The main causes of this pathology
As a rule, such a tooth is either not visible in the mouth at all or is barely noticeable. There are actually quite a few reasons for the occurrence of such an anomaly. The most common reasons:
- Weakened body due to persistent infectious diseases;
- Incorrectly selected artificial formula for the child;
- Delay in replacing baby teeth with molars;
- The influence of other diseases on the human body;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Incorrect location of molar buds in the jaw bone;
- The presence of additional or supernumerary teeth along the way.
- The walls of the dental sac are too thick.
In addition, the risk of this pathology increases with the removal of baby teeth, poor nutrition and a decrease in the body’s immune defense.
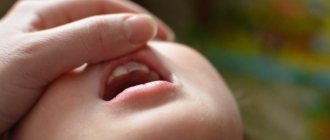
The fang grows on the gum
In pediatric dentistry, a phenomenon often occurs in which a child’s tooth grows in the gum and does not come out.
This anomaly of a temporary or permanent rudiment has a medical name - retention. What to do if a child has an unerupted tooth in his gums, and what complications may arise from dental retention.
What is tooth impaction? Kinds
Retention in dentistry is an anomaly of an already formed rudiment, in which an incisor or molar cannot erupt naturally and remains inside the gum in an incorrect position.
In modern dentistry, the following types of anomalies of germ eruption are distinguished:
The tooth grows under the gum and cannot be seen without the help of an x-ray. As a rule, such a problem is detected during a dental diagnostic examination, when there is already a problem with the bite and maxillofacial system.
With this problem, only the upper coronal part peeks out from the gum, while the neck and root are still under the gum. When examining the mouth, it may be observed that the tooth grows on the side of the gum or towards the oral cavity itself.
The position of the buds inside the gums in children can be different: vertical, horizontal, angular. In all cases, improper tooth growth causes discomfort and leads to unpleasant consequences.
Reasons for tooth growth into the gums in children and adults
A lying or abnormally growing tooth in adults and children can be the result of reasons such as:
- incorrect breastfeeding technique in infancy;
- removal of primary incisors and molars at a time when the rudiments of permanent teeth are not yet formed;
- inaccurate removal of temporary teeth and damage to the crown of permanent rudiments;
- hereditary predisposition;
- late or early replacement of milk teeth with molars;
- growth retardation of the upper palate of the mouth;
- pathologies of the development of the upper or lower jaw;
- initial incorrect location of the rudiment in the periodontium;
- Oral infections that prevent normal eruption of the bud.
Symptoms of abnormal tooth growth under the gum
Normally, children's teeth should erupt without any signs of inflammation or other pathological processes. Symptoms of dental retention may be as follows:
- the tooth lies horizontally in the gum and is not visible in the oral cavity;
- growth of the bud in the buccal, labial, palatal or lingual side;
- redness of the gums in the problem area;
- deterioration of health and increase in body temperature;
- difficulty opening the mouth (occurs in adults when the third molar erupts).
- aesthetic discomfort (with incorrect positioning of incisors and canines).
Complications when a tooth grows into the gum
Undiagnosed problems in time and ignoring retention lead to difficult-to-treat complications:
- Pericoronitis (pericoronitis).
- Localized periodontitis.
- Periodontitis (cyst).
- Abscess of the “hood” of an unerupted tooth.
- Periostitis (flux).
- Sinusitis.
- Bite disorders and changes in facial configuration.
Pericoronitis
As is already known, the most common complications of a horizontally growing rudiment in the periodontium are inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
Based on the volume of tissues involved in the inflammatory process, the complication can be limited and widespread. With limited inflammation, hyperemia of the gums is observed in the area of one incisor.
A common inflammatory process affects the periodontium near the entire dentition.
What to do if a tooth grows out of the gum
If a child’s tooth grows on the gum anatomically incorrectly, you should consult a dentist as soon as possible. At the first visit, a diagnosis is carried out, including:
- collection of patient complaints;
- examination of the oral cavity;
- targeted x-ray or orthopantomogram;
- lateral view of the jaw.
After receiving the examination results, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and refers the patient to an orthodontist or dental surgeon.
