Possible cause of tooth darkening
The most common reason that a child’s baby tooth has darkened is mechanical impact on it. A bruise can occur for a large number of reasons, which sometimes depend and sometimes do not depend on the child.
Children are considered the most common population group to experience tooth discoloration. This happens due to a mistake made by a parent, or due to a child’s inattention.
The most common cause of darkening of a baby tooth in a child is mechanical impact on it.
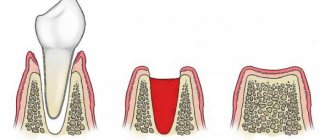
A tooth bruise is a mechanical injury caused by a hard object. In the case of which the tooth itself does not suffer, the main blow falls on the periodontium. It can lead to bleeding and severe tissue rupture.
With a strong blow, vessels can be damaged, damage to which leads to hemorrhage, and pulp tissues are affected. In this case, there is no need to panic; most of these symptoms are reversible if you consult a doctor immediately after the first sign of a bruise.
Many parents do not take this fact seriously, because baby teeth are a temporary phenomenon; permanent teeth will grow in their place. These are deeply erroneous thoughts; they, of course, will grow, but darkened baby teeth without appropriate treatment will negatively affect their structure.
Therefore, at the first suspicion of a bruise, even if no serious violations are observed with the naked eye, it is recommended to take the child to see a dentist.
Blue gum in a child
There are several reasons why a child’s gums turn blue. This can be caused by a blow or injury, an infectious or inflammatory process, or teething. Depending on the provoking factor, a treatment strategy is selected.
Blue gums in a child - causes of pathology
The occurrence of blue gums in a child may be due to the following reasons:
- the child hit the gum, resulting in a hematoma;
- eruption of milk teeth or replacement of them with molars, permanent ones;
- consequences of infectious and inflammatory processes in soft tissues;
- other injuries, bruises and damage to integrity;
- complication of carelessly performed dental manipulation;
- anemia.
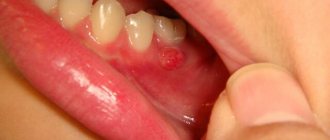
Bruised gums
There is a network of blood vessels located on the gums. As a result of bruising of the gums, capillaries and small vessels are damaged and ruptured, hemorrhage occurs and a hematoma forms under the mucous membrane, which has a bluish color. Additionally, if a child hits his gums, he is concerned about possible violations of the integrity of the tissues and their soreness.
Teething
Due to injury, bruise and tissue damage during tooth eruption, a child may develop a complication - a blue spot or cyst. This occurs due to the rupture of blood vessels approximately 2-3 weeks before the tooth emerges.
The process is accompanied by the formation of a pocket between the bone and the gum and bleeding into it, a bruise of various sizes and colors.
The last characteristic is influenced by the size of the damaged capillary: the larger the vessel, the larger the area of the gums will turn blue.
The following symptoms may also occur that require you to contact a specialist:
- temperature increased to 38 degrees;
- hematoma suppuration;
- the bruise does not go away for more than 3 weeks;
- large size of the hematoma (over 2 cm) and disturbing severe pain.
Important! If a hematoma appears when a child’s teeth are coming out, it is forbidden to open it yourself or exert any mechanical influence. Failure to comply with this nuance can lead to the development of an infectious process, further spread of the bruise and other undesirable complications.
Infectious and inflammatory gum diseases
With inflammation and infection of the tissue, the development of gingivitis, stomatitis, blue discoloration is noted.
The first disease develops most often due to improper or poor oral hygiene and is manifested by bleeding gums, redness or blueness, bad breath and an excessive reaction to cold or hot foods. In the second case, the patient is bothered by ulcers on the mucous membrane, pain and inflammation.
Methods for treating blue gums
Treatment depends on the cause that caused the blue gum due to the appearance of a hematoma. It should be aimed simultaneously at reducing the focus of the bruise and eliminating the factor - facilitating teething, curing infection or inflammation, opening an abscess.
To alleviate the condition, if a child has hit or fallen, or has torn off and severely injured the gums, cooling compresses and painkillers are used. Warm or hot compresses are unacceptable at first, as they increase blood flow and increase the area of the hematoma on the gum.
Treatment of hematoma due to gum injury
If a child’s gums are blue due to a blow, injury, or bruise, immediately apply a cold compress for 10–15 minutes. As prescribed by the doctor, it is possible to apply ointments for better resorption of the bruise - Heparin and Troxerutin.
