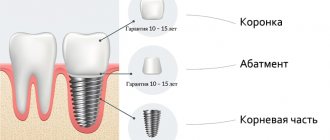
Surgical dentistry is not only about removing complex teeth. This area of medicine includes several other important procedures necessary for the treatment of the dentition. It is closely related to orthopedics and traumatology, as well as implantation and treatment of periodontal disease.
The dental surgeon provides assistance to maintain the healthy condition of the tissues of the oral, cervical and maxillofacial area. Operations in surgical dentistry are quite complex, and therefore require highly qualified doctors, as well as timely execution. The latter depends on the patient, who should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
What problems does surgical dentistry solve?
Surgical dentistry is a dental specialty in which more radical methods of treatment are practiced: tooth extraction operations, bone grafting, preparation and direct implantation of teeth, surgical treatment of inflammatory diseases, etc. Depending on the tasks performed, surgical dentistry is divided into several sections:
- purulent,
- traumatology,
- oncology,
- plastic (reconstructive).
The most common type of procedure in dental surgery is tooth extraction. If conservative treatment is ineffective and there are indications for removal, then the dental surgeon professionally, quickly and painlessly removes the necessary tooth. Removal is resorted to when a wisdom tooth has erupted incorrectly or is in the way.
Another common reason for the use of surgery in dentistry is inflammatory diseases of the teeth and the oral cavity as a whole. They are represented by a very extensive list:
- alveolitis;
- abscess or boil;
- phlegmon;
- maxillary osteomyelitis;
- periodontitis and periodontal disease;
- complicated stomatitis, etc.
Follow all doctor's recommendations
If you take all the medications prescribed by your doctor in a strictly prescribed dosage, you will easily be able to avoid inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, as well as serious diseases. But in addition to medications, you should comply with a number of other requirements regarding your own health. For example, if a patient has a high temperature for several days after surgery, you should not wait until it goes away on its own or constantly bring it down with improvised means. First of all, you need to seek help from a doctor. An experienced dentist in Minsk will determine and eliminate the cause of the inflammatory process, neutralize the wound and help maintain healthy teeth and avoid complications. It is also necessary to contact your doctor if the prescribed medications do not help or cause side effects.
Surgical dentistry services
Surgical dentistry involves not only planned, but also emergency care for the patient when he is diagnosed with life-threatening disorders: injuries, acute inflammation, shock, bleeding. Planned interventions are carried out only after a comprehensive diagnosis, which helps to identify the problem and determine exactly how to eliminate it.
- treatment of alveolitis after tooth extraction;
- bone grafting of the alveolar process;
- solving problems with abnormal dental development;
- removal of impacted teeth that cannot erupt properly;
- elimination of infectious diseases of the salivary glands and tissue inflammation;
- treatment of pathologies of maxillofacial fibers;
- fight against tumor diseases of the oral cavity;
- congenital or acquired defects of the oral cavity;
- treatment of injuries to the jaws or soft tissues in the oral cavity.
Surgical dentistry is associated with periodontitis, since tooth extraction surgery is one of the methods of treating the disease. Alternative therapy may include resection of the root apex or amputation, hemisection of the tooth, or coronal-radicular separation.
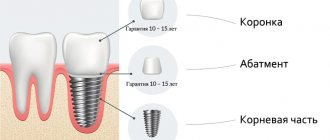
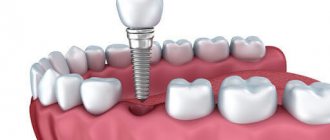
After dental implant surgery
After surgery to install an implant, it is important to follow recommendations that are developed taking into account dental practice and have a positive effect on the healing process. Your dentist will tell you how to lead a healthy lifestyle after implantation. The recommendations you will receive from your doctor mainly cover the rehabilitation period during the first week. What should we remember during this period?
If you are driving, you should avoid participating in road traffic after surgery. Why? The thing is that anesthesia actively affects a person’s physical condition. Side effects such as confusion, dizziness, headache, etc. may occur. It's better to call a taxi or get home by public transport.
Pain after surgery is normal. Therefore, if you experience unpleasant pain after anesthesia, you should take painkillers prescribed by your doctor. Cool painful areas only on the outside of your face. Before using the cold pack, wrap it in a towel. Do not rinse your mouth with cold water or apply ice cubes to the wound.
Light bleeding in the mouth after surgery is also normal. Don't be nervous or stressed about it. Such bleeding is very rarely life-threatening. By cooling the wound site and resting, it usually goes away within six hours. Also keep in mind that mixing blood and saliva creates the impression of more severe re-bleeding. But this is not true at all. If this bothers you, insert a swab pre-treated with an antiseptic on top of the wound and bite it lightly.
Swelling always occurs after oral surgery. It disappears within two or three days. How to deal with swelling? Cool the surgical site with ice. Minimize physical activity and avoid strenuous exercise, as this can cause swelling and re-bleeding. Be aware that swelling increases at night. This is a normal reaction of the body to the warmth of the bed and body position.