The goal of orthodontic treatment is to achieve an even and correct bite. Therapy includes several stages:
- Installation of a brace system and preparation of a place for an impacted tooth.
- Surgical removal of the underlying crown.
- Inclusion of the impacted germ into the bracket system.
- Pulling the tooth from the gum into the desired position.
Orthodontic treatment lasts from several months to 2 years.
If the molar lies in the gum and shows signs of inflammation, surgical treatment is prescribed, including:
- Conducting local anesthesia.
- Dissection of the gums and removal of the inflammatory focus using an instrumental method.
- Extraction (if the tooth cannot be saved).
- Application of suture material.
- Removal of suture threads 10–14 days after surgery.
For inflammatory processes, the patient is prescribed antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. Rehabilitation takes place under the supervision of the attending physician.
Prevention measures
If a tooth grows crookedly from the gum or does not erupt outward at all, you need to consult a dentist and take an x-ray. But in order to avoid growth abnormalities of molars and canines, it is recommended:
- During the period of embryonic development - maintain a healthy lifestyle, stop using antibiotics and other highly toxic drugs.
- During breastfeeding, follow all feeding rules.
- Start cleaning the oral cavity after the first primary incisor has erupted.
- From a young age, monitor the condition of the oral cavity and at the first signs of caries, consult a dentist for sanitation.
- Monitor the timing of the eruption of temporary and permanent buds. If necessary, start orthodontic or surgical treatment on time.
- Give up bad habits and carry out daily hygiene procedures with oral care products.
There is no need to wait for the embryo to move into the right place on its own. Without dental care, dental impaction can cause many serious complications that interfere with daily life and affect the appearance of the face.
A fang grows on a child’s gum
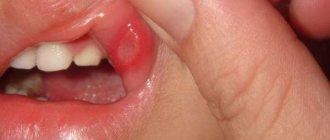
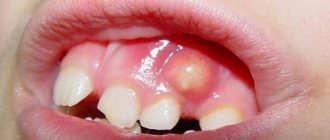
This is a common problem that occurs at any age. It does not always indicate the presence of a serious pathology, but requires attention. More often, the appearance of a tumor indicates that an infection has been introduced into the oral cavity from the outside. Considering the circumstances of exposure to an aggressive agent, children suffer from such dental disorders more often than other age groups.
Healthy gums should be pale pink in color without inclusions or swelling. It is not difficult to detect a growth, which in medicine is usually called a cyst. The disease looks like a dense, painful formation on the surface of the gum.
palate, tongue or inner cheek. As swelling develops, the inflamed area transforms into ulcers. Subsequently, a fistula is formed from the cavity of which the contents ooze.
This scenario for the development of the disease is extremely undesirable, as it leads to blood poisoning. Therefore, if a growth appears on the gum, this phenomenon cannot be left without due attention.
Immediately after detecting unpleasant sensations: a painful reaction when pressing, eating, or the formation of an inflamed lump in the oral cavity, you should immediately seek help from a dentist.
The reasons why growths appear on people's gums vary. Dentists divide them into groups. First of all, a growth found in the mouth indicates a malfunction of the human body. The following provoking factors are identified:
- weakened immune system;
- avitaminosis;
- unhealthy lifestyle (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- abnormal bite;
- presence of an infectious agent;
- single symptom of poisoning;
- formation of fibropapilloma;
- oral trauma;
- purulent abscess;
- advanced stage of periodontitis.
In addition, if a growth appears on the child’s gum. then unsuccessful teething or the appearance of the first milk tooth is added to the list. Children often get infections or injure the oral cavity, so of a number of reasons, these are in first place.
Types of anomaly
Not only adults, but also children can face this problem. This pathology occurs differently in each person with certain characteristics. Therefore, experts distinguish some of its varieties.
When it comes to baby teeth, there are 2 types of retention:
- In which all teeth erupted during time, except for the canines;
- The second type is often called prolonged retention, i.e. The interval between teething is quite long.
In childhood, as a rule, an impacted baby tooth or canine is not removed, even if it is crooked. If it poses a threat to the molar, then in this case another treatment is used.
