If even most adults, when they hear the word “dentist,” their palms begin to nervously sweat, what can we say about children, who have absolutely no idea why this formidable doctor is trying to look into their mouth with all these gizmos in his hands.
However, a visit to the dentist is usually an unavoidable event in childhood. Another thing is that it is not always productive due to the fact that the little patient cannot be calmed down and convinced to open his mouth, and sometimes it can even be dangerous if the baby suddenly begins to twitch and squirm right during dental procedures.
It is in order to avoid such unpleasant situations that the practice of treating children’s teeth under general anesthesia has been around the world for quite a long time. In what cases is anesthesia necessary for children during dental treatment, how this procedure is carried out, and whether it has a negative effect on the child’s body - read on.
Types of anesthesia for dental treatment for children
In modern dental practice, three main types of anesthesia are used for dental treatment for children. This:
- Intravenous anesthesia , which is performed by injecting an anesthetic drug into a vein. For children, injections are often given with the drug Diprivan or its analogues (Diprivan, Propofol, etc.). The effect occurs in approximately 30 seconds.
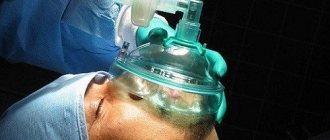
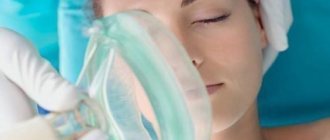
- Inhalation anesthesia , which is considered the most acceptable and gentle for the baby. As a rule, putting on a special mask through which an anesthetic mixed with medical oxygen and air is supplied, the little patient is immersed in a medicated sleep within 10-20 seconds. Most often, a high-quality American drug, Sevoran, is used for this type of anesthesia.
- Sedation , which does not involve putting the child into medicated sleep as such, but only provides a state of “semi-sleep” that suppresses activity and feelings of fear, using the so-called “laughing gas” (nitrous oxide).
Technique for mask anesthesia for adults and children
Anesthesia can be administered intravenously, intramuscularly or inhalation. The mechanism of action of the latter method is to inhale gaseous substances (ether, fluorothane, pentran, nitrous oxide). It can be performed by the endotracheal or endobronchial method (when substances are delivered directly into the respiratory tract through a tube), or as mask anesthesia (involves inhaling a mixture of gases through a special mask).
Children at the preparatory stage before anesthesia are given a sedative to relieve tension and reduce the likelihood of complications
The combination of anesthetics is selected by the anesthesiologist individually depending on the patient’s condition and the type of medical procedure. Their main goal is to minimize the body’s negative reaction to aggressive medical manipulation. Anesthesia should not only induce sleep, but also reduce the severity of the body's automatic reactions and relax the muscles.
After taking a comfortable position, the doctor brings a face mask to the patient’s face. After about a minute, the substances begin to act.
Tip: In the intermediate stages of falling asleep, the child may become disoriented, try to sit up, breathe rapidly or wheeze. This is considered a normal reaction of the body to immersion in anesthesia.
In pediatric dentistry, mask anesthesia is often used for long-term medical procedures, because it causes a quick effect and is easily regulated (the child will wake up only after the supply of the gas-narcotic mixture is stopped). For inhalation anesthesia, I most often use substances such as fluorotane, sevorane and nitrous oxide, which enter the lungs through inhalation. Endotracheal anesthesia for children is preferable only in certain cases: large and complex operations, plastic surgery of the lower jaw, interventions on it.
In what cases is it recommended to treat a child’s teeth under anesthesia?
Of course, if the baby calmly tolerates visits to the dental clinic or needs minor dental intervention, then there is no need for general anesthesia. However, there are a number of specific cases when anesthesia is simply necessary:
- dental treatment for children under 3 years of age;
- serious and traumatic surgical interventions for abscess, complex tooth extraction, lymphadenitis, jaw injuries, etc.;
- excessive gag reflex, which does not allow full access to the diseased areas;
- inability to administer local anesthesia, for example, due to allergies or severe swelling of soft tissues;
- panic anxiety in a young patient or dental phobia resulting from a previous negative experience of a visit to the dentist;
- the baby has mental or neurological diseases (epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, etc.).
Types of anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
Methods of dental treatment without anesthesia are long gone, and any dentist carries out procedures with the preliminary use of painkillers. Young patients – children under 6 years old – require a special approach from the doctor. They have a low pain threshold, so treatment of the oral cavity cannot be carried out without anesthesia. It is important to properly prepare the child for further procedures.
