4815
Not only adults, but also children are susceptible to periodontal inflammation. The most common disease is gingivitis. It affects the mucous membrane of the gums and is characterized by pronounced symptoms.
If left untreated, the pathology leads to complications that affect adjacent bone tissue and internal organs.
Varieties
There are several types of this pathology, differing in symptoms and intensity of their manifestation:
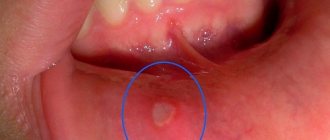
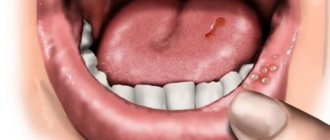
- Catarrhal . It occurs with minimal symptoms: redness and bleeding of the gums.
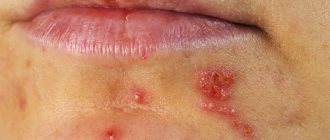
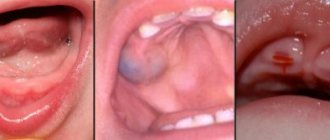
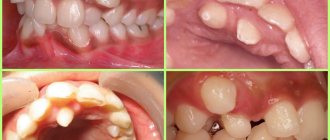
- Ulcerative . It is characterized by severe symptoms: swelling of the gums increases, they become blue. With a slight touch, blood and gum fluid are released from under the papillae.
- Ulcerative-necrotic . It goes away with a deterioration in general health and the formation of bleeding ulcers on the gums in the neck of the teeth. The bases of the crowns are exposed.
- Atrophic. It is characterized by a decrease in the volume of gum tissue in the neck of the teeth, which leads to its exposure.
Stages of the disease
Depending on the symptoms manifested, several stages of gingivitis are distinguished:
- first (initial) . Inflammation covers only the tops of the interdental papillae, which become red and painful;
- second . From the interdental papillae the disease spreads to the edge of the gums
- third . The pathology extends to the soft tissue of the alveolar ridge.
The disease in its acute form without proper treatment becomes chronic.
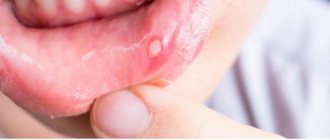
Symptoms
The onset and development of gingivitis is signaled by the following symptoms:
- soreness of the gums on palpation;
- bleeding;
- increased salivation ;
- swelling;
- soft tissues in the area of the roots of the teeth lose their density , becoming loose;
- change in gum color : redness or blueness;
- discomfort when chewing;
- deterioration of general condition : lethargy, fever, pallor of the skin;
- swollen lymph nodes.
How does acute catarrhal stomatitis manifest: symptoms at different stages.
You need to know how to properly use Tantum Verde spray for children. Here are the official instructions.
Follow the link https://zubovv.ru/detskaya-stomatologia/polost-rta/stomatit/chem-nado-lechit.html for a list of how to treat oral stomatitis in children (1 year old).
Dr. Komarovsky about gingivitis
According to the famous pediatrician Komarovsky, any diseases of the oral cavity, including gingivitis, should be observed in the dentist’s office.
There is no need to start giving your child antibiotics right away ! It is worth understanding that anti-inflammatory therapy started on time has a very good effect. In order to avoid relapses of gingivitis, you need to teach your child to properly and regularly care for their teeth from early childhood.
Gingivitis can cause fever
Therapy
Gingivitis is a rapidly developing disease. Lack of timely treatment often leads to complications . This is especially important in childhood.
In order to eliminate the disease at the initial stage of its development, local therapy using gentle techniques .
To cure the advanced stage, it is necessary to use general therapy with antibiotics . surgery can help .
If symptoms are detected, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible. Depending on the cause of the disease, you may need the help of other specialists: pediatrician, endocrinologist, immunologist, otolaryngologist .
In the clinic
Treatment in a clinical setting, regardless of the degree of development of the pathology and its type, must include:
- Professional cleaning with complete removal of tartar and soft bacterial plaque. This procedure is carried out using ultrasound, which does not injure the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
It allows you to completely remove hard deposits not only on the visible part of the tooth, but also from under the gums, deeply cleaning the gum pockets. Cleansing procedures are completely painless.After exposure to ultrasound, the crowns are polished using a special brush and dental paste, and the gums are coated with a soothing agent.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy . It is used to speed up the healing process and relieve symptoms of gingivitis. Depending on the type and form of the disease, local or general drugs are used.
- Hardware physiotherapy . For this, a course of intraoral electrophoresis, laser therapy, and ultraviolet radiation is prescribed. The main effect of these techniques is to stimulate metabolic processes that affect the restoration of periodontal tissue.
In the treatment of complex forms of the disease (ulcerative, necrotic, hyperplastic and atrophic gingivitis), in addition to the listed methods, others are used.
As a rule, such techniques involve direct action on the gum tissue. These methods include:
- Gingivectomy (gum excision) .
