Methods for treating gingivitis in adults
Treatment of acute and chronic gingivitis includes 3 components:
- Sanitation of the oral cavity
Removing tartar and bacterial plaque, eliminating carious cavities, removing decayed teeth. This will prevent further spread of the infection.
- Local anti-inflammatory therapy
Antiseptic rinses, applications of anti-inflammatory and wound-healing gels, use of natural toothpastes with herbal ingredients.
- General restorative therapy
Taking vitamin-mineral complexes and immunomodulators. This promotes the regeneration of soft tissues and increases the body's defenses to fight infection.
Causes of chronic gingivitis
The main reason for the development of chronic gingivitis is insufficient oral care, as a result of which facultative microflora accumulates in dental plaque. The risk of gum inflammation is especially increased in children due to lack of proper oral hygiene, as well as in the presence of the following diseases: rheumatism, tuberculosis, diabetes, liver pathologies, gall bladder, etc.
A sharp edge of a deformed tooth, a poor-quality filling with a hanging edge, orthodontic appliances, tartar or artificial crowns, irritating the gum tissue for a long time, can cause chronic gingivitis. Also, malocclusion, lack of antagonists, breathing through the mouth, crowded teeth, exposure of the gums to acids, alkalis, heavy metal salts, thermal burns, smoking, drug intoxication and other provoking factors can contribute to the development of this dental disease.
Against the background of existing endocrine changes (diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, menopause, puberty), when the body's resistance is significantly reduced, chronic gingivitis develops. In adolescence, hormonal imbalance contributes to the manifestation of hypertrophic chronic gingivitis.
It was revealed that pathologies of the digestive system, skin, allergic, systemic infectious diseases are a favorable environment for the development of chronic gingivitis.
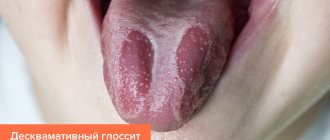
Means for the treatment of catarrhal gingivitis
The catarrhal form of the disease refers to the initial stage of inflammation. It can be easily eliminated with ultrasonic cleaning and drug therapy.
Physiotherapy is also useful, for example, hydromassage of the gums, exposure to short-spectrum UV rays, electrophoresis, etc. These are painless procedures that improve tissue trophism and remove accumulated toxins. The course of treatment includes 5-10 sessions.
Drug treatment
- Rinse with chlorhexidine;
- applying oil solutions with vitamins A and E;
- the use of antimicrobial ointments and sprays - Romazulan, Metrogyl Denta, Cholisal or others.
Chronic inflammation of the gums can develop as a result of dental deformations. In this case, you should definitely see an orthodontist to correct your bite.
Treatment options at home
Gum inflammation can be treated using different methods. In any case, in order not to harm your health and prevent the development of more serious diseases, before starting treatment, you must consult a dentist to determine the diagnosis.
In serious cases, the doctor will prescribe treatment, in combination with which additional home remedies will provide a good effect .
In simpler cases, it is enough to use at home products that provide anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, decongestant and analgesic effects.
When talking about ways to treat gums at home, a distinction is made between pharmaceutical (medicinal) and folk .
Pharmacy products
Pharmaceutical products include rinses, sprays, applications, toothpastes and gels. All pharmaceutical preparations are supplied with instructions for use, which must be followed and followed in order to obtain the desired result.
, safe and effective drugs based on healing natural remedies and medicinal plants .
For bleeding and inflammation of the gums, various pharmaceutical products are used that relieve inflammation, relieve pain, eliminate bleeding, itching and burning, relieve swelling and disinfect the mucous membrane from microorganisms and bacteria.
Antiseptic rinses include:
- Listerine (2 times a day for 30 seconds) is one of the most effective rinses.
- Stomatophyte (3-4 times a day for 10-15 days).
- Furacilin (2-3 times a day).
- Chlorhexidine (spray 0.2% for periodontal disease and 0.05% for childhood gingivitis - after each meal until recovery).
- Miramistin (3-4 times a day).
- Chlorophyllipt (3 times a day with a diluted solution).
