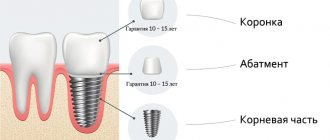
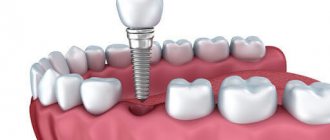
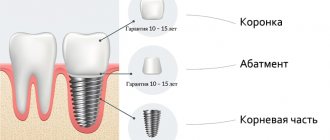
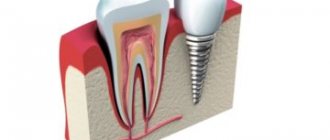
What is a sinus lift?
Sinus lifting (sinus floor elevation, raising the bottom of the maxillary sinus) is a procedure for increasing bone tissue in the area of the maxillary sinuses. They are located on the upper jaw to the left and right of the nose. In most people, the roots of the chewing teeth of the upper jaw are initially located in the maxillary sinuses, so after the removal of these teeth there is not enough bone tissue to install an implant. Closest to the maxillary sinuses are the molars (sixth and seventh teeth), less often the premolars (fourth and fifth teeth), and sometimes the canines.
The orthopantomogram shows the boundaries of the bottom of the hamoyr sinuses and the apex of the alveolar ridge. There is not enough bone tissue to install implants.
Treatment
Treatment of perforations of the maxillary sinus floor depends on what changes are present in the sinus cavity itself.
Treatment without surgery is possible only in cases where perforation occurred during tooth extraction and was detected immediately, and according to radiography there are no signs of infection of the sinus cavity or the presence of even minor foreign bodies in it. With this option, the doctor’s tactics are to preserve the blood clot formed in the socket as carefully as possible, as well as to prevent its infection.
To do this, a small gauze swab soaked in iodine solution is inserted into the lower part of the hole. Usually it is tightly fixed in the wound cavity on its own, but sometimes sutures are required on the gum. This treatment with iodine continues for at least 6-7 days until full granulations are formed and the defect is closed. In this case, the tampon is not removed from the hole so as not to damage the blood clot.
It is also possible to temporarily close the defect with a small plastic plate, which is fixed to adjacent teeth with clasps. It separates the oral cavity and sinuses, which promotes healing of the perforation.
At the same time, a course of preventive measures is prescribed, aimed at preventing the development of inflammatory complications. It includes taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, drops with a vasoconstrictor effect. This course is carried out on an outpatient basis or at home.
Indications for sinus lift
To install an implant without a sinus lift, a minimum of 10 mm of bone tissue is required to the maxillary sinus. Otherwise, elevation of the maxillary sinus floor is indicated.
1) If the distance to the sinus is 8-10 mm, it is possible to perform a closed sinus lift with simultaneous installation of implants. The term “closed” means that this procedure does not require additional incisions. This can be compared to endoscopic operations. As a result, the postoperative period is easier.
2) If there is bone tissue from 5mm to 8mm, an open sinus lift is performed with simultaneous installation of implants. An open sinus lift is a classic version of a sinus lift. This technique creates access to the maxillary sinus from the cheek. The mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus is peeled off, lifted up, and bone-replacing material is placed in the resulting space, which is subsequently resorbed and replaced with its own bone.
3) If the distance to the maxillary sinus is less than 5 mm, an open sinus lift is performed without installing implants. For immediate installation of implants, a certain amount of bone tissue is required in which they will be stabilized. If it is not enough, then an open sinus lift is performed first. After 6-9 months, implants are installed. After another 6 months, crowns are installed on the implants. Thus, with severe atrophy of bone tissue in the upper jaw, the treatment period can be more than a year.
Causes of edema
As a result of soft tissue injury, swelling is normal in the first 3 days after surgery. Every day, redness and swelling of the soft tissues decrease, and by the 5th day of the postoperative period there is no trace left of them. Swelling should not be a concern for the patient if:
- it has a clear localization at the site of surgery and does not spread to healthy facial tissues;
- the severity of swelling decreases daily;
- not accompanied by pain;
- does not lead to an increase in body temperature;
- there is no blood or purulent discharge from the wound.
