:
- cracks in the base of the structure;
- fracture;
- breakdown of clasps;
- chips on artificial units;
- violation of closure.
The reasons leading to such defects can be very different:
- Laboratory and technical errors.
- Careless attitude to the design.
- Violation of the rules of operation and storage.
- "Aging" of the material.
- Changes in the condition of tissues in the mouth (progressive atrophy).
If a prosthesis is found to be broken, you should contact the laboratory and the dentist. Repairing it without a doctor’s recommendation and lack of subsequent adjustments will certainly lead to another breakdown.
The following types of restoration work are carried out in the laboratory:
- an acrylic device can be glued together with a self-hardening resin, overlaying a new layer of polymerized plastic or with a special glue;
- if an artificial tooth is broken, it can be built up or a new one can be implanted in its place;
- if there is a problem with the clasp, the artificial unit and gums are first removed from the arch, and then the matrix and clasps are laser-soldered;
- the broken parts of the nylon device are connected with a fastening mass.
Trying to repair the structure yourself is not recommended. Experts do not advise doing this for the following reasons:
- The adhesive at hand can cause allergies or severe poisoning.
- The duration of operation of a self-repaired prosthesis is a week.
- Under an unsealed seam, food debris will accumulate and pathogenic microorganisms will multiply.
- It is impossible to properly restore the integrity of the structure at home.
Important! To extend the service life of the device and prevent its breakdown, it is necessary to correct it every six months and remove small, barely noticeable scratches by polishing.
Price
Removable dentures are slightly cheaper than their fixed counterparts. Their final cost consists of the following factors:
- Material used in manufacturing.
- Method of fixation in the mouth.
- The required amount of work and the number of units to be restored.
- Qualification of specialists involved in the manufacture and installation of the structure.
- Applied technologies and equipment.
- Clinic location.
The approximate cost of removable dentures of different types is presented in this table.
| Type of removable denture | Approximate cost, thousand rubles |
| Full of acrylic | From 10 to 20 |
| Partial acrylic | About 15 |
| Made of plastic for 1-2 units | From 3 |
| Clasp with clasp fastening | From 20 to 30 |
| Single-sided clasp with micro-locks | From 40 to 50 |
| Similar double sided | About 80 |
| Clasp on implants | From 90 to 200 |
| Full of nylon | From 25 |
| Nylon partial | From 20 |
| Nylon for 1-2 teeth | From 10 |
The video shows the stages of making a clasp prosthesis.
Reviews
Modern prosthetics is the use of the latest technologies and equipment that make it possible to produce a removable prosthesis that is comfortable in all respects, has high aesthetics and wear resistance.
The presence of several varieties of these designs allows you to choose the most suitable one according to the indications and financial capabilities of the patient.
You can share your experience and impressions about restoring lost teeth using one of the removable dentures by leaving a comment on this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: removable dentures
Did you like the article? stay tuned
No comments yet
Advantages of dental prosthetics in Moscow from Denta-Labor:
Working for many years, our dental laboratory has become a center of excellence in the production of dentures in Moscow. Services are provided with the most favorable conditions:
- a wide range of work - from repairing prostheses to urgent production of new ones;
- reasonable prices - we save by receiving consumables and equipment directly from manufacturers;
- high professionalism - we can handle work of any complexity;
- innovation and technical innovations - we use equipment from well-known manufacturers (for example, KaVo and Renfert).
If you are tired of enduring discomfort, dial our number (495) 162-08-25 , and we will advise you and tell you the approximate cost of making dentures. We approach your problems individually!