Good day, dear readers of our dental blog. We regularly publish articles and reviews for you on important topics. Today's material is devoted to a new problem. Some people may suddenly find that their gum is moving away from their tooth. Let's try to figure out why this happens, how dangerous it is and how to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
When the gum moves away from the tooth, the neck is exposed. This is a very unpleasant moment. Firstly, the neck is not protected by a dense layer of enamel. Therefore it reacts to hot and cold. Secondly, food debris gets trapped in a gap called a periodontal pocket. This leads to negative consequences, including suppuration.
Why does the gum move away from the tooth?
List of causes of gum peeling that require prompt medical attention
Not many people think that a beautiful smile and healthy teeth depend on the health of the gums. The thing is that the gums perform important functions - they hold the teeth in the correct vertical position, and also saturate them with nutrients and minerals through connective fibers. Usually, if any problems arise with the gums, they do not pay attention to them, thinking that everything will go away on its own. Meanwhile, various gum pathologies are fraught with many dangers.
For example, if you suddenly notice that the gum is moving away from the tooth, you need to visit the dentist as soon as possible. Why? Below in the article is useful information about the possible complications of this unpleasant phenomenon, the causes of its occurrence and methods of treatment.
Description of the problem
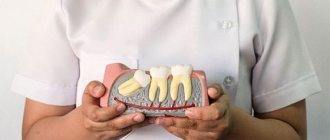
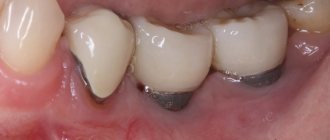
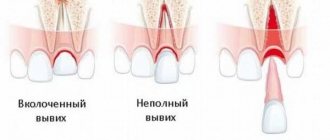
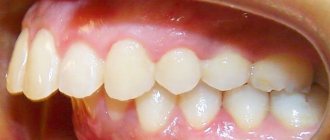
The receding of the gum from the tooth is called “recession” in dentistry. Recession can be localized (the gum has receded between one or two teeth or from the front tooth) or generalized (the lower or upper gum has receded from all teeth, i.e. the pathology extends to the entire row or even to both jaws at the same time). The problem is often associated with abrasion, peeling of the gum margin and exposure of part of the tooth, its root. This leads to the formation of periodontal pockets and receding gums.
The tooth becomes vulnerable to various pathogens, which easily penetrate into the resulting pockets and cause various dental diseases. If the pathological process is not stopped in time, as a result of the destruction of periodontal tissue, as well as the ligaments around the tooth root, the patient may lose one, several or even all teeth.
In the first stages of development, recession makes itself felt by increased sensitivity of teeth affected by pathology. Also, upon visual inspection, it is clear that these teeth look longer than the rest. The presence of these signs is already a reason for an immediate visit to the dentist.
Causes of scratches on the gums
Periodontal tissues and hard parts of the periosteum are reliably covered with a mucous membrane - soft gums. This is a large area in the mouth responsible for blood supply and nutrition to the roots of the teeth. It is penetrated by tiny capillaries and nerve endings, so damage is always painful and unpleasant. Based on their condition, the doctor visually determines the health of the entire mouth and identifies possible foci of inflammation and disorders.
Even a small scratch on the gum is a reason to visit the dentist. After all, on the tongue and the inner surface of the cheeks there is always an active microflora, consisting of hundreds of species of bacteria, fungi and spores. Some of them are classified as opportunistic. This means that when they penetrate soft tissue, they can disrupt the processes inside the periosteum and lead to periodontal infection.
Often, a scratch on the gum appears due to poor hygiene or due to other trivial reasons:
- Using a toothbrush that is too hard. Sharp villi, when pressed, can rub and injure the delicate mucous membrane, which leads to irritation and microscopic damage.
- Chewing foreign objects. This may include toothpicks and matches, pen caps or pencil tips. If you move carelessly, it is easy to scratch your gums and create a painful wound. Often the problem occurs in children who unknowingly pull various surrounding objects, tools and toys with sharp edges into their mouths.
- Violations of technology when filling or removing teeth. A dentist in a hurry can touch the soft periodontal tissue with a needle or drill, or accidentally catch them when installing a prosthesis. The patient does not notice the unpleasant moment, because his jaw is anesthetized with potent drugs.
- Damage to the mucous membrane when chewing too hard food: candies and grilled sweets, crackers, seeds.
Read also: What to do if your gums are inflamed
In most cases, such a wound on the gum hurts only a few minutes after application, and the unpleasant discomfort gradually subsides. Under favorable conditions, it quickly becomes covered with a layer of healthy epithelium and disappears without a trace after a few days.
Causes of recession
Recession is not an independent disease. A bare neck of a tooth indicates inflammation of the periodontal tissues – periodontitis or periodontal disease, which in an advanced state in 90% of cases is the reason why the gums move away from the tooth1. These diseases lead to a reduction in the volume of gum tissue and disruption of its metabolic processes.