To reduce tissue swelling in the early postoperative period, it is advisable to:
- apply a cold compress;
- treat the wound with antiseptic solutions;
- use medications to reduce swelling and inflammation.
It is necessary to use medications only as prescribed by the attending physician. Remember that self-medication can be dangerous to the patient's health!
To prevent infection of the wound surface, before performing plastic surgery, it is mandatory to sanitize all foci of chronic infection. After this, professional teeth cleaning is carried out to remove plaque and tartar. Thanks to these measures, it is possible to minimize the risk of developing an infectious process after surgery on the jaw tissue. In rare cases, implant failure may occur, which is also accompanied by pain and swelling of the tissue. This complication directly depends on the state of the patient’s immune system and the body’s perception of foreign bodies.
Many patients resort to tissue warming to reduce pain. After bone grafting, it is strictly forbidden to use thermal procedures. Also, you should not take hot baths, visit saunas or saunas. High temperature in the first days after surgery can cause unwanted complications, as well as bleeding from the postoperative wound.
During the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to follow all doctor’s prescriptions, as well as carry out preventive measures:
- brush your teeth regularly;
- sleep with the head of the bed raised or on a high pillow;
- Do antiseptic oral baths daily;
- drink enough water;
- avoid physical activity;
- do not sleep on the side of the surgical intervention;
- avoid air travel;
- Diving and snorkeling are prohibited;
- eat mechanically processed food;
- avoid chewing load.
To avoid discomfort from this cosmetic defect, it is necessary to discuss all the nuances with the attending physician and together choose the most appropriate time for surgical treatment, when the patient’s social activity is reduced. Most often, these manipulations are planned for the end of the work week so that the patient has days off to recover. If necessary, the doctor will be able to issue a certificate of incapacity for work. All these points should be thought out and discussed in advance with the attending physician.
Contraindications for sinus lift
In addition to general contraindications (type 1 diabetes, recent radiation therapy, etc.), there are a number of factors that may carry additional risks for sinus lift. The most common limitation is the presence of inflammatory diseases in the maxillary sinus area (sinusitis). In this case, it is necessary to identify the source of inflammation. Additional consultation with an ENT specialist may be required. Also, previous operations in the area of the maxillary sinuses can create a certain difficulty.
Causes
If the occurrence of sinusitis is associated with dental implantation, then the pathological condition is a consequence of damage to the cavity of the sinuses lying in the maxillary bone.
Injury most often occurs after a sinus lift. The operation, when restoring large areas of bone, can affect one or both maxillary sinuses on the maxillary front of the skull, and thereby cause an inflammatory process in them.
Important! Sinusitis after implantation without thickening of bone tissue occurs only in isolated cases.
The incidence of various forms of the disease after implantation with sinus lift is 3.9%. In some sources you can find other figures (9%-27%). The lack of accurate data is due to the fact that the studies were conducted by physicians of different specialties using different criteria for assessing complications.
The main cause of inflammation in the maxillary cavity is a change in ventilation in the sinuses. Such a violation is fraught with the penetration of infection and the rapid development of pathology.
Other factors leading to sinusitis are:
- Failure to comply with the rules of aseptic processing, due to which infectious agents are introduced into the sinuses.
- Incorrect assessment of bone tissue parameters by a doctor.
- Choosing an artificial root that is too long.
- The development of swelling of the mucous membrane, which clogs the anastomoses.
- Closing with an implant the anatomical connections (ostium) connecting the nasal cavity with the maxillary sinus.
- Entry of osteoplastic material or bone fragments into the sinuses.
- Impaired release of mucus from the maxillary cavities due to changes in the functionality of the cilia of the mucous membrane caused by its extensive detachment.