This method is used only in special cases when other treatment methods have failed. Surgery is performed only under general anesthesia. During the procedure, the doctor excises only the pathologically overgrown tissue. After this, to avoid relapse and bleeding, the operated area is cauterized or frozen. - Freezing It is used not only as an additional, but also as an independent method of relieving pathology.
The essence of the procedure is as follows: a solution of calcium chloride or dextrose is injected into the inflamed periodontium, which has a freezing effect.After injection, the interdental papillae completely harden, which temporarily stops their pathological growth.
- Chemical cauterization . It involves applying a special mixture containing sulfuric acid and ether to painful areas. Due to the influence of these components, the upper layer of the periodontium burns and cell necrosis occurs, which helps stop the disease.
- Exposure to electric current . At its core, this procedure resembles the previous one. Here they also provoke a burn of the mucous membrane, only for this they use a current of no more than 5 amperes. The manipulations are painful and are therefore performed under local anesthesia in children over 5 years of age.
- Necrolysis . Allows you to remove pathological cells by resorption. To do this, a special preparation is applied to the mucous membrane, which includes sodium chloride and trypsin (an active enzyme). Penetrating into the cells of the gum tissue, the drug promotes their gradual destruction.
Medicines
Treatment of gingivitis is not complete without medications, which, depending on the severity of the pathology, can be used locally or form part of general therapy.
In any case, only forms with a dosage designed for children are used.
For the treatment of gingivitis in childhood, it is permissible to use the following topical agents:
- Kalgel. Intended for the treatment of catarrhal and ulcerative gingivitis. Presented in the form of a gel, which is easy to apply and adheres well to periodontal tissue. The gel has a pronounced aseptic and analgesic effect.
The composition includes components that allow the drug to be used to treat even yearlings children. For a quick recovery, it is necessary to apply about 7 mm of gel to the painful area no more than 6 times a day.The approximate cost of the drug is 330 rubles.
- Propsol. It is a spray for treating mucous membranes, made on the basis of propolis. The product has a pronounced aseptic and anti-inflammatory effect, effective against catarrhal gingivitis.
In addition, the spray has analgesic properties. Recommended for use by adults and children from 5 years. Treatment regimen: 2 times a day, 3 injections. The spray can be used until complete recovery.The cost of the product is 180 rubles.
- Eludril is a chlorhexidine-based mouthwash solution. Shows high effectiveness in all forms of gingivitis.
Using the solution helps relieve inflammation and pain. The drug can be included in the treatment of children from 3 years. For the procedure, dilute 2 teaspoons in 150 ml of water and rinse your mouth for 30 minutes.The price of the drug is 240 rubles.
- Holisal. This is a dental gel used to treat catarrhal, necrotic and ulcerative gingivitis. In addition to pronounced anti-inflammatory properties, it has high activity against bacteria.
The gel is indicated for the treatment of children starting from infancy. The therapeutic effect occurs when the gel is applied twice a day.The average market price of the gel is 250 rubles.
- Chlorhexidine (0.05%). Effective for catarrhal form of gingivitis. The product is available in the form of a solution and is intended for rinsing about 2 times a day. Solution has no age restrictions.
With daily use, a decrease in the intensity of the symptoms of the disease is observed.Chlorhexidine has a low cost - about 14 rubles.
- Miramistin – spray for irrigation of mucous membranes. Designed to relieve symptoms of catarrhal gingivitis. Can be included in the treatment of children from 3 years.
The spray relieves inflammation well and, in addition, anesthetizes periodontal tissue. Use 3 times a day for no more than 10 days.The cost of the drug is approximately 240 rubles.
- Metrogil Denta is an antimicrobial drug, made in the form of a gel, effective in the treatment of acute and chronic gingivitis.
Used in the therapy of children from 6 years. Helps relieve symptoms and promote rapid tissue regeneration. The gel is applied to the mucous membrane 3 times a day.Its average market price is 250 rubles.
If local therapy is not effective, treatment with antibiotics is prescribed. The choice of antibiotic should only be made by the dentist.
The most common antibiotics used to treat gingivitis are:
- Amoxicillin . Available in the form of tablets or suspension. The drug belongs to the penicillin series and is distinguished by its speed of action against pathogenic bacteria. Amoxicillin can be purchased for 50–80 rubles.
- Metronidazole . This is a combined action drug that has an antibacterial and antiprotozoal effect. Can be used in combination with antibiotics. The price of the drug starts from 70 rubles.
- Erythromycin - available only in tablet form. This antibiotic belongs to the group of macrolides and has a bacteriostatic effect. The cost of the drug is 90 rubles.
The treatment regimen and dosage are prescribed by the doctor individually in accordance with the patient’s age, body weight and the severity of the pathology.
Every mother should know the timing of the eruption of baby and permanent teeth in her child.
Which gum gel helps with teething? Here is a list of drugs.
