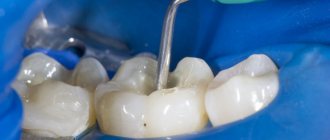
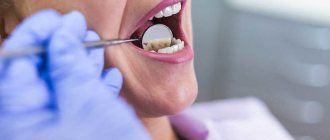
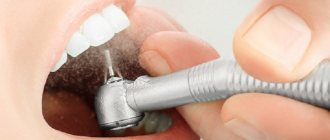
Why does a tooth hurt after root canal cleaning?
Pain after canal cleaning occurs in 98% of cases. The causes of negative sensations are the impact on soft tissues in the oral cavity and damage to the gums for medical purposes. Main reasons:
- Delayed visit to the doctor.
- Serious inflammatory processes in the oral cavity (after successful cleaning, the inflamed periodontium remains, which causes pain).
- Individual intolerance of the body. Itching adds to the pain, swelling of the gums and hyperemia appear. Additionally, there are symptoms of allergic rhinitis (reactions to medications or materials used).
- A splinter remains in the tooth; to get rid of the pain, the reading procedure is repeated.
- There was a poor-quality placement of the filling - sometimes during the process, perforation of the root occurs or the filling composition fills the space and extends to the top of the tooth.
The main manifestation of the problem is unpleasant, uncomfortable sensations when pressing on the gums. Pain occurs when a person bites into hard food.
The cause of toothache can be:
Thinning of tooth enamel as a result of its demineralization due to a lack of vitamins and microelements such as calcium, phosphorus and fluorine. In this case, toothache is aching in nature and occurs mainly during meals, especially sweets, or when drinking cold and hot drinks.
Scuffs, cracks and chips of teeth - all of them are of traumatic origin and are manifested by special sensitivity of the teeth to temperature changes and the chemical effects of food.
A wedge-shaped defect in the cervical area of a tooth can also cause pain that occurs due to mechanical, thermal and chemical irritation of the tooth.
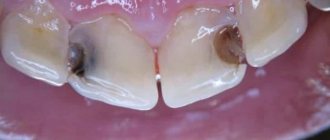
Caries. Superficial caries does not cause pain, but deep caries can cause anxiety. Carious pain is rarely severe, more often it is aching in nature, occurs mainly when food gets into the cavity formed in the tooth and disappears almost immediately after its cleansing.
Pulpitis is the result of deep caries and a consequence of the spread of the inflammatory process to the soft tissues of the tooth - the pulp. Pain with pulpitis occurs both when eating and regardless of it, for example, at night. It is twitching and so strong that it seems as if not just one tooth hurts, but the entire jaw or even half of the head.
Periodontitis is characterized by inflammation of the connective tissue that surrounds the roots of the tooth and holds the tooth in place. The pain with periodontitis is not severe, but progresses with load on the tooth and is accompanied by a feeling as if it has grown and become taller than the rest of the dentition.
The formation of an abscess, or purulent abscess, at the root of a tooth is initially accompanied by aching toothache, which intensifies when the jaws are closed. Then, as the abscess grows, the pain intensifies, becomes tugging, bursting, the gum swells, and soon a protrusion becomes noticeable on its surface - the abscess itself.
The causes of pain in the teeth can be very far from the oral cavity. For example, pain may radiate to the teeth and jaws during angina pectoris and myocardial infarction. The source of pain can be diseases of the ear, nose and throat, injuries of the cervical spine, pathology of the temporomandibular joint, nerve diseases and malignant tumors of the maxillofacial area.
Sometimes tooth pain is psychosomatic in nature, that is, it occurs as a result of severe stress and is not associated with any diseases.
Pain after dental treatment, which lasts up to three days, is a completely natural reaction of the tooth to medical manipulation. The occurrence of pain after tooth extraction is the result of natural trauma to the tissues surrounding it.
In what cases is this normal?
Pain is considered normal if it does not intensify and gradually decreases. Unpleasant sensations can persist for a long time – up to 1 month. If the pain intensifies or becomes sharp 2-4 days after the procedure, it is necessary to repeat the cleansing or have the dental canals filled.
A gradually decreasing intensity of pain is a normal reaction of the body to the intervention in the gum tissue. Rinsing will help eliminate discomfort in the area of the treated tooth. It should be based on decoctions of medicinal herbs such as chamomile or sage.
Important! Increasing negative feelings and ignoring the problem can lead to tooth extraction.
When it's not ok
Carrying out the procedure for cleaning dental canals requires high skill and professionalism from the dentist. If a mistake is made, the patient will experience discomfort, the pain will intensify, and an inflammatory process will develop.