A factor is identified that has no effect on the occurrence of sinusitis after dental implantation. This is a traumatic rupture of the mucosa, which occurs in half of all cases.
Is it possible to carry out implantation for periodontal disease and which method is the most reliable?
Come here to learn more about implantation tactics for diabetes.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/implantatsiya/metodiki/kak-nedorogo-i-nadezhno.html read how to inexpensively carry out dental implantation.
Open sinus lift
Open sinus lift is one of the most common types of not only sinus lifting, but also bone tissue augmentation in general. The sinus lift technique was developed decades ago.
The first step is to numb the surgical site. Anesthesia for sinus lifting is the same as for treating teeth in the upper jaw. The procedure itself is absolutely painless.
At the second stage, an incision is made in the gum in the area of the missing teeth, the gum itself is pushed upward, exposing the underlying bone tissue. Then access to the maxillary sinus is created. With the help of special instruments, the wall of the maxillary sinus is thinned, limiting it from the oral cavity. The inside of the maxillary sinus is lined with mucous membrane (Schneiderian membrane). During the sinus lift process, the mucous membrane is peeled off and lifted upward.
Bone replacement material is placed in the resulting space, which eventually dissolves and is replaced by its own bone. Despite the apparent complexity of the procedure, open sinus lift has its advantages. Firstly, it is possible to significantly increase the volume of bone in the area of the maxillary sinus, even in cases where the distance to it is only 1 mm. Because The operation is performed under direct visual control, then it becomes possible to take into account all anatomically complex areas and avoid many complications, for example, rupture of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus.
Open sinus lithography with immediate installation of implants.
Preventive measures
Inflammation of the maxillary sinus is a rather dangerous complication that occurs after dental implantation and sinus lift surgery. Despite the rarity of the development of such a complication, it is necessary to prevent the development of pathology through prophylaxis.
Doctors recommend the following measures:
- Promptly treat all inflammatory and carious lesions in the oral cavity.
- Before the implantation procedure, perform a complete sanitation of the oral cavity.
- Carefully monitor dental hygiene.
- Follow all doctor's instructions for taking medications.
- Avoid excessive load on the implant.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking.
- After implantation, avoid flights and pressure changes.
- Do not blow your nose and try not to sneeze or cough.
- Do not use vasoconstrictor drugs.
Remember! Even if minor symptoms of inflammation appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Closed sinus lift
Unlike open sinus lift, closed sinus lift is performed only simultaneously with the installation of implants. The gum incision is the same as for conventional implantation, because... there is no need for severe gum peeling.
First, preparations are made for implant installation. A bed for the implant is formed. Then a special instrument is installed through it, it is called an osteot, with the help of which the bottom of the maxillary sinus is raised. After raising the sinus floor, the implant is installed.
The advantages of this method include a minimally traumatic procedure and an easier operating period. However, in this case it is possible to raise the bottom of the sinus only by 2-3 mm. If you try to carry out a closed sinus lift with the concept of the sinus floor at 4-5 mm, then there is a risk of rupture of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus membrane.
Closed sinus lift. First, a bed is formed for installing the implant. Through it, the bottom of the maxillary sinus is raised - sinus lift. The procedure involves one-stage installation of implants.
Implantation without sinus lift
Today, many well-known brands of implants have reconsidered their position regarding bone grafting and offer solutions that allow the installation of implants without additional operations to build up bone tissue. In cases where there is not enough bone tissue to reach the maxillary sinus, it is possible to install a shorter implant without performing a sinus lift.
The Straumann company offers implants 4 mm long, German Ankylos implants 6.6 mm. According to studies, the length of the implant does not matter if the installation protocol is followed. Thus, it is possible to avoid additional surgical procedures by installing a shorter implant.
Do not forget that this approach has its limitations, and it is not in all cases possible to install implants without sinus lifting. If a large number of teeth are missing, it is possible to install extreme implants at an angle of up to 45 degrees, bypassing the maxillary sinuses. Thus, implants of the required length are installed without sinus lifting. Read more about this technique in the article about All-on-4.
