Causes and risk group
Rotovirus infection or viral gastroenteritis is a type of intestinal infection, the development of which is provoked by viruses of the Rotavirus genus from the Reovirus family of types A, B and C. In adults, rotavirus infection in most cases is caused by type A virus. There are several risk factors, the presence of which increases the risk get sick, these include:
- unfavorable social and living conditions;
- unbalanced diet, eating low quality foods;
- severe chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- immunodeficiency states;
- weak immunity due to constant colds, long-term treatment with antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs.
Differential diagnosis
Very often, the diagnosis is made based on the patient’s symptoms and complaints. At the same time, the most reliable method for diagnosing rotavirus infection is a specific stool analysis (immunochromatography). Other studies are not indicative of a quick diagnosis.
Rotavirus infection should be differentiated from diseases that have similar symptoms. These include:
- cholera;
- dysentery;
- Escherichiosis;
- gastrointestinal form of salmonellosis;
- intestinal yersiniosis;
- some types of protozonoses (giardiasis, cryptosporoidosis and balantidiasis).
As a rule, in an adult the pathology proceeds without any peculiarities, in the usual uncomplicated form. But in case of untimely diagnosis, initiation of treatment and significant suppression of immunity, complications may arise.
Routes of transmission
The main route of transmission of rotavirus infection is fecal-oral, that is, through dirty hands. The infection can also enter the body through the use of household items of a sick person or someone who has recently recovered from illness, or through the consumption of raw water or poor-quality food.
The causative agent of rotavirus infection is quite stable in the external environment; for example, in water it can remain viable for up to 2-3 weeks. The virus is highly contagious (infectious) and spreads quickly in confined spaces - this means that if one family member becomes ill, the infection is likely to be transmitted to everyone. As a rule, outbreaks of rotavirus infection occur in the autumn and winter periods, as a result of which it is also called intestinal flu.
What it is?
Rotavirus infection is an infectious disease caused by rotaviruses. It is the most common cause of diarrhea in children. This disease is characterized by an acute onset, moderate symptoms of gastroenteritis or enteritis, and a frequent combination of intestinal and respiratory syndromes in the initial period of the disease. Rotavirus infection is often incorrectly called "stomach flu", although rotavirus is not related to influenza viruses.
What happens in the body when an infection occurs?
When pathogens enter the gastrointestinal tract, they penetrate the mucous membrane of the small intestine. By multiplying, rotavirus disrupts protein synthesis, the absorption capacity of cells and the evacuation function of digested food. As soon as all the vital resources of the intestinal cell are exhausted, the infected cell dies, releasing a huge amount of toxins that are absorbed into the blood and disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. All this is accompanied by the development of severe enzymatic deficiency and signs of gastroenteritis - an inflammatory process of all parts of the digestive tract.
Under the influence of toxic substances, the patient's process of water absorption in the intestines is disrupted, resulting in diarrhea. The accumulation of toxins in the blood provokes repeated vomiting, which significantly increases the risk of developing fluid and electrolyte imbalances and dehydration. If the patient is not provided with adequate medical care and rehydration is not started, then soon, due to diarrhea and vomiting, the volume of circulating fluid in the body decreases, signs of dehydration appear and hypovolemic shock develops.
