Concept
An impacted tooth according to ICD10 is a mature unit with fully formed enamel and a neurovascular bundle that cannot erupt. Such a tooth can be located both in the periodontium and in the bone tissue of the alveolar ridge.
Most often, impacted teeth are also dystopic or impacted . Despite the fact that they are located under the gums, they are also susceptible to bacteria and caries.
Localization
Most often, impacted wisdom teeth are the last ones to erupt. This localization of the anomaly occurs in 45% of cases of retention.
Due to the deep location of the buds and limited space for growth, most often they erupt only partially, forming a gingival hood.
At the same time, the wisdom teeth of both the upper and lower jaws suffer equally .
In second place in terms of frequency of retention are the canines located on the upper jaw. The last place is occupied by the second premolars of the lower jaw or, if we use numbers, fives.
Who is at risk?
Retention is most often observed in children with metabolic disorders and diseases of the skeletal system. In this case, the problem can be either congenital or acquired.
In addition, the risk group includes people who have hereditary preconditions. If the parents experienced retention, then the probability of its occurrence in children is 37%.
Also, the anomaly was often diagnosed in patients with chronic periodontal diseases.
Milk teeth in dogs and cats
“At what age should baby teeth be removed from dogs and cats?.. Do they need to be removed?.. Can they be left?.. Will they fall out on their own?.. Are baby teeth removed from dogs and cats with or without anesthesia?.. What’s worse is anesthesia or remaining baby teeth teeth?.."
These questions are asked by every puppy or kitten owner.
Let's try to figure it out...
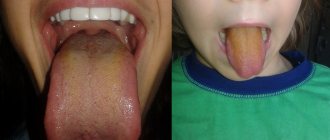
Changing baby teeth to permanent ones in a cat.
Replacement and removal of baby teeth in puppies and kittens
Milk, or temporary, teeth must be replaced with permanent teeth at the age of 4 to 6 months in puppies and kittens.
The change of teeth begins with the change of incisors, followed by the change of premolars and canines.
The age for removing baby teeth is not a specific number. Everything happens individually for each animal, and to say, for example, that the optimal age is 8 months is wrong. Each animal has a different age for extraction; some require removal of persistent teeth as early as 5 months of age.
Persistent teeth in dogs and cats
Temporary teeth that do not fall out, which are already being replaced by permanent teeth, are called persistent and must be removed at the first visible changes in the bite.
It is impossible to leave persistent teeth, because the dentition of an adult dog is designed for 42 teeth, and for a cat it is 30, and if there are more teeth, periodontitis will begin.
Imagine the situation: you are flying on an airplane, there are 3 seats in a row, designed for 3 passengers, and suddenly 3 more larger passengers are seated next to them - the first 10 minutes are still nothing, but after 8 hours nothing good will happen in this situation. It's the same with teeth.
Persistent tooth on the upper jaw of a dog.
Anesthesia for tooth extraction in dogs and cats
The removal of any fixed teeth, no matter whether they are temporary or permanent, must be carried out using anesthesia and analgesia. Dental pain is a moderate pain and proper analgesia is required for every patient.
To the question, is it possible to anoint the gums with something anesthetic or give local anesthesia like in humans, I will answer right away - no, it is not possible.
Local analgesic gels will anesthetize the mucous membrane of the gums and tongue and increase salivation in the dog, which can lead to vomiting and aspiration of vomit into the trachea, and in cats their use is even more dangerous, since such gels can lead to laryngospasm and respiratory arrest.
Unfortunately, a local injection into the gum cannot be carried out without the use of sedatives that induce sleep. I have a hard time imagining a cat or dog whose gum someone tries to stick a needle into. But even if this happened, after such an injection no patient will ever be allowed near him again.
To questions about what can be done without sedation and without analgesia, just take it and pull it out, and it doesn’t matter with forceps or threads, I answer: “No!”
If the temporary tooth is mobile and “almost transparent to the light”, there is no need to remove it at all - let the animal chew on something in which to sink the teeth (for example, a not very hard “chew” or a large treat), and, believe me, the tooth will fall out on its own .
But if temporary teeth are stationary, then removal should be carried out only with anesthesia.
But many owners, especially small animals, still experience fear.
