Causes
The only reason that allows for a wait-and-see attitude is the period of changing teeth. So, if the gums of a 5-year-old child bleed in the area of a loose tooth, this rarely means anything more than a minor and natural injury to the gums in such cases.
The remaining causes of bleeding gums are closely related to health:
- Gingivitis. Acute inflammation of the gums often causes bleeding. Moreover, this disease is quite common in preschool children - children’s insufficient attention to the requirements of personal hygiene, combined with poor quality of teeth cleaning, leads to the active proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
- Stomatitis. Some types of stomatitis, such as candidiasis and aphthous, can manifest themselves as bleeding of pathological areas after injury (during chewing food or when accidentally or intentionally tearing off the aphtha or film).
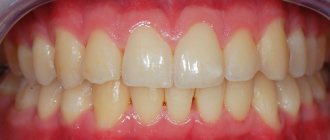
- Periodontitis. Inflammation of the tissues of the musculoskeletal system of the tooth is characterized by bleeding from the gums, which is most pronounced when brushing the teeth - “rusty” marks remain on the brush, and the saliva turns pink.
- Avitaminosis. A deficiency of vitamins C and K, as well as B vitamins, can cause fragility of blood vessels and increased injury. Accordingly, when there is stress on the gums (brushing teeth, chewing hard food, etc.), the vessels can be injured, which results in bleeding.
- Bite abnormalities. In this case, the gums may be subject to chronic trauma, which leads to tissue damage and bleeding.
Why do my child's gums bleed?
Traces of blood on a child’s toothbrush may indicate an inflammatory process in the oral cavity caused by the following disorders:
- stomatitis or gingivitis,
- herpetic infection,
- periodontitis,
- failure in metabolic processes,
- deficiency of vitamins in food,
- improper oral hygiene, the formation of bacterial plaque on the gums and teeth.
There are also non-infectious causes, namely:
- Various injuries. Many children like to pick their mouths with pencils, pens, and other objects, including those with sharp edges.
- Malocclusions, teething.
- Incorrect placement and processing of the filling.
INTERESTING: ointment for gums during teething in infants: review of the best
Stomatitis or gingivitis
With both gingivitis and stomatitis, gums bleed. Diseases are provoked by the following factors:
- viral or bacterial infection,
- prolonged vitamin deficiency,
- mechanical damage to the oral mucosa,
- dirty food, toys or hands,
- friction with subsequent irritation on poorly placed crowns or dentures,
- a poorly selected toothbrush or toothpaste containing irritating components,
- some medications that affect the secretion of the salivary glands,
- broken bite.
These factors cause stomatitis as an independent disease, but frequent relapses indicate the presence of gingivitis. Its symptoms are the following:
- the gums become red and swollen, in the advanced stage they become covered with a gray coating,
- with the catarrhal form of the disease, itching of the gums occurs,
- gradually the oral cavity becomes covered with erosions,
- pain when eating,
- bleeding gums and bad breath,
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- elevated temperature.
Gingivitis develops gradually and goes through the following stages:
- The initial stage is characterized by satisfactory well-being of the patient. There is only some swelling of the gums, as with stomatitis, slight pain and bleeding.
- At the middle stage, the edges of the gums become deformed, pus accumulates, small necrotic spots and bad breath appear. Enlarged lymph nodes and slight hyperthermia are possible.
- In the severe stage of the disease, inflammation spreads to the palate, cheeks, and sometimes to bone tissue. The patient has a high temperature. The tongue becomes covered with a viscous coating, changes color, and saliva thickens.
Gingivitis is a severe infectious disease of the oral cavity. It is provoked by pathogens of various natures:
- The bacterial form is caused by streptococci and staphylococci localized on the tonsils and mucous surface. As a result, ulcers appear, which periodically open up and ulcers form.
- Herpes is caused by a viral infection.
- Candidal gingivitis, which often occurs in young children, is fungal in nature.
- Allergy, the only non-infectious form of the disease, is a reaction to food to which the patient is sensitive.
Lack of vitamins and microelements
Vitamin deficiency, which can lead to such a severe form of gingivitis as scurvy, is very rare in our time. A lack of vitamins and microelements in food contributes to the development of stomatitis and gingivitis. These diseases develop when the immune system is weakened. Thus, a lack of selenium, B vitamins, iron and zinc leads to barrier dysfunction of the gums, weakening their natural protection against pathogens.