Causes of inflammation
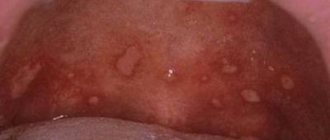
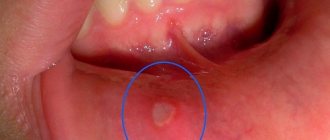
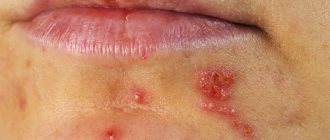
An infectious process in the oral cavity can be triggered by various reasons. The main ones:
- mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, in which pathogenic bacteria and viruses enter the body through cracks in the gums and lips;
- poor nutrition, with insufficient amounts of vitamins and minerals;
- excessive consumption of sweet, starchy, sour foods, which leads to disruption of protein metabolism, fermentation of carbohydrates and the production of lactic acid - an ideal environment for the proliferation of bacteria in the mouth;
- thick, viscous saliva - with insufficient fluid intake, salivation is impaired, as a result of which the teeth are not washed enough, the mucous membrane dries, peels and itches - and this is a sure way to the development of an infectious process;
- concomitant infectious diseases that are at an acute stage in the body - a favorable condition for the proliferation of fungi and viruses in the oral cavity;
- pregnancy - in this state the female body becomes more vulnerable to attack by pathogenic bacteria;
- stressful situations – frequent nervous overload leads to malaise, decreased immunity, and as a result – to inflammatory processes in the body;
- allergic reaction - may well provoke the development of an infectious process; to treat this type of inflammation, it will be enough to eliminate the main cause, and then get rid of the symptoms of secondary infection;
- insufficient oral hygiene
Symptoms of rotavirus infection in adults
From the moment the virus enters the body until the first clinical signs of infection appear, 1 to 3 days pass. Rotovirus infection in adults, as a rule, occurs as food poisoning and is characterized by a number of symptoms:
- the appearance of pain in the epigastric region;
- nausea;
- excessive salivation;
- weakness, chills;
- dizziness;
- tachycardia;
- hand tremors;
- repeated vomiting, which brings relief only for a while;
- diarrhea up to 10 times a day;
- cutting pain in the abdomen.
Such signs may persist for 3-7 days. After vomiting and diarrhea stop, the patient will continue to experience weakness, lethargy, and poor appetite for several days (up to a week).
Rotovirus infection is insidious in that after the illness the patient does not develop immunity, that is, if he encounters the pathogen again, infection will occur again.
Possible complications
The main and life-threatening complication of rotovirus in adults is dehydration, which occurs as a result of the loss of large amounts of water and salts during vomiting and diarrhea and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- dry mouth, increased thirst;
- headache;
- dry skin and mucous membranes;
- reduction, and then complete absence of urination;
- tachycardia, shortness of breath;
- the appearance of acetone odor from the mouth, which is due to the accumulation of ketone bodies;
- drowsiness, weakness, lethargy;
- sunken eyes in severe cases.
Important! If the listed signs of dehydration appear, the patient should be taken to the hospital, where he will be given rehydration therapy with intravenous drips.
Principles of disease treatment
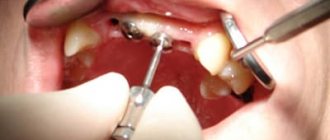
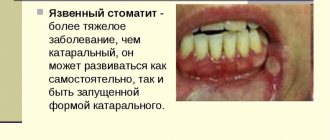
After making a diagnosis, the doctor selects the appropriate treatment. For stomatitis, mouth rinses with Furacilin or an antiseptic solution are prescribed; in severe situations, it is necessary to take broad-spectrum antibiotics.
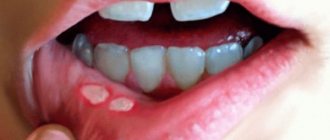
The herpes virus is eliminated by taking Acyclovir tablets, rinsing the mouth with Furacilin and treating the affected areas with Acyclovir ointment. For gingivitis and periodontitis, removal of plaque and tartar and strengthening of the gums by rinsing the mouth with various herbal infusions are prescribed.
Glossitis is treated with antiseptic treatment and taking medications, and candidiasis is treated with rinses and antifungal agents. The only way to get rid of papilloma in the mouth is through surgery.
The general principles of treatment for oral infections are as follows:
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions, herbal infusions,
- treatment of the oral mucosa with antibacterial or antifungal agents,
- antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal therapy,
- drug treatment of symptoms: painkillers, decongestants,
- strengthening therapy: vitamin-mineral complexes, immunomodulators.
To achieve results, folk remedies may be recommended. In severe situations, surgical intervention is indicated.
Treatment of rotavirus infection in adults
For a favorable outcome of the disease, the patient is prescribed symptomatic treatment, that is, aimed at combating the clinical signs of rotavirus and eliminating its consequences. The standard treatment regimen includes:
- oral rehydration;
- enterosorbents;
- diet.
In severe cases and when signs of dehydration appear, the patient is given IV drips, which help replenish fluid in the body and restore the balance of mineral salts in the blood.
Oral rehydration therapy
Since rotavirus infection is accompanied by profuse diarrhea and vomiting, in order to avoid complications such as dehydration and in order to replenish the volume of lost fluid, the patient should immediately begin taking oral rehydration solutions. They can be purchased at the pharmacy and prepared according to the instructions. The optimal content of electrolytes and microelements in the following products:
- Regidron;
- Humana electrolyte;
- Trihydron;
- Hydrovit.