Helpful information! Periodontal disease is associated with a general disorder of metabolic processes in the body. But periodontitis is caused by infections that have penetrated into the periodontal tissues, which are responsible for holding the tooth in the socket. However, periodontitis is the most common disease. It often occurs in children around 10 years of age. The disease affects unformed tissues that react sharply to the slightest irritants, and causes the gums to recede from a child’s tooth. In some cases, periodontitis develops during pregnancy because... A woman’s body uses nutrients to form a fetus.
Teeth may also become exposed for the following reasons:
- poor hygiene procedures, which leads to the formation of plaque and tartar, which can result in the development of gingivitis, which helps reduce the volume of gingival tissue,
- regular injury to the gums with a hard brush, rough movements when brushing, incorrectly selected dentures or crowns,
- incorrect bite: for example, with an open and deep bite, blood circulation is disrupted, because of this, gum tissue decreases. Recession often occurs against the background of crooked teeth and their crowding,
- unbalanced diet: with a predominance of soft foods, due to the lack of active chewing, the blood flow of the gums weakens, salivation slows down, food deposits form in the oral cavity,
- hormonal changes during puberty, in women during menopause, pregnancy, which make the mucous membrane more sensitive and vulnerable,
- the process of natural aging of the body, as a result of which the epithelium atrophies, gingival tissues lose tone,
- bad habits: for example, the problem of smokers is brown plaque, which subsequently negatively affects the health of the gums.
In addition to local causes, the occurrence of a recession can be influenced by serious chronic human diseases: weak immunity, diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the cardiovascular system of capillary circulation, vitamin deficiency and others. All of them are associated with changes in metabolic processes, which disrupts cell nutrition.
What factors provoke the problem?
The situation when the gum is detached from the tooth can arise due to a number of reasons. Dentists divide them into two large, conditional groups - general or local. The first of these are associated with the development of certain diseases in humans that significantly affect changes in important processes occurring in the human body:
- Metabolic disease.
- Changes in hormone balance.
- Decreased immune defense (local).
- Poor circulation (begins with a decrease in blood circulation in the capillaries).
Such processes are characterized by general symptoms - increased susceptibility of tissues (mucous, soft), including those located in the oral cavity, to microbial, bacterial effects, development and progression of inflammation, and their cellular nutrition deteriorates.
But in most patients, changes associated with the gums occur due to local effects on soft tissues; they are provoked by:
- poor-quality cleaning of the oral cavity, incorrect or irregular implementation of the procedure (it all starts with pain in the gums when brushing teeth);
- formation of plaque, then tartar;
- lack of professionalism of the doctor when dental fillings or prosthetics are performed incorrectly;
- exposure of gums to chemicals, high temperatures (hot food), injury;
- incorrect structure of the jaw, when some areas of it may rub due to increased mechanical pressure;
- lack of solid food in the diet;
- decorating the tongue with piercings, since such an accessory can injure the tissues of the oral cavity;
- smoking.
Symptoms of the pathological process
Symptoms depend on the degree of development of the pathology. Initially, the patient notices minor gum bleeding and feels almost no pain. As the recession progresses, its signs intensify. The most characteristic symptoms are:
- receding and mobile gums,
- the appearance of pockets between the gum and tooth,
- redness, swelling, itching of the gums and their soreness, aggravated by eating, brushing,
- visually the crowns appear longer, the gaps between them at the bases become very noticeable,
- purulent taste in the mouth and bad breath,
- hypersensitivity of teeth and their mobility.
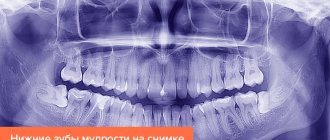
The most pronounced symptoms are when the gums move away from the wisdom tooth. Recession of wise teeth (as wisdom teeth or numbers of eight are called) is accompanied by severe pain, inflammation, swelling and hyperemia of the surrounding soft tissues. There may be an increase in temperature and a slight enlargement of the lymph nodes.
How to strengthen your gums
Oral hygiene
Cleaning is needed at least twice a day. The procedure should last at least three minutes. After each meal you should rinse your mouth with water.
The spaces between your teeth should be cleaned with special floss every time after eating. Do not neglect mouth rinses.
Rules for using dental floss
Diet
To keep your gums healthy and strong, it is advisable to include the following in your daily diet:
- foods rich in vitamin C (lemons, oranges, kiwi, pineapples, strawberries, onions, etc.);
- fermented milk products (calcium is useful not only for dentin, but also for gums);
- solid vegetables (chewing apples and carrots is an excellent massage for the gums);
- nuts (prevent the appearance of tartar).
Have you noticed the listed symptoms of exposed teeth? Sign up for a consultation at one of the clinics below.
How is diagnostics carried out?
Everyone knows that a correct diagnosis is a guarantee of effective treatment and recovery. Therefore, if the gum moves away from the tooth and hurts, you should not hesitate to visit the dentist. In order to understand what the problem is, the doctor uses differential and instrumental methods. A differential approach involves finding out the real cause of the pathology by excluding other possible ones. The specialist examines the oral cavity and collects anamnesis.