It must be remembered that the canals are very small in size, it is difficult to examine them without the use of special equipment, therefore, in 80% of cases, an x-ray is prescribed before the procedure.
The pain should subside on the second day (but discomfort may persist longer - this is normal). Deviations are considered to be an increase in pain and its persistence for several days without a decrease in the intensity of sensations.
Their origin is closely related to a violation of the technology of cleaning the dental canal; the patient may also encounter deviations from the norm if an error was made during the placement of the filling. In addition, there are the following factors that influence the deterioration of the condition:
- Extension of the filling material beyond the root apex (refers to a filling error or to individual characteristics of the structure of the oral cavity).
- The dental canals are not cleaned (the procedure must be repeated).
- An instrument that broke off during the dentist’s work remained in the dental canal.
- Root perforation has occurred.
- An element of the tooth itself remains in the dental canal.
An allergic reaction that occurs as a result of contact with medical substances can negatively affect a person’s condition.
Attention! If the pain does not subside for a long time or intensifies, you should not engage in self-treatment, since inflammation can spread to nearby tissues in the oral cavity and cause the formation of pus.
How to eat if you can't eat?
Immediately after installing braces, you need to wait at least an hour. The glue that holds the structure in place must dry completely. During bite correction, food should be in liquid and pureed form. This will help the oral cavity get used to the foreign object faster.
Include the following products in your menu:
- porridge;
- puree;
- chopped meat (preferably chicken due to its softness);
- all kinds of yoghurts;
- cheese and cottage cheese;
- boneless fish;
- broths.
Baby food is great as a temporary alternative to solid fruit. Save the stringy meats, ice cream and hot tea for later.
You will need to brush your teeth often and very thoroughly , as food will constantly get stuck there, forming plaque. Take it with you to work, school, etc. you need to carry all the braces care products to avoid carious spots around the structure: brush, paste, rinse. Failure to follow the recommendations may damage the brace system or increase pain.
The use of tinctures, rinses and other medications should be discussed with your doctor in advance. Even the most harmless medications have contraindications. An example of this is chamomile infusion. It helps very well with irritation of the mucous membrane, provided that the patient is not allergic to it.
Once you remove your braces, the straightened teeth will tend to return to their original position. In some cases this causes discomfort. To consolidate the result, patients are highly recommended to install retainers . Not all patients decide to wear them, because... The period of their use sometimes exceeds the time of wearing braces.
But this problem can also be solved thanks to removable retainers - mouth guards. A non-removable plate or a transparent removable mouthguard will fix the teeth in the desired position and relieve discomfort.
Gums hurt after root canal cleaning
In some cases, after cleaning the dental canals, not only the intervention site hurts, but also the gums. The reasons for this process are as follows:
- Doctor's mistakes.
- Non-standard structure of the tooth or gum (deviation from the anatomical norm).
- A channel left without cleaning.
- Breakage of a dental instrument (it puts pressure on the tissue, which leads to pain, including in the gum area).
- There has been damage to the gum tissue (there is a slight swelling in the damaged area).
- There is a disease of the trigeminal nerve.
- The canals have not been completely cleaned or the dental debris has been removed.
If there is pain in the gum area, seek help from a dental surgeon.
First aid
If a tooth hurts, how to relieve the pain? If you experience any discomfort, you should contact your dentist.
If it is not possible to do this, but your tooth hurts, how can you relieve the pain at home? You can take a pain reliever. For example, this could be the drug Ketorol. But you should remember that it will relieve pain for a certain period of time. In the future, medical assistance should still be provided.
The temperature has risen
In some cases, after visiting a dental clinic, the patient’s body temperature rises to 37-38 degrees. After cleaning the canals, the body may react in a similar way, since there has been intervention in the tissue, as well as exposure to dental materials, which can be perceived by the immune system as foreign bodies.
Additional reasons that need to be taken into account in order to promptly seek professional medical help:
- The beginning of the inflammatory process.
- Attachment of a secondary infection.
- Injury to tissues inside the tooth, on the gums.
- Tooth canal cleaning was carried out during a cold.
The body can respond with an increase in temperature even if the patient has shown excessive emotionality before or during the procedure. A stressful situation for the body is expressed in these specific symptoms. The norm is a temperature no higher than 37.2 degrees, which lasts 1-2 days. All other cases are violations requiring medical supervision.
What can you do at home?
If toothache does not go away after the brushing process or causes serious discomfort, you should use medications or folk remedies to relieve symptoms. It is important to remember that any thermal effects on the area where dental intervention was performed are prohibited.
