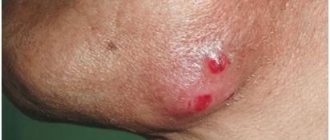
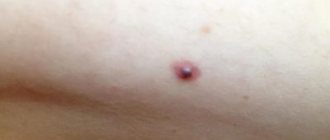
Lump on the lower jaw on the chin
Most often, swelling will be associated with inflammation of the lymph nodes. There are a lot of them in the neck area, and therefore in the chin area, and they always react to any inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and nasopharynx. Lymphocytes accumulate here, which actively fight infection or other pathogens, and the lymph nodes are the result of their accumulation. Here, lymphocytes are produced and sent by the immune system to the site of inflammation. If pathogens penetrate the lymph node itself, it too begins to become inflamed, called lymphadenitis, defined as a lump under the skin. This lump can form literally overnight: in the evening before bed there was nothing yet, but in the morning the lump has already appeared. To the touch it is quite dense, painful, mobile, and rolls under the skin. In this case, there may be a deterioration in health in the form of malaise, low-grade fever, pain in the lump.
If symptoms do not go away within 2-3 days, this may indicate a purulent process. When lymphadenitis becomes chronic, the bumps remain enlarged, but do not hurt. But this does not mean that the node cannot become inflamed and infected again, and then a pain syndrome immediately forms. Lymphadenitis never occurs on its own, it is always the end result of advanced inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs, and below the jaw or on the chin on the right or left it most often occurs with caries. But it must be remembered that lymphadenitis can be the starting point for cancer, so examination and diagnosis by a doctor are necessary.
Lymphadenitis can have an acute and chronic course. If there is no treatment for purulent lymphadenitis, it may result in sepsis.
Lymphadenitis is far from the only reason for the appearance of bumps. A lipoma can also form under the chin on the jaw - elastic, soft, mobile. It is usually asymptomatic, and only when it grows can it compress the nerve endings and then pain appears. And another reason for the appearance of a lump on the lower jaw - on the right or left, or in the middle of the chin - is the formation of an inflamed follicle, which goes through the stage of an internal pimple (like a painful lump under the skin) before appearing on the skin. Banal folliculitis occurs as a result of blockage of the sebaceous gland and is the most common. Stomatitis, herpes, atheroma, lipoma, skin cyst, folliculitis can appear in the form of bumps. A subcutaneous ball may appear as a result of facial trauma. In these cases, the formation has clear boundaries and is solid. In the area of the chin on the lower jaw, bumps also often appear due to boils and acne, especially when they become infected.
What diseases may be indicated by the appearance of a lump under the jaw?
» Problems with the jaws
The appearance of a lump under the jaw on the right, left or near the ear can greatly alarm a person. But this does not mean that you have suffered a dangerous disease. To figure out what it is, you need to see a doctor, he will clarify the diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment specifically for your case.
Such formations can be of very different etiologies and require consultation with several specialists. From a common pimple and clogged sebaceous glands to tumors (benign or malignant) - a bump can indicate anything. Therefore, it is worth getting examined in a timely manner.
Under the chin
Sometimes they are located on the chin closer to the teeth or lower, in the neck area. There are many reasons for such formations. The most common are the following:
- A lump under the jaw on the right or left indicates inflammation of the lymph nodes, lymphadenitis. In this case, one or several hard balls are formed that roll under the skin. They are quite mobile, but painful. In addition, body temperature may rise, general condition may worsen, and other symptoms of the underlying disease may appear.
- If a lump under the jaw on the left or right does not go away for too long and the reasons for its appearance are not addressed in any way, it can become more dense and become a chronic form of formation. At the same time, the size increases, it becomes hard, and the pain goes away. The absence of clear symptoms does not indicate the safety of the process and the end of inflammation. Even such a tumor needs to be checked and understand where it came from. Any diseases of the ENT organs, teeth, throat or lymph nodes will lead to increased discomfort.