To ensure full gum immunity, the body needs a sufficient amount of the following vitamins:
- Group B1, B2, B6, B12, B18. These substances do not accumulate in the body, so they must be present in food constantly. This family of vitamins takes part in the oxygen exchange of soft tissues. This is an essential nutritional component for gum health. It is important to know that they cannot be taken at the same time to avoid an allergic reaction.
- Fat-soluble C, A, E, PP. These vitamins must be taken only with food because they are absorbed in the presence of fat. A daily portion of vegetable salad seasoned with vegetable oil is what a child needs to replenish the supply of these substances.
- Minerals. Iron and selenium deficiency increase the frequency of inflammatory processes in the gums. Calcium and zinc strengthen them; with a lack of these elements, the elasticity of the gums decreases.
Injuries
Stomatitis can occur in a child as a result of mechanical trauma to the oral cavity (see also: what to feed a child with stomatitis: therapeutic diet). In infancy, when teething occurs, the baby puts everything in his mouth to scratch his itchy gums. One of these objects can scratch the delicate oral mucosa. A child at 1-2 years of age, exploring the world around him, tastes different objects, including piercing and cutting ones (see also: dental diseases in a 2-year-old child).
In older children, gum damage can occur as a result of malocclusion. In addition, mistakes by a pediatric dentist when filling a tooth can also cause injury, subsequent bleeding from the gums and stomatitis. In all these cases, the problem is eliminated with timely treatment.
What should you pay attention to?
It is not always possible to detect that a child’s gums are bleeding. But problems that have arisen can be clearly indicated by other circumstances that should be paid attention to:
- The child has changed his eating habits. He began to refuse salty, sour, and hot foods and began to prefer dishes with a neutral taste and chilled ones.
- The child refuses to brush his teeth or has begun to care for his oral cavity very carelessly.
- There were complaints of discomfort, pain, burning in the mouth.
- The child points out the “strange” taste that is present in any dish.
- General weakness, lethargy.
- Hematomas appear on the child’s body even after slight pressure on the skin.
The listed signs should be a reason to contact a dentist or pediatrician, who, after a comprehensive examination, will determine the cause of these symptoms and the direction of treatment.
Possible complications
The cause of complications is not the actual bleeding of the gums, but the disease or condition that provoked this symptom.
Thus, infectious or inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity (gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis, etc.) can quickly lead to the spread of the pathological process to healthy tissues, and the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx and oropharynx are the first to be affected. Such consequences are especially common when the gums of a child 4 years old - 6 years old bleed (at this age the immune system is especially vulnerable, and anatomical features facilitate the migration of pathogens from the oral cavity into the nasal cavity, onto the mucous membranes of the throat and even into the middle ear). This leads to frequent diseases of the throat, pharynx, trachea, or to chronicity of existing diseases.
No less dangerous are complications for the child’s dental system itself. Against the background of long-standing gum diseases, their hypo- or hyperplasia may develop, which inevitably entails incorrect formation of temporary and permanent occlusion.
Therefore, treatment for bleeding gums should be started immediately, without waiting for this condition to be complicated by serious illnesses.
General prevention of stomatitis
Prevention of stomatitis helps prevent recurrence of the disease. The most effective way is to treat the disease that caused stomatitis. General recommendations concern oral hygiene.
If there is a predisposition to such a disease, then you need to rinse your mouth after eating. At least twice a day you need to brush your teeth and also your tongue, the inside of your cheeks, and clean your gums.
About toothpastes
It will be useful to avoid toothpastes that contain sodium lauryl sulfate. This substance is found in oral hygiene products and toothpastes.
Numerous studies show that sodium lauryl sulfate affects the occurrence of stomatitis. If a child’s gums bleed after stomatitis, then most likely the disease has not been completely cured and re-treatment is required.
Diagnosis of stomatitis
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed in accordance with the identified causes of the symptom:
- Infectious diseases of the oral mucosa require the prescription of antiseptics (antimicrobial, antiviral, antimycotic or combined - depending on the type of pathogen that caused the disease). These agents can be used for topical use as rinses and applications, or prescribed for oral administration if the doctor has reason to suspect a systemic nature of the infection.
- Inflammatory diseases require anti-inflammatory therapy (taking specialized drugs or NSAIDs), as well as regular treatment of the oral cavity with solutions that reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process and accelerate tissue regeneration.