Drug therapy
To temporarily eliminate pain of varying severity, it is recommended to use some analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Tempalgin, Baralgin, Nurofen, as well as Ketorol or Analgin. Before use, you should carefully study the instructions for use of the drug.
In what cases is it necessary to contact specialists?
You will need to see a doctor in the following cases:
- Pain that persists for more than 2 days.
- Increasing pain.
- The appearance of inflammation.
- Allergic reactions.
Such negative symptoms indicate that microorganisms have entered the body, leading to inflammation or the appearance of pus.
Dentist actions
Technique for re-cleaning canals:
- X-ray.
- Visual inspection.
- Thorough rinsing of the oral cavity and the space of the dental canals with special dental compounds (antiseptics).
- Cleaning the canal walls (cutting instruments are used). This is necessary in order to remove inflamed and damaged tissue, and also not to disturb the anatomical shape of the canals.
Then repeated exposure to antiseptic drugs is performed. It will take some time to dry the dental canals. Finally, the filling is re-installed.
Thus, pain after cleaning the dental canals can be both a normal reaction of the body to interference in the tissue, and a signal that processes are occurring in the body that require medical control. The symptom cannot be ignored, as various complications can arise.
The nature of pain with pulpitis
Toothache with pulpitis depends on the stage of the disease. Dentists in their practice most often use the following classification:
The symptoms will depend on the form. In the acute form of pulpitis, there are 2 stages of the disease: focal and diffuse.
The chronic form is classified into the following stages:
In its acute form, the disease is characterized by the following clinical picture:
- The pain is paroxysmal, but very strong; the condition can only be alleviated by taking painkillers. They usually appear at night, but can also occur during the day.
- The nature of the pain is cutting, shooting, tearing.
- Provoking factors for pain syndrome are cold, hot and sweet. However, unlike caries, the pain does not go away immediately after removing the irritant.
- The pain lasts for 2-3 weeks, after which it becomes easier.
- The tooth cavity in acute forms of pulpitis is usually covered with softened dentinal tissue.
The focal and diffuse forms of pulpitis differ in that in the first case the causative tooth is easy to detect. In the diffuse form, pain spreads along the branches of the trigeminal nerve. This leads to the fact that the patient may not understand that it is the tooth that hurts.
Pain with chronic pulpitis is aching in nature. However, sometimes the disease is completely asymptomatic, bypassing the acute stage.
In the fibrotic form, if the disease is characterized by pain, it is provoked by hot and hard foods. The tooth cavity is usually opened, which leads to exposure of the neurovascular bundle. Pain syndrome complicates the cleaning process, so plaque and food debris can accumulate in the cavity, which leads to an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity.
Sometimes the disease is asymptomatic, and if the carious cavity is hidden, that is, located under the gum or in the interdental space, only a dentist can identify the disease during an examination.
The hypertrophic form of chronic pulpitis is rarely diagnosed and usually in children. Diagnosis is not difficult, since pulpitis is characterized by the growth of soft tissues in the resulting carious cavity. Such a tooth begins to ache when eating food, especially hard food, or during hygienic care of the oral cavity.
The clinical picture of the gangrenous form of the disease depends on whether the pulp chamber is opened or not. The picture is more pronounced when the cavity is closed. A painful attack can occur spontaneously. But more often its appearance is provoked by a hot irritant. The pain is aching, bursting in nature.
If the tooth cavity communicates with the external environment, then the picture of the disease becomes more blurred. In this case, only a dentist can make an accurate diagnosis after a thorough examination.
The general condition of pulpitis usually does not suffer. Body temperature appears rarely and does not exceed 38 °C. This usually occurs in children or in people with reduced immunity. Of all forms of the disease, an increase in body temperature is most often observed with chronic gangrenous pulpitis.
Features of dental canal treatment
Differences in the structure and functions of the “representatives” of the dentition largely determine the nature of the treatment approach. Treatment of canals for different groups of teeth has its own nuances.
Front tooth canal treatment
The front teeth most often have one canal. They are often curved and difficult to pass through for instruments. In order to preserve aesthetics, the opening of the cavity of these teeth is carried out from the vestibule of the oral cavity. Due to their frontal location, it is important to prevent tooth enamel from darkening, so filling materials containing dyes are not used.
Treatment of wisdom tooth canals
Wisdom teeth can have more than 5 canals; they often have a branched structure, which is not always revealed by x-ray examination. These factors, along with the marginal location of the “eights”, significantly complicate the high-quality treatment of root canals. At the final stage of treatment, various filling pastes are traditionally used.