If the tooth is completely hidden under the gum and cannot be felt when pressed, we are talking about complete retention. This means only one thing: the tooth is covered not only with gum tissue, but also with bone tissue. This anomaly occurs most often when a baby tooth is lost due to injury.
If a small edge of the tooth is visible, this is called partial retention. You will learn how this problem is solved below in the article.
Also, such teeth are classified according to their position to fully erupted teeth:
- Vertical;
- Horizontal;
- Angled or inclined.
In addition to this, there is one more situation that is extremely rare - a reversely impacted tooth, i.e. the root of the tooth faces the gingival margin, and the crown faces the body of the jaw bone.
How do you “stretch” impacted teeth with braces?
Impacted teeth are abnormally located teeth that cannot erupt into the oral cavity on their own and remain “sit” in the jawbone for years. To designate such an anomaly of the dental system, dentists use the term “retention” (translated from Latin as “retention”, “restraint”).
Many dental patients have had to deal with problems caused by impacted wisdom teeth. Unfortunately, not only the “eights” are susceptible to retention, but also the canines, as well as the lateral and central incisors.
Impacted teeth can be called a time bomb, as they can create a lot of trouble for their owner.
Impacted teeth are often detected by dentists in children. They are brought to the appointment by parents who have noticed that after a baby tooth fell out, a permanent tooth did not erupt in its place.
Quite often, the problem is revealed during medical examinations of children aged 11–12 years - when the eruption of permanent teeth is delayed.
So, if by this time there is still a primary canine in the oral cavity, the child is prescribed an x-ray.
The ideal option for diagnosing tooth impaction is an orthopantomogram. A panoramic photograph of the jaws clearly shows all the upper and lower teeth, located both physiologically and abnormally.
Some patients aged 20–30 years have baby teeth, the roots of which have not been resolved due to retention of permanent teeth.
Using an overview image, the doctor determines the type of retention, assesses the complexity of the situation and develops a treatment plan.
What are impacted teeth?
Retention of primary and molar teeth occurs for several reasons:
- with an abnormal location of the tooth germ;
- when there is not enough space in the dentition for tooth eruption;
- when a tooth is blocked by “neighbors” who have taken its place.
Depending on the complexity of the pathology, the tooth can be completely covered by gingival and bone tissue (full retention) or partially protruding from the gum mucosa (partial retention). It can be located in its place - vertically, horizontally or at an angle, or outside the border of the dentition (impacted dystopic tooth). Sometimes teeth even grow upside down.
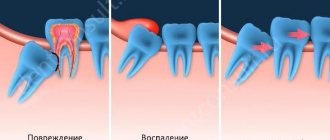
Why is retention dangerous?
A partially erupted tooth is covered with a “hood” of adjacent tissues, under which food debris collects and colonies of pathogenic microflora develop, which can provoke purulent inflammation. With complete retention, another problem arises: a tooth embedded in the tissues constantly affects its “neighbor,” causing it to move from its correct position. The situation may sooner or later become more complicated:
- caries of adjacent teeth and resorption of their roots;
- malocclusion, crowded teeth and other dental anomalies;
- pulpitis and periodontitis;
- periodontal cyst;
- pericoronitis (inflammation of the gingival “hood”) and its complication, periostitis;
- purulent lymphadenitis;
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve;
- abscess and phlegmon.
Therefore, when diagnosing retention, the patient is offered the optimal way to solve the problem.
What can be done about an impacted tooth?
- According to indications, based on the general clinical situation, removal of an impacted wisdom tooth may be recommended (especially for patients undergoing treatment with braces for an abnormal bite).
- In some cases, not accompanied by obvious problems, when removal is not necessary, the doctor will suggest observing the tooth.
- Healthy impacted incisors and canines located in the smile zone, subject to certain conditions, can be “pulled out” from the dental tissues and returned to the dentition.
How is impacted teeth treated?
The orthodontist and surgeon are involved in moving the tooth into the correct position.
- Preparatory stage. First, the patient is fitted with braces to create the currently missing space to place a tooth. During treatment, the dentition is aligned in parallel.
