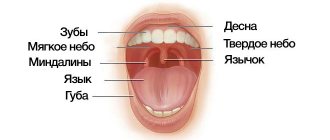
Causes
The formation of mouth ulcers on the palate occurs for various reasons. Most often their appearance is provoked by:
- consumption of foods that injure the oral mucosa: crackers, chips (also leads to the formation of ulcers);
- taking hot drinks, food;
- oral care rules
Other causes of ulcers on the palate:
- Incorrectly installed or poorly selected dentures .
- extraction and filling .
- Brushing your teeth with a paste that contains sodium sulfate: the mucous membrane becomes susceptible to bacteria and food acids.
- Genetic predisposition. If relatives experience frequent relapses of stomatitis, the likelihood of developing the disease increases several times.
- Malocclusion .
- Allergies to food (chocolate, citrus fruits), oral care products.
- Taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs.
- Eating unwashed fruits and vegetables.
- Fungal infections.
- Hormonal imbalance is one of the causes of ulcers on the palate in women during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause.
- Alcohol abuse , tobacco addiction.
- Frequent stress.
- Low immunity.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Deficiency of fluid, vitamins and minerals in the body.
On this topic
- Sores
How to quickly cure sores on the inside of the lip
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 4, 2020
Sometimes sores on the palate are a sign of systemic diseases. The appearance of mouth ulcers may indicate:
- Tuberculosis.
- Syphilis.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas and thyroid gland (the appearance of wounds on the mucous membrane of the palate is observed in diabetes mellitus, toxic goiter).
- Necrotizing gingivostomatitis.
- Oncological disease. A malignant tumor may also be accompanied by the appearance of long-term non-healing ulcers on the palate, but they are rare.
It is difficult to independently determine what caused the wounds on the palate. But if you pay attention to the clinical signs of pathology, you can help the doctor quickly make a diagnosis and select effective treatment.
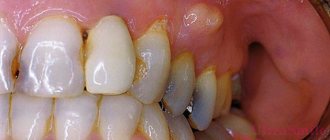
Ulcers on the roof of the mouth: causes, symptoms and treatment
The oral mucosa is capable of quickly regenerating, since it is lined with several layers of epithelium, which is constantly renewed. In addition, it is resistant to irritants of various origins and infections.
However, small ulcers often occur on the lining of the mouth, particularly the roof of the mouth, causing discomfort and pain.
Ulcers on the roof of the mouth appear due to:
- Eating crackers, nuts, fish. Products with sharp edges can scratch the epithelium, leading to the formation of ulcers.
- Chemical and thermal burns of the palate (hot food and drinks, careless handling of acids).
- In children, the mucous membrane can be damaged due to improper and rough oral hygiene.
Ulcers as a symptom of the following diseases:
- candidiasis;
- herpes;
- tuberculosis;
- stomatitis;
- syphilis;
- scarlet fever;
- endocrine disorders.
Ulcers, or in scientific terms aphthae, cause a lot of inconvenience, so they cannot be asymptomatic and a person will immediately understand that the mucous membrane of the palate is not in order:
- Due to the appearance of ulcers, the mucosal tissues swell, and this can make speech difficult.
- It is impossible to eat hot, spicy, sour and salty foods, as they will irritate the damaged surface of the palate.
- A person, even with his mouth closed at rest, may experience pain, and in advanced cases, the ulcers bleed.
Not all canker sores are harmless. Of course, if they were formed due to mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, they will go away on their own in the shortest possible time.
If the ulcers do not go away, you need to track the accompanying symptoms in time to begin treating systemic diseases:
- When the herpes virus enters the oral mucosa , a person’s condition generally worsens, body temperature may rise, lymph nodes enlarge, salivation increases, and then small wounds form on the palate.
- Often, with a decrease in immunity or long-term use of antibiotics, it is possible to develop a disease such as candidiasis or thrush of the oral mucosa. In this case, a burning sensation is felt, taste sensations are lost, and a characteristic white coating of a cheesy appearance forms on the entire mucous membrane; eventually, aphthae can form on the palate, which sometimes bleed.