- Rotokan (until inflammation is eliminated).
- Hydrogen peroxide (solution 1 tbsp in 100 ml of water 2 times a day).
- Malavit (10 drops/glass of water for rinsing 1 week daily).
- “Forest balm” (after each meal until symptoms disappear).
The effect of treatment with rinses can be enhanced by simultaneously using compresses and applications with medicinal pastes, gels and ointments.
Therapeutic gels and ointments form a protective film on the mucous membrane. They are applied to the gums several times a day, after rinsing. The most effective means:
- Periodontocyte including mint, clove, sage and oregano (series of rinse or spray, toothpaste and gel).
- Gengigel with hyaluronic acid for tissue regeneration. Tissue healing occurs twice as fast, inflammation decreases, and tissue blood supply improves.
- Stomatofit A - as a pain reliever with long-term therapeutic effects.
- Cholisal is an instant-action gel for rubbing into the gums 2-3 times a day for 5-7 days, lasting for several hours.
- Asepta is a balm with propolis that provides tissue restoration and eliminates bleeding.
- Metrogyl denta - paste (apply 2 times a day, after cleaning the mouth).
- Solcoseryl - gel or ointment (applied 2-3 times a day) for rapid restoration of the mucous membrane and anesthesia.
- Dental (apply by massaging 3-4 times a day). Relieves pain and heals.
Special toothpastes have also proven effective in treating and preventing bleeding and inflammation of the gums. They contain extracts of medicinal herbs and anti-inflammatory ingredients. For gum inflammation, it is recommended to use toothpastes:
- "Parodontax";
- “Lakalut” (the series also includes rinsing);
- "The president";
- "Mexidol dent phyto";
- Toothpastes with tea tree oil.
It is not recommended to use medicated toothpastes for longer than one month, after which you should take a break.
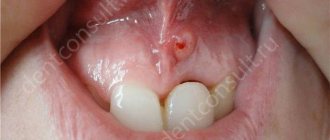
Drugs for the treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis
The cause of the hypertrophic form of inflammation often lies in hormonal imbalances, as well as diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, do not be surprised if your dentist refers you to a specialist in the appropriate field - an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist.
And to relieve local symptoms, the following therapy is used:
- applying dressings with antimicrobial ointments;
- taking oral antibiotics - Erythromycin, Amoxicillin, Metronidazole;
- darsonval, electrophoresis and other methods of physiotherapy;
- at an advanced stage - injections of hypertrophic solutions into the gingival papillae - calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, glucose.
In the most severe cases, surgical excision of damaged gum tissue is used.
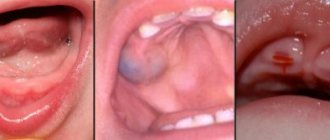
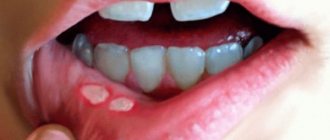
Treatment methods for atrophic and ulcerative gingivitis
Atrophic and ulcerative forms of the disease are accompanied by necrosis (destruction) of the marginal gum. At this stage, it is important to save living periodontal tissue, since atrophied areas can no longer be restored.
As a rule, dentists prescribe:
- local anesthesia with a solution of novocaine or lidocaine;
- systemic antibiotic therapy;
- oral baths with antiseptics (furacilin, miramistin, chlorhexidine).
Dead gum tissue is removed mechanically or treated with Trispin. This is an enzyme that promotes the resorption of necrotic epithelium.
Antibiotic therapy
Most often, adult patients with purulent inflammation of the gums, gingivitis, are prescribed metronidazole. It is effective against protozoa and various anaerobic bacteria. It is taken three times a day, the daily dose of the drug is 1500 mg. The course lasts 10 days.
In dental practice, metronidazole is necessarily prescribed in combination with lincosamides. This group of drugs includes lincomycin and clindamycin.
Lincomycin
Fights infections caused by gram-positive cocci and anaerobic bacteria (daily dose – 1500 mg, divided into three doses of two capsules).
Clindamycin
It differs from lincomycin in its effectiveness against protozoa, taken 300 mg three times a day.