- In the most advanced cases, such a formation develops into a malignant tumor. Then the general symptoms and condition of the patient worsens significantly. In this case, purulent processes and the formation of fistulas may begin, which indicate severe infection of the tissues.
- Lipoma is quite soft and elastic to the touch, mobile. When large volumes are reached, it compresses the nerve endings and manifests itself as painful sensations.
- An inflamed follicle, that is, an internal pimple that forms under the skin for a long time. It's quite painful. This happens as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands. This is the most common cause of a lump on the neck under the jaw.
- The same formations sometimes manifest themselves in other diseases - herpes, stomatitis, atheroma, skin cyst, dermatological problems, etc.
- Another cause of a formation on the chin can be a common injury. Then an internal hematoma will immediately form in the affected area. It will be hard and dense to the touch, have clear boundaries and be quite painful.
In the ear area
A lump appears near the ear in a variety of places. It can be localized under it, behind the ear, or closer to the chin and jaw. Such formations are quite rare and account for no more than 0.2% of all other facial defects. Their consistency, structure and reasons can also be very different.
- The same lymphadenitis, which changes its location depending on the affected area and the accumulation of infection. And although it is not considered a life-threatening disease, it is still necessary to eliminate the source of inflammation as early as possible. It can become acute or chronic, become purulent, and, in the absence of proper treatment, end in sepsis.
- Similar to previous formations, lipoma can also affect the ear area. This is a benign tumor, popularly called a “wen.” It is more of a cosmetic problem than a serious disease.
- Hormonal imbalances, low immunity, hypothermia and even excessive sweating are all common companions of parotid lumps.
- Their appearance is also caused by various general infections, which carry pathogenic bacteria through the bloodstream to various parts of the body.
- As a result of otitis media and other ear diseases, a lump may appear immediately behind or under the ear.
To distinguish a specific pathology, the doctor must examine the patient and prescribe certain tests. For example, inflammation of the lymph nodes is characterized by rapid rapid growth. And the atheroma increases in volume very slowly, gradually, reaching 5 cm. Secretions of the sebaceous gland accumulate inside it and become denser. It looks like a capsule filled with fat, with clear outlines, and a black dot is noticeable in the center, which indicates a blockage of the gland.
An infectious disease such as mumps (mumps) also leads to tumors behind the ears. In this case, the salivary glands located next to the ears become inflamed and significantly increase in volume.
In addition to swelling in the jaw, the patient’s temperature rises, chills, weakness, and pain in the affected areas occur.
It must be remembered that this disease requires not only medical intervention, but also isolation of the patient, since the infection is highly contagious.
The difference between a malignant tumor is that the skin around it is slightly darker. And the tumor itself is most often motionless and seems to be fused with the surrounding tissues. When palpated, high density and pain are noted. And most of the benign cones are elastic, soft and quite mobile, as if they were rolling under the skin.
Lymphoma is manifested not only by the presence of tumors, often several at once, fused together, but also by mild swelling of the post-auricular area. And although even with pressure there is no painful sensation, over time a person begins to feel general fatigue, depression, decreased tone, and weight drops sharply.
All this indicates a rather serious pathology, a malignant formation, which should not be ignored.
On the jaw under a tooth
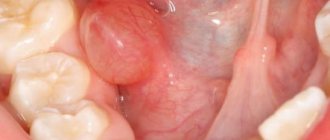
Also, similar bumps appear closer to the dentition - above or below. Sometimes this formation is on the cheek under the skin in the jaw area, and in other cases it is completely located on the mucous membrane, in the mouth. Then you need to contact a dentist who can determine the main reason for their appearance:
- internal fistulas - looks like a red lump with a diameter of about 5 mm, in the middle there is pus, which is secreted along the edge by a white dot;
- a consequence of periodontitis - which can also manifest itself in the form of a purulent formation, but does not cause pain;
- periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum, which in a neglected state ends with the appearance of an abscess that breaks into the gum and releases pus;
- cyst - a pathological formation, dense to the touch, painless, but provokes constant bad breath;
- benign tumors of the jaw system;
- as a result of the eruption of baby or permanent teeth, which is normal, but requires examination and consultation with a doctor;
- even untreated caries can lead to the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria in the form of a lump on the mucous membrane, closer to the root of the tooth;
- as in all previous cases, this problem can arise as a result of injury to the tooth or jaw.