“Anesthesia is so scary!!! A small dog, weighing less than 1 kg or a little more, it’s so harmful and scary for him, he could die from anesthesia!” - they are afraid.
I’ll answer with a question: “Why should a clinically healthy animal in the hands of an anesthesiologist die from anesthesia? Is it the job of an anesthesiologist to bring his patient to death?
Let's imagine the situation: the patient is a dog weighing 1.5 kg, which is held by 2-3 people. It takes so many people to hold the animal completely still, and at the same time you have to try not to break anything.
With every second, salivation and attempts to bite increase, in the eyes of the dog there is universal horror and fear... This situation can really lead to the death of the patient from a symptom complex called “shock”.
Or did you imagine it somehow differently? Unfortunately, this is exactly what the picture looks like.
What to do if the crown of a temporary tooth is broken?
If temporary teeth were removed and the crown was broken, leaving the root in the gum with the words “it will resolve on its own,” I answer – no, it will not resolve.
Why should the root of a tooth dissolve because you have broken the crown? It will remain in the gums as a foreign body and at a certain time can cause the process of periodontitis of adjacent teeth or osteomyelitis of the jaw bones.
And one more thing - in no case should you “bite off”, “saw off” or break the crowns of temporary fangs if they “bite” into the gums or to “improve” the change of teeth.
With any injury to the crown of a temporary canine, traumatic pulpitis occurs, and as a result, periodontitis develops with an abscess on the jaw, inside of which there is a rudiment of a permanent canine.
Trauma, pain, inflammation and the possible loss of not only a temporary, but also a permanent canine - this is the price to pay for an incompetent attempt at self-medication.
In case of traumatic pulpitis of a temporary canine, the tooth must be immediately extracted (removed).
A broken tooth crown on the upper jaw of a dog. The tooth is subject to immediate extraction (removal).
Signs of teeth changing in puppies and kittens
If your puppy has bad breath, look inside his mouth. Perhaps there is an active change of teeth, and your help is needed.
In some puppies and kittens, the change of teeth occurs with an increase in body temperature and a decrease in appetite, sometimes even with a refusal to feed. In such situations, it is better to consult a doctor for help.
In cats, during the change of teeth, a very strong odor from the oral cavity is not a strong pathology, and if you see double rows of teeth (both permanent and temporary), know that this occurs normally. But if you notice that your permanent teeth are starting to grow and interfere with each other, you need to consult a specialist.
In some breeds of cats prone to gingivitis (Maine Coons, British cats, Orientals, Sphynxes), it is necessary to conduct a daily examination of the oral cavity during the change of teeth and, at the first signs of gum inflammation, go to an appointment with a veterinary dentist to begin timely treatment.
Learn more about veterinary dental services
Conclusion
Teeth change occurs in absolutely all breeds of cats and dogs. There is no such thing as that only miniature dog breeds or, for example, only Maine Coons can have problems with changing teeth.
Believe me, it is often necessary to extract persistent canines from large and giant breeds of dogs.
Untimely or incorrect removal of baby teeth can lead to bite pathologies, and correcting the bite is another story and at a different price.
Be healthy you and your pets and don’t forget that healthy teeth mean a healthy body.
Best regards, Veronica Gil.
Source: https://gilvet.ru/stati/molochnye-zuby-u-sobak-i-koshek/
Causes
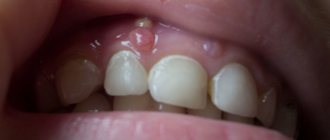
Photo: impacted tooth
There are several reasons that can cause teething problems :
- abnormal position of the primordium at the time of its formation;
- an excessively dense gum capsule, which does not allow timely setting of the correct direction of tooth growth;
- the gums are too loose, not allowing the root to remain in its normal position;
- premature loss or early removal of teeth;
- late loss of baby teeth, as a result of slow resorption of roots;
- pathology of the development of the jaw arch;
- close location of the primordia.
Types of retention
When diagnosing this pathology, an expanded classification is used, which is based on the nature of eruption and its position at the same time.
According to the nature of eruption
Based on this feature, there are 2 types of retention:
- Complete, in which the outer part is completely immersed and covered with periodontal tissue. This type of pathology is most often discovered only after symptoms of tissue inflammation appear.