The duration of such treatment for a bruise is 5–7 days, then if the child’s symptoms and complaints persist or intensify, it is necessary to contact a dentist and pediatrician.
Painkillers
If there is a bruise on the gum due to contusion and its pain, it is not always possible to do without painkillers, available in the form of syrups, tablets, suppositories and gels for topical use. The choice of medication, dosage and application rules depend on the severity of the symptom, the age of the child, possible violations of tissue integrity and individual characteristics.
In pediatric practice, the following drugs are used for pain relief as prescribed by a specialist:
- Ibuprofen or Nurofen (suspension, tablets, suppositories);
- paracetamol-containing medications (Efferalgan, Paracetamol, Cefekon, Panadol - the same release forms);
- Kamistad Baby, Holisal, Dentinox, Leader in the form of gels.
For infections and inflammations that cause blue tissue, antiviral suppositories Viferon and Genferon are prescribed as an additional remedy. The second medication has an analgesic effect.
Help with teething
To relieve pain, eliminate the bluish area, and improve the child’s well-being, you can help in the following way.
- Use special teethers containing liquid that have a cooling and antipruritic effect, or chewing teethers. For the same purpose, you can use gauze soaked in a cool infusion of chamomile in the form of applications on the painful and damaged blue gum of a baby.
- Topically apply gels to the area that have an analgesic and antiseptic effect, recommended to facilitate teething. In children's practice, Cholisal, Kamistad Baby, Lident, Baby Doctor First Teeth are used.
- To reduce restlessness, tearfulness and capriciousness of the baby, relieve pain, inflammation of tissues, and improve sleep during teething, homeopathic drops Dantinorm baby are recommended. You can also calm the baby by placing it on the mother's breast if he is breastfed.
- To relieve fever, pain and other clinical manifestations of teething and blue gums, Viburkol suppositories are used. They are safe and used for very young children. Among the undesirable manifestations, diarrhea is noted in some cases.
Attention! If a child is bothered by an excessively high temperature, pain, severe swelling of tissues and redness or yellowing with pus, an infectious process may develop. In this case, it is necessary to immediately contact a pediatrician to prescribe urgent, comprehensive treatment.
If the blueness is large, the bruise and suppuration do not go away, and the child is unable to erupt a tooth, surgical treatment is resorted to. To do this, the area of blue or burgundy gums is anesthetized, the mucous membrane is dissected, and the hematoma and pus, if any, are removed. Finally, the wound is washed with antiseptic solutions and recommendations for further treatment and care are given.
Treatment of inflammatory gum diseases in children
To get rid of inflammatory and infectious processes, it is necessary to establish the type of disease that provoked it and eliminate them. For gingivitis the following are prescribed:
- rinsing with antibacterial and antiseptic solutions, if the child does not know how, then applications and wiping;
- application of gels with antimicrobial and antibacterial properties;
- choosing the right toothpaste and brush.
Gingivitis can be caused by insufficient, absent or poor-quality oral care. One of the treatment measures is to eliminate this factor by teaching the little patient the correct actions.
For stomatitis, antiseptics in the form of gels for local application and rinsing, painkillers, and regenerating medications are also used. Antibiotics can only be prescribed by a doctor.
How to treat bruised gums at home
One of the reasons for the appearance of a hematoma on the gum is that the child fell, tore off the mucous membrane and damaged it. In this case, for better healing, prevention or treatment of inflammation, rinsing with antiseptic solutions is necessary - Chlorhexidine, Rotocan, tincture of calendula, chamomile, sage, etc.
Medicines are prescribed in advanced cases, when in addition to bruising, high temperature, soreness of damaged tissue, and suppuration are a concern.
Hemorrhage and hematoma on a child’s gum can occur for various reasons: tooth decay, trauma, oral diseases. To eliminate the symptom, it is necessary to establish the provoking factor together with the doctor and follow his recommendations.
- P. I. Ivasenko - Emergency conditions in outpatient dental practice, M.: Medical book, 2009.
- Major M. Ash, Stanley J. Nelson - Wheeler's Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion - Saunders - 2002.
- Kuryakina I.V., Kutepova T.F. - Diseases, periodontal disease, N. Novgorod: NGMD, 2000.
- V. A. Zelensky, F. S. Mukhoramov. - Pediatric surgical dentistry and maxillofacial surgery, M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008.
- Persin L.S., Elizarova V.M., Dyakova S.V. - Pediatric Dentistry, Medicine, 2006.
- Vinogradova T.F., Maksimova O.P., Melnichenko E.M. — Diseases of periodontal and oral mucosa in children, M., 1983.
