What are the lymph nodes on the face for and where are they located?
Lymph nodes (L/N) are located along the lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes of the face and neck are necessary to remove metabolic products, toxins, and create a barrier to infection.
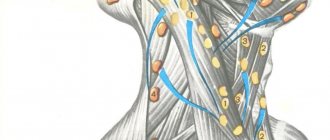
In the facial area, several main groups of lymph nodes (glands) can be distinguished:
- superficial and deep parotid (in the projection of the parotid salivary glands on both sides);
- directly facial (buccal and mandibular lymph nodes, as well as a small number of innominate ones);
- submental (between the bellies of the digastric muscle);
- submandibular.
Strictly speaking, the last two groups of nodes (submental and submandibular) are located not on the face itself, but in the neck and under the chin. But they are also closely related to the lymph glands of the face, so they are also worth adding to this list. Lymph from all the lymph glands of the face flows through the lymphatic vessels into the cervical lymph nodes.
The location of the lymph nodes on the face depends on the degree of development of the facial muscles and subcutaneous tissue; genetic factors also play a role. Below is a schematic representation of the facial lymph system against the background of facial muscles and large blood vessels. Facial lymph nodes can be located in the thickness of the cheek, in the cheekbone area. Closer to the angle of the lower jaw are the mandibular nodes.
Causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes of the face
Lymphadenitis of the maxillofacial region is rarely an independent disease.
The causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes in this area can be:
- infectious diseases (colds, herpes infection, measles, purulent tonsillitis, mononucleosis, etc.);
- decreased immune response;
- various tumors and oncological diseases (including leukemia);
- hypothermia;
- traumatic injury to this area of the face;
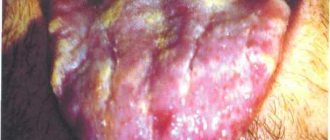
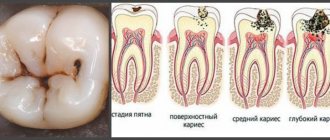
- diseases of teeth and gums (periodontal disease, gingivitis, caries);
- introduction of pathogenic microbes from the outside (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci, streptococci) from purulent-inflammatory foci on the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the facial area;
- allergic reactions.
Lymphadenitis of the facial node
Inflammation of the lymph nodes on the cheek often occurs against the background of acne, or acne. This disease is caused by special propionobacteria. In the development of the inflammatory process, the state of the immune system and hormonal system are of no small importance.
Lymphadenitis of the parotid and postauricular nodes
Inflammation of the lymph node near the ear near the cheek occurs with mumps (inflammation of the salivary parotid gland). The causes of lymphadenitis of the pre-auricular lymph nodes can be otitis media, mastoiditis (inflammation of the mastoid process) and some other inflammatory processes in this area.
Enlarged nodes in the lower part of the face
If inflammation affects the mental lymph nodes, it can be assumed that the cause of the disease is caries, periodontal disease and other diseases of the oral cavity. This also applies to the mandibular nodes.
Traditional methods
Treatment of parotid lymph nodes with folk remedies is not entirely competent. They are unable to relieve inflammation from the inside and normalize the outflow of lymph. Their use is sometimes appropriate as an additional means of treatment, but not as a primary one.
Folk remedies can be recommended by your doctor. These could be some compresses made from mint, dandelion juice, or wasteland. But without the use of special antibacterial therapy, the disease will not go away.
The use of exclusively folk remedies to eliminate inflammation of the lymph nodes is appropriate if it has not progressed to an acute stage. Enlarged nodes disappear within a short time if you use:
- chicory compress;
- infusion of oregano;
- infusion of St. John's wort;
- lime tea;
- walnut leaves;
- garlic;
- onion;
- beet juice.
You should be selective and extremely careful in choosing a treatment. It should be as safe as possible and not cause discomfort or side effects. Individual intolerance to certain substances should also be taken into account, which must be taken care of in advance.