- Partial, when the tooth protrudes slightly above the level of the gum, or is located in it (semi-retinated), but is partially covered with a gum hood.
This type of anomaly often causes problems, since this position contributes to the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms.
By location
Retention varies according to its intragingival location into 4 types :
- Horizontal . It is characterized by the location of the abnormal unit at a right angle to the general row and parallel to the jaw arches. Accompanied by loosening of neighboring teeth and changes in their position.
- Vertical . It is a classic option for teething, in which they assume a normal position, corresponding to the rest of the row.
- Corner .
It differs in the angle of inclination during eruption and growth, which is less than 90°C. The anomaly can have a slope in any of the directions: medial, buccal, distal, lingual. Basically, it is accompanied by permanent injury to soft tissues. - Reverse . In which the chewing part faces the alveolar ridge, and the root part faces the periodontium. Most often, this position is taken by the 8th tooth (figure eight).
In addition to the listed provisions, retention is distinguished according to its depth , localized:
- in soft periodontal tissues . Is the norm for this pathology, treatment will depend on the position of the abnormal unit;
- in the jaw bone . It is the most complex type of pathology, requiring the use of an atypical method for removal.
How to prevent dental dystopia, read in a new publication.
In a separate article, we will discuss how long braces are typically worn on teeth.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/ryadov/kak-ubrat-shhel-mezhdu-perednimi-vse-sposobyi-korektsii.html we analyzed the main causes of diastema.
Is a persistent tooth an anomaly or an acceptable norm?
122
Human teeth have two generations - permanent and milk. Depending on the group, “milk jugs” erupt in the first 6-24 months of a child’s life. The lower incisors appear first, and the upper molars appear last.
Complete replacement of temporary teeth with permanent teeth occurs between 6 and 12 years of age. However, there are cases where they persist longer than they should. This phenomenon is called persistence (from the Latin “persistere” - “to remain”).
Explanation of the term
Persistent teeth are those that have not fallen out within 2 years after they were supposed to fall out. That is, if the upper primary molar is retained after 14 years, it is called persistent.
Such elements are quite rare. Even less common are cases where persistent teeth linger after 30 years. The maximum age at which the presence of persistent elements was noted was 78 years. Typically, “long-lived milk jugs” are located on the lower jaw; the upper ones fall out much earlier.
The permanent units, which were supposed to replace the persistent ones, can be in different states - absent altogether, erupting next to the persistent ones, being partially erupted, remaining in the gum in the form of an embryo.
Reasons for formation
“Milk jugs” fall out due to the resorption of their roots, which occurs under the influence of permanent units growing under them. The embryos rest against the roots of temporary teeth and start the process of their resorption.
Naturally, if the embryo is absent or displaced to the side, resorption of the roots of the “milk jugs” does not occur, and they become persistent.
Consequently, the main reason for the formation of persistent teeth is the absence or displacement of the germs of permanent units. This can be caused by underdevelopment of the alveolar process, genetic predisposition, disorders in the embryonic period, diseases of women during pregnancy and other factors.
Clinical picture
Persistent units often appear as shell-like remains of crowns and roots next to the erupted permanent elements. However, although relatively rare, there are cases when they completely retain normal morphology, intactness, functionality, and function on a par with permanent units. In such cases, the question arises, what to do with them next?
In their morphology and structure, healthy milk teeth are similar to permanent elements, although they have some differences from them - thinner enamel, wide dentinal tubules, shortened roots. They have a pulp that can become inflamed and, like permanent units, are susceptible to caries.
The clinical picture in the case of their diseases is identical to that of permanent units. Persistent units give discomfort, pain, become sensitive to hot and cold, and the periodontium becomes inflamed in the area of their growth.
In addition to caries, pulpitis, gingivitis and other pathologies, diseased persistent teeth may experience:
- complete or partial resorption of roots;
- their fusion with the alveolar bone (ankylosis);
- occlusal disharmony - discrepancy between the chewing or cutting surfaces of neighboring elements (infraposition is more often observed - “recession” of a persistent unit into the alveolar process);
- change of position relative to the row - displacement, tilt, rotation.