Lincomycin in capsules often causes side effects - gastrointestinal disorders, allergic rash. It is better to replace lincomycin capsules with a 30% solution for intramuscular injection (2 ml twice a day) or give preference to clindamycin. The latter, by the way, can also be taken in the form of intramuscular injections - 2 ml (300 mg) twice a day.
For patients with diabetes mellitus and/or resistance to other antibiotics, drugs based on norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin or ofloxacin are prescribed. For example:
- nomitin – 400 mg twice a day;
- tarivid – 500 mg in two doses;
- Siflox – 250 mg twice a day.
Antibiotic therapy is prescribed only by a doctor; it is prohibited to take antimicrobial drugs on your own!
Injecting antibiotics into the gums is an outdated and ineffective method that only further injures the soft tissue. Antimicrobial drugs are prescribed only orally (by mouth) or intramuscularly (injections into the gluteal or deltoid muscles, the front surface of the thigh).
How to use rinses correctly?
Rinsing removes food debris from the mouth, disinfects the cavity, and soothes sore gums. Most often they are prescribed:
- to relieve acute symptoms of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis - procedures increase blood flow, which helps remove toxins and tissue decay products from the diseased tooth;
- as a preventive measure after tooth extraction - no earlier than on the 3rd day;
- as an auxiliary therapy for gum inflammation, infectious and purulent processes - periodontitis, cyst, granuloma, gumboil.
Rinsing for toothache is only an auxiliary method.
To make the procedure as effective as possible, follow the following recommendations :
- before rinsing, remove food debris from the interdental areas with floss, clean the teeth and surface of the tongue from plaque;
- the temperature of the solution should be from 36°C to 45°C - cold or hot liquids will increase inflammation and burn the mucous membrane;
- during manipulation, attention is paid to the affected area, it is rinsed most intensively;
- rinsing must be done after meals and at night;
- the optimal frequency of manipulations is once every 1 – 2 hours;
- You need to rinse the aching tooth for at least 10 – 15 minutes;
- It is not advisable to eat or drink for half an hour after the procedure.
The rinse solution should be warm.
Rinse your teeth as follows. Approximately one sip of liquid is taken into the mouth. The inflamed area is intensively irrigated for 20–30 seconds, then spat. Repeat several times.
Important! You should not heat the sore spot. Heat accelerates the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and accelerates the development of inflammation.
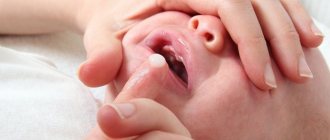
Treatment of gingivitis in children
Therapy for children is not very different from treatment for adults, but there are a number of features. The course of events includes:
- Ultrasonic teeth cleaning
The procedure lasts on average 20 minutes and is painless.
- Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy
Applying gels such as Cholisal (for children of any age) and Metrogyl Denta (from 6 years) to the mucous membrane. Mouth rinse with Chlorhexidine or Miramistin.
- Strengthening the immune system
Vitamin therapy will help speed up recovery. Oil solutions with vitamins A and E have a positive effect on the regeneration of gingival tissue.
- Orthodontic treatment
For young patients who have chronic gingivitis due to malocclusion.
Brushing teeth to prevent gingivitis in children
If a child has been diagnosed with necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, after the first stage of treatment, doctors remove dead soft tissue under local anesthesia and cauterize the gums with an electric current. Before and after the procedure, pain-relieving gels with lidocaine are used - Kalgel, Bobodent, Kamistad.
Of great importance in the treatment of gingivitis is teaching children oral hygiene. After all, without proper dental care, inflammation will appear again.
It is also worth mentioning that children without teeth and infants are treated differently for gum inflammation. It is enough to massage the gums and clean them from germs with a special silicone brush that is placed on your finger.
Characteristic symptoms
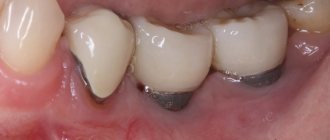
The gums are covered with soft tissue that slowly adapts to the hard material of artificial teeth. At the initial stages of using removable dentures, inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes are almost always present. They are accompanied by pain, which intensifies when chewing. These are the main signs of pathology.