- When infected with syphilis at the beginning in the oral cavity , a rash may occur, which then develops into ulcers on the soft tissue of the palate and cheeks.
- Aphthous stomatitis. A chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa and the appearance of ulcers on the palate. Besides. such stomatitis can be a symptom of generalized aphthosis, a disease that affects all mucous tissues in humans (gastrointestinal tract, genitals, eyes). Ulcers form gray-yellow in size from 2 to 10 mm, depending on the course and stage of the disease. They are quite deep, painful, do not heal for a long time and often recur.
- With pulmonary tuberculosis , initially small compactions in the form of reddened tubercles may form on the palate, which then transform into shallow round wounds.
Read also: Ulcer on the cheek from the inside
Features of manifestation
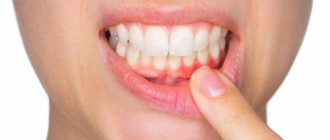
It is impossible not to notice wounds or pustules in the oral cavity: they are visible upon visual examination and cause significant discomfort to the patient. Common symptoms of mouth ulcers:
- swelling of the palate;
- difficulty speaking;
- pain when eating salty, sour or hot foods;
- bleeding from the mouth.
The clinical picture may be supplemented by other symptoms: it all depends on the form of stomatitis.
Catarrhal - manifests itself in the form of white spots, which gradually turn into wounds. Signs:
- excessive salivation;
- pain when chewing food;
- bad breath .
On this topic
- Sores
How to quickly get rid of tongue ulcers
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 4, 2020
Aphthous - characterized by the appearance of ulcers with a gray coating, cell death at the site of their occurrence. If its course is complicated, it is possible:
- damage to the salivary glands;
- scarring of palate tissue;
- deformation ;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Allergic – appears upon contact with an allergen. The development of stomatitis of this form is possible when taking medications or dental interventions. The patient has complaints about:
- dry mucous membranes;
- itching, metallic or sour taste in the mouth;
- difficulties with eating .
Candidiasis is caused by fungi that constantly live in the oral cavity. If the immune system is impaired or the rules of dental care are neglected, their number increases. This results in sores on the roof of your mouth, gums, or cheeks. Its main features:
- burning sensation in the mouth;
- a coating on the palate of a cheesy consistency.
On this topic
- Sores
How to quickly get rid of an abscess on the gum
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- September 2, 2020
Bacterial - caused by the herpes virus, staphylococci and streptococci. Usually occurs with chickenpox, measles, influenza, rubella. With a long course of the disease, the following symptoms appear:
- high temperature ;
- weakness ;
- purulent discharge from the mouth (observed if there is an infection);
- sepsis (in advanced cases).
When ulcers on the palate are a manifestation of systemic diseases, the clinical picture is slightly different.
| The reason for the appearance of wounds on the sky | Characteristics of ulcers | Associated symptoms |
| Tuberculosis | After the Koch bacillus is introduced into the mucous membrane of the mouth, small tubercles appear on the palate. Over time, ulcers form in their place, at the bottom of which bleeding epithelium is visible. If left untreated, the size of the wound increases and other complications of the disease arise. | Weight loss |
| Increased plaque on the tongue | ||
| Excessive sweating | ||
| Low-grade fever | ||
| Acute necrotizing gingivostomatitis | Ulcers with soft, uneven edges, a dirty green coating on the surface. When it is removed, a loose bleeding bottom is revealed | Swelling of the mucous membrane |
| Pain in the palate when touched | ||
| A sharp decrease in working capacity | ||
| Loss of appetite | ||
| Insomnia | ||
| Syphilis | Penetration of Treponema pallidum into the oral mucosa leads to the formation of round or oval wounds on the palate with raised, smooth edges. They are painless and have a shiny, dark red bottom. | Primary: enlarged lymph nodes, with the addition of a staphylococcal infection - pain, increased depth of the ulcer, gray-yellow coating on its surface |
| Secondary: fatigue, general weakness, low-grade fever, headaches | ||
| Tertiary – characterized by damage to bone tissue and periosteum. Occur: bone necrosis, extensive defects of the oral cavity, perforation of the hard palate. | ||
| Diabetes | A round ulcer that is white or pale yellow in color | Constant feeling of thirst |
| Dizziness | ||
| Increased appetite | ||
| Increased urine output | ||
| Malignant formation | Wounds with compacted edges. At an early stage of development it does not cause pain. As the ulcer grows, it takes on a crater-like shape. | Discomfort |
| Pain when chewing food or drinking drinks (occurs when a secondary infection occurs) |
The clinical manifestation of stomatitis and systemic diseases have similar symptoms. If you self-medicate, this can lead to a deterioration in your health and the development of complications. Recommendations for the treatment of mouth ulcers should be given by a doctor after determining the cause of their occurrence.
