How can you get infected with herpes
The content of the article
The disease is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV, Herpes simplex virus). Of the eight types of this pathogen, genital lesions are the result of two infectious agents. HSV-2 causes 80% of cases of the disease, and HSV-1 - 20%. There are also combined infections, in which both viral types are to blame.
There is a misconception that herpes on the lips and genitals are completely different diseases. In fact, both types of pathogens often “swap places” during domestic infection and oral sex. And both infections are equally dangerous.
Both types of virus are transmitted:
- For all types of sexual contact - vaginal, oral, anal, during which the virus enters the body through microdamage to the mucous membrane. You can also become infected from a partner who does not have rashes on the genitals or other manifestations of the disease. This condition is possible with strong immunity, when the virus lies low and waits in the wings. A person becomes a carrier of a herpes infection, but does not experience any health problems.
- Through common objects - washcloths, sponges, bed linen, towels. A person with a cold sore caused by the type 1 virus can become a source of genital herpes infection.
- During autoinoculation (self-infection), when the patient transfers the pathogen from the face to the genitals.
- A child becomes infected from a sick mother when the virus penetrates from the vagina into the uterus or transplacentally through the placenta. During childbirth, infection occurs as the newborn passes through the birth canal.
Statistics of hidden and overt forms of herpes
The body cannot overcome the pathogen on its own. The virus settles in the roots of the spinal cord, and the infected person continues to live with the disease throughout his life.
The pathogen can remain in the body for many years without causing symptoms. Therefore, it is impossible to know without testing for herpes whether a person is infected with the virus. According to WHO, type 1 herpes, which causes a rash on the lips and genitals, affects 67% of the world's inhabitants, and type 2 affects 11% of people. Only 20% of the disease occurs in the classical form, which is beyond doubt. In the rest, the course of the disease is latent or asymptomatic.
Herpes on the lips hospital
Sick leave will be given if the patient is urgently hospitalized due to a complication and the addition of bacterial inflammation.
Other cases are not a reason to go on sick leave. God, there is so much panic about common herpes. And what is this nonsense about baths? You could have snatched it many years ago when kissing or drinking from a poorly washed glass, etc.
And he only came out now. It may never come out again or once every few years for 3-5 days. The panic is just inappropriate. Yes, most people go with it, even those who The famous salicylic acid and the ointments and pastes made on its basis for herpes on the face are also useless.
Primary herpes
There are three periods of illness:
- Prodromal
(precursor period), during which the temperature rises, the inguinal lymph nodes become inflamed, weakness, fatigue, and headache appear. A person experiences a condition similar to the symptoms of flu and colds. If you take an antiviral drug during this period, the disease may not develop. If the symptoms are ignored and treatment is not started on time, the second period of the disease begins. - A rash
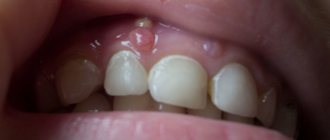
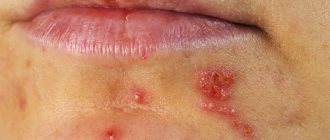
that occurs three to four days after the onset of a flu-like condition. Common symptoms include pain, heat, swelling, itching in the genital area, anus, buttocks, pubis and perineum. Soon, numerous blisters filled with clear liquid appear on the inflamed skin and mucous membranes, reminiscent of a “cold” on the lips. The rash causes pain and itching, worse at night and leading to insomnia. - Ulcerations.
After some time, the blisters burst and ulcers (erosions) form in their place, surrounded by a focus of inflammation. Contact with stool and urine on the eroded surface increases pain and complicates tissue regeneration. - Healing,
during which the ulcers gradually heal. If the genital organs are poorly cleaned, the immune system is weak, and infection occurs, the healing process is delayed.
After the ulcers disappear, the disease goes into remission. During this period, despite the presence of the virus in the body, there are no rashes on the genitals.
The process of infection from a biological point of view
Speaking in the language of the common man, avoiding deep scientific terms and definitions, it should be noted that herpes is a sophisticated and insidious infectious resident.
Its abilities are such that, penetrating through damaged skin or mucous membrane, it is able to integrate into the DNA chain in order to further reproduce its own kind for further movement throughout the body.
It is immediately worth noting its cunning, it is contained in a paradox - it is not an active enemy for humans.
Having encountered a persistent immune system on its way, it hides in cellular space, so to speak, until “better times.”