Types of anesthesia used in dental treatment in children
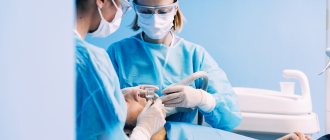
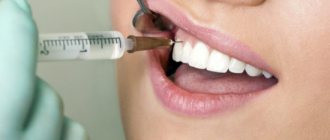
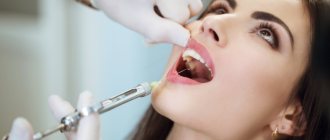
- local anesthesia;
- the anesthetic is injected using a syringe into the gum or cheek, providing an analgesic effect within a radius of 10 centimeters, respectively, the patient himself remains conscious, sees and hears everything that happens near him.
Local anesthesia is used when there is a risk of touching nerve endings, which will cause severe pain. In some cases, the dentist decides to give an injection even when treating simple periodontal diseases. It is mainly used if it is necessary for the child to remain conscious, sometimes this is required to make a more accurate diagnosis: the minimum dosage of the drug dulls the pain, but the patient still feels it, which helps the doctor determine the source of the disease.
It should be noted that for active children it is better to choose a different type of anesthesia, since the child may begin to be capricious while waiting for the procedure to be completed. Of course, various toys and the ability to watch cartoons in the office make it possible to entertain the baby, however, it turns out to be difficult to keep his attention.
This type of anesthesia is safe for a child, since the medication does not affect the entire nervous system of the body, but blocks the impulse of only one area.
General anesthesia
- The patient becomes completely unconscious.
Indications for use:
- inability to use local anesthesia due to an allergy to its drugs;
- high activity of the child who is able to carry out the procedure;
- the need to carry out treatment unnoticed by the patient (relevant for children with nervous disorders);
- an operation that is too long, when a person needs to be in the dental chair for several hours in a row;
- acute gag reflex;
- low pain threshold, at which the child is not able to come to terms with the unpleasant sensations that arise during local anesthesia;
- rare: the presence of dental phobia, when the patient becomes horrified as soon as he gets to the doctor’s office.
Anesthesia is prescribed to children only after undergoing a blood test and EGC, after which a conclusion is made about the possibility of using this method of pain relief. During dental treatment, the child's condition is monitored by an anesthesiologist. Frequent use has a negative effect on the functioning of the central nervous system, causing heart rhythm disturbances and weakening of the immune system. It is prohibited to treat children suffering from rickets, asthma, infectious diseases, pneumonia, heart and blood diseases under anesthesia.
Alternative Methods
This group of pain relief in dentistry includes hypnosis and sedation. The first is used extremely rarely due to the lack of concentration and attentiveness in children. But sedation allows not only the child, but also his parents to remain calm. During anesthesia, the baby inhales a mixture of oxygen and nitric oxide, due to which pain is felt mildly and the feeling of fear disappears. The method is considered the safest. If there are contraindications to the use of anesthesia, then sedation in combination with local anesthesia may be a good alternative.
Safety issues in the use of anesthesia
In order to make the use of anesthesia as safe as possible, before the procedure the baby must undergo a thorough medical examination to exclude possible contraindications: an ECG, a general blood test, an examination by a pediatrician and a consultation with an anesthesiologist.
When administering anesthesia and further treatment under its influence, an anesthesiologist-resuscitator must be present to monitor the condition of the baby: its respiratory rate, heartbeat, etc.
Nowadays, the stereotype that general anesthesia is necessarily harmful is considered quite outdated, since modern drugs do not contain toxins and have the most gentle effect on the child’s body.
Believe me, it is much more harmful to forcefully expose a child to stress, which can later result in various psychological and neurological disorders.
How to properly prepare a child for anesthesia?
According to modern concepts, any surgical interventions, painful procedures, diagnostic studies in children (especially young children) must be carried out under anesthesia or sedation! Young children simply do not know what is in store for them, and no premedication is needed.
Regardless of what type of anesthesia the operation is planned under, the patient is first prepared for surgery. Groups of children by age: newborns, up to 6 months, 6-12 months, 1-3 years, 4-6 years, 7-9 years, 10-12 years, over 12 years.