In this https://zubovv.ru/detskaya-stomatologia/d-zubi/prorezyivanie-z/kak-imenno-rastut.html article, doctors explained how a child’s molar grows.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies that also have anti-inflammatory and aseptic effects can help with drug therapy:
- rinsing the mouth with a decoction based on chamomile, sage and oak bark . To prepare, you need to pour 3 tablespoons of each plant into 250 ml of boiling water. After leaving for 60 minutes, rinse at least 6 times a day;
- St. John's wort oil . To prepare it, you need to pour 150 ml of sunflower oil into the herb and leave for 12 hours to infuse. Lubricate inflamed areas of the mucous membrane with the resulting oil about 3 times a day;
- Shilajit has a good effect . It is heated in a water bath and then mixed with kefir. Rinse your mouth with the resulting mixture for 3 minutes.
How to treat?
Treatment of gingivitis in children under one year of age is complicated by the fact that many drugs that doctors prescribe to them (without reading the instructions) are allowed only from two years of age, and sometimes even from 10-12. Yes, yes, you can send doctors through the forest who write on a piece of paper the name of some gel, the instructions of which say in black and white that children up to... cannot be given it.
That's not all, gentlemen. If you search the Internet for an article about lidocaine, you may turn gray. The American office responsible for medicines and products published a report in which it described how a popular anesthetic can lead to serious health problems and even the death of a small child. And the “humor” is that we are not talking about an overdose. Cases of use within the framework of doctor's orders were checked.
Treatment of childhood gingivitis
Therefore, when starting treatment for gingivitis in children under 2 years of age, it is important to take into account such factors as individual reactions of the body, allergies, etc.
For older children, the plan is simple.
- We remove plaque and tartar. Doing this at home correctly and 100% is impossible. Tested, proven.
- If there are teeth with caries, we treat them and fill them.
- Once the sources of bacterial contamination have been eliminated, you can move on to “phase 3” - the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. Rinses and baths with a solution of chlorhexidine, as well as regular infusions (without alcohol, as it will dry out and burn the mucous membrane) of herbs (chamomile, sage, oak bark, you can add mint and eucalyptus).
- Cholisal and Metrogil Denta are suitable gels. The first one can be small. It contains no dangerous substances and lidocaine.
"Holisal"
"Metrogil Denta"
The use of such simple remedies makes it possible to treat gingivitis in children at home. Of course, after they had the plaque and tartar removed. If soft and hard plaque remains on your teeth, all your efforts are a waste of time, nerves and money on medicine. Therefore, we are not lazy, we take the kids to the dentist.
Propolis tincture
Let's not forget about such a wonderful remedy as propolis. It is useful, harmless to children, relieves inflammation, and has an antiseptic effect. What is no less pleasant is that it costs a penny when compared with any ordinary medicine from a pharmacy. If children are not allergic to bee products, then this option is suitable.
Let me remind you once again that alcoholic tinctures of propolis should not be given to children. For the reasons mentioned above. In addition, alcohol is absorbed into the mucous membrane and is unlikely to be useful, for example, to a one-year-old baby.
Propolis for children
If teeth are being cut, it immediately becomes clear what’s going on. We apply the gel, rinse, and wait for it to go away. If the temperature rises and does not go away, we call a doctor at home.
I hope you found my recommendations useful. However, this is not a guide to action; treatment should be carried out by an experienced specialist!
Consequences
Gingivitis is a pathology that requires mandatory treatment. And in childhood this issue is especially acute, since during this period the active development of the jaw apparatus and internal organs occurs.
A disease that is not stopped in a timely manner can lead to the formation of malocclusion and disruption of the functioning of body systems , which quickly takes on a chronic form.
In addition, if left untreated, complications such as:
- periodontitis , which threatens tooth loss;
- addition of purulent infections ;
- caries development;
- periodontal disease;
- heart pathology;
- infection of the jaw bone.
Gingivitis is a disease that can be treated well in its early stages.
For timely treatment, you just need to contact your dentist on time. This will save the child from more complex problems that undermine his health.
In this video, Dr. Komarovsky talks about gingivitis and stomatitis:
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: gingivitis in children, oral cavity
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Prevention
The following recommendations will help avoid the problem of bleeding gums:
- The child's oral hygiene must be maintained. Parents need to keep an eye on this. The child should be taught how to brush their teeth correctly. Teeth brushing should begin as soon as the first tooth appears.
- The child should limit his intake of sweets and increase foods containing calcium in his diet. Citrus fruits will reduce inflammation and bleeding. It is also useful to eat apples, pears, black currants, raspberries, blackberries, cabbage, zucchini, and carrots.
- Lack of vitamins is a common cause of gum disease. The doctor may prescribe vitamin complexes or mandatory consumption of vegetables and fruits.
- If proper care is impossible due to braces or jaw injury, toothpastes with medicinal ingredients will help.
- The child should be taken to the dentist twice a year.
If your child's gums begin to bleed, you should consult a doctor immediately, without waiting for complications.