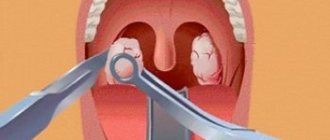
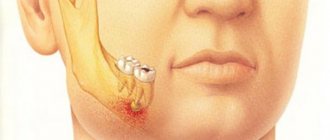
Abscess of the hard palate
Apart from secondary abscesses in osteomyelitis of the palatine process of the upper jaw of specific (syphilis, tuberculosis) and nonspecific origin, the usual source of an abscess in the area of the hard palate is an infection emanating from the upper lateral incisors and first upper premolars. This is facilitated by the often observed deviation of the apex of the root of the upper lateral incisor and the palatal root of the first premolar towards the palate.
Abscesses of the hard palate associated with inflammatory processes in the area of the apexes of the palatal roots of molars are observed relatively less frequently.
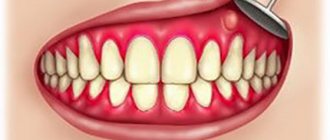
Clinic. With abscesses of the hard palate, pus accumulates in the depths (under the periosteum). On the corresponding half of the hard palate, the mucous membrane appears swollen and hyperemic (Fig. 124).
Sometimes swelling and redness spread to the soft palate. There are pains, both spontaneous and when touching the swelling even with the tongue, difficulty eating, temperature within 38°, but more often subfebrile. Due to the absence of loose tissue in the anterior part of the hard palate, fluctuation is usually determined only after 2-3 days from the beginning of the process. A protracted course of an abscess of the hard palate, exfoliating soft tissue from the bone, can result in necrosis of the bone area (cortical osteomyelitis) within the location of the abscess.
Essentially, in cases of abscess of the hard palate, one most often has to deal with either purulent periostitis or osteomyelitis of the palatine process of the upper jaw.
When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to keep in mind ulcers on the palatal surface of the alveolar process of the upper jaw, caused by the presence of deep bone-gingival pockets due to periodontal disease, ulcers in the middle of the hard palate, formed as a result of osteomyelitis of the nasal septum, as well as a suppurating cyst of the lateral incisor, which caused melting of the bone walls of the hard palate.
Treatment. Surgical treatment of a hard palate abscess involves an early incision down to the bone. The incision is made along the palate, sparing the palatine and incisive arteries (parallel to the alveolar edge). For successful treatment, it is necessary to keep the edges of the incision gaping by introducing gauze turundas into the wound. Otherwise, when the edges stick together, the outflow of pus is disrupted, which leads to a protracted course of the process (Fig. 125).
If conservative treatment of the tooth is ineffective, a root apex resection operation is performed; in extreme cases, the tooth is removed.
The sublingual space is located between the inferolateral surface of the tongue and the body of the mandible on both sides. Only abscesses of such areas of this area as the maxillo-lingual groove and sublingual ridges have “their own” clinic. In other cases, clinical manifestations associated with inflammation of the sublingual space are observed mainly with phlegmon affecting the floor of the mouth.
Limited abscesses of the sublingual space as a result of infection of certain parts of the area (for example, when injured by a fish bone, etc.) do not differ in features (abscesses caused by salivary stones).