The distance to the maxillary sinus is 7 mm. Instead of performing a sinus lift, a short Ankylos implant, Germany, 6.6 mm long, was installed without additional surgical procedures.
Possible complications
Swelling after installation of a dental implant is normal, but it can increase and persist for a long time due to pathologies; you can read more about the complications at the link. After surgery, complications may arise due to the fault of the doctor, the patient or extraneous factors (exacerbation of body diseases, individual characteristics). Possible complications:
- Inflammation of soft tissues;
- Bleeding;
- Seam divergence
- Peri-implantitis;
- Infection and gum suppuration.
Rehabilitation period after sinus lift
On the day of surgery after sinus lifting, pain is possible, which can be relieved by taking anti-inflammatory painkillers (Nurofen, Nice, Nimesil). Starting from the next day, the need for painkillers is much less, 1-2 tablets per day for 2-3 days is enough. Swelling may occur in the area of the operation. The swelling increases for 3 days, and begins to subside on the fourth. Therefore, it is not recommended to heat the surgical site or engage in physical labor for several days after a sinus lift. In some cases, nasal congestion may occur, which can be relieved with vasoconstrictor nasal drops. To prevent complications, it is recommended not to fly on an airplane for 1-2 weeks after a sinus lift. This is due to the pressure difference in the plane, which theoretically could lead to a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus.
If a sinus lift was carried out with the immediate installation of implants, then on average after 6 months crowns are installed on them. If there was significant bone tissue atrophy, and the sinus lift was performed without installing implants, then the waiting period is 6-9 months.
When is it better to seek help from a specialist?
There are a number of alarming signs, in the presence of which one should think about the development of a complication or an abnormal reaction to surgery that requires immediate correction. These include:
- high rate of development, rapid increase in edema in size, transition of edema to the soft tissues of the face;
- the swelling is dense, the consistency of an eraser;
- lack of positive dynamics, that is, swelling does not begin to decrease from the 3rd day after the operation;
- increased body temperature above 38 degrees for longer than 24 hours;
- severe pain, with an interval of less than three hours (while taking painkillers);
- discharge of a large amount of ichor, bleeding from the wound against the background of significant swelling;
- the addition of a bacterial infection, manifested in the development of suppuration in the wound area;
- impaired speech and chewing function due to swelling.
- strange odors from the post-operative area.
If one or more of the above symptoms appear, you should immediately contact the dentist who performed your bone grafting. Find him and explain the situation, don’t delay. It is dangerous to self-medicate in such a situation, so entrust the treatment of the emerging complication to an experienced specialist. If you are undergoing treatment at our Center, immediately contact the 24-hour support service by calling from your card.
What bone replacement materials are used in sinus lifting?
The reference material for sinus lifting is the patient’s own bone. It has maximum regenerative potential and 100% biocompatibility. However, to get your own bone you need to get it from somewhere. This is the disadvantage of this method, because... it is more traumatic. In addition to surgery in the maxillary sinus area, it is necessary to perform a second operation to obtain your own bone tissue. Most often it is obtained from the angle of the lower jaw, or from the chin area.
Today, there are bone replacement materials that give a similar result as the patient’s own bone. They are produced in the form of granules and are obtained from the bones of cattle, or are completely synthesized. These are absolutely safe materials, the most famous of them is called Bio Oss from the Swiss company Geistlich. The mechanism of action of bone replacement materials is that they create the basis for the germination of one’s own blood vessels and cells. Over the course of 6-9 months, bone replacement materials gradually dissolve, being completely replaced by the patient’s own newly formed bone.
What do pain, bleeding and fever indicate?
In the first few days after surgery, all patients are under the supervision of a specialist, whose first visit should take place three days later. During the examination, a highly qualified doctor immediately understands whether the patient followed all the instructions or not, and corrects the problem on the spot. However, there are cases when a patient ends up with an unprofessional doctor who pays little attention to his well-being. In this case, it is important to independently identify signs of possible complications, which are characterized by the appearance of fever, impaired nasal breathing and heavy bleeding.
