Symptoms
The pain some time after the filling is installed has different variations, as it depends on the factors causing it. Unpleasant feelings when biting can be:
- Temporary or long-term.
- Immediately after treatment or a few hours later.
- With aching or acute manifestations.
The increase in sensitivity that occurs when pressing while chewing food is often caused by drying out the cleaned tooth cavity. In this situation, the nerve endings in the dentin are irritated.
Acute toothache (including throbbing) after completion of the filling process can be observed in case of inflammation of the pulp. The occurrence of pulpitis is caused by poor-quality treatment and unremoved remnants of the affected tissue.
Periodic pain often occurs in the chronic form of pulpitis. They are observed 2–3 days after filling. An aching pain is felt when pressing on the problematic tooth, and goes away immediately after the pressure on its surface is removed.
Pain after caries treatment
Pain syndrome after dental canal filling can be caused by:
- firstly, excessive trauma to dental tissues, which need some time to recover. Such cases occur when the carious lesions were deep and extensive;
- secondly, improper adherence by the dentist to dental canal filling technologies. For example, in case of under-dried or over-dried dental cavity before the procedure of filling the dental canals.
Norm
The occurrence of mild periodic aching pain after treatment of caries indicates that it is not pathological. Moreover, the pain syndrome in this case will gradually subside, and swelling of the cheek and gum tissue will not be observed.
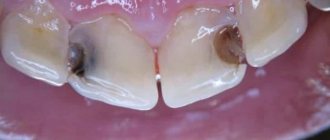
Often pain occurs after deep caries has been removed. In this case, the bottom of the carious cavity is located close to the pulp. And due to the mechanical effect on the surface of the filling, this effect also affects the pulp tissue. Pain may occur when:
- pressure is applied to the filling, even if it is insignificant;
- solid food gets on the filled tooth (during chewing);
- Scrape along the surface of the filling with a toothpick or fingernail.
After 1-3 months, such pain weakens and then disappears completely. The fact is that the pulp produces a protective layer of dentin, which allows you to “fence off” the filling. Until this happens, the patient may feel pain due to mechanical and thermal effects on the filling.
A slight dull pain can also be a reaction to procedures performed during the treatment of caries:
- “exposure” of the filling material with halogen rays;
- treatment of carious cavities with antiseptic agents;
- processing of tooth tissue using a drill.
If pain of this nature is observed for no more than two weeks, it is not pathological.
Pathology
If the pain after treatment of caries occurs suddenly, mainly at night, is acute and pulsating, the development of acute pulpitis is most likely occurring.
If pain occurs during and after eating cold and hot food, as well as when pressing on the surface of the causative tooth, it can be assumed that chronic pulpitis has begun to develop.
Also, when a tooth reacts to temperature stimuli, if the filling is located in close proximity to the gum, it is necessary to evaluate whether one of the edges of the filling material is overhanging (a step or gap between the edge of the filling and the tooth).
If you detect uneven edges of the filling, you should consult a doctor. After all, such a defect will systematically injure the gums, which will lead to the development of inflammatory processes in its tissues. The next stage of this complication will be the exposure of the tooth root, which is not covered with enamel and therefore reacts sharply to various irritants.
A clear sign of developing pathology after caries treatment is the concentration of pain in the area of only the tooth that was filled.
You should contact your dentist after caries treatment if the following symptoms occur:
- the treated tooth reacts acutely with pain to the process of chewing food, as well as eating hot, cold, sweet and sour foods;
- toothache occurs without any impact on the tooth, mainly at night;
- the pain is paroxysmal;
- the pain syndrome does not stop even after a month after caries treatment;
- the pain is not relieved even by taking painkillers.
Causes
There are several common reasons that provoke pain when biting after teeth filling.
Consequences of caries treatment
In the first days, it is considered normal for a condition in which pressing on the filling causes slight pain. This often happens when the tooth is deeply damaged, when the problem area is close to the nerve endings. The resulting pressure during chewing of food affects the pulp.
High-quality polishing of the filling allows you to reduce the level of sensitivity. It is necessary that the new bite line does not intersect with the boundaries of the antagonist tooth. Otherwise, in addition to discomfort, the enamel quickly wears off.
In addition, when using low-quality filling material, shrinkage often occurs or microcracks form, causing complications and pain.
Perforation of the tooth root
This occurs due to medical error during root canal treatment. In recent years, this problem has become increasingly common as dentists switch from manual cleaning and root expansion to automatic techniques.
On this topic
- Seals
Let's find out why a tooth hurts after a temporary filling
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 5, 2020
One wrong movement can result in drilling through the root wall. This results in bleeding and severe pain. During the filling process, the cementing material extends beyond the root walls through this hole.
The client will feel a prick during perforation, even with current anesthesia. In the future, this can cause suppuration around the roots.