Whatever the reason, it must be eliminated. Most often, such purulent formations are caused by either local or general infections, as well as a sharp decrease in immunity. And even if you have a harmless tumor that does not show pain or other symptoms, it is advisable to consult a specialist to prevent it from developing into something more dangerous to health or life.
These bumps, which are the result of clogged sebaceous glands or are painful pimples, may go away on their own over time and leave no trace. Still, you should not hope that the tumor will resolve on its own. The sooner it is diagnosed, the easier it is to remove.
Doctors list the following dangerous symptoms, in which you should immediately contact a medical facility:
- a sharp increase in the size of the cone;
- its large size;
- there is sensitivity and pain in the affected area;
- the formation appeared for no apparent reason, there was no known viral or infectious disease;
- the skin on the tumor changes color and darkens;
- there is a noticeable accumulation of pus inside;
- there are other signs of general malaise - fever, headache or ear pain, etc.
: lymph nodes in the neck are inflamed.
Diagnosis and treatment
So that the doctor can accurately determine what exactly the formation is associated with and what its origin is, you need to undergo an examination using X-rays and ultrasound. Based on these indicators, the specialist will accurately diagnose and distinguish one disease from another.
Among the treatment methods, a variety of manipulations can be used, everything will depend on the specific pathology. Thus, for inflammatory processes and infections, specific drugs are prescribed that can eliminate the main focus of the disease. When a cyst, atheroma or benign tumors forms, a minor operation is usually performed to remove it.
If a malignancy is suspected, an additional biopsy and histological examination are performed. If cancer is still detected, the oncologist will deal with the treatment process.
In cases of dermatological problems, acne formation, blockage of the sebaceous glands and frequent recurrences of boils, the doctor prescribes special treatment to prevent further similar conditions.
If the cause is diseases of the ENT organs or dental pathologies, they should be treated by a dentist as early as possible. After all, an infection from a diseased tooth or ear quickly spreads to other organs and leads to additional diseases.
If there are purulent formations in the oral cavity, you can perform antiseptic rinses with special solutions along with general treatment. But you shouldn’t decide on their choice on your own. Any folk recipes or pharmaceutical products are used only after consulting a specialist.
It is highly recommended not to do the following before consulting a doctor:
- heat the affected area;
- apply cold compresses;
- take any medications without prescription;
- squeeze out purulent or fatty formations;
- pierce the tumor and physically influence it in some other way.
All this can lead to an increase in unpleasant symptoms or a complication of the underlying disease, the spread of infection to other areas.
Loading …
Dental reference book
Tooth structure
Source: https://infozuby.ru/shishka-pod-chelyustyu.html
Diagnosis of the disease
An oncologist will help diagnose the disease by examining the patient and using cancer detection methods:
- Otoscopy. Inspection using magnification of damaged areas of the mucous membrane and ear canal. Helps to identify the locality and extent of the lesion.
- X-ray. An image of the skull will determine the degree of development of the disease and the depth of the tumors.
- Biopsy. Study of biomaterial to determine the type of tumor. Histology studies the obtained material for malignant formations.
- MRI. Detects cancer in the early stages, reflects affected areas and metastases.
- Blood analysis. The determining factor will be the rate and sedimentation of erythrocytes. It is increasing. At the same time, the hemoglobin level drops.
Swelling of the ear
If there is swelling near the ear with swelling spreading to the auricle, there is a high probability of perichondritis. When diagnosing, you should pay attention to the following characteristics of this disease:
- discomfort when touching the ear,
- swelling and swelling, spreading to all areas except the lobe,
- pain in the ear, followed by possible discharge of pus.