What to do if a child’s lymph nodes are inflamed, watch our video:
Lymphadenitis of the facial area: symptoms
Inflammation of the lymph nodes on the face is manifested by redness and swelling of the skin in the corresponding area. The affected node enlarges significantly and can be very painful; when pressing on it, the pain intensifies. If the node undergoes purulent melting, it may break through to the surface of the cheek or other area. With a pronounced inflammatory process, the temperature often rises, the patient is bothered by weakness and headache.
Important: enlarged lymph nodes on the cheeks, cheekbones, chin and other facial areas are dangerous for the development of severe complications including meningitis, encephalitis (inflammation of the meninges and brain) and sepsis (blood poisoning).
Therefore, in case of any purulent processes in this localization, you should immediately contact a surgeon.
Types of lymphadenitis
The classification of lymphadenitis takes into account the nature of the course, the form of inflammation and other factors. Thus, lymphadenitis can be acute or chronic.
According to the causative factor, they distinguish:
- specific lymphadenitis (against the background of syphilitic infection, HIV infection, tuberculosis);
- nonspecific lymphadenitis (caused by staphylococci, streptococci and other common microbes, toxins).
Taking into account the nature of the exudate, there are purulent and non-purulent inflammations of the lymph nodes on the face. A photo of purulent lymphadenitis is presented below.
Diagnostics
Since damage to the lymph glands in most cases is only a manifestation of the underlying disease, for successful treatment it is necessary to determine the cause. For diagnostic purposes, the doctor examines the patient, palpates the inflamed nodes and lymphatic vessels.
Depending on the location of the inflammatory process, the specialist carefully examines the oral cavity and the area of the salivary glands. To make it easier for the doctor to find out the cause of the pathology, you need to tell in detail about the symptoms and past illnesses, existing diseases.
It should be borne in mind that other diseases can occur under the guise of lymph inflammation. For example, inflammation near the ear occurs with mumps, inflammation of the cheekbone - with atheromas, deep acne and subcutaneous abscesses.
Reason to visit the doctor
A person needs medical attention if they have symptoms that indicate inflammation and tenderness of the parotid lymph nodes.
It is not recommended to wait until the inflammation goes away on its own. If the pathological process is not suppressed, the disease will progress. As a result, the patient will experience complications that will significantly worsen his overall health.
If you suspect inflammation of the formations of the lymphatic system, you need to go to the hospital. With such problems, it is customary to go to an appointment with a therapist or infectious disease specialist.
Enlarged lymph nodes: causes
The main reason for contacting a specialist is an enlarged parotid lymph node. By itself, this education cannot become larger. Before starting therapy, it is necessary to find out the reasons that could lead to inflammation. A competent specialist will help you cope with this task.
The parotid lymph node becomes inflamed due to the influence of the following unfavorable factors on the human body:
- Inflammatory process in the tissues of the salivary glands.
- Acute bacterial infection.
- Staphylococcal or streptococcal infection.
- Long-term course of allergies.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Psoriasis.
- Dermatitis.
- Fungal infection.
- Inflammatory processes in the upper part of the respiratory tract.
- HIV infection.
- Diseases of the oral cavity.
- Tuberculosis.
- Oncological lesions.
- Ear inflammation.
If the lymph node located in front of the ear is inflamed, it means the person is sick. This disease can even be caused by damage to the skin, which is located as close as possible to the formations of the lymphatic system.
A slight change in the lymph node in the parotid zone on one side may indicate its active work. This applies to cases where there are no other symptoms of the lesion.
An enlarged node indicates parotid lymphadenitis. The disease requires adequate treatment under the supervision of a qualified physician.
Pain
Severe pain in the parotid lymph nodes is the main signal indicating an inflammatory process in the body
Inflammatory processes that affect the lymph node in the parotid zone are usually accompanied by pain. This symptom is one of the first to appear. Pain does not allow a person to ignore the ailment, so he is forced to see a doctor.