Root canal treatment of temporary teeth
Endodontic treatment of tooth root canals is usually used only at the stage of root stabilization. When choosing the optimal treatment tactics, it is necessary to take into account the specific structure of temporary teeth. The small thickness of the canal walls, the insignificant degree of dentin mineralization and the relatively large size of the apical foramen are the main reasons for special caution during instrumentation. Zinc oxide eugenol and iodoform pastes, as well as materials based on calcium hydroxide, are usually used as filling agents. They are not toxic to the permanent tooth germ and are able to dissolve along with the temporary root.
What to do if pain occurs?
You can relieve or reduce toothache due to pulpitis by taking an anesthetic drug, preferably a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. However, such a move is not a treatment. Medicines can only relieve pain temporarily. Pulpitis can only be cured in a dentist’s office, so you must make an appointment.
The dentist will prescribe a number of tests:
- visual inspection;
- instrumental examination;
- X-ray diagnostics;
- electroodontodiagnostics.
Based on them, an accurate diagnosis will be made and the correct treatment will be prescribed. What medical treatment methods exist:
- treatment without damaging the inflamed pulp.
- treatment with removal of the inflamed neurovascular bundle.
The latter method involves partial or complete removal of the pulp. In any case, the treatment will not cause pain, since it is performed under anesthesia. This method is called vital. Treatment is carried out in one visit. Anesthesia may not be necessary if a non-vital method is chosen for treatment. It is characterized by the fact that a ball of devitalizing paste is placed on the exposed pulp horn, which mummifies the neurovascular bundle of the tooth.
Previously, arsenic paste was used for this purpose, but due to toxicity, dentists stopped using it. Currently, a paraformaldehyde-based product is used. It can be left in the tooth for 2 weeks. After which the tooth is prepared, instrumental and medicinal treatment of the canals is carried out and they are filled to their entire length under X-ray control.
Treatment without damaging the pulp is carried out using a biological method. To do this, a calcium-containing preparation, often ProRoot MTA, is placed on the exposed pulp horn to close the defect, and the cavity is filled with temporary filling material or glass ionomer cement. Treatment is carried out using a delayed method. Reviews from patients and clinical observations from doctors show the positive dynamics of this treatment.
Stages of tooth canal treatment
Endodontic treatment usually lasts several hours and includes a number of stages.
- Removal of the pulp (pulpectomy).
The inflamed soft tissue of the tooth is eliminated. - Root canal sanitation.
The procedure is a “cleaning” of bacteria and dead tissue elements. Pulpectomy and canal sanitation pursue one of the most important goals - eliminating existing inflammation. - Channel formation.
The root canal, freed from pathological contents, undergoes appropriate treatment. In addition to ensuring good passage of the canal, it is imperative to ensure that its apex reaches the apical part of the tooth. - Canal filling.
The last stage of the intervention is filling the root canal with filling material, followed by grinding.
Treatment of teeth with problematic root canals
Filling dental canals
A relatively simple technology for treating tooth canals is filling with a special paste with or without a pin. According to the “gold standard” of endodontics, the canals are also filled with a latex-like material - gutta-percha. Several methods of its use have been developed, including the Termafil system, lateral condensation, injection or liquid thermogutta-percha (vertical condensation). In some cases, in particular when treating a tooth canal cyst, filling is carried out with a substance based on calcium hydroxide (copper-calcium hydroxide “depopheresis” method). However, special nanocomposite materials are increasingly used in dentistry.
Treatment under a microscope
The age-old “tough nut to crack” for the dentist is curved or branched root canals of the teeth. A dental microscope, often in combination with a laser, allows you to completely pass through them and adequately process them along their entire length to reduce tissue trauma. Sometimes it becomes necessary to treat a sealed tooth canal with the evacuation of remaining material of various nature, for example, fragments of fillings, tissue fragments and even instruments. Then a microscope also comes to the rescue. Read more about the technology in a separate article.
If your tooth hurts after root canal treatment
If after root canal treatment your tooth hurts when you press it, this is normal. This phenomenon is associated with insufficient anesthesia in the area of endodontic intervention. Another reason why a tooth hurts after canal treatment is excessive treatment with the instrument moving beyond the apical foramen.
How long does a tooth hurt after root canal treatment? Sometimes pain persists for several days due to intensive intervention in the tissue structure in such a limited area. A similar situation occurs when an excess amount of filling material is placed into the canal, which causes discomfort when pressure is applied to the walls. As a result, the tooth “aches” after canal treatment. In any case, the presence of post-filling pain signals the need for a second visit to the dentist.
Useful video about pulpitis
They treated and treated, but it still hurts: the most common causes of post-filling toothache.