In the absence of timely assistance, the following symptoms may additionally appear:
- Discomfort when talking.
- Unpleasant sensations while eating.
- A constant burning sensation is felt at the point of contact of the product with the gums.
- Due to the displacement of the denture, gum pockets form underneath it.
In most cases, you can get rid of these symptoms by adjusting the product from a specialist. However, the patient will have to walk without artificial teeth for some time to give the mucous membranes time to regenerate.
The video below clearly shows the causes of calluses on the gums from a removable denture and ways to avoid it:
Another characteristic symptom of gum inflammation is its swelling. The tissue that has increased in size comes into contact with the prosthesis over a larger area and, accordingly, is more injured. Because of this, the pathological process worsens. The following unpleasant symptoms may occur:
- Putrid odor from the mouth.
- Metallic taste in the mouth due to constant bleeding gums.
- Ulcers and bedsores form on the mucous membranes.
- There is a local increase in temperature.
- Severe inflammation can cause fatigue.
Incorrectly fitted crowns can affect not only the gums, but also the tongue. For example, removable dentures of the lower jaw often rub it and it can become inflamed. First, redness appears, accompanied by unpleasant sensations, and then an ulcer may appear.
Treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women
The so-called “gingivitis of pregnant women” develops against the background of hormonal surges, as well as a deficiency of vitamins and microelements in the body of the expectant mother. Therefore, patients are necessarily prescribed vitamin therapy.
During pregnancy, taking antibiotics is contraindicated, but in any case, the dentist should remove dental plaque and recommend safe antiseptics. Vacuum massage of the gums is also indicated.
You can rinse your mouth with a chamomile decoction at room temperature, this will help relieve bleeding and swelling of the mucous membrane. All oral medications should be used only after consultation with a gynecologist.
To protect your gums from mechanical damage, it is recommended to use toothbrushes with soft bristles, and also avoid eating too hard foods.
What should you not rinse your mouth with?
In an effort to quickly get rid of unpleasant sensations, patients resort to methods that are not always effective and dangerous. If you have a toothache, you should not rinse your mouth:
- Gasoline or kerosene. They are ineffective and can significantly damage the gums, esophagus, and stomach walls.
- Manganese solution . The beneficial effect has not been confirmed; it often leads to burns of the mucous membrane.
- Alcohol. Some home recipes and ready-made preparations are made based on it. The action is justified by the antiseptic properties of ethanol. However, it must be used with caution, as it can burn the gums. The solution is always diluted with water; it is not recommended for use by children under 12 years of age, pregnant or lactating women.
Use traditional medicine recipes with caution, it is better not to risk your health and consult a doctor.
Mouth rinses and baths are indicated for inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. This is a helper method. It is not able to completely relieve pain and get rid of the problem. However, it reduces the activity of pathogenic microorganisms and promotes the outflow of pus and toxins. The most effective are solutions made from salt, soda, decoctions of chamomile, sage and pharmaceuticals.
Prices
The cost of dental treatment for gingivitis depends on the methods used and procedures performed. In all cases, therapy includes professional cleaning:
- 200 rubles for mechanical removal of plaque from one tooth;
- from 4,000 rubles for removing tartar using an ultrasonic scaler;
- from 4300 rubles for cleaning using the Air Flow method.
An additional fee will be charged for the treatment of periodontal pockets:
- 100-200 rubles for closed curettage of one pocket;
- from 2,000 rubles for open curettage in the area of one tooth and from 9,000 rubles for a quadrant (around 6-7 teeth).
After removing the stone, many patients experience pathological sensitivity of the teeth, so immediately after cleaning it is recommended to carry out fluoridation - saturation of the enamel with minerals. Coating one crown with fluoride varnish costs an average of 150 rubles.
If for complete rehabilitation it is necessary to cure a carious tooth, 3,500 rubles are added to the total price of therapy - the average price of a filling.
Air Flow device for the prevention of gingivitis