In fact, after the rehabilitation period there should be no pain or complications. Therefore, any abnormal conditions, be it pain or poor health, are the first signal that it is time to consult a specialist.
Platelet Rich Plasma
To stimulate the growth of the patient's own bone, PRP technology is used - platelet rich plasma - platelet rich plasma. Before the sinus lift begins, a test tube of blood is taken from a vein. It is placed in a centrifuge, in which it is separated into fractions within 12 minutes, one of which is platelet-rich plasma. Using this method, it is possible to obtain bone growth factors. Unlike collecting your own bone, which also contains growth factors, obtaining a tube of venous blood is much easier. By using the patient's own blood, the risks of incompatibility and allergic reactions are eliminated.
Various sinus lift techniques
Today, there are a large number of instruments specifically designed for sinus lifting in order to reduce risks and complications. One of the most common complications is rupture of the maxillary sinus membrane. It occurs during an open sinus lift, when access to the maxillary sinus is created, or during its membrane peeling. Therefore, special burs and cutters have been developed that do not injure the membrane of the maxillary sinus even if they accidentally touch it.
Another sinus lift option is the endoscopic sinus lift . It is performed without additional incisions, like a closed sinus lift, but with its help you can significantly raise the bottom of the maxillary sinus. With a conventional closed sinus lift, control of the condition of the maxillary sinus membrane is carried out only tactilely, therefore, using this method, the bottom of the sinus does not rise more than 2-3 mm. But under the visual control of an endoscope, it is possible to expand the indications and conduct a closed sinus lift even in cases where an open one is indicated.
The most important advantage of endoscopic sinus lift is its low-traumatic nature and easy postoperative period. Unfortunately, only a few clinics have the necessary expensive equipment to carry out such a procedure.
What complications can there be?
Important conditions to prevent the problem:
- thorough diagnosis;
- correct choice of implant length;
- checking the condition of the sinuses during sinus lifting or implantation;
- exact adherence to therapy technology.
The patient should also carefully follow the postoperative recommendations:
- you can't blow your nose;
- sneeze carefully;
- stop taking vasoconstrictor drops;
- quit smoking.
A lot depends on the responsible and competent approach of the surgeon. If sinus lifting is performed taking into account all the requirements and technology, then the result most often meets the expectations of the patient and the surgeon. The likelihood of any complications if an experienced professional takes on the matter is reduced significantly.
Basically, complications are associated specifically with the maxillary sinuses. After surgery, ENT diseases may develop. In some cases, sinusitis, sinusitis, chronic runny nose, rupture of mucosal tissue, bleeding, impaired outflow of fluid from the sinuses, and edema were observed. By the way, regular ice applied to the cheek helps with swelling.
As we have already written, most often a correctly performed sinus lift does not lead to complications. But sometimes they still happen. We will look in detail at how to behave if rehabilitation after surgery does not go so smoothly. After a sinus lift, all sorts of consequences are possible. They can vary in degree of manifestation and potential danger.
Sometimes complications after surgery are associated with the septum, which is located in the sinus. To avoid causing unnecessary injury to the patient, the doctor makes a hole on both sides. Complications are more common with open sinus lift than with closed sinus lift. In most cases, they are associated precisely with doctor errors. Most often, such a mistake becomes a rupture of the mucous membrane. This complication is eliminated by applying patches and sutures.
The second most common complication is penetration of infection into the cavity. It requires immediate treatment to prevent tissue inflammation and suppuration from developing.
Another common complication is slight mobility of the implant. This is because there may be some loss of bone mass after surgery. According to statistics, the frequency of complications directly depends on the skill and responsibility of the surgeon, high-quality equipment and materials that were used.
Any surgical intervention may be accompanied by some complications. It all depends on the doctor’s experience, the complexity of the operation performed and some other factors, including how the patient himself will follow the instructions prescribed to him after the operation.