Allergic reactions to fillings
When filling the dental canals with a certain type of cementing material, a person prone to allergies experiences severe pain that is not eliminated even after taking painkillers.
In addition to pain when biting, the patient experiences swelling of the gums, cheeks and lips. The difficulty of this problem lies in its timely identification. The doctor may not immediately determine the cause of the complications. There are cases when the old filling is replaced with a similar material, and pain when chewing rough food occurs again.
The result of periodontitis treatment
Sometimes during a routine examination, the dentist informs the patient about periodontal inflammation, even if the tooth has never been disturbed before. After the treatment procedures, a person experiences inflammation, increased sensitivity to touch and pressure, throbbing and slight aching pain. This reaction is considered natural and does not indicate the doctor’s incompetence.
During periodontitis, bacteria accumulate in the bone tissue. After filling the canals, their access to movement is limited, the source of infection is localized, and the body can easily cope with it. However, side effects are observed in cases of weakened immunity.
Prevention methods
To minimize pain after caries treatment, you must follow your doctor's instructions. However, it is also worth choosing a professional specialist who will carry out the work efficiently. Tips for preventing post-filling pain will be as follows:
- in the first days after treatment, you should refrain from eating too hot/cold foods, spicy and sweet foods, mechanically hard foods (seeds, chips, nuts),
- special attention should be paid to oral hygiene, use a brush with medium-hard bristles, dental floss, irrigator, brushes and mouth rinses,
- in the first week after filling a tooth, it is better to refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol,
- dress according to the weather, avoid hypothermia or overheating of the body, especially if we were talking about the treatment of pulpitis or periodontitis,
- Visit the dentist once every 6 months to promptly identify repeated carious lesions or filling defects.
At the same time, doctors strongly recommend not to self-medicate, not to heat, not to apply ice to a sore tooth. If a tooth under a filling hurts for more than 10 days, then it is better not to delay a visit to the dentist.
Video on the topic
What to do
In most cases, pain after filling gradually disappears on its own. However, you have to endure discomfort from one hour to several weeks. To reduce the unpleasant feeling you should:
- Regularly rinse your mouth with baking soda solution, herbal decoction or rinse;
- brush your teeth after every meal;
- for acute pain, take painkillers ;
- fever and inflammation can be eliminated with antibiotics, but with prior consultation with a doctor.
Causes of pain
It is difficult to imagine how many complications there are after treatment of caries, especially deep ones. All of them ultimately lead to severe pain.
Improper drying of the tooth cavity before filling
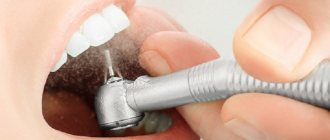
Before placing filling material into a carious cavity, the dentist must dry it well with special instruments. Without this procedure, installing a filling is useless: the cement will not adhere tightly if the walls are too wet, since liquid droplets prevent adhesion. As a result, the composite will simply tear away from the tooth, and low pressure zones will appear in these places, which will cause pain. In dentistry, this phenomenon is called debonding.
Overdrying the cavity is also undesirable. Ideal condition: slight moisture in fabrics. It is often compared to wet sand, when the surface is not dry, but drops of liquid are not visible. Otherwise, adhesion will also be impaired.
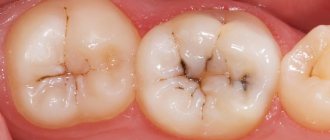
Repeated caries
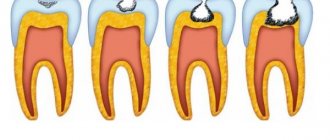
Sometimes the tooth hurts and aches due to the development of secondary caries, which forms in several stages:
- Formation of small gaps between the composite and the tooth.
- Bacteria getting into microcracks.
- Active reproduction of microorganisms. During their life, various toxins are produced that negatively affect hard tissues.
The reasons for the development of recurrent caries may be as follows:
- Not all affected tissue was removed.
- Incorrect preparation of the tooth for filling (we recommend reading: what to do if the tooth hurts when biting after canal filling?). The composite does not adhere tightly to hard tissues, as a result of which microorganisms cause disease.
- Shrinkage of the filling. This is typical for light-polymer materials.
- Improper care of the composite. Eating too hot and cold, chewing hard foods, etc. will destroy the filling.
- Bruxism is a condition characterized by grinding of teeth during sleep. As a result, the filling material is destroyed.
Complications of caries
One of the consequences of deep caries is pulpitis. The disease is characterized by an inflammatory process in the living part of the tooth – the pulp. This disease takes a long time to develop, but the symptoms are very unpleasant - severe pain. Toothache caused by pulpitis will disappear only after surgery - the pulp is either completely removed or mechanically cleaned.