Eating immediately after surgery should be avoided. In the future, you should follow a soft and liquid diet, that is, consume foods in liquid and soft form. Drinking alcohol, coffee, cola, and black tea is strictly prohibited.
Eight hours after surgery, it is recommended to thoroughly rinse your mouth with a disinfectant liquid or an aqueous solution with an antiseptic. Rinse should be repeated two or three times a day. This should be done very carefully. Otherwise, the first protective fibrin (blood clot on the wound) may be washed away and re-bleeding will begin. Use an electric toothbrush and oral irrigator if possible
After surgery, smoking is strictly prohibited. Smoking reduces blood flow to the wound and weakens the body's defenses. Toxins actively interfere with the healing process. It is necessary to abstain from smoking for as long as possible.
After successful implantation, do not forget that poor oral hygiene is the main reason for denture failure. Implant dentures must be cleaned with dental floss and brushing at least twice a day. In addition, it is necessary to carry out cleaning (up to four times a year) at an aesthetic dentistry center. This will help you keep your gums healthy and extend the life of your dentures.
Prices for surgical dentistry
| Removal of a tooth or root of the first category of complexity | RUB 3,490 |
| Tooth extraction of the second category of complexity with PRF | RUB 13,490 |
| Flap surgery, open curettage for periodontitis (sector) | RUB 34,990 |
| Raising the floor of the maxillary sinus (open sinus lift) | RUB 59,990 |
| Splitting of the alveolar ridge | RUB 44,990 |
| Consultation with a doctor (physical examination, analysis of studies, drawing up a treatment plan) | 3,000 rub. |
| Clinical tests "Hospital surgical complex" | 4,900 rub. |
*Draw your attention to!
This price list reflects the most basic items of medical services **Information on the full list of medical services and details can be obtained from the medical registrar.
The price list shows prices for tooth extraction and other basic surgical procedures that are performed most often. The cost may depend on many factors, including the complexity of the clinical case and the materials needed to restore the tooth structure.
Thus, the price for removing a wisdom tooth may differ depending on the condition: it has not erupted, is in the wrong position, has not fully erupted, or may have caused inflammation. This determines the list of manipulations that the surgeon will need to perform to remove the tooth, and these, in turn, make up the final cost. The same principle is used to determine other prices for dental surgery.
Avoid bleeding
The first few days after dental surgery, the patient may observe a pinkish tint to his saliva - in fact, this is a normal phenomenon. But if there is bleeding for a long time that does not go away, and usually it should last no more than a couple of hours from the moment of surgery, you need to contact your doctor. Of course, the cause of this phenomenon may be medications taken (aspirin, etc.) that affect the blood clotting process, but in any case, prolonged bleeding in the oral cavity is not normal. To avoid this phenomenon, try not to injure the wound after the operation: do not overdo it with rinsing your mouth with water, do not smoke at first, and try to eat on the other side (the one that did not undergo the operation), under no circumstances touch the wound with your hands, and even more so, don't pick at it. This can not only provoke repeated bleeding, but also cause an infection, which can lead to serious consequences. By the way, you should not brush your teeth or rinse your mouth during the first 8 hours after surgery!
Treatment of alveolitis
Alveolitis , or inflammation of the tooth socket after extraction, most often develops when the patient does not comply with the rules of oral care after tooth extraction surgery. If you suspect alveolitis, you should immediately contact the clinic, since the inflammatory process can spread to soft tissue, bone, and maxillary sinuses (when removing maxillary molars and premolars).
Symptoms after tooth extraction, in which you need to immediately consult a doctor:
- Pain in the socket persists for several days.
- There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- The gums and cheek on the side of the extracted tooth swell.
- The wound does not heal, pus is released from it.
- Appetite worsens, chewing food becomes difficult.
- Body temperature rises.
>
How is alveolitis treated:
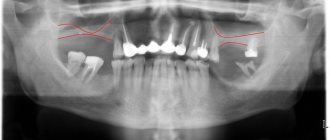
- The surgeon conducts an initial examination and sends the patient to the X-ray room. An X-ray helps to clarify the cause of the inflammation if it is caused by tooth fragments or a previously undetected root cyst.
- After making a diagnosis, the doctor performs local anesthesia.
- Treatment of the hole with antiseptics, removal of necrotic masses, bone fragments, cysts.
- After the hole is cleaned, the surgeon installs a turunda soaked in a medicinal composition into it. The patient goes home.
The treatment of the hole is repeated if necessary, and the dentist’s office is visited several times until the inflammation is eliminated and the healing process begins. Our doctors explain to patients in detail the rules of oral care during the treatment period in order to speed up recovery.
What are the dangers of malocclusion?
People with malocclusion suffer from pathology every day. According to statistics, deficiency is observed in 80% of the world's population. In some situations, the defect is purely an aesthetic imperfection, but sometimes its presence entails functional and psychological problems.
DETAILS: What is dental implantation and how is it done?