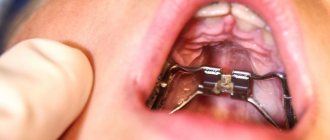
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment of wounds on the palate is impossible without a preliminary examination. First, the patient visits the dentist. He examines the oral mucosa, collects complaints and medical history. After this he prescribes:
- microscopic examination of an oral smear;
- culture for candidiasis with determination of resistance to antifungal drugs.
On this topic
- Sores
All about ulcers under the tongue
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- August 1, 2020
If another mechanism for the occurrence of ulcers on the palate that is not associated with dental diseases is suspected, the patient is referred to an appropriate specialist. In such cases, additional examination is carried out. It includes:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- X-ray, CT or MRI of the head;
- biopsy (if necessary).
Regardless of the cause of sores in the mouth, it is important to immediately begin taking therapeutic measures after diagnosis. The earlier treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of a quick recovery and the lower the risk of developing complications of the disease.
Ulcers on the roof of the mouth, causes and treatment
The oral mucosa is capable of quickly regenerating, since it is lined with several layers of epithelium, which is constantly renewed.
In addition, it is resistant to irritants of various origins and infections. However, small ulcers often occur on the lining of the mouth, particularly the roof of the mouth, causing discomfort and pain.
Ulcers on the roof of the mouth appear due to:
- Eating crackers, nuts, fish. Products with sharp edges can scratch the epithelium, leading to the formation of ulcers.
- Chemical and thermal burns of the palate (hot food and drinks, careless handling of acids).
- In children, the mucous membrane can be damaged due to improper and rough oral hygiene.
Ulcers as a symptom of the following diseases:
- candidiasis;
- herpes;
- tuberculosis;
- stomatitis;
- syphilis;
- scarlet fever;
- endocrine disorders.
Ulcers, or in scientific terms aphthae, cause a lot of inconvenience, so they cannot be asymptomatic and a person will immediately understand that the mucous membrane of the palate is not in order:
- Due to the appearance of ulcers, the mucosal tissues swell, and this can make speech difficult.
- It is impossible to eat hot, spicy, sour and salty foods, as they will irritate the damaged surface of the palate.
- A person, even with his mouth closed at rest, may experience pain, and in advanced cases, the ulcers bleed.
Not all canker sores are harmless. Of course, if they were formed due to mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, they will go away on their own in the shortest possible time.
If the ulcers do not go away, you need to track the accompanying symptoms in time to begin treating systemic diseases:
- When the herpes virus enters the oral mucosa , a person’s condition generally worsens, body temperature may rise, lymph nodes enlarge, salivation increases, and then small wounds form on the palate.
- Often, with a decrease in immunity or long-term use of antibiotics, it is possible to develop a disease such as candidiasis or thrush of the oral mucosa. In this case, a burning sensation is felt, taste sensations are lost, and a characteristic white coating of a cheesy appearance forms on the entire mucous membrane; eventually, aphthae can form on the palate, which sometimes bleed.
- When infected with syphilis at the beginning in the oral cavity , a rash may occur, which then develops into ulcers on the soft tissue of the palate and cheeks.
- Aphthous stomatitis. A chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa and the appearance of ulcers on the palate. Besides. such stomatitis can be a symptom of generalized aphthosis, a disease that affects all mucous tissues in humans (gastrointestinal tract, genitals, eyes). Ulcers form gray-yellow in size from 2 to 10 mm, depending on the course and stage of the disease. They are quite deep, painful, do not heal for a long time and often recur.
- With pulmonary tuberculosis , initially small compactions in the form of reddened tubercles may form on the palate, which then transform into shallow round wounds.
Diagnostics
If aphthae occurs on the roof of your mouth, you should contact your dentist.
The doctor will examine the oral mucosa and may ask the following clarifying questions:
- How long ago did the ulcers appear?
- How painful are they?
- Do they bleed?
- Does the patient smoke or not?