Pain syndrome is caused by the same factors that lead to enlarged lymph nodes.
Associated symptoms
If the parotid formations of the lymphatic system are inflamed, then only enlargement and pain will not do.
At the very beginning of the development of lymphadenitis, the patient does not show pronounced symptoms of the disease. A person may feel only slight pain at the site of the lesion. Most often it is detected behind the ear areas at the time of palpation.
If the disease is non-purulent in nature, then its symptoms will be limited to slight pain, enlargement of the nodes and their mobility when pressed.
The pathology, which is characterized by a purulent course, is accompanied by aggravated symptoms. It can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- Pulsating pain.
- Weakness.
- Increased local and general body temperature.
- Increased size of the lymph node.
- Pain when moving the jaw.
- Limited inflamed formation.
- Headache.
Having identified the symptoms of malaise that characterize lymphadenitis of the parotid region, you need to immediately seek medical help. The patient should be recommended a course of therapy that will relieve him of pain and other manifestations of the pathological process.
Treatment
If the lymph nodes near the ear, face or chin become inflamed, you should definitely consult a doctor. Treatment of lymphadenitis of the facial area is usually carried out by a maxillofacial surgeon.
Therapy includes the following components:
- etiological treatment (impact on the cause of the disease);
- symptomatically (reduce symptoms of lymphadenitis);
- general strengthening of the body.
Etiotropic therapy
To eliminate inflammation in the lymph nodes of the face, it is necessary to first act on the root cause. When the disease is infectious, antibiotics with a wide spectrum of action are used.
If the enlargement of lymphatic vessels and nodes is associated with measles, herpes, mumps or mononucleosis, antiviral agents are used. Allergic diseases are treated with antihistamines or glucocorticosteroids (only in cases of severe allergization).
In case of mental lymphadenitis, which develops against the background of caries and periodontal disease, sanitation of diseased teeth is carried out. To treat inflamed gums, rinsing with medicinal decoctions and antiseptic solutions is prescribed.
Symptomatic treatment
For inflammation of the lymph nodes on the face and near the ears, symptomatic treatment includes the use of:
- anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and painkillers (mainly non-steroidal analgesics - Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, etc.);
- detoxification drugs.
Detoxification may be required in case of a pronounced reaction of the body, which is most often associated with an underlying disease.
The use of symptomatic remedies allows you to normalize body temperature, relieve pain and swelling in the area of lymphadenopathy. Sometimes, with the help of symptomatic therapy, it is possible to reduce the symptoms of the underlying disease, which led to the inflammatory reaction of the lymph nodes on the face.
General strengthening agents
Lymphadenopathies not only of the facial area, but also of various parts of the body are almost always associated with a weakened immune system. Therefore, immunomodulators, vitamin complexes, minerals and general tonics are often included in the treatment of the disease.
Surgical methods
With severe inflammatory damage to the lymph nodes on the face, sometimes they resort to surgical opening of the purulent focus. This is necessary to prevent complications. The operation is performed under local anesthesia with subsequent observation.
Causes
Banal hypothermia can cause inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes. Incorrectly selected clothing and ignoring hats in cold weather can easily provoke a cold, and then parotid lymphadenitis.
A negative reaction, unfortunately, is caused not only by cold weather and weak immunity. The following reasons can provoke the development of such an unpleasant problem:
- acute bacterial reaction;
- infection with streptococci and staphylococci;
- inflammation of the salivary gland;
- conjunctivitis;
- adenovirus;
- dermatitis;
- psoriasis;
- long-term allergic reaction;
- complication after an infectious disease.
Lymph nodes absolutely always react to all sorts of changes in the body, which can in one way or another affect the normal functioning of its functions. There is no need to panic too much if there is a slight enlargement of one lymph node.
Normally, the size of the node should not exceed 5 millimeters. It should also be easily palpable and not painful.
How much does a lymph node enlarge?