Perichondritis is a general name for diseases associated with damage to the perichondrium, inflammation of the cartilage of the middle ear. Pathogens: Pseudomonas aeruginosa (more often), streptococcus, staphylococcus. The infection can penetrate both from the outside through the skin with impaired integrity (primary), and from the inside, through the bloodstream, moving from infected organs (secondary).
With two different forms of the disease - serous and purulent - the symptoms have their own specifics.
- For serous form:
- glossy shine of the shiny surface of the auricle,
- first increasing and then decreasing swelling, turning into a painful compaction,
- local increase in skin temperature.
- For purulent form:
- swelling is uneven and lumpy, spreading to the area of the shell where there is cartilage tissue,
- as the process develops, the redness acquires a bluish tint,
- localized pain upon palpation transforms into diffuse pain, moving to the temples, back of the head and neck,
- Body temperature rises to 38 0C.
With the help of diaphanoscopy (transparency of tissue), perichondritis is first distinguished from other diseases with similar manifestations in the early stages (for example, erysipelas). Then, when the diagnosis is confirmed, they proceed to systemic treatment with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Moreover, depending on the pathogen, the selection of funds will vary.
For example, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is suppressed by tetracycline, erythromycin, oxytetracycline, streptomycin, polymyxin, etc., since it is insensitive to penicillin.
For the serous form, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out, which are contraindicated for the purulent form. In the first case, conservative treatment is often sufficient, in the second, drug treatment is possible only in the early stages, and in the next stages surgical intervention is indicated.
Lumps behind the ears
The outer ear consists of a large number of sebaceous glands and adipose tissue. Lumps near the ear can be a manifestation of atheroma, lipoma, fibroma and papilloma. These benign lesions near the ear make up only 0.2% of all other facial lesions. The bumps can be different in structure and consistency: soft and hard, painful or not noticeable. Most often they lead to an aesthetic defect. But even if they are small and unnoticeable, you should definitely consult a doctor to find out their nature.
A lump behind the ear is often a consequence of the same lymphadenitis. It is round in shape, painless, dense and mobile. Does not pose a health hazard. With lymphadenitis, the lump can also be localized under the ear. It may happen that all the symptoms subside on their own and disappear after 1–2 weeks, the lump becomes motionless and dense. This indicates the proliferation of connective tissue. Lymphadenitis can have an acute and chronic course. If there is no treatment for purulent lymphadenitis, it may result in sepsis. In case of lymphadenitis, it is necessary to treat the cause of inflammation - a disease of the ENT organs.
In addition to lymphadenitis, a lump behind the ear can be the result of a blockage or infection of the sebaceous gland, which are present in large quantities here. In addition, the reasons may lie in the following:
- hormonal imbalance and decreased immunity;
- increased sweating;
- a consequence of seborrhea or acne;
- hypothermia of the body;
- lack of hygiene;
- lipoma;
- atheroma;
- chronic infections - TBC, diabetes, HIV infection, infectious mononucleosis;
- injuries;
- mumps;
- otitis and dental diseases;
- oncopathology of the lymphatic system.
For diagnosis, the doctor will definitely perform an ultrasound, which will provide complete information about the condition of the lymph nodes.
If it is atheroma (blockage of the sebaceous gland), it appears and grows slowly, over several months, when it does not show itself in any way. Sometimes fat may come out of it, but it is better not to squeeze it out yourself to avoid infection. Its dimensions can be from 5 mm to 5 cm; in this case, the sebaceous gland ceases to function and turns into a seal. Atheroma is a sebaceous gland, stretched due to blockage of its excretory duct, a cystic formation. Its contents are thickened sebum. It can be located behind the ear or under the ear. Blockage always provokes the formation of a cyst. Its outlines are clear, it is filled with fat, and has a capsule. The skin above it does not fold; upon careful examination, a black dot is visible - a clogged duct, this is its difference from a lipoma. When its size is more than 5 mm, it begins to itch and burn. But if it becomes infected (and this often happens), the temperature rises, it turns red, hurts when touched, itching and burning behind the ear, and swelling appear.