- What are the common chronic diseases, and what diseases were recently suffered?
- Do any of your relatives have similar ulcers?
Your doctor may order a blood test and, in extreme cases, a biopsy. If the dentist believes that aphthae appeared as a result of some disease that is not within his competence, he will refer you to the appropriate specialist. Otherwise, he prescribes treatment himself.
If wounds on the palate appear as a result of mechanical damage, then no special measures should be taken.
The only thing is to eliminate the cause of their formation, that is, avoid foods with sharp edges, brush your teeth more carefully, take a break from eating sour, salty and hot foods. The epithelial tissues will renew themselves, and the palate will return to normal.
You can rinse your mouth with a collection of medicinal herbs such as chamomile, sage, calendula.
Treatment of aphthae caused by some diseases of the body must be carried out in three directions:
- Eliminating the cause of ulcers.
- Local treatment of ulcers, their permanent treatment.
- Relieving pain.
To eliminate the causes, you must first increase your overall immunity. The doctor may prescribe general health-improving medications and vitamin-mineral complexes.
To eliminate swelling, antihistamines are prescribed at the discretion of the specialist. If the wounds cause severe discomfort, painkillers containing paracetamol or ibuprofen are used. In case of acute pain, before contacting a specialist, it is possible to use lidocaine in a spray.
If the cause of aphthae on the palate is a disease such as candidiasis, the doctor will prescribe antifungal drugs, for example, Diflucan or Flucostat.
If the cause lies in herpes, antiviral drugs are used, for example, Zovirax or Acyclovir.
Ulcers caused by bacterial infections require more serious treatment with antibiotics of various groups.
Aphthae that appear against the background of tuberculosis, syphilis and other infections are treated with appropriate anti-tuberculosis, anti-syphilitic and antiviral drugs.
For local treatment of ulcers, doctors usually prescribe rinsing with antiseptic solutions (for example, chlorhexidine solution or miramistin). Rinsing with pharmaceutical herbs has also proven to work well. Levomekol can be used as an ointment.
Read also: Chronic osteomyelitis of the lower jaw
Folk remedies for the treatment of ulcers on the palate
For rinsing, you can use thyme herb, brewed in boiling water, waiting until it cools to room temperature.
There are many traditional medicines that can relieve pain from wounds on the palate or help relieve inflammation:
- Dilute 1 teaspoon of salt and 1 teaspoon of soda in a glass of boiled warm water. Rinse your mouth with this solution 3 times a day.
- Dilute 2 teaspoons of calendula tincture in a glass of boiled water, rinse 2 times a day.
- Use freshly squeezed carrot juice diluted with water for rinsing 3-4 times a day.
- Grate raw potatoes on a fine grater and use the resulting pulp as a lotion for canker sores.
- Many people find that smearing ulcers with honey helps.
- One of the folk recipes suggests using the following option: you need to mix half a glass of milk with 1 egg yolk and a spoonful of honey. Mix the mixture well until smooth, then wrap your finger in a clean sterile cloth or bandage, dip it in the mixture and wipe the wounds. It is enough to wipe 3-4 times a day for 3 days.
It should be remembered that you should not get too carried away with folk remedies. With their help, you can relieve symptoms, relieve minor inflammation, or help the mucous membrane regenerate faster. The search for and treatment of the main cause of ulcers on the palate should be carried out by a specialist.
Prevention
What to do and what not to do:
- It is necessary to strictly observe oral hygiene.
- Visit the dentist 2 times a year.
- It is advisable to minimize sour, spicy, salty foods in your diet, and try not to eat too hot food, which can burn the mucous membrane of the palate.
- It is necessary to determine whether there are any allergies to any food products, because they can cause ulcers to appear on the palate.
- It is recommended to take vitamin complexes, and also monitor the level of iron, zinc and folic acid in the body, because their lack provokes aphthae.
- Doctors also recommend strengthening the immune system and avoiding emotional stress.
If you follow preventive measures and start treatment at an early stage, you can avoid such troubles as ulcers on the palate.