- Ralph E. McDonald, David R. Avery, Jeffrey A. Dean - Dentistry For The Child And Adolescent - Mosby - 2004
Source: https://DesnaZub.ru/detskaya-stomatologiya/sinyaya-desna-u-rebenka
Causes of tooth bruise
As with any mechanical impact, a tooth bruise can be caused by a number of reasons. There are several of the most common cases that can result in such an injury:
- In the process of playing sports, a tooth can be injured in an accident. For example, when playing football, the ball may fly out unsuccessfully and hit the child in the jaw area. Such an injury can be serious, and the bruise will be noticeable on the external surface.
- A car accident also often causes a tooth bruise. In a car accident, you can suffer a large number of injuries of various types. And even if everything turned out well at first glance, the child in any case must be taken to the doctor.
- Domestic trauma is perhaps the most common cause of severe injury. Moreover, it can be caused by a seemingly harmless object. Even careless use of the cup in some cases causes severe bruising of the teeth.
The most vulnerable teeth are the front incisors. In most cases, the impact falls on the upper teeth, this is due to their anatomical structure.
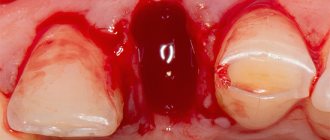
Hematoma on the gum. Teething bruise
Often, when caring for their teeth, people forget about their gums, but the health of the oral cavity depends on their condition. The appearance of a bruise on the gum causes confusion and fear and requires a mandatory visit to a specialist.
Causes of hematomas on the gums in adults
hematoma on the lower gum
Hematoma on the gum is not considered an independent disease. It is formed due to damage to small capillaries of the gums. Although the defect does not seem serious, in some cases it provokes serious problems with oral health and can lead to tooth loss. When a hematoma is accompanied by swelling and pain, it is necessary to urgently go to the dentist.
The reasons for the formation of a bruise are as follows:
- various effects of the dentist on soft tissues and teeth, drainage, installation of dentures;
- changes in blood pressure;
- congenital pathologies of blood clotting;
- injuries, blows;
- use of painkillers;
- inflammatory processes;
- a piece of tooth stuck in the gum.
Sometimes the cause of hematoma in adults is problematic wisdom teeth. When they do not have enough space in the jaw, adjacent teeth become displaced and the periosteum is damaged. Then the hematoma swells and hurts very much, the person suffers from high fever and weakness.
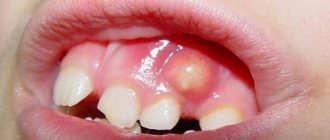
Bruise on the gum of a child during teething
hematoma during the eruption of the upper gum incisors before tooth eruption
Sometimes parents notice bruises on their baby's gums. The reason for their formation is careless games - for example, attempts to chew toys. However, more often in infants and older children, hematomas are formed due to teething. The child then suffers from the following symptoms:
- swelling of the gums;
- sleep disorders;
- copious amounts of saliva;
- appetite disorders;
- heat;
- weakness.
The baby chews on everything he can get his hands on because his gums itch. Baby teeth are not sharp enough to cut through the periosteum, so small vessels are damaged and a hematoma is formed.
This situation worries parents, because the sight is truly frightening, although often the intervention of doctors is not required.
You should be concerned if, when teething, the baby suffers from cough, stomach upset and other atypical symptoms.
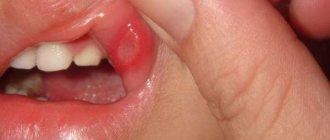
Symptoms of hematomas in the mouth, appearance, photo
The main symptom characteristic of bruises in the mouth is compaction in problem areas and darkening. The surrounding tissues swell, and the pain radiates to the jaw or cheek area. Possible high temperature, purulent inflammation, signs of poisoning. Experts divide the manifestations of this problem into two groups:
- The accumulation of blood in the gum gives it a bluish tint. The tissues increase in volume, the person feels uncomfortable and cannot close his mouth completely. There are problems with chewing and speech. These manifestations are typical for damage to dental pockets.
- If blood pours into the gum pockets, a round swelling is formed that spreads to the cheek from the inside. Such symptoms are often confused with gumboil: patients report severe pain, irritability, and abnormal facial shape. The gums tighten, fever and impairment are possible.
Bruised gums due to injury, inflammation of the gums
During the course of treatment, the disturbing symptoms are erased, and the cyanosis of the gums gradually disappears. A hematoma on the gum resolves in the same way as on other parts of the body. Usually the defect is corrected within a few weeks.