Are additional medications needed?
Despite the fact that the infection is caused by a virus, the use of antiviral drugs, which are used to treat colds, is impractical and ineffective. The use of drugs from this group does not in any way affect the duration of the infection or the outcome of the disease. The main principles of rotavirus treatment are drinking regimen, sorbents and diet, and the body can handle the rest on its own.
Dietary nutrition for rotavirus infection in adults
For the first 2 days from the onset of the development of rapid clinical symptoms of rotavirus, the patient cannot eat anything, but, as a rule, he already has no appetite due to constant nausea and vomiting. Particular attention is paid to the drinking regime - saline solutions, compote of dried fruits, apples, uzvar, raisin decoction, sweet tea.
On the 3rd day, when vomiting and diarrhea stop, the patient can prepare boiled rice porridge without oil in water or vegetable soup with rice cereal. Portions should be small, it is better to eat often and very little, so as not to provoke vomiting again. As soon as the stool improves, the diet is gradually expanded, adding mashed potatoes in water without oil, boiled grated vegetables, fruit puree, biscuits, poultry meat without skin and fat. Jelly and berry decoctions, white bread crackers, bagels, and sweet crackers with raisins are allowed.
Exclude from the diet:
- milk and all dairy products (sour cream, cottage cheese, kefir, fermented baked milk, cream, cheese and others) - this rule should be followed for at least 1 month after rotavirus infection;
- pork, fatty meat, offal;
- fatty fish (mackerel, herring, salmon) and caviar;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- smoked meats;
- sausages;
- pasta;
- spices, vinegar;
- bakery products and pastries;
- candies, shortbread cookies, sweets.
All dishes are served to the patient boiled, stewed or baked without crust. This table should be followed for at least 1 month in order to minimize the load on the inflamed intestines.
If a strict diet is not followed or ignored, the patient develops enzymatic deficiency, and the symptoms of rotavirus resume - diarrhea, vomiting, total inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Drug treatment
As already mentioned, there is no special medication for the treatment of rotavirus infection in adults. If the symptoms are severe, then drug treatment is aimed at eliminating specific symptoms. Due to the fact that the disease is contagious, the patient must be isolated during treatment, thereby limiting the spread of rotavirus infection.
Painful sensations and intestinal spasms can be relieved with the help of a regular no-spa. You can lower the temperature when the temperature is above 38 degrees, since most rotaviruses die at high temperatures. To relieve fever, you can use antipyretics:
- Paracetamol;
- Aspirin;
- Analgin;
- Nurofen;
- Coldrex;
- Rinza.
Getting rid of intoxication involves taking sorbents that absorb toxins and remove them from the body. For example:
- Smecta;
- Enterosgel;
- Polysorb;
- Activated carbon;
- White coal;
- Liferan;
- Intravenous administration of glucose with colloidal solution.
A rehydration solution is necessary in case of frequent diarrhea and vomiting. Because of them, the body rapidly loses fluid, and if the disease is accompanied by a high temperature, then the risk of dehydration increases sharply.
Therefore, to preserve fluid, the drug rehydron is prescribed - this is a powder that is dissolved in water and drunk in large (but limited) quantities in small sips every 10-15 minutes. If you don’t have rehydron, you can include a saline solution prepared at home in your diet. Forcing someone to drink is prohibited, as this provokes vomiting and disruption of the water-salt balance.
As you can see, if rotavirus infection occurs, treatment in adults is not so difficult. However, only if you start it in a timely manner can you count on getting rid of the disease as soon as possible. Otherwise, as mentioned above, the risk of developing various complications is very high.
Methods for preventing rotavirus infection
There is no specific prevention of rotavirus (vaccines), so absolutely everyone can get sick, especially those at risk. To reduce the risk of morbidity and prevent the development of rotavirus infection, follow simple rules:
- always wash your hands with soap after using the toilet and before eating;
- vegetables and fruits must be washed under running water before consumption;
- do not consume products of questionable quality;
- Do not drink raw water from unknown sources.
If someone in the family is sick with rotavirus infection, then the patient should have separate dishes, towels, bed linen and household items, which should be soaked daily in disinfectant solutions and thoroughly washed with hot water or boiled.