- The intermediate stage involves surgery performed under local anesthesia. By making a small incision, the surgeon exposes the surface of the crown of the problem tooth, glues a bracket to it, attaches a thin wire to it and sutures the wound. The wire will ensure contact of the “hidden” tooth with the oral cavity and the brace system. For speedy rehabilitation, a course of antibiotics and antiseptic rinses is prescribed. The patient must follow a certain diet and other recommendations from the dentist.
- The main stage begins a few weeks after the gums have completely healed. Using a wire attached to the bracket, in accordance with the drawn up program, the orthodontist slowly “pulls out” the impacted tooth, initially monitoring its movement using X-rays. A few months later, after the crown part of the tooth comes out of the soft tissues, the process becomes easier. By periodically re-taping the bracket, the orthodontist gradually moves the tooth to its intended place.
To avoid complications during treatment, it is necessary to conduct a full, thorough diagnosis to take into account the characteristics of the patient’s bite, facial structure, etc. In addition to an orthopantomogram, a teleroentgenogram in a lateral projection, and sometimes a CT scan, may be needed.
| Doctor: Sudzhaev Sergey Romanovich Patient age: 25 years Diagnosis: distal occlusion, transversal incisal occlusion, crowding of the frontal sections of the upper and lower dentition, edentulous teeth 1.4;2.4;3.4;4.4. Duration of treatment: 12 months Equipment: Clarity SL bracket system | TO THE DOCTOR |
| BEFORE | AFTER |
How to find us?:
Multi-line phone:
+7
Mon-Fri from 9 to 20
Moscow, Spartakovskaya Square, 14, bldg. 2 (entrance from Baumanskaya St., 13, bldg. 3)
Source: https://studia-ulybki.ru/pro-breketi/kak-vityagivayut-breketami-retinirovannie-zubi/
Symptoms
If we are talking about partial retention, then the area around the tooth becomes swollen and hyperemic. As a rule, pain occurs when palpating this part. The area around a semi-impacted tooth has a bright red tint.
If we are talking about complete retention, then this pathology is asymptomatic. As a rule, it is detected by X-ray examination. It is extremely rare that this pathology can be detected by the human eye - the main sign is protrusion of the gums.
If such a tooth begins to put pressure on neighboring ones, then their displacement and painful sensations may occur when chewing food or when opening the mouth.
Sometimes the patient's temperature may rise slightly and their health may deteriorate.
Possible consequences of this anomaly
Retention of a tooth or canine is a rather dangerous phenomenon, under the influence of which dire consequences can arise:
- Odontogenic cyst. This is nothing more than an inflammatory formation that is located in the jaw bones. If you do not contact a specialist in a timely manner, the cyst begins to grow, destroying bone tissue and covering other teeth.
- Displacement, loosening and loss of adjacent teeth.
- Swelling of the gums.
- Violation of facial aesthetics.
- Carious lesions of crowns.
- Pulpitis or periodontitis.
In order to prevent such complications, it is recommended to regularly visit the dentist.
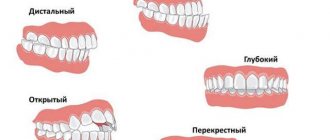
Types and features of retention
Nature provides that each tooth should come out at a certain time and in the right place. Increasingly, patients are turning to specialists for whom this system is failing. The next molar remains in the middle of the soft tissue or only a small crown is visually visible. The process can affect the primary incisor or fang and subside for many years.
Dentists distinguish two types of pathology:
- Complete: the tooth grows into the gum and is not visible without X-ray equipment. In many cases, the rudiment is formed in early childhood, completely unpalpable during palpation. The patient becomes aware of it when problems with bite or chewing occur.
- Partial: a whitish tip is visible on the surface. It can appear on the side of the main row or stand as a second stripe. The tooth grows into the gum
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Medical pad
Diagnostics
A semi-retinated fang is quite easy to detect; part of it is visible above the gum, and when you feel this area, you can clearly determine its contours.
But a tooth that is completely hidden under the gum during a routine examination is difficult to notice. We can only assume retention on the grounds that the tooth is taking too long to erupt. To confirm his suspicions, the specialist prescribes an x-ray examination.