The anesthesiologist takes an active part in preparing the child for surgery. For planned operations, all preparation can be divided into general medical and pre-anesthesia: psychological and pharmacological premedication. An obstetric history is important: how the pregnancy and childbirth went (on time or not), the child’s anthropometric data - the correspondence of body weight and height to his age, psychomotor development, visible disorders of the musculoskeletal system, behavioral reactions.
We also recommend reading: Venipuncture: technique and indications
Psychological preparation: hospitalization for a child is a difficult moral test; he is frightened by separation from his mother, people in white coats, the environment, etc. The anesthesiologist, attending physician and ward nurse help and explain to the mother how to behave.
Doctors recommend not always telling your baby that general anesthesia is coming. The exception is cases when the illness interferes with him, and he wants to get rid of it. However, if the children are old enough, it is necessary to explain that a special children's anesthesia will be carried out, as a result of which they will fall asleep and wake up when everything is already done and not a trace remains of the previous illness.
It is advisable that the baby is calm and not afraid. It is necessary to provide rest, both emotional and physical. The main thing that parents need to remember is that the baby should wake up after anesthesia and see the people who are dearest and closest to him. Once again about the most important thing in this video:
Preparation for dental treatment under anesthesia
In addition to carrying out all the necessary preparatory studies and consultations, on the day of using general anesthesia, you must also adhere to the following rules :
- do not give the child solid food 6 hours and drinks 4 hours before the intended manipulation;
- for babies who are still breastfed or mixed fed: do not give breast milk at least 4 hours before anesthesia, and infant formula at least 6 hours before ;
- Do not brush your child’s teeth 6 hours before the intended procedure, as he may swallow the toothpaste;
- carefully ensure that he does not eat anything on his own, because even one accidentally eaten cookie can lead to serious complications when using anesthesia.
How does the procedure work?
Immediately before the procedure, the anesthesiologist once again examines the small patient and makes the final decision on the use of general anesthesia.
As a rule, parents are also required to provide written permission for this manipulation. After this, the child is injected or allowed to inhale anesthesia (sometimes this is done in a different room where the treatment will take place, so as not to frighten the baby) and after a few seconds he falls into deep sleep.
At the same time, all his vital signs must be monitored using special equipment and an anesthesiologist present throughout the entire treatment.
After the dental intervention, the anesthesiologist once again makes sure that all vital signs are stable, and everyone can only wait for the baby to wake up. As a rule, the little patient remains in the clinic for some time after waking up under the supervision of medical staff.
Features of local anesthesia in children
It is often difficult to use local anesthesia for children due to fear of injections, pain during injection, and a feeling of “numbness” of tissues. Therefore, the pediatric dentist must not only choose the right drug, but also the tactics of local anesthesia.
Local anesthesia is most often carried out in two stages. First, the injection site is treated with an application gel or aerosol to disable surface receptors and painlessly inject the anesthetic.
To administer the medicine, pediatric dentists use syringes with a very thin and short needle with a specific cut, which makes the injection completely painless. Local anesthetic drugs act within 1-2 hours. After treatment, you need to ensure that the child does not injure the tissues of the lips and cheeks with his teeth due to lack of sensitivity.
This type of anesthesia is indicated for children over 4 years of age. Used for tooth extraction, treatment of medium or deep caries, pulpitis of milk or permanent teeth.
When anesthesia is contraindicated
It is not always possible to carry out dental treatment in this way, since there are a number of certain contraindications, including:
- the presence of acute respiratory diseases (ARVI, bronchitis, tonsillitis, pneumonia) and elevated body temperature at the time of manipulation;
- various diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- anemia;
- recent vaccination (less than 14 days ago);
- allergies to drugs used for general anesthesia (read more about allergy symptoms in babies);
- long-term use of glucocorticoid drugs;
- frequent attacks of epilepsy;
- thrombocytopenia;
- various pathologies of the endocrine system.
The effect of anesthesia on a child's body
Whatever one may say, general anesthesia is a fairly serious medical intervention, which is why before using it it is always necessary to conduct thorough preparation and examination for any contraindications, since there is a possibility of the following risks:
- the appearance of an allergic reaction to an anesthetic drug;
- asphyxia with vomit during the procedure due to non-compliance with the “fasting regime” before the use of anesthesia;
- exacerbation of the child’s chronic diseases, which were not identified due to negligent preparation for this event.
The possibility of medical error or failure of special equipment cannot be ruled out, however, to avoid such a development of events, you just need to choose a clinic with a good reputation, which has all the necessary documents and conditions for dental treatment under anesthesia.