Another complication of caries is the development of periodontitis, which affects the tissue surrounding the tooth. The diseases are interrelated as follows: first caries appears, then pulpitis, and then periodontitis, if they are not cured in time. The danger of periodontitis is that the ligaments that hold the tooth roots are destroyed.
Medical error when removing a nerve
One of the common mistakes is bleeding from the canal. This error occurs as a result of the carelessness of the doctor. However, toothache may not appear later if the doctor takes all necessary measures.
Sometimes, in a hurry or due to the dentist’s negligence, the nerve is not completely removed. The diagnosis is residual pulpitis, when the tooth hurts due to a repeated inflammatory process in the remaining nerve (we recommend reading: how long does a tooth usually hurt after removing the nerve and cleaning the canals?). Added to the painful sensations is a change in the color of the tooth enamel, whereas normally it should fade.
With such pain, no folk remedies will help, since the problem is located under a filling, where decoctions or applications cannot reach. You should file a complaint with the dentist, who is obliged to replace the filling with a better one.
The tool is broken
In rare cases, a dental instrument may chip inside the root. This is not always the dentist’s mistake; you need to take into account that teeth sometimes have difficult-to-pass canals.
A good doctor should immediately warn the patient about what has happened. He takes an x-ray to find out where the debris remains. Although in some cases you can get it out without this - if it is stuck shallow. Medicine is familiar with cases where patients lived for a long time with a fragment of an instrument in their tooth and did not experience discomfort.
Allergic reaction
Typically, an allergy occurs to anesthesia and is a type of drug intolerance. A patient who knows about its presence should notify the dentist. The risk of an allergic reaction increases with:
- rapid administration of the substance;
- use on an empty stomach;
- exhaustion from illness.
Allergies are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Swelling of the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
- Redness of the gums.
- Feeling of increased pressure at the injection site.
- Soreness of the tooth and gums.
- Hives. The skin turns red, swells, itching and rash occur, general weakness, headaches, fever or decreased blood pressure occur.
- Quincke's edema is sometimes combined with urticaria. Rapidly increasing swelling of the eyes, nose, lips, cheeks, larynx, and bronchi forms. The skin turns pale, breathing becomes difficult, and a cough appears.
- Anaphylactic shock. Characterized by weakness, dizziness, itching, the presence of two previous pathologies, nausea, vomiting, difficulty breathing, etc. Very dangerous.
Other reasons
Sometimes, when treating a tooth, the dentist may inadvertently perforate the tooth, and an extra hole appears in the crown, which is clearly visible on an x-ray. Correcting the error is difficult and expensive because special materials are required to cover the holes. If the doctor's guilt is proven, the hospital is obliged to provide treatment free of charge.
When to see a dentist
Depending on the complexity of the disease and the characteristics of the treatment performed, tooth filling may cause pain for a certain period of time.
However, it should be understood that prolonged pain may indicate the development of complications requiring medical intervention. For each specific case, this period and symptoms are individual.
Thus, the impact on the pulp after filling is eliminated within several months, when a layer of dentin forms between the soft tissues of the tooth and the filling.
Why does a tooth hurt under a filling?
There are several factors influencing the development of pain; it even happens that a combination of them causes discomfort. For example, a defect in a filling can cause relapse of caries or inflammation of the nerve. There are several main causes of post-filling pain:
- poorly performed treatment (under-drying or over-drying of dentin),
- complications of carious lesions (pulp inflammation),
- caries relapse,
- defect of the filling (it extends beyond the boundaries of the tooth, voids inside, etc.), that is, it literally puts pressure on the nerve due to the fact that it does not correspond to the bite,
- foreign body in the canal,
- allergic reaction to the components of the filling material,
- formation of a gum pocket due to poor oral hygiene. In this situation, the treatment was most likely carried out correctly, and the reason lies in inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Only a doctor can determine the cause of the discomfort; however, it is also useful for the patient to know what processes are occurring in the tooth and why it hurts under the filling.
Underdrying of dentin
The technology for caries treatment is vaguely reminiscent of room renovation. First you need to remove infected and destroyed tissue, then treat the area with acid to get rid of small “garbage”. Next, the surface should be treated with a special adhesive composition so that the filling material adheres firmly to it. However, before using a dental “primer”, the surface must be dried. If this is not done, the moisture contained in the saliva will become an intermediate layer between the dentin and the adhesive and provide a breeding ground for microbes.
Insufficient drying of the surface leads to the fact that the “primer” is not absorbed into the walls of the cavity, and, consequently, the filling material is not installed tightly: voids appear between it and the tooth wall, which will cause discomfort under mechanical or thermal load.
Overdrying of dentin
Another mistake in treatment, which can result in unpleasant sensations for the patient. If the doctor overdoes it and overdries the surface, then the nerve endings, deprived of moisture, can be injured by the adhesive drug absorbed into the dentin or by the rays of the lamp that hardens the material.