As a rule, they carry out:
- Sight radiography, i.e. a small photograph of one tooth or group of teeth (3 - 4);
- Orthopantomography is a panoramic image in which you can see the condition of the roots of the teeth, as well as their rudiments.
In rare cases, a specialist prescribes a computed tomography scan; as a result of such a study, he receives a layer-by-layer image of the patient’s jaw. All drawings can then be combined into one overall image. It can be used to determine the position of the impacted canine in relation to other teeth.
In children, it is much easier to suspect retention; the main sign is the long eruption of permanent teeth.
Does your child's tooth grow incorrectly above the gum? what to do?
Does your child's tooth grow incorrectly above the gum? What to do?
This question should be asked at an appointment with an orthodontist. Even if someone shares their experience in solving a similar problem, it will be just someone’s example, nothing more. Since no two organisms are alike, the solution to even a similar problem is individual. The sooner you show your child to a specialist, the faster and more effective the treatment will be, and the more predictable the result.
In cases where any anomalies and disorders are detected, one should not delay visiting a doctor, because a child’s body is very plastic, and while it is growing, many problems can be solved easier and faster than in an adult.
It depends on how old the child is. If you are more than twelve years old, then you should contact an orthodontist; if you are younger, then you need to wait until all the baby teeth fall out. This usually happens if a baby tooth is removed ahead of time and the place that was supposed to be preserved thanks to it is closed, and the permanent tooth is looking for another place to come out. But while the jaw is growing, everything can form on its own; if not, then it can be corrected.
Of course you need to see a dentist. Now there are many ways to correct the direction of tooth growth in children and others. The most important thing is that this needs to be corrected at a young age, otherwise it will be painful.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Yellow coating on the tongue temperature
Most likely, dentists will recommend braces. As a last resort, they suggest removing the tooth because there is not enough space for the tooth above the gum. But it’s unlikely that anyone will want this, and the consequence is that the teeth will corrode and there will be a chip. If the tooth has just begun to grow, you need to quickly resolve the issue with braces, i.e. when all the teeth grow in, it will remain above the gum.
If the teeth are baby teeth, then there is nothing to worry about. If they are permanent, then see a dentist. Now there are many methods for straightening teeth, fortunately medicine has even come to this in Russia.
Contact your dentist; most likely your child will need to wear braces so that he has beautiful and straight teeth. Also check the child’s age, whether it is a baby tooth or a molar. I don’t think they will do anything with the milk, but with the indigenous it already needs adjustment, correction and treatment.
I can’t advise anything other than the fact that you urgently need to go to the dentist. Only from a dentist can you get high-quality, qualified care, and if a child is afraid to go to the doctor, don’t give in to his whims and urgently take him to the hospital, he will also thank you that He has grown such even and beautiful teeth.
It all depends on how old the child is and what kind of tooth is growing, milk or molar. My child’s teeth came out wrong a couple of times, very high. These were real teeth, molars, and they climbed high - because there were milk teeth below (they took up space and did not let the molars in). In this case, you need to pull out the baby tooth.
We went to the dentist at the clinic, where we had a baby tooth removed, and subsequently the molar fell into place on its own, without braces. Another time, when a molar tooth was also coming from above, we did not go to remove it; the child himself gradually loosened the milk tooth and pulled it out, making room for another tooth. Now everything is smooth. In any case, of course, you need to see a dentist, the matter can be fixed, but only he can give qualified advice.
Is it necessary to remove such a tooth?
If the dentist discovers such a pathology, then he builds an algorithm for his work, which is individual in each specific case. Contacting a specialist in a timely manner will help you save time in the future when troubleshooting more serious problems.
If such a pathology is detected, the specialist makes one of the following decisions:
- Save the tooth;
- Pull it out;
- Delete.
This pathology is a source of serious complications, so you should not delay going to the dentist. It is recommended to visit a specialist at least 2 times a year.
Pull
If, according to the results of the examination, it turns out that the roots of a vertically located canine have not yet formed, then it may well erupt on its own: it is enough to just eliminate the reason that prevents it from doing this. Such reasons include additional or supernumerary teeth or retained milk teeth. Both are removed.
