What is malocclusion surgery?
Correction of a jaw defect using surgery is called orthognathic. The procedure includes a series of sequential actions that restore the symmetry of the joint and increase its performance. This method of intervention is considered the most effective, in contrast to wearing corrective systems (braces, brackets or plates), since it gives an instant effect.
In medicine, this operation is called osteotomy. This means that during the intervention, bone structures are dissected. After this, not only the jaw, but also soft tissues are transformed. Osteotomy allows you to lengthen the bone or make it shorter, correct the proportions of the chin or prepare the dental system for further intervention.
The operation has some age restrictions, and this criterion depends on the individual characteristics of the patient. Osteotomy is performed only after complete formation of the jaw structures. On average, this process is completed by 18-19 years of age.
Therefore, malocclusion surgery is recommended only for adult patients. In children and adolescents, defects in the dentofacial system are treated using more gentle techniques - special gymnastics, wearing corrective plates.
On this topic
- Bite correction
All about bite trainers
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 4, 2020
Thanks to modern equipment, surgery is performed quickly and painlessly for the patient. If you refuse surgery, bite defects may worsen and manifest as additional pathologies.
Among the complications of the problem, it should be noted: complete loss of dentition, significant impairment of diction, the appearance of pain in the jaw, inflammation of the gums, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract due to poor digestion of food.
Causes of open bite
The reasons that cause the formation of an open bite are very diverse. This could be unfavorable heredity, various diseases of a woman during pregnancy, harmful influences that led to the incorrect position of tooth buds, jaw deformities, cleft lips and palate.
In the postnatal period, the leading causes of open bite are considered to be rickets, hypovitaminosis, mineral metabolism disorders, early removal of baby teeth, nasal breathing disorders (adenoids, nasal polyps, allergic rhinitis, deviated nasal septum). Often, an open bite in children occurs as a result of such bad habits as thumb or toy sucking, prolonged pacifier sucking, nail biting, or sticking out the tongue between the teeth.
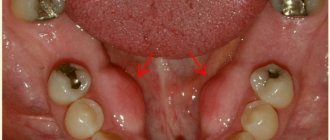
Dental retention, late eruption, absence of teeth associated with early loss, and shortened frenulum of the tongue also play a negative role in the occurrence of open bite.
Some scientists believe that the cause of an open bite is the insufficient density and hardness of the foods that a person eats. The human chewing apparatus simply does not receive the load that nature provides for it, and therefore develops poorly.
Methods
Surgery is used in several cases.
For the treatment of open anterior bite
The technique is carried out with the aim of giving a normal position to both jaws. To do this, the specialist first makes an incision in the upper jaw, in the area of the nasal septum and the base of the bone structure. Then, part of the jaw is excised from the distant side and moved to its normal anatomical position.
This procedure allows you to achieve closure of the incisors of the same name. The doctor fixes the jaws with mini-plates that are held on by screws. In most cases, this type of intervention is not accompanied by further complications.
For correction of lateral bite
The technique of distraction osteogenesis is used. Surgery can restore the normal size and shape of the jaw structures or remove some segments of bone.
First, the specialist performs a fracture in the area where the defect is observed, and then shifts the elements of the jaw until the teeth of the same name are completely closed. At the last stage, the doctor installs correction plates that stimulate bone tissue growth.
To eliminate chin dysplasia
The intervention begins with a soft tissue incision. After opening access to the bone structures, the jaw is completely opened. The surgeon achieves the normal position of the structures by installing titanium plates.
For the treatment of deep bite
Before the intervention, long-term therapy with orthodontic structures is carried out. In severe cases, the doctor may decide to remove one or more teeth.
Classification of open bite
Depending on the cause of occurrence, rachitic and traumatic open bite are distinguished. Rachitic or true open bite is caused by inferiority of the jaw bones. Traumatic or false open bite is caused by bad habits. Depending on which teeth in the patient do not close, an open bite can be frontal or lateral, unilateral or bilateral.