Fluctuation can be determined by palpation. Treatment is surgical in the form of removal of the atheroma with the capsule. Atheroma can also be removed with a laser. With good immunity, the lump can open on its own, then all its contents come out: blood, fat, pus. After healing, small scars remain.
Epidemic parotitis, or “mumps,” is an infectious inflammation of the parotid salivary glands. In this case, a rise in temperature, chills, malaise, weakness, pain in the tumor, neck and ears are noted. The disease is contagious and requires isolation of the patient. Treatment is required. The infection can occur in children and adults, in whom it is more severe and has complications.
Why does my jaw crunch? Read more >>>
Lipoma, or wen, is a benign tumor that does not cause concern. It looks like a tumor behind or under the ear. It is a cosmetic problem, especially if it is large in size.
This proliferation of adipose tissue is a consequence of lipid metabolism disorders, slagging in the body and hereditary predisposition. Discomfort appears only when it is large. In these cases, it is excised. If a lump appears behind the ear and it hurts, this may be a consequence of existing otitis media, eustacheitis and inflammation of the postauricular lymph node.
Clinical manifestations
Lymphadenitis is an inflammatory reaction following the destruction of the structure of the node, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Swelling and swelling around the ear. The visible manifestation of edema is an increase in the size of the node and the appearance of a lump near the auricle. In addition, dysfunction of the lymphatic system can cause lymph retention, which leads to puffiness.
- Pain. It occurs as a result of compression of nerve receptors in the skin and tendons by swelling. The sensitivity of the receptors increases due to the influence of biologically active substances released during cell destruction. During this period, the pain may be pulsating and bursting. Then sensitivity decreases and is felt only when pressing on the node or when palpating the site of inflammation.
- Hyperemia. Visually detected by redness of the skin over the enlarged node, which is associated with dilation of blood vessels and stagnation of blood.
- Local increase in temperature. Increased blood flow and activation of the cellular process leads to an increase in the temperature of the integument in the affected area.
Depending on how exactly the disease develops, different clinical manifestations are observed, both acute and chronic.
- Chronic productive type. The “bump” grows slowly and almost imperceptibly over several months (2-3). The process may either accelerate or slow down, but the swelling does not subside completely. The appearance of the skin remains unchanged, and the tissue is not fused to the underlying tissue. The lymph node is mobile and when pressed it causes little or no pain.
- Chronic abscess type. The next stage in the development of the disease. A limited cavity filled with pus appears in the thickness of the lymph node. The lump thickens, becomes painful and begins to fuse with the underlying tissues, which reduces its mobility. The general condition of the patient against the background of intoxication also worsens.
- Acute serous-purulent type. The inflamed soft, elastic lymph node increases to one and a half to two centimeters, which is almost not accompanied by painful sensations and does not affect the condition of the skin (slight redness may occur). Both the “ball” itself and the skin are not welded to the underlying tissues and are mobile.
- Acute purulent type. Associated with an abscess (filling of an organic area with pus). Soreness ranges from moderate to severe. The skin over the formation turns red, and the soft tissue around it swells. The “bump” itself gradually loses its mobility, fusing with the underlying tissues. At the same time, the patient’s general well-being practically does not change.
- Acute adenophlegmon. A form of the disease that occurs when pus leaks from the capsule into the surrounding areas. Accompanied by intense throbbing pain of a diffuse nature. The general condition also worsens (fever, weakness, aches, lack of appetite).
Symptoms of this pathology
When a lump appears in the earlobes, a person may notice several symptoms that indicate various pathologies. The tumor may be soft or hard. In some cases, the ball can be movable, that is, during certain manipulations with the fingers, it moves a little (if it is a lipoma or a wen).
Usually the lump in the earlobe hurts. Painful sensations can intensify when they touch the affected area of the hearing organ. The skin temperature may rise in the area where the ball is located. Such a symptom means that the process of inflammation has begun. If the ball hurts, the lump in the earlobe needs urgent treatment.