Pain in the teeth is an extremely unpleasant phenomenon that simply drives many people crazy.
There is an absolutely natural desire to get rid of pain as quickly as possible.
For this purpose, a person suffering from toothache goes to the dentist.
Often a completely reasonable question arises: “Can a tooth hurt after filling?” And if the answer is yes, then is this normal?
Possible complications
Not all cases go smoothly. Let's consider the main problems that arise after the procedure.
- Perforation.
The phenomenon is the formation of holes between the dental canals and surrounding tissues. Treatment of perforation consists of medicinal treatment and filling. - Cheek swelling.
The reason why the cheek is swollen after root canal treatment is believed to be the impregnation of the periodontal tissues and mucous membranes with an anesthetic drug, which themselves are quite loose and easily absorb liquid. - Instrument fracture.
The probes for passing through the channels are very thin. If they break during medical procedures, the fragments are removed with special devices. Modern dental instruments made of nickel-titanium alloys are less susceptible to wear and break less often. - Adverse reactions to medications.
The range and severity of side effects of modern anesthetics are minimal. Before treatment, the doctor must collect an allergic history - information about drug intolerance - and the likelihood of a full-blown allergic reaction is practically reduced to zero. Adverse reactions of moderate and minor degrees are mostly short-term, can be easily corrected or can be overcome by changing the drug. - Other complications.
Situations such as swallowing particles of fillings, tooth dust, and small instruments now practically do not occur thanks to the use of a rubber dam - a latex plate that separates the tooth or teeth being treated from the oral cavity.
When is tooth extraction necessary after root canal treatment?
It happens that you have to part with a treated tooth. Typically, such a sad outcome is due to the following factors:
- initially unsatisfactory root canal treatment with the development of poorly controlled inflammation;
- some cases of wisdom teeth treatment;
- the complexity of the anatomical structure of roots and canals in a particular patient;
- late request of the patient for specialized help, in which adequate therapeutic measures do not lead to the desired result.
Periodontitis. Open tooth. What to do next?
Moderator: Lesya
Periodontitis. Open tooth. What to do next?
Post by Nurgul » Wed Nov 02, 2011 23:06
I wanted to consult with you.
While on vacation in Istanbul, the 6th upper right tooth began to hurt (there was a growing, aching and throbbing pain). In the end, I decided to go to a local doctor (Dent Istanbul Clinic).
Having taken a panoramic photo of the jaw, she said that there might be damage to the canal (or root or even a crack - the conversation was in English and my knowledge of dental terminology in English is quite poor) and it would be possible to find out only by cleaning the canals from the filling material. She also said that if she manages to do this, it will be possible to treat the tooth, which may take about 4-5 weeks with a change of antiseptic and temporary filling.
She cleaned the canals and said that there was no damage and it needed to be treated. She put some three red needles in the canals and put a temporary filling, after which she told me to come back in a week to change the antiseptic and filling.
I planned to go see her right before my flight, but I had to fly earlier.
By the time I got home (7 days after I put the antiseptic on), the tooth began to hurt slightly again.
I found one clinic already at home and they said that they treat periodontitis.
The young dentist removed the temporary filling, washed out the canals and left the tooth open. He told me to come in 4 days. If before this there is no pain, then he will put a temporary filling for a couple of days, and if in this case there is no pain, then they will put a permanent one. Well, if it hurts, they will remove it (for free).
At the same time, he said to rinse the tooth 5-6 times a day and close the hole in the tooth with a cotton ball, and after eating, rinse it (but did not say what, apparently, by default, saline solution).
I do all these procedures. Tomorrow I’m supposed to go for a temporary filling, but I’m overcome with doubts. When biting the tooth does not hurt, but when rinsing (intensely) there is a very slight painful sensation.
Now I am overcome with doubts. I’m not a dentist, but I’m a little embarrassed that he didn’t prescribe antibiotics along with rinsing, plus he didn’t mention treatment with antiseptics or any other means, but just a temporary filling (and, as far as I understand, just a filling without anything (antiseptic)). And this dentist’s hand was shaking when he cleaned my canals. Apparently a young specialist.
How long can a tooth bother me?
How long the treated tooth will bother depends on the cause. Ideally, it should not make itself felt at all. If the therapy was carried out under anesthesia, the aching pain under the filling lasts about two hours, then goes away. When it does not disappear or grows, you need to go to the doctor.
If canals were filled during therapy, your teeth may hurt when you bite into the temporary filling. This is the reaction of living tissue to the therapy of deep caries, the treatment of canals, and the introduction of filling material into them. This pain does not last long and disappears within seven days. Then the treatment continues, the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one.