The extent to which the open bite is pronounced is judged by the height of the gap that has arisen between the dentition and the number of teeth that do not close together. Based on this, they distinguish:
- I degree - vertical gap reaches 5 mm, lack of contact in the area of the front teeth;
- II degree - the vertical gap has a height of 5 mm to 9 mm, lack of contact is observed in the area of the anterior teeth, as well as premolars;
- III degree - the vertical gap exceeds 9 mm, lack of contact is observed in the area of the anterior teeth, as well as premolars and first molars.
An open bite can also be symmetrical or asymmetrical. In addition, there are mandibular, maxillary and combined forms of open bite.
Indications and contraindications
The following problems are indications for bite correction:
- inability to bite food;
- defects ;
- swallowing dysfunction ;
- imbalances leading to an abnormal condition;
- unnatural proportions between the jaws;
- supernumerary elements;
- unnatural arrangement of teeth in the oral cavity;
- injuries resulting in facial asymmetry.
On this topic
- Bite correction
6 effective methods for correcting deep bites
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 4, 2020
Among the contraindications to the procedure, the following should be noted:
- age under 18 years;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- diabetes ;
- weakening defenses ;
- infection ;
- oncological diseases;
- problems with clotting ;
- tuberculosis;
- neurological abnormalities.
In case of diabetes mellitus, surgery is not prescribed due to the fact that the disease will contribute to slow tissue healing after the intervention. In exceptional cases, surgical correction of the bite is prescribed in childhood, for example, if other correction methods do not produce results or if the problem is significant.
Symptoms of an open bite
An open bite has a number of distinctive features - facial, intraoral and functional.
Facial signs (symptoms) of an open bite include a clearly elongated lower third of the face, a sloping chin, an open or half-open mouth, and a smoothed chin fold. The upper lip in such cases is flaccid and shortened. It does not close with the bottom. From under the lip you can see the lower edges of the front teeth and the tongue covering the gap between the teeth. Sometimes the patient tries to compress his lips tightly to hide his aesthetic defect.
The main oral sign of an open bite is the lack of contact of the frontal or posterior teeth with the opposing teeth and the presence of a gap of different sizes between them. In the case of a traumatic open bite, the shape of the gap can repeat the position of the object that the child is used to holding in the mouth. With an open bite, the anterior teeth are usually crowded, often affected by caries, have signs of insufficient enamel development and an uneven contour of the incisal edge. There are multiple dental deposits on the teeth (plaque and tartar). Often, a patient with an open bite experiences swelling, bleeding, and proliferation of gingival papillae, which indicate hypertrophic gingivitis.
Functional disorders that accompany an open bite include difficulties experienced when biting, chewing, swallowing food, mouth breathing, and speech disorders. Violation of the chewing process leads to the development of periodontal disease and TMJ dysfunction. The main defect in sound pronunciation is considered to be interdental sigmatism. In addition, with an open bite, the pronunciation of lingual and labial phonemes also suffers. Asymmetry and narrowing of the dental arches leads to changes in the bottom of the nasal cavity, the shape of the upper palate, and disruption of the development of the paranasal sinuses. Mouth breathing leads to dryness of the oral mucosa.
Stages of the operation
Osteotomy is performed in 3 stages:
- Preparatory measures, during which the patient is prescribed the necessary tests, and computer modeling of the jaws is performed.
- Surgical intervention.
- Recovery period.
On this topic
- Bite correction
Effective ways to correct your bite
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 4, 2020
Before osteotomy, patients are prescribed a comprehensive examination, including:
- X-ray to assess the severity of the defect and its type;
- MRI of the deformed area to determine the general condition of soft tissues and identify inflammatory processes in them;
- ECG, which determines the preferred type of anesthesia (under general or local anesthesia);
- laboratory blood examination - biochemical analysis, coagulogram;
- Ultrasound;
- detailed blood test.