At the same time, a healthy, intact persistent tooth, as a rule, does not cause any trouble to its owner, regularly performs its functions, working on a par with permanent teeth.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis involves interviewing the patient, examining his oral cavity, radiographic examinations, and determining the condition of the pulp and periodontium.
During the inspection it is established:
- fact of existence;
- the condition of its coronal part - the presence of carious cavities, the nature of percussion, the results of probing, the absence or presence of mobility;
- position in a row in relation to neighboring units, the presence or absence of free space for their eruption and growth;
- periodontal condition (gingivitis, periodontitis, gum pockets, gum recession).
X-ray examination is very important and informative. It allows you to install:
- condition of roots and periodontium;
- the presence or absence of nearby primordia or retained units;
- condition of the bone tissue of the alveolar process - deficiency or sufficiency of bone, its structure.
The vitality of the pulp is checked using a cold test.
Treatment tactics
The following tactics are possible for persistent teeth:
- deletion;
- treatment;
- non-interference.
Removal is indicated in case of significant destruction of the coronal part, root resorption, or periodontal damage. In short, in all cases when the “milkman” loses the ability to perform his function.
It is also recommended to remove it if the pulp is inflamed. Depulpation is considered inappropriate due to the fact that the depulped “milk jug” will be quickly pushed out of the alveolar socket.
If the condition allows for restoration of functionality with standard prosthetic or restorative treatment, it is recommended that this be done.
Small carious cavities are filled with composite or amalgam. To restore the coronal part, inlays, onlays, and crowns are used. If root resorption occurs, but the coronal part is in satisfactory condition, the option of embedding the crown into a bridge is possible.
Non-intervention is recommended if full functionality of the tooth is maintained and the clinical picture is characterized by:
- absence of patient complaints of pain, discomfort, inconvenience or inability to chew;
- intact crown;
- healthy periodontium;
- living, non-inflamed pulp;
- normal occlusion;
- absence of pathological changes in the periodontium (according to radiography results).
In case of mild violations of occlusal relationships (minor infraposition), you can also do without intervention.
Having made such a decision, the doctor usually recommends improving hygiene in the area of the persistent unit and sets a schedule for visits to monitor its condition.
Prevention measures
As preventive measures, standard methods of preventing any anomalies are recommended. This:
- maintaining health during pregnancy - good nutrition, a healthy lifestyle, regular examination by a doctor;
- control and elimination of bad habits in infants;
- timely transition to normal food, a diet that is complete in composition and structure;
- regular visits to the dentist with your child for preventive purposes;
- following all doctor's recommendations.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Reviews
Persistent teeth are most often a problem that requires medical intervention. If you had to remove or treat persistent milkworms, tell us how it happened.
Particularly interesting are cases of long-term normal functioning of temporary teeth. If you are “lucky enough” to have such personal experience, be sure to share it with us.
Source: https://zubovv.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/percystentnyi.html
Signs and symptoms
In most cases, you can recognize the presence of an impacted tooth yourself at home.
The main signs for this are:
- soreness in the gum area, which can radiate towards the ear, temple and along the location of the trigeminal nerve;
- regular injury to one area of the mucosa;
- swelling, numbness and hyperemia of the periodontium;
- with slight eruption, gingivitis or pericoronitis may begin;
- protrusion of a limited area of the gum;
- displacement or loosening of adjacent teeth;
- discomfort while eating or opening the mouth;
- the presence of a cyst or purulent formation may be observed;
- During the inflammatory process, the general condition worsens: the temperature rises, chills, headaches, and weakness appear.
Diagnostic methods
In case of partial retention, a visual examination and instrumental examination may be sufficient for diagnosis. To clarify the position of the tooth, targeted radiography is used.
In some cases, orthopantomography and computed tomography are prescribed to obtain a comprehensive picture.
Treatment
In case of pronounced retention, to eliminate the problem, they resort to removing the abnormal tooth. This procedure is complex, so it must be performed painlessly, under local anesthesia. This means that the question of whether it will hurt is not relevant.
Often, the removal of impacted teeth requires the presence of not only a dental surgeon, but also an orthodontist.
In what cases should it be deleted?
The doctor decides what to do in a particular case. Removal of an impacted tooth is indicated only in certain orthodontic situations.