As soon as they occur, and this is, first of all, a weakening of the body’s protective shield as a result of many circumstances, the main one of which is human illness, herpes immediately begins to show its vile character.
The virus leaves the affected cell, moves along the nerve endings, reaching the mucous membranes and breaking out to the surface of the skin.
Unfortunately, only then, having seen scaly blisters on the lips that irritate and inflame the skin, do the patient and those around him think about how to avoid transmitting this disease to other people.
Recurrent herpes
In 50%-70% of people the disease becomes chronic. This is facilitated by:
- untimely or incorrect treatment;
- decreased immunity, including that caused by taking medications that suppress the immune system;
- presence of other STDs;
- strict diets, vitamin deficiencies;
- state of chronic stress.
Why do patients develop relapses, during which the disease affects the same parts of the body? There are several reasons for this:
- Having penetrated the body, the virus settles in the tissues of the genital organs. As it multiplies, it affects cells deeper and deeper until it reaches nerve cells - neurons connected to each other by processes - axons. Through them, like bridges, the pathogen reaches the cells of the spinal cord, into which it introduces its DNA.
- An infected brain cell becomes an “incubator” for viruses, which periodically return via axon bridges to the mucous membrane or skin, causing new rashes. Schematically, the process is similar to the migration of birds, constantly returning to their “native places.”
- The immune system cannot kill viruses hidden in the spinal cord, but it deals with those that have left the “shelter”. Therefore, with high immunity, relapses occur rarely or not at all. But as soon as the body “loses its vigilance” - weakens, gets sick, catches a cold, is exposed to stress - the pathogens begin to overcome the immune defense. As a result, they reach their target - the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs. Here, the increased reproduction of viral particles inside the “captured” cells begins. Cellular structures, dying, release myriads of viruses that cause inflammation, redness, swelling and the appearance of blisters. Herpes is causing another aggravation.
- Gradually, the immune system fights back the virus, and within 10 days the ulcers at the site of the rash dry out and heal. Everything returns to normal, so that at the slightest weakening of the immune system it can start again.
From the mechanism of exacerbations, it becomes clear why herpetic eruptions appear in the same places. It’s just that the virus cells return back only through the nerve cell from which they penetrated deep into the body.
Types of recurrent herpes
Depending on the number of exacerbations, several types of the disease are distinguished:
- mild, occurring up to 3 times a year;
- moderate severity, in which exacerbations occur 4-6 times a year;
- severe, accompanied by frequent exacerbations, intervals between which do not exceed a month;
- arrhythmic, in which after a period of imaginary well-being, lasting from a month to five, rashes appear. This form of herpes is characterized by a pattern - the longer the remission, the more severe the disease;
- menstrual, manifested by rashes during menstrual periods. This type of disease is severe and difficult to treat;
- subsiding, in which the manifestations of the disease constantly become weaker, and the inter-relapse periods become longer. The subsidence of the manifestations of the disease indicates the positive dynamics of treatment and the restoration of immune defense that suppresses the virus.
Classification of infection
In case of herpes, the doctor must give sick leave, since the disease is infectious in nature. The infection can be transmitted to colleagues, so the employee must be suspended from work for a certain period of time. It must be remembered that if an infection occurs with one of the types, then in parallel the process of infection with another form of the disease can occur.
If you provide sick leave, the patient will spend time at home, gain strength, strengthen the immune system, and take medications in a timely manner. All this has a positive effect on the general condition of the body and leads to a speedy recovery.
Sick leave for cases of herpes infection is issued for various periods. It depends on the type of herpes infection and its manifestation. If we consider the disease based on clinical signs, we can distinguish typical and atypical forms. The first option manifests itself in the form of blistering rashes. They can occur on the skin and mucous membranes. The atypical form is less pronounced, the manifestations in the form of bubbles are similar, but they are almost invisible.
Depending on the severity of herpes (mild, severe and intermediate), a sheet is given for 5 days or more. Localization makes it possible to determine the duration of treatment, which directly affects the time a person spends on sick leave. Experts highlight:
- genital shape;
- stomatitis that occurs with herpes;
- skin herpes;
- herpes damage to the central nervous system;
- form that appears before our eyes.
The sick leave will be given to the patient for several days, with special attention paid to the course of the disease. Depending on this parameter, herpes is classified into the following types:
- spicy;
- primary;
- chronic;
- recurrent.