- In case of malocclusion that causes bleeding gums, drug therapy for inflammation is first carried out, and after that orthodontic treatment is prescribed. It consists of wearing braces, fixed or removable plates and brackets, caps - the choice of design is determined by the severity of the anomaly, the age of the child and other circumstances.
In case of vitamin deficiencies, in addition to dental treatment, it is mandatory to use medicinal vitamin preparations for oral administration, and diet therapy is prescribed.
Home Remedies
Methods used at home can significantly speed up the recovery and restoration of gum health:
- Eliminate from the child’s diet any food that can injure the gums (dry hard foods, very heated or cooled foods), as well as sour, salty, spicy foods that irritate the mucous membrane and slow down its recovery. Give preference to soft, slimy, mushy foods.
- Make sure that after each meal the child thoroughly rinses his mouth with slightly warm boiled water (if bleeding is caused by infectious diseases, the doctor may recommend a decoction of chamomile, oak bark, soda solution, chlorhexidine, etc.).
- Monitor the cleanliness of your child’s hands, especially if he is still at an “unconscious” age and cannot yet be convinced not to put his hands in his mouth. Also pay attention to feeding accessories - thoroughly disinfect nipples, spoons, sippy cups and other items after each feeding.
Instructions
Try to determine the cause of bleeding from the mouth.
You should make sure that it is not associated with any other serious problems in the body, such as the stomach, intestines, larynx, etc. If there are no wounds, swelling or redness in the oral cavity, be sure to call an ambulance. Tooth extraction is usually accompanied by bleeding, and the necessary measures to stop it are carried out immediately. For a quarter of an hour or a little longer (up to 45 minutes), a sterile gauze swab is applied to the damaged area. During this time, a blood clot forms in the hole and the bleeding stops.
If this does not happen, the wound is treated with hemostatic agents (tamponed) or sutures are placed. After this, all you have to do is follow your doctor’s recommendations. If, after some time, blood flows from the wound again, make a small but tall and dense tampon from a sterile bandage or gauze, place it on the hole and bite it with your teeth.
Try not to rinse your mouth during the first 24 hours after tooth extraction. Also refrain from hot food and drink, because... all this can lead to the removal of the blood clot and the resumption of bleeding.
If you were unable to stop the bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth with a simple tampon, try soaking it in a diluted solution of 3% hydrogen peroxide (1:3) and apply it to this place again.
Try to stop bleeding due to any wound in the mouth or damage to the gums by applying a sterile swab or napkins. Rinse your mouth with a diluted solution of hydrogen peroxide or calendula tincture. You can also slightly narrow the blood vessels by placing pieces of ice wrapped in gauze on the cheek on the desired side. Or rinse your mouth with ice water more often. You can take a pill to stop the bleeding.
If major blood vessels in the mouth have been damaged and bleeding is profuse, place the person face down or on their side to prevent blood from entering the stomach and causing vomiting. Free the oral cavity from blood clots and place a cotton ball soaked in a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution to the bleeding site.
Most often, the blood in the oral cavity stops quickly; it is enough not to provoke irritation (for example, not to eat hot food during the day after tooth extraction). But sometimes people have to take extra measures to stop bleeding.
3% hydrogen peroxide;
Posting sponsor P{amp}amp;G Articles on the topic “How to stop bleeding in the mouth” How to treat gums during pregnancy How to stop bleeding from hemorrhoids How to treat a pimple on the tongue
Try to determine the cause of bleeding from the mouth. You should make sure that it is not associated with any other serious problems in the body, such as the stomach, intestines, larynx, etc. If there are no wounds, swelling or redness in the oral cavity, be sure to call an ambulance.