To activate the eruption process, the following methods are used:
- Massage the tooth root area with your fingers;
- Electrophoresis and lidase injections;
- Vacuum massage and vibration massage;
- Laser stimulation.
After the canine has erupted, if there is not enough space for it, treatment is carried out to expand the dentition.
If the roots of such a tooth were fully formed, but eruption did not occur, then in this case the canine is pulled out with the help of braces.
Treatment plan
Correcting malocclusion caused by the presence of impacted teeth is a complex task, the solution of which can only be in the hands of an experienced orthodontist. By removing an impacted tooth, the problem cannot be completely solved. Depending on the situation, you will need to install an implant or undergo orthodontic treatment. A thorough examination of the patient, which includes
- orthopantomogram;
- teleroentgenogram;
- creation of diagnostic models.
The further treatment plan for an impacted tooth usually includes a surgical and orthopedic stage. The surgical intervention consists of creating an incision in the gums at the site of projection of the impacted tooth in order to gain access to it. At this same stage, the bracket is glued to the tooth.
Removal
The reasons for removal are: tooth dystopia, lack of space in the dentition, inflammatory processes and formations, additional or supernumerary teeth, as well as destruction of the neck of the tooth.
- This operation differs from conventional removal in its complexity. Before her, the specialist checks the tolerability of the drugs that he will need during the operation.
- If inflammation is detected, then antibacterial therapy will be required. Sometimes the patient may be prescribed sedatives.
- Before the process begins, the patient is given anesthesia (both local and general are used). This procedure lasts about 2 – 3 hours.
- The specialist cuts the gum.
- Using a special device, a small hole is drilled to provide access to the root.
- Removal of a tooth.
- Cleaning and treatment of the cavity.
- Applying a suture.
- Prescription of special medications by a specialist
- Re-appointment after a few days.
- Removing stitches.
In the future there is a long process of rehabilitation. The first weeks after such an operation are accompanied by pain. But they can be reduced by simply following simple rules and recommendations. You can apply ice to your cheek to reduce swelling. If the pain cannot be tolerated, then you must take painkillers. To quickly restore tissue, a day after surgery you can use special rinsing solutions. Do not apply any warm lotions or compresses. It is also recommended to refrain from visiting saunas for several weeks.
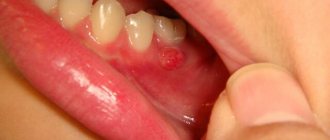
Signs of tooth growth into the gum
In the vast majority of identified clinical cases, the growth defect begins in infancy. The first manifestations begin during the period of active eruption of baby teeth or their replacement with permanent ones. Parents notice a strong delay in the emergence of the next incisor and see a double row of molars.
The second problematic point: the pathology of the development of wisdom teeth that erupt in adolescents or adults. By the time they appear, the jaw has already been formed and there may simply not be enough space to accommodate such large formations. Eights have to make their way through periodontal tissue and bone, so complications are quite common.
Retention can go unnoticed for a long period even with careful hygiene. The main symptoms of pathology indicating the formation of a dental defect:
- In place of a molar or baby tooth, an empty hole remains; the incisor breaks through only a few millimeters. The impacted tooth may come out at the base of the row closer to the roots, “looking” at the inner surface of the cheek or tongue.
- The gums may become swollen and red, and become very swollen. At the site of the apex, a compaction or lump appears, resembling a purulent fistula.
- Against this background, the temperature rises, and there is general weakness or burning. The patient cannot get enough sleep and eat food. The tooth grows into the gum
The process is especially difficult when cutting through eights. They are larger and do not have a sharp top, so they go hard. They seem to make their way and can damage blood vessels, injure periodontal tissue and cause acute pain. It is poorly relieved even by the most effective analgesics and is aggravated by touch.
Cost of the procedure and contraindications for removal
Each clinic sets its own price for such an operation. Approximately it ranges from 1 – 5 thousand. And also do not forget about the cost of consultation and photography.
There are a number of contraindications to such an operation: pregnancy, menstruation, the presence of viral diseases, cardiovascular pathologies. You should also not have surgery if you are taking a course of antibiotics.