A herpetic infection can affect almost all human organs and systems. In this regard, various specialists are fighting the disease and working to improve methods of treating the disease. But most often people have to contact a dermatologist or venereologist, who will issue a medical certificate of temporary disability.
Atypical forms of herpes
Sometimes genital herpes is erased. These forms of the disease account for 65% of cases of the disease:
- In women,
atypical herpes resembles inflammation of the vagina or vulva. There is pain, itching and swelling of the genital organs, profuse leucorrhoea and pain during sexual intercourse. External manifestations are limited to areas of redness or pinpoint rashes. - In men,
the atypical form of the disease is similar to inflammation of the head and foreskin (balanitis or balanoposthitis). A reddish rash appears on the mucous membrane of the penis, accompanied by pain and burning, which does not look like a herpetic rash. Inflammation of the prostate gland occurs, causing pain radiating to the anal area. Damage to the urethra leads to pain and burning when urinating, and the appearance of traces of blood in the urine.
There is a latent form of the disease in which there are no clinical manifestations, but despite this, the person remains a source of infection. But imaginary well-being does not last forever. With hypothermia, loss of strength, decreased immune defense, pregnancy, stress, severe concomitant diseases and other unpleasant conditions, the virus begins to multiply rapidly and the person becomes ill.
The disease is activated by concomitant sexually transmitted infections, especially ureaplasmosis. Due to the ability to rapidly “bloom” against a background of weakened immunity, herpes occurs in 90% of HIV patients. Therefore, if herpetic rashes appear, you need to be examined for other STDs.
Features of the course of genital herpes during pregnancy
The number of positive (seropositive) reactions to herpes viruses 1 and 2 in pregnant women is 50-70%. Due to the increased load on the body and decreased immune defense, herpes often relapses during this period. But only 30% of women experience the classic development of the disease. Basically, the symptoms of herpes during pregnancy are limited to the appearance of areas of redness and cracks, which women mistake for irritation.
The manifestation of a herpetic infection caused by recurrence is not dangerous for the child. The woman’s body has already built up immunity to infection by producing antibodies—substances that protect her from the virus. Some of the antibodies will pass from mother to baby, protecting him from infection.
Only a relapse that occurs immediately before childbirth is dangerous. To prevent infection of the baby and rupture of inflamed tissues, women with a herpetic rash on the genitals are advised to deliver by cesarean section.
It is much worse when the infection is primary. Herpes belongs to a group of infections, infection of which for the first time during pregnancy leads to the birth of children suffering from developmental delays and congenital defects.
Herpes tests for pregnant women: interpretation and prognosis of pathologies in the fetus
To determine the degree of risk for the baby, a woman’s blood is taken for IgM and IgG antibodies, the concentration of which determines when infection occurred. The analysis is carried out using the ELISA method (immunofluorescence), which reacts to IgM and IgG antibodies to the virus. By the presence or absence of antibodies, you can find out whether a woman is infected and when the infection occurred:
- IgM antibodies
appear after 2-3 weeks. after the onset of the disease, therefore indicating a “fresh” infection or relapse of infection. These antibodies disappear after 1-2 months. after recovery. The presence of IgM in the analysis is a bad sign. - IgG class antibodies
- appear as protection against the virus after 2 weeks. field of infection, quickly increase the titer (concentration) and persist throughout life. Their detection means that the body encountered a herpes infection and managed to cope with it.
It is bad if a fourfold increase in IgG is combined with the detection of IgM. This means that antibodies are being formed right now, i.e. the woman is sick.
Infection with the herpes virus is determined in the laboratory. It is better to undergo such an examination twice - before pregnancy and during it.
Table of interpretation of results for herpes
| IgM | IgG | What does it mean | What to do | |
| — | — | The woman is healthy (seronegative) - she has never had herpes | Before pregnancy | During pregnancy |
| In order not to become infected, you need to avoid contact with people who have manifestations of herpes, incl. on the lips. Periodic antibody monitoring is recommended | ||||
| — | + | Female carrier (seropositive) | The infection occurred a long time ago and does not pose a danger to the child, no measures are needed | |
| + | — | Recent infection | It is better to plan pregnancy after acute symptoms subside and re-examination | Consult a doctor and undergo additional diagnostics to find out if everything is okay with the baby. |
| + | + | Exacerbation of infection | It is better to plan pregnancy after acute symptoms subside | Recurrent herpes is less dangerous than primary herpes, so the likelihood of complications and intrauterine infection is only 0.02% |
Fetal pathologies in children infected with herpes during pregnancy
The most dangerous thing for a child is primary infection of the mother during pregnancy, which leads to many complications.
| Gestational age at primary infection | Possible complications |
| I trimester (up to 13 weeks) | Fading pregnancy, miscarriages, severe malformations |
| II trimester (14-27 weeks) | Child infection, internal organ defects, fetal death |
| III trimester (29-40 weeks) | Intrauterine infection, death of a child after birth, premature birth, hearing, vision, and nervous system defects of the child. Subsequently - mental retardation. |
Is it transmitted through a kiss?