These include:
- constant severe pain in the area of the affected tooth;
- severe swelling of the gums of the face due to constant pressure on the nerve endings;
- high degree of change in the position of abnormal or adjacent teeth;
- the need for prosthetics;
- osteomyelitis or periostitis;
- periodontitis or pulpitis in chronic form;
- caries damage;
- the presence of a periodontal or follicular cyst.
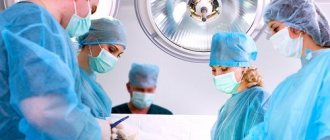
Features of the operation
Removing an impacted tooth requires a highly qualified doctor. The procedure is performed under local infiltration anesthesia; sometimes, at the patient’s request, general anesthesia is prescribed.
Ultracaine is most often used as an anesthetic drug. It has limited contraindications and minimal side effects.
Watch the video for the operation procedure:
How much the procedure will cost depends on the complexity of the situation. Its duration can vary from 1 to 3 hours, most of the time the root is pulled out. This must be done as carefully as possible to avoid consequences.
The surgical removal operation takes place in several stages :
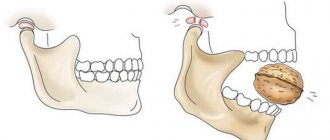
- Detachment of mucous tissue . The surgeon makes an incision into the mucosa and periosteum using the patchwork method. Next, using a scalpel, the tissue flap is moved to the side, and the bone bed is exposed.
- Preparing the surface for extraction . In order to remove, it is necessary to gain access to the root part of the tooth. To do this, the dentist uses a drill, with which he drills a hole in the bone tissue of the jaw.
- Removal .
To do this, I use a milling cutter with a straight tip. The doctor cuts off the top part of the tooth and then removes it entirely. To remove the root system, the root is divided into elements. Using an angular extractor, each element is outlined at a right angle. In this way, all periodontal ligaments are broken. After which the root is removed from the hole in parts. - The open wound is cleaned of bone tissue particles and washed with antiseptics.
- In case of extensive damage, the drug is applied and the damaged tissue is sutured with several interrupted sutures.
If severe inflammation was observed before removal, then iodoform turunda is placed in the hole, which must be periodically replaced in the future.
Insufficient qualifications of the doctor can lead to complications: it is extremely rare, but if carried out roughly, even a jaw fracture is possible.
To avoid such problems, you should carefully consider the question of which clinic to perform the removal.
The cost of the procedure in private dentistry can vary significantly (in some, this service is included in the compulsory medical insurance program), but you should focus not on the price, but on patient reviews.
Postoperative period
After a complex extraction of an impacted tooth, the rehabilitation period can last from 3 to 10 days. During the first days after surgery, the patient complains that his gums hurt and he has difficulty opening his mouth and chewing.
Also, swelling and redness of the tissues of the operated area is allowed. Subsequently, the symptoms reduce the intensity of their manifestation.
a number of rules must be followed during the rehabilitation period :
- in the first 15 minutes after removal, it is necessary to hold a cotton swab between your teeth to stop the bleeding;
- It is recommended to apply a cold compress to the cheek for several hours after removal;
- in the first 3 days it is recommended to use antiseptic preparations for rinsing. Chlorhexidine is good for this. Rinsing should be done carefully to prevent the blood clot from being washed away;
- To relieve painful manifestations, it is recommended to use painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Suitable, for example, are Ketorolac, Ketorol, Nurofen, Analgi; - Within 3 hours after the operation, you must stop drinking, eating and smoking.
What are three teeth, read in a new review.
In this article we will talk about the stages of surgical correction of malocclusion in adults.
At the link https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/zubov/polozheniya/krivyie.html we will discuss why crooked teeth appear in children.
Complete tissue healing is observed only after 3 or 4 weeks . During this period, it is necessary to monitor the clinical picture and symptoms that arise from dental inflammation. If the suture festers, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Prevention measures
As preventive measures, standard methods of preventing any anomalies are recommended. This:
- maintaining health during pregnancy - good nutrition, a healthy lifestyle, regular examination by a doctor;
- control and elimination of bad habits in infants;
- timely transition to normal food, a diet that is complete in composition and structure;
- regular visits to the dentist with your child for preventive purposes;
- following all doctor's recommendations.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.