Effective medical assistance
Seeking help from a doctor if you have a lump on your head near your ear is the best decision. First of all, he finds the starting point and finds out whether the patient has any diseases, since the formation of a lump can be affected by:
- infection getting under the skin. Most often this happens due to an unprofessional puncture of the earlobe or ear cartilage from behind;
- development of a chronic disease, such as diabetes, etc.;
- increased production of sebaceous glands;
- weakened immune system;
- increased sweating.
Lump on jaw near ear
Lymphoma is always a malignant tumor. It may appear as a painless swelling behind the ear. When palpated, it is defined as a group of lymph nodes that are fused to each other and to the skin and are motionless. Attention is not paid to such formation due to its painlessness. But if a person experiences weight loss over a short period of time, loses interest in life, and doesn’t want anything, they should consult a doctor urgently. This is especially dangerous in children. With oncology, in addition to bumps, there are other changes: thickened gums, loose teeth, neuralgic pain. In such cases, in addition to ultrasound, a biopsy of the formation is required, followed by histology.
Tumors on the lower jaw occur 3 times less frequently than on the upper jaw, and more often they form in men whose age category is from 40 to 60 years.
If any lump appears, you should never squeeze it out or heat it, as this can increase inflammation or accelerate the process of malignancy. You cannot lubricate the lump with iodine, rub it, pull it, or expose it to the sun's rays. Folk remedies are also not applicable without a doctor's permission.
An urgent visit to a doctor if a lump appears behind the ear is necessary if:
- lymph nodes enlarge strongly and quickly;
- the lump grows quickly;
- the appearance of the lump is not associated with a cold or other infection;
- the lump begins to change its color and pus appears in it;
- the seal is very sensitive and painful;
- In addition to the lump, some new symptoms appeared.
Treatment methods
Each disease has its own treatment method. To diagnose a type of lump, it is necessary to undergo tests, and in rare cases, to take a biopsy of the growth to determine whether it is oncological in nature and prone to malignant neoplasms. Having determined the type of your pathology, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis, and then offer treatment. The most used techniques are listed below, and the doctor can choose alternative methods to eliminate swelling behind the ear.
Surgical treatment of a lump is:
- Atheroma . It is treated with surgery, the operation takes 15 minutes. This is an exclusively cosmetic procedure, because the defect causes inconvenience only due to its size and appearance.
- Lipoma . Lipoma symptoms indicate surgery. After consultation with an oncologist, who will confirm the benignity of the tumor, removal surgery is performed. The intervention lasts 30 minutes under local anesthesia.
- Fibroma . Like atheroma, it is removed surgically due to its external unattractiveness.
Drug treatment:
- Lymphadenitis . The doctor prescribes medication. This is a complex of painkillers, antibiotics and anti-edema tablets. As a last resort, surgery is performed to remove the swollen lymph node.
- Infection . The disease is treated with a strict diet and bed rest for two weeks. Antipyretic, anti-inflammatory drugs and vitamins are prescribed.
- Mastoiditis . A course of antibiotics is prescribed, and the infected area is first opened.
Treatment of lymphadenitis
Treatment of lymphadenitis begins with identifying and eliminating the source of infection, which involves anti-inflammatory and antibiotic therapy using broad-spectrum antibiotics (sulfonamides, cephalosporins).
However, if after the procedures the condition and size of the “bump” have not changed, the doctor’s attention should be drawn to this fact.
Treatment is accompanied by the use of drugs that:
- reduce acute and chronic inflammation (antihistamines),
- harmonize the immune response (immunomodulators),
- activate immune cells (vitamin complexes, in particular those containing vitamin C).
In parallel with this, for acute serous and chronic forms, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out, including:
- electrophoresis that prevents tissue fusion using proteolytic enzymes,
- helium-neon laser irradiation,
- exposure to ultra-high electromagnetic waves.
Purulent forms of the disease are treated surgically by opening the capsule, removing pus from it and antiseptic rinsing. When suturing, drainage is left to drain exudate and pus.