Many people believe that it is impossible to get infected with herpes on the lips, and all the warnings are nothing more than a myth. In fact, it's the other way around. It is easy to get infected with herpes if you kiss a person who has such a cold on their lips.
Herpes infection is transmitted:
- During direct contact. If a person touches the patient's sores, the infection will spread. If a conditionally healthy person was a previously infected carrier without precedents of rashes, he will experience a relapse. The same thing will happen when people kiss. Parents of children under 4 years of age need to be attentive to the disease. The virus causes great damage to immune defenses that have not yet been fully formed. Adults with herpes on the lips should avoid kissing their child.
- By airborne droplets. When a person suffers from a cold accompanied by sneezing and coughing, virus particles spread when sputum is released into the air. The patient’s immunity at that moment is weakened by another infection, there is a high concentration of the virus in the body. A person may cough, spreading the herpes infection at this time.
- In a household way. Viral particles remain viable on the surface of household objects; they are easily transmitted by airborne droplets. It is important to ensure individual use of hygiene items, cutlery, various accessories and clothing.
- During operations, dental and salon procedures. Infection is facilitated by blood transfusion or non-compliance with sanitary standards in places of public services.
- During intimate contact. HSV microparticles are present in the secretions of the reproductive system. Such proximity has a high degree of contagion.
- During pregnancy and during childbirth from mother to child. There is a high probability of transmission of an infectious disease during the intrauterine development of the fetus and at the birth of the baby. This is facilitated by a decrease in immune defense during pregnancy in a pregnant woman.
There are many ways of transmitting a dangerous disease. To avoid infecting others or avoiding your own infection, you should adhere to the rules of personal hygiene and precautions.
Herpes in newborns
A child becomes infected with the pathogen from the mother in utero or by passing through an infected genital tract during childbirth. In newborns, the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth, skin, and genitals are affected. When the pathogen enters the child’s brain, meningoencephalitis occurs, causing death or severe disability.
A generalized form is possible, in which all organs and systems of the newborn are affected. The child experiences jaundice, respiratory distress, and urinary retention. Children are restless, do not latch on to the breast, and are vomiting. Death occurs from shock, bleeding, dehydration, intoxication, and organ failure.
The likelihood of infection increases with primary infection of the mother in late pregnancy.
Diagnosis of herpes
If genital herpes is suspected, after an external examination, scrapings from the affected areas, blood, and urine are taken for examination. This will allow you to differentiate the disease from other skin lesions that have similar symptoms.
For diagnostics the following is used:
- Cultural method - during the study, the contents of the vesicles are transferred to a growing chicken embryo; if it dies, the disease is confirmed. The method is reliable, but too time-consuming.
- PCR is a test that detects viral DNA in tissues. The method allows you to calculate the pathogen even from a small amount of viral material. Effective for diagnosing any form of disease, incl. hidden. The method can be used immediately after infection before symptoms of the disease appear. PCR not only detects the virus, but also determines its type.
- Methods aimed at determining antigens and antibodies to the pathogen: ELISA - immunofluorescence diagnostics, CFR (complement fixation reaction), various types of agglutination reactions. With their help, you can identify the type of pathogen, determine its quantity and duration of infection.
A complete diagnosis of herpes virus infection allows you to make the correct diagnosis in order to prescribe treatment.
Is it possible to get sick leave for an infection or cold if there is no fever?
If a person is unable to work due to illness, he will receive sick leave regardless of whether he has a temperature or not.
The doctor looks at symptoms that determine health status. For example, the patient does not have a fever, but has severe weakness or other symptoms indicating that he cannot be at work. In this case, the doctor may decide to issue a certificate of incapacity for work.