If serious bite correction is required, a specialist may resort to surgery. For uncomplicated pathology, removable and non-removable systems are sufficient. An inharmonious bite often becomes the cause of self-doubt and complexes. At the physiological level, there is increased sensitivity of soft tissues and an increased risk of injury.
The situation can be aggravated by the appearance of problems with the gastrointestinal tract, since food often does not receive proper processing in the oral cavity and enters the stomach in “piecemeal” form. Today, bite treatment is used by orthodontists in any age group. With a properly prescribed set of procedures, the deficiency can be eliminated easily and painlessly. Even if a surgical method is used, the use of anesthesia in a difficult situation neutralizes pain impulses.
DENTAL SURGERY PRICES
Tooth extraction according to complexity: | |
| Removing a baby tooth | 1 500 |
| Tooth extraction of 1st category of complexity | 2 500 |
| Tooth extraction of 2nd category of complexity | 3 500 |
| Tooth extraction of 3rd category of complexity | 5 800 |
| Removal of impacted-dystopic tooth according to complexity: | |
| Removal of impacted-dystopic tooth of category 1 | 8 000 |
| Removal of impacted-dystopic tooth of category 2 | 10 100 |
| Removal of impacted-dystopic tooth of category 3 | 11 750 |
Postoperative wound treatment: | |
| Alvogil, neo-cone, iodoform tampon | 165 |
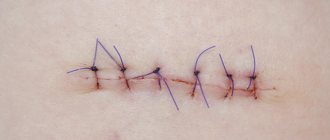
| Suturing the tooth socket | 690 |
| Layer-by-layer suturing of a postoperative wound with the application of a continuous periodontal suture | 2 210 |
| Antiseptic treatment of a postoperative wound | 210 |
Treatment of purulent inflammatory disease: | |
| Opening a category 1 abscess | 1 660 |
| Opening abscess category 2 | 3 450 |
| Opening abscess category 3 | 4 850 |
| Wound drainage | 85 |
| Washing the wound with an antiseptic solution | 70 |
| Using an antiseptic dressing in the form of gel/sentopok | 210 |
| Surgical treatment of alveolitis | 3 040 |
Treatment of salivary gland diseases: | |
| Bougienage of the salivary gland duct | 490 |
| Washing the gland duct with saliva | 210 |
| Removing a stone from the salivary gland duct | 7 730 |
| Removal of stone from the parenchyma of the gland using saliva | 16 700 |
| Plastic surgery of the salivary gland duct | 4 420 |
Tooth-preserving operations: | |
| Resection of the root apex of a single-rooted tooth in the upper jaw | 10 350 |
| Resection of the root apex of a single-rooted tooth in the lower jaw | 13 100 |
| Resection of the root apex of a multi-rooted tooth in the upper jaw | 22 770 |
| Resection of the root apex of a multi-rooted tooth in the lower jaw | 22 400 |
Surgical treatment of cysts: | |
| Cystectomy category 1 | 4 400 |
| Cystectomy category 2 | 12 300 |
| Cystotomy category 1 | 3 200 |
| Cystotomy category 2 | 8 560 |
| Removal of soft tissue formations of category 1 | 6 500 |
| Removal of soft tissue formations of category 2 | 10 770 |
Bone grafting: | |
| Osteotomy category 1 | 11 300 |
| Osteotomy category 2 | 17 250 |
| Osteotomy category 3 | 33 540 |
| Alveolar bone augmentation (category 1) | 23 500 |
| Alveolar bone augmentation (2 categories) | 35 880 |
| Bone grafting using autograft of category 1 | 33 800 |
| Bone grafting using category 2 autograft | 42 100 |
| Use of one titanium fixing screw | 140 |
| Removing one titanium retaining screw | 700 |
| Using a non-absorbable membrane | 22 100 |
| Using a resorbable membrane | 14 500 |
| Use of artificial bone biomaterial 0.5 g. | 10 350 |
| Operation of “open” raising of the maxillary sinus floor of the first degree of complexity | 41 400 |
| Operation of “open” raising of the maxillary sinus floor of the second degree of complexity | 48 300 |
| Operation of “open” raising of the maxillary sinus floor of the third degree of complexity | 55 200 |
| Operation of “closed” raising of the maxillary sinus floor of the first degree of complexity | 20 000 |
| Operation of “closed” raising of the maxillary sinus floor of the second degree of complexity | 25 530 |
| Operation of “closed” raising of the maxillary sinus floor of the third degree of complexity | 30 350 |
| Local treatment of postoperative purulent wound | 20 700 |
| Secondary sutures (cosmetic) | 34 500 |
| Application of secondary sutures (interrupted) | 20 700 |
| Removing secondary sutures | 4 150 |
| Double jaw splinting | 27 600 |
| Removing double-jaw splints | 6 900 |
| Observation of the patient after double-jaw splinting, changing the rubber traction | 6 900 |
| Observation after application of secondary sutures, removal of secondary sutures | 13 800 |
| Maxillary sinusotomy | 57 500 |