As a rule, the patient experiences discomfort while eating. The treated tooth reacts to hot or cold food, and pain occurs when biting or tapping on the filling. Occasionally, pain may occur upon contact with cold air (for example, on the street) or after hypothermia.
Attention! Post-therapy discomfort is a normal condition. Painful sensations of varying degrees of intensity and nature can persist for several days: the bone tissue adapts to the filling material, which shrinks and adheres to the surface of the crown. If the pain is mild and short-lived and occurs less frequently or becomes weaker every day, then you do not need to see a doctor.
Complications of caries
If the pain under the filling is spontaneous, pulsating, if it occurs mainly at night, if it does not go away within one or two minutes after the irritant stops, then we can talk about a complication after treatment of deep caries - acute or chronic pulpitis.
Inflammation of the nerve endings occurs when pathogenic bacteria enter the pulp chamber. The development of pathogenic flora provokes inflammation of the nerve. The same thing happens if, when cleaning the canals, the dentist incorrectly removes the nerve. Then the damaged tissue also begins to become inflamed under the influence of microflora. Pulpitis can develop a month or even more after the tooth is treated, and it is always characterized by severe pain.
Recurrence of caries
As a rule, this is a complex reason, which is based on incomplete extraction of the affected tissue. Its small particles remain under the filling, where microbes continue to develop and destroy dentin.
In addition, there are cases when caries relapse begins due to poor quality or incorrectly selected filling material. Under mechanical stress during chewing, the filling cracks; bacteria penetrate into these cracks, causing repeated carious lesions.
Seal defect
Modern materials used in the treatment and filling of canals require layer-by-layer application. In this case, each layer must be prepared in a special way for applying the next one - drying or treatment with acid, an adhesive preparation, and so on. After hardening, the filling should shrink slightly, but if one of the layers is applied incorrectly, voids will form in the filling during shrinkage. When chewing, when pressure is applied to the filling, due to these voids the load is unevenly distributed over its surface, and it turns out that some part of the filling puts more pressure on the surface of the tooth.
The same thing happens if part of the filling material extends beyond the boundaries of the tooth in the root area or above the crown. Incorrect distribution of the chewing load leads to pain or cracks in the filling.
Foreign body in the canal cavity
It is very rare, but it happens that the tip of the instrument breaks off during treatment and gets stuck in the tooth canal. If the doctor notices this, he may take action to remove the foreign material or use depophoresis to decontaminate the area. But the doctor may not notice the breakdown, and then a piece of the instrument causes a protective reaction in the body. The tooth will do its best to reject the foreign element, and this can lead to inflammation.
Allergic reaction
Each body has its own pain threshold and its own susceptibility to medications. Modern materials and instruments used in dentistry for treatment are hypoallergenic, but an individual reaction to some components can cause an allergy. As a rule, such a reaction appears some time after treatment - from a couple of weeks to several months.
Gum inflammation
If the patient does not take good care of the oral cavity, then pain may occur for a reason that has nothing to do with the tooth (although the opposite will seem). It is quite possible that the gums are simply inflamed or a sufficiently large amount of food has accumulated between the teeth, which causes pressure and inflammation. It is enough just to carry out high-quality cleansing (including at the dentist), as well as rinsing with antiseptics - the situation will improve in just a couple of days.
Reasons for the development of periodontitis
The source of infection is dental plaque.
The plaque itself is not only safe, but also useful. Nature created this pale yellow biofilm to protect teeth from damage and infection. But pathogenic microorganisms choose dental plaque as a convenient breeding ground. Through the film they penetrate to the surface of the teeth and into the interdental spaces. Therefore, plaque must be removed regularly by brushing your teeth. A fairly large amount of plaque accumulates over the course of a day. Two or three days without brushing your teeth leads to the gradual formation of tartar. Removing stone is no longer as easy as plaque. This requires medical assistance.
Tartar plaques gradually increase in size and damage the teeth and surrounding tissues. Basically, gingivitis, an inflammation of the gums, develops first. Chronic gingivitis forms “pockets” between the teeth and gums. These spaces are an excellent breeding ground for bacteria. Their toxins begin to destroy the bone and connective tissue that holds the teeth. Teeth become so loose that they may fall out.
What to do if your tooth hurts after treatment.
If the pain that bothers you after a visit to the dentist is not pronounced, gradually decreases over time and there is positive dynamics, you just have to rely on the strength of your body and wait for a complete recovery. However, acute, severe and paroxysmal pain that does not subside but increases over time, swelling and fever are sure signs that it is time for you to see a doctor. The specialists of the Vega Dent clinic will help you find out the causes of toothache and, if necessary, provide qualified medical care.
/post/bolit-zub-posle-lecheniya-chto-delat"
dental forums on zub-zub.