Why are hematomas dangerous?
Usually a hematoma is associated with teething or the actions of the dentist. When it appears on the gums of an adult, it is advisable to consult a dentist, since due to lack of space, the erupting tooth can cause big problems. In children, this process is harmless if there are no warning signs.
When a hematoma forms after an injection of painkillers, swelling and swelling of the tissue is quite normal. In a couple of days the gums will return to normal. If the size of the swelling increases or there is severe pain, a visit to the dentist is required.
Hematoma often occurs after tooth extraction in children and adults, installation of dentures, or cleaning of dental canals. In this case, the body reacts to a traumatic intervention. Healing is related to the scale of the “work front”, and dentists often recommend the use of special preparations.
Thus, the danger of this defect is directly related to its cause. Sometimes dangerous diseases lie behind a hematoma, so excessive swelling and pain should be an incentive to visit a doctor.
Methods for treating bruises on the gums
When bruises appear on the gums, people think that they will disappear spontaneously. Sometimes this happens, although if a bruise appears due to tooth extraction, it is unacceptable to ignore it. Causative agents of various diseases can enter the wound, causing pus to accumulate, fistulas and abscesses to form.
The doctor acts based on the extent of the damage. Occasionally you have to cut the gum so that the liquid comes out. They may install drainage to speed up this process. Be sure to rinse the problem area to kill bacteria. For independent use, the patient is prescribed:
- broad spectrum antibiotics (“Tetracycline”);
- means to relieve fever and pain (Nurofen, Paracetamol, Nise, Nimesil);
- rinse the mouth with antiseptics three times a day (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine);
- To get rid of discomfort in the gums, they use gels or ointments (Metrogil Denta, Kamistad).
Sometimes compresses are prescribed and kept on the sore spot for some time. With timely treatment, the bruise on the gum will quickly resolve and will no longer bother the patient.
How to avoid hematoma
It is impossible to completely protect yourself from bruising your gums. It is worth trying to strengthen the tissue structures of the oral cavity. First you need to learn how to brush your teeth correctly, in order to not only clean them of plaque, but also massage the soft tissues. Dentists advise using whitening toothpastes once a week.
It is useful to take a course of vitamins, especially in the off-season. The lack of useful microelements negatively affects the condition of teeth and gums.
The main method of prevention is systematic visits to the dentist. Preventive examinations allow you to promptly notice diseases of the oral cavity and prevent their aggravation. It is enough to carry out this event once every six months, and inflammation of the teeth and gums will not bother you.
If bruises are caused by other diseases, it is also better to treat them in a timely manner. It is important to alert your dentist to problems with blood pressure or blood clotting.
With the right approach to your health and a timely visit to a periodontist, a bruise on your gums will not cause any particular trouble. Reasonable use of medications and folk remedies will allow you to quickly get rid of a bruise, avoiding dangerous complications.
Source: https://DesnaZub.ru/simptomy/gematoma-na-desne
How is a bruise diagnosed?
How to behave if a child’s tooth has darkened after a blow? Try to remain calm, the child needs to be shown to the dentist urgently. The doctor will order an x-ray examination , based on which a diagnosis can be made. A visual inspection of the damaged area is also performed, the severity of the injury is determined and treatment is prescribed.
The attending physician will tell you how long it will last and by what means it will be performed. Be sure to insist on an x-ray examination, because only an x-ray can reveal all possible disorders and consequences that the injury could lead to.
An impact may result in a fracture of the tooth root, or significant trauma to the alveolar process . These injuries are dangerous and without appropriate treatment can cause irreparable harm not only to baby teeth, but also to permanent teeth.
The first days, treatment should take place under the close supervision of a doctor. The doctor continues to examine the affected area and at the first symptoms of tissue death, immediately removes the affected parts. This prevents further spread of necrosis.
Features of trauma in children
In a child, damage to a baby tooth can end sadly. This is due to the fact that their dental system is not fully formed. The only plus is that the injuries in this case are independent in nature and do not cause damage to other facial parts. Treatment of bruises in children is difficult, since young patients are not patient and are much more sensitive.
The most common injury in children is bruising of the front teeth, which occurs in 20% of cases. When injured, a child can lose several teeth at once, which is accompanied by serious aesthetic disturbances.
If treatment measures are not taken in time, there is a risk of developing an inflammatory process. This can stop the formation of the permanent teeth system and can cause a decrease in the functioning of the jaw structures.