Complications of implantation include bleeding, infection of the tissues surrounding the implant, as well as injury to nerves, blood vessels, paranasal sinuses (which are located above the teeth of the upper jaw) and the nasal cavity.
When implanting in the lower jaw, the surgeon may damage the nerve that runs in the mandibular canal (lateralization of the mandibular nerve), which houses the mandibular nerve and blood vessels. Its thickness reaches several millimeters. However, in cases where this channel is too high, it may interfere with the placement of dental implants, as the length of the implants must be adequate to ensure their strength and reliability.
What can be done in this case, since the implant cannot pass through this channel? In this situation, the so-called “lateralization” of the nerve and blood vessels passing in the mandibular canal is carried out, that is, their movement (from lateral - side part, branch). A situation where there is a place on the lower jaw where its canal runs quite high and prevents the installation of dental implants of the appropriate length, usually occurs in the molars of the lower jaw: molars and premolars, when these teeth are lost.
How to avoid risks and complications?
Although the sinus lift has been used worldwide for over 30 years, it is a technically challenging procedure. Additional complications may arise from anatomical formations in the maxillary sinus, for example, septa dividing the sinus into several cells. Also, in some people, the membrane of the maxillary sinuses can be so thin that it ruptures during a sinus lift from a banal exit through the nose.
So how can you avoid health risks if you are indicated for a sinus lift? The most important thing is to trust a qualified implantologist who will take the correct treatment tactics even in a difficult case. Be prepared for the fact that the treatment period for severe bone tissue atrophy can be significant, a year to a year and a half.
And finally, it’s worth saying that the best bone grafting is the one that didn’t happen. If it is possible, without compromising the reliability of the treatment plan, to avoid a sinus lift, then you can install shorter implants or bypass the maxillary sinus by installing implants at an angle.
Sinus lift and sinusitis
Often people accidentally find out that they have problems with the maxillary sinus. This usually happens during a routine examination by the dentist, or an orthopantomogram was taken for another issue, and the dentist noticed that the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus is thickened.
What to do in this case? First of all, don't panic. There are many reasons for thickening of the maxillary sinus membrane, and not all of them require any additional treatment. The simplest thing is that the picture was taken at a time when the patient was infected with ARVI. A cold can cause the lining of the maxillary sinus to thicken as the body's response to illness. It is necessary to repeat the picture some time after complete recovery, and only then can conclusions be drawn.
In any case, it is recommended to obtain additional advice from an ENT specialist who will accurately determine the nature of the thickening of the maxillary sinus membrane. In the absence of inflammatory phenomena, there are no contraindications for sinus lifting. Otherwise, an additional course of treatment for the maxillary sinuses may be required.
The sinus lift operation→ requires good manual skills, a developed sense of the tissue structure under the instrument and good knowledge of the various topographic anatomy of the area. No matter how much you want it (after 30–50 successfully installed implants, you get the feeling that everything in dental implantation is already clear and uncomplicated), I strongly recommend moving on to sinus lift operations after 150–250 installed implants. Of course, the point is not in the specific number of implants installed; it’s just that operations on the maxillary sinus require special sensitivity in your hands and fingers. But it doesn’t come right away!In addition, I strongly recommend that a patient undergoing sinus lift surgery be referred for a consultation with an otolaryngologist. A very important condition for a favorable postoperative course is good natural drainage of the sinus through the anastomosis with the nasal cavity. It is this anastomosis that should be examined by a specialist, and if its lumen is insufficient, it is very advisable to widen it.
One of the most common complications during sinus lift is perforation and rupture of the sinus membrane. Being quite elastic and pliable, it can nevertheless rupture from the slightest overstrain at the most inopportune moment, when it seems that the operation is actually completed.
If a rupture occurs, stop immediately and carefully examine the remaining membrane inside the sinus. If the membrane itself is sufficiently elastic, try to separate it inside the sinus 1–2 cm along the periphery of the perforation site and then insert a resorbable membrane there. If this is not possible, a fragment of the bone window hanging on a piece of sinus membrane must be removed! It will never grow on its own.