Other news on the topic:
Careless handling of sharp objects or an accident can cause serious injury. Sometimes a deep cut occurs due to careless handling of a knife, opening a can, or accidental contact with broken glass. To stop bleeding,
Bites, injuries - all this can lead to bleeding in a dog. So that this does not come as a surprise to you, you need to have a first aid kit on hand and know the basics of first aid. You will need - antiseptics; -first aid kit. Posting Sponsor P{amp}amp;G Articles on the topic “How to
Modern dentistry tries to fight for the tooth to the last. But there are situations when it is no longer possible to save him. The occurrence of infection and damage to most of the tooth by caries is an indication for its removal. But the patient’s suffering does not end with this operation, especially if he has no
If there is a bleeding person next to you, and specialists have not yet arrived, you must provide first aid to the victim. To do this, it is important to determine the nature of the bleeding, since for different injuries, first-aid measures will differ. Posting Sponsor P{amp}amp;G Articles on the topic “How to
A broken or cut lip may bleed. If the wound is small, you can do it yourself. For large cuts, it is necessary to provide first aid, focusing efforts to stop the bleeding, and consult a doctor. You will need - a sterile bandage or gauze; – peroxide
There are many methods and medications to help stop bleeding. In most cases, small wounds bleed only for the first few minutes; you should not stop the bleeding during this time, as it washes away some of the bacteria that have entered the wound. So you just need to stop
We suggest you read Why the bleeding does not stop after tooth extraction
Bleeding from the ear can begin as a result of a strong blow, a fall, after removing wax or a foreign object due to a ruptured eardrum, or burst blood vessels. After serious injuries, blood mixed with cerebrospinal fluid may leak from the ear. The victim must be provided
Bleeding can be capillary, venous and arterial. If in the first case it stops quite quickly on its own, then if the vein is damaged, it is already necessary to apply a tampon or a pressure bandage. Arterial bleeding can only be stopped with the help of a surgeon. For tongue injuries
The causes of nosebleeds can be mechanical violations of the integrity of the walls of blood vessels in the nasal cavity or disturbances in the functioning of the blood coagulation system. Hemophilia, hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, chronic diseases of the nasal cavity, renal pressure, sunstroke, physical activity also
As a rule, the first reaction to a nosebleed is panic. Blood does not evoke pleasant feelings, and if it appears on a child’s face, anxiety is inevitable. But all emotions must be left behind and the main task must begin – stopping the bleeding. Posting Sponsor P{amp}amp;G Articles on the topic “How to
- – 3% hydrogen peroxide;
- - tincture of calendula.
Nosebleeds are a fairly common occurrence and there are many reasons for their occurrence:
- mechanical damage to the nasal mucosa and cavity;
- surgical intervention in the nasal cavity;
- acute infectious diseases;
- arterial hypertension and other diseases of the vascular system and heart;
Of course, if you experience nosebleeds, it is advisable to immediately consult a doctor, but if this is not possible, we offer you several ways to stop nosebleeds. After providing first aid, be sure to go to the hospital. So, you can stop nosebleeds in the following ways: - If the bleeding is minor, you can try to stop it by simply pressing the wing of the nose against the nasal septum with your fingers or placing a napkin with ice or a handkerchief soaked in cold water on the nasal septum. You can also lie on your back and put ice or a compress of cold water under your head.
- It is also recommended to insert a cotton swab into the nasal passage, previously moistened with hydrogen peroxide or Vaseline, then press it through the wing of the nose to the nasal septum.
- If the simplest methods to stop the bleeding do not help, then anterior tamponade of the nasal cavity is used: moisten a long gauze swab with hydrogen peroxide or petroleum jelly, then sequentially perform all the recesses of the nasal cavity. An ice pack is applied to the back of the head. After the operation, the area that is bleeding can be cauterized with silver nitrate, chromic or trichloroacetic acid.
- If the previous methods of stopping did not produce results, then posterior tamponade is performed, for this you should definitely consult a doctor.
- You can put a few drops of freshly squeezed lemon juice into your nose.
- Also, to quickly stop nosebleeds, you can insert a cotton swab, previously moistened with fresh nettle juice, into the nostril.
- You can also periodically inhale through your nose a salt solution or a solution of water with the addition of vinegar (1 tbsp. water, 1 tsp. vinegar), or lemon juice (juice of 1/4 lemon, 1 tbsp. water). The liquid is drawn into the nose, then held for several minutes, the nostrils are pinched and a cold wet towel is applied to the forehead and nose.
- Yarrow juice and decoction are also used as nasal drops. You can also grind fresh yarrow and insert it into your nose like a turunda.
- Alternative medicine also suggests cutting the head of an onion and applying the cut to the back of the neck.
- It is also believed that you can stop a nosebleed by doing the following manipulations: if the bleeding started from the right nostril, then raise your right hand above your head and pinch the right nostril with your left. If blood comes from the left nostril, you need to do a similar manipulation, but in a mirror way. You can also use this method by placing both hands behind your head and using outside help to close both nostrils. stop nosebleeds
In this case, it is necessary to put the patient to bed, ensure complete rest and urgently call a doctor. We suggest you read: How to stop bleeding after wisdom tooth removal at home and how long does bleeding from the gums last?