The instrumental approach is the use of diagnostic methods such as radiography and computed tomography, which make it possible to see pathological changes that are not visible to the naked eye. These are the most popular and accurate diagnostic methods. To get ahead of the form and stage of the disease, the doctor can use an orthopantomogram - a panoramic image of the entire jaw. It will show how deeply the gums have sunk and whether there is destruction of bone tissue.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor prescribes individual treatment and also gives general recommendations for combating the disease.
What to do if the gum has moved away from the tooth
Why does part of the periodontal tissue recede? If the gums have separated from the teeth, you need to visit a doctor or clinic.
Timely diagnosis is important for proper treatment. It includes an examination of the oral cavity by a dentist, an x-ray showing the expansion of cracks and scales, and a periodontogram.
In advanced cases, when the gums have corroded, surgical techniques are used - open or closed curettage, gum flap technique. The procedure is carried out under anesthesia, during which tartar, deposits, pus are removed, and the oral cavity is treated with antiseptics.
If the gums have eroded, it is necessary to determine the cause of the condition. For tartar, cleaning with ultrasound or special instruments is used. If the disease is caused by gingivitis, periodontal disease or periodontitis, concomitant treatment is prescribed.
Depending on the cause, the following may be prescribed:
- glucocorticoids;
- antibacterial and antiseptic agents;
- drugs for the correction of immunity, diseases of the endocrine and hematopoietic systems.
If the gums have receded from the teeth and are worried about their loosening, teeth splinting and bone tissue restoration are used.
Special attention and qualified assistance are required in cases where a piece of a child’s gum has fallen off and is hanging, or the condition worries a pregnant woman, when part of the periodontal tissue comes away from several teeth.
Treatment
Treatment methods are selected depending on the stage of the disease, its cause, and the individual characteristics of the patient. The dentist removes deposits if dentures, veneers or crowns are installed incorrectly - this also needs to be corrected.
Gum tissues are treated with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs. In advanced cases, antibiotics are used (Doxycycline, Lincomycin, Ciprofloxacin with Tinidazole).
Antiseptics in the form of a solution are used after each meal to remove microorganisms and food debris, and the microflora is restored. The most common:
- aqueous Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin;
- Stomatophyte;
- herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula, sage, St. John's wort).
Solutions of sea salt or soda can be used for rinsing.
During treatment, it is important to brush your teeth properly. The dentist will recommend products for caring for the mucous membrane - soft toothbrushes, rinses, pastes, threads to remove food debris.
An additional measure for effective treatment is taking vitamin and mineral complexes based on vitamin C.
Use of gels, ointments and balms
To heal wounds, reduce pain, eliminate swelling and redness of the gums, gels, ointments and balms based on antiseptics are used.
Twice a day, the gums are lubricated with medicinal gels:
- Metrogil Denta or Metrodent;
- Holisal;
- Kamistad;
- Asepta.
To do this, use sterile cotton swabs or napkins.
For bleeding and inflammation of the gums, use mouth rinses after each meal - Forest Balm, Asepta, Rox, Colgate, Listerine, President.
Methods of treating the pathological process
As with any other disease, the earlier treatment begins, the more effective it will be. Therefore, the logical answer to the question “what to do?” – is to see a doctor. Treatment of the pathological process occurs as follows:
- At the preparatory stage, the doctor carries out the necessary diagnostics. In addition to the visual examination, X-rays are taken,
- The second step is the removal of plaque and stones. Initially, the dentist removes supragingival deposits, then performs deep cleaning of the subgingival area. In advanced stages it may be necessary
- At the final stage, the doctor treats the crown and periodontal pockets with antiseptic agents. Dental gel is also applied to soft tissues, which reduces pain, redness, and swelling. Additionally, a course of antibiotics may be prescribed.
In addition, the dentist gives the patient individual recommendations for caring for the problem area because... due to improper hygiene procedures, poor brush paste, rinse aid, a relapse may occur. In some situations, they resort to surgical intervention - gum surgery, which allows for correction of the position of the mucous membrane.
Surgical intervention
Based on the general picture of the situation, the specialist may resort to surgical treatment. Thus, at an early stage of the pathological process, when the periodontal pocket does not exceed 5 mm, subgingival deposits and granulation changes in the gum are removed (closed curettage).
In advanced cases, you will have to make an incision in the gum, and then remove the mucous layer by layer; the doctor will also implant synthetic materials into the gum, and finally apply sutures. Sometimes a flap operation is used to eliminate foci of prolapse: an incision is made in the gingival margin, exfoliated tissue is removed, and a flap of tissue from another place in the oral mucosa is pulled in its place.
Important! Traditional methods of treatment involve rinsing with various medicinal decoctions from oak bark, chamomile, strawberry leaves, St. John's wort, and calendula. However, you should not self-medicate, because... Traditional medicine can only weaken the symptoms, but not eliminate the cause of the pathology.
The postoperative stage usually lasts several months and ends with complete healing of the damaged tissue.