If necessary, consultation with highly specialized specialists is required - neurologist, endocrinologist, etc. The preparatory stage, in addition to diagnostic measures, also includes:
- discontinuation of medications containing heparin and aspirin;
- cessation of drinking alcohol and smoking;
- Stop eating and drinking 12 hours before the intervention.
Before osteotomy, patients should warn the specialist about their existing health problems. Any pathologies suffered in the past may affect the choice of pain relief method and surgical technique.
Computer modeling is performed using a special computer program. During the procedure, the contours of the face are given a new image, which surgeons will focus on during the operation. This technique provides a greater guarantee of successful therapy.
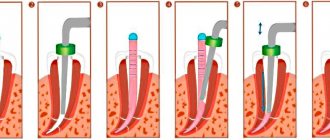
The operation itself occurs in stages:
- Consultation with an anesthesiologist regarding the patient’s allergies to injected drugs.
- Carrying out pain relief.
- Making incisions in the oral cavity using special surgical instruments. This is how the doctor opens access to bone structures.
- Correction of position . The surgeon moves the bone into the desired position and secures it with plates and screws.
- Splinting . This device is worn for 14 days. The splint is used to ensure that the jaws quickly adapt to the new location relative to each other.
Often, surgery to correct the bite is complemented by wearing orthodontic devices. The need to wear a mechanism depends on the condition of the bone structures, including teeth.
Prognosis and prevention of open bite
The best results in open bite correction are achieved if treatment and the use of appliances are started at an early stage. In this case, it is possible to improve facial features, achieve normal jaw development, and relieve the young patient from psychological worries. A traumatic open bite can be eliminated much faster and easier than a true bite.
Prevention of open bite consists of preventing the pathology of pregnancy, proper nutrition of the expectant mother, organizing breastfeeding of the newborn, preventing rickets, ridding the child of the habit of sucking a finger, pacifier or toy, and ensuring free nasal breathing. To prevent open bite, it is very important to control the eruption of teeth, as well as to carry out timely treatment of caries and prosthetic teeth in their absence.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is the longest stage of treatment. It begins from the moment the patient is splinted. The bandage is designed to limit jaw movement.
On this topic
- Bite correction
Details about vestibuloplasty
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 4, 2020
When wearing a bandage, the patient must adhere to certain rules:
- do not open your mouth wide;
- stop eating solid foods;
- chew food slowly and thoroughly
- Don't blow your nose too harshly.
During the recovery period, patients are recommended to take antibacterial agents (the first 3-5 days after surgery). Without antibiotics, it is difficult to prevent the development of an infectious process in the body.
The doctor removes the stitches 2 weeks after the intervention. Screws are removed 4-5 months after correction of the malocclusion.
During the first time after osteotomy, patients feel discomfort during conversation and notice bruises on the face. During the rehabilitation period, oral hygiene may also be difficult.
However, all these problems gradually disappear as the patient adapts to the new arrangement of the dentofacial apparatus. Surgical operation to correct the bite gives excellent results and is becoming more and more popular every year.
Artistic or composite restoration
In composite teeth whitening, a thin layer of a very light-colored composite material is applied to the outer surface of the tooth. In this case, the tooth is not treated with burs! In order for the composite material to adhere to the surface of the tooth enamel, it is first etched with a weak acid for 1 minute.
In this case, the enamel does not suffer, since the etching depth is thousandths of a millimeter. An adhesive (glue) is first applied to the tooth surface, then a thin layer of composite material of the desired shade is laid out. At this stage, a lot depends on the doctor’s skill. The layer of material must be uniform so that the tooth color is the same everywhere.
DETAILS: Straightening teeth with braces in a year
Typically, the service life of composite teeth whitening is 5 years. Then you can update the coating or remove it.