It happens that you have to apply for sick leave in cases where the illness does not interfere with work, but the appearance of your colleagues may confuse you. For example, with conjunctivitis or herpes. If the patient has to communicate with people at work, the doctor may decide to issue sick leave due to a viral infection. But this will only happen if the doctor considers the patient’s condition serious. A small cosmetic defect will not exempt you from work.
But a professional singer who has lost his voice will be given sick leave without question, because in this case the voice is a professional instrument that the singer temporarily cannot control.
Photo: Reuters
Complications of herpes
The worst thing is that a herpes infection brings not only unpleasant symptoms. This virus causes many terrible complications. The most obvious ones are:
- Irritation and dryness of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- Cracks in the genitals caused by metabolic disorders in tissues caused by herpes;
- Adhesive and cicatricial deformities of the labia, vaginal opening, perineum, urethra and rectum. The complication arises due to the specific feature of herpetic rashes appearing on the same areas of the skin and mucous membranes
- Cervical erosion leading to cancer of the reproductive organs.
- Lacerations during childbirth caused by poor distensibility of inflamed perineal tissue.
- Infection of ulcers due to microbes entering tissues not protected by the mucous membrane;
- cicatricial deformities of the penis, provoked by constant inflammatory rashes and ulcerations.
- Chronic herpetic lesions of the genitourinary area, spreading to the urethra, bladder and kidneys.
- Herpetic proctitis is inflammation of the rectum.
- Erectile dysfunction and male and female infertility.
- Neurological symptoms caused by a viral infection of the nervous system. Patients complain of pain in the sacrum, lower back, and groin. With recurrent lesions on the inner surface of the thighs, hypersensitivity of the skin occurs, manifested by a burning sensation, crawling “goosebumps”, tingling.
In severe cases, with a pronounced weakening of the immune system, viremia occurs - viral infection of the blood leading to damage to the brain, liver, lungs, adrenal glands, and intestines. This condition, even with adequate treatment, is often fatal.
Treatment of genital herpes
It is difficult to cure such a dangerous disease. Treatment of genital and labial herpes is long and complex. Therapy includes:
- Prescription of antiviral agents that slow down the reproduction (replication) of viruses. To maintain the effectiveness of treatment during long-term therapy, it is necessary to constantly change the prescribed medications.
- The use of drugs based on interferons - proteins released in response to viral invasion. Scientists have found that a lack of this substance provokes exacerbations of the disease.
- The use of local antiviral ointments, gels and sprays that kill viruses that have penetrated the skin and mucous membranes.
- Prescribing symptomatic medications that combat the general symptoms of the disease - reducing pain, swelling, inflammation, lowering temperature, normalizing sleep.
- Local procedures - baths and irrigations that relieve pain and prevent the penetration of secondary infections.
- Taking immunoglobulins, immunomodulators and stimulators of cellular immunity, which improve the functioning of the immune system, activate the production of antiviral antibodies and prevent relapses.
Patients suffering from genital herpes are advised to avoid wearing synthetic underwear.
Prevention of infection consists of a thoughtful choice of sexual partners, compliance with hygiene rules, periodic examination by a gynecologist and the use of emergency measures at the first symptoms of the disease.
Where to get tested and cure herpes in St. Petersburg, prices
Doctors at the modern Diana Clinic treat herpes infections in St. Petersburg. Here you can take express tests for all infections - smears, blood, etc. Tests are performed using the best methods - PCR, ELISA, etc. The cost of visiting a doctor based on test results is 500 rubles. The price of tests depends on the type of examination. For example, the cost of taking blood from a vein is only 170 rubles.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Incubation period
The incubation period of herpes on the lips depends on whether it is a primary or secondary form. With a primary infection (first contact with the infection), symptoms appear within 1 to 2 days. Most often occurs in childhood. The secondary form has an incubation period of 2–14 days. A person who has previously had an acute respiratory viral infection while taking antibiotics will encounter symptoms of the disease much earlier.
Taking the necessary medications in a timely manner can prevent the occurrence of a rash. Only after visible signs appear does a person realize that he or she is infected.
The disease is often accompanied by general symptoms of malaise - pain in the lips, local hyperthermia, increased body temperature, headache and fatigue.
From the appearance of the first symptoms of herpes to conditional recovery, at least 1 week passes. On average, this period lasts 7 – 10 days. The time of the stage is influenced by the person’s condition. If the patient suffers from acute illnesses, the presence of the bubbles will last. There are cases when a relapse occurs immediately after the last wound has healed. This phenomenon indicates a severe weakening of the immune system and requires medical intervention.