The beauty of the technology is that under the layer of artificial enamel, the tooth’s own enamel remains untouched, so you can always return to its original state without harm to your own teeth. If necessary, the layer of composite material is removed with special silicone heads that are not capable of damaging the enamel of a natural tooth.
- You can choose any of 20 shades of white
- The tooth is not ground down
- Snow-white smile in 3 hours
- Color does not change over time
- Low cost
- Safety for enamel
- You can hide enamel imperfections
- You can slightly adjust the shape of your teeth
Restorative teeth whitening is especially in demand among newlyweds, when there is no time and money for full-scale dental restoration or veneers, but in photographs they want to show off a snow-white smile. In just 3-4 hours you can become the owner of a snow-white smile without harm to your teeth. Or these are patients before some important event in their life - an anniversary, an award presentation, etc.
Let's look at a few examples of composite teeth whitening together.
Until now, artistic restoration of teeth is confused with extensions due to similar technologies, but these are two fundamentally different procedures. The restored tooth will look like new, but things rarely go beyond aesthetics - chewing functions are partially restored, which imposes a number of restrictions on nutrition and lifestyle.
Teeth are restored in two ways:
- The direct method is similar to veneers, when a composite material is layered onto the problem area in one visit to the dentist.
- The indirect method is the installation of ceramic overlays.
The main pitfall of restorations is a large number of contraindications:
- Bruxism.
- Increased salivation.
- Severe bite distortions, especially deep and cross bites.
- Allergy to materials used.
The restored tooth will require special care and enhanced daily hygiene. If this is not done, even an expensive porcelain overlay will begin to darken, crack, and deteriorate within a couple of years.
Risks and complications
A whole team of specialists is working to eliminate bite pathology, so the risk of developing side effects after the intervention is minimal.
In addition, to prevent negative consequences, the operation is supplemented with drug therapy. Before the intervention, the patient is carefully examined for any contraindications to the procedure, and the anesthesiologist selects the drug for each individual case.
Despite the competent actions of doctors and diagnostic measures, the following consequences are possible after osteotomy:
- Swelling of soft tissues. The sign most clearly manifests itself 2-3 days after the intervention. After this, the swelling gradually subsides, and the face acquires new contours.
- Nausea and weakness. This is how the body reacts to the administration of anesthetic drugs used for general anesthesia.
- Painful sensations. The symptom is typical for any type of surgical intervention. Therefore, it is more correct to consider this symptom as an inconvenience after surgery, rather than a complication.
- Inflammation of soft tissues. The sign may indicate the development of an infectious process in the operated area or displacement of the dentofacial apparatus.
- Difficulty speaking. Serious speech problems require the help of a speech therapist. The defect, which appears to a minor extent, disappears on its own.
- coming apart . If there is a significant discrepancy in the material, the doctor may prescribe a repeat procedure for securing the tissue.
Diagnosis of open bite
The diagnosis of an open bite is made by a doctor based on an examination of the patient. During the initial examination, a conversation is carried out with the patient, a visual assessment of the signs and degree of open bite, and measurement of the distance between the antagonist teeth. To establish the shape and degree of open bite, a photometric examination of the face is performed, orthopantomography, and TRG of the head with X-ray cephalometric analysis are performed. If a patient with an open bite has speech defects, he is prescribed a consultation with a speech therapist. If nasal breathing is impaired, there is a need to consult an otolaryngologist.
Dangers of surgery
Any operation is a risk to life: you can never be 100% sure that during the procedure no unforeseen and unpredictable events will occur due to technical features, anatomical anomalies or complications that arise. Any surgical treatment can cause the following dangerous situations:
- bleeding of varying severity;
- pulmonary embolism;
- traumatic shock;
- infectious and inflammatory complications;
- damage to neighboring organs;
- sudden death due to cardiac arrest.
Often a person experiences greater fear before anesthesia (what if I don’t wake up) rather than before an operation: the risk to life during anesthesia is much lower than during surgery.