After this, it is advisable to close the entire bone window you have formed with a resorbable (preferably two-layer - it will take longer to resorb) collagen membrane. And with the obligatory wide overlap. Then we suture the wound as carefully as possible.
I categorically do not recommend checking the quality of the work done through the so-called nasal test (when they pinch the patient’s nose with their fingers and ask him to blow forcefully into it). Excessive pressure in the sinus will only cause harm by breaking up the blood clots that are forming and tearing the collagen membrane away from the bone. And the air bubbles formed between the mucoperiosteal flap and the periosteum also do not contribute to speedy healing.
Unfortunately, despite the high regenerative capacity of the sinus membrane, repeated surgery after a few years is ineffective. We definitely prescribe antibiotics and antihistamines, and also give recommendations that were discussed in the “Sinus lifting” section [read]. There are cases of pushing the implant into the cavity of the maxillary sinus. This can happen both during surgery and during the installation of a gum former. If an attempt to localize the position of the implant through the entrance hole and remove it with a thin hemostatic clamp does not bring the desired result, then it is necessary to tightly suture the wound and prescribe antibiotics. Next, you need to refer the patient for a consultation with an otolaryngologist who works with a fiber-optic sinusoscope. He may try to remove this implant through the natural anastomosis with the nasal cavity, slightly expanding it. If this is impossible, then you will have to resort to extensive operations, up to radical maxillary sinusotomy.
Also, from time to time a situation arises when a sinus lift is carried out without the slightest complications, and the volume of bone material rebuilt over several months is clearly not enough to install implants. The body always takes its “angel's share” in the form of a certain amount of material that you use during sinus lift. The problem is that it is simply impossible to accurately predict how much more bone material needs to be placed during the operation so that there is enough left after 4–6 months! Periodically indicated data that it is necessary to lay 10–30% more of the required volume is very approximate. Even a 50% increase is not a guarantee!
I have repeatedly encountered the fact that more than a sufficient volume of material placed in the sinus, during the restructuring process, not only decreased in volume, but also spread under the sinus membrane, occupying those places where separation was not even carried out! At the same time, the coverage area increased, and the total height in the desired location decreased.
It is likely that during nasal breathing, a significant degree of air pressure is transferred to the sinus membrane and it begins to work like a pump piston, crushing the underlying material in all directions directly under the sinus membrane.
What to do in this case?
During the installation of implants, the bed under them must be formed using osteotomes, essentially performing a repeated soft sinus lift. Only the tomia must be carried out extremely carefully so as not to break the bone formed after the first operation. Accordingly, the waiting time after implantation must be increased.
One of the biggest difficulties during sinus lift surgery is the inability to mobilize the corner of the mouth to the required distance, which makes it extremely difficult to carry out all the necessary manipulations. Even before surgery, pull the patient's lips and corner of the mouth and see carefully if you can adequately perform the operation in the given area!
4.7.-1 Rupture of the sinus membrane when attempting to separate the bone window.
4.7.-2a 3D reconstruction one year after bilateral sinus lift. Apparently, in both cases there was a rupture of the sinus membrane. The osteoplastic material is not where it should be at all.
4.7.-2b Axial sections of the case shown in 4.7-2a. Note the destructive changes in the right sinus, the remains of material in the distal part and the complete absence of pneumatization.
4.7.-3a When installing the gum former, the implant rotated in place and went deeper into the sinus. An attempt to expand the bone bed and remove the implant led to the opposite result - the implant fell even deeper into the sinus.
4.7.-3b Position of the implant on the cross-section. The implant has completely fallen into the maxillary sinus.
4.7.-3c The axial section clearly shows the position of the implant. Since the patient lies on his back during the CT examination, the implant fell into the lower point of the sinus. High pneumatization of the sinus indicates that the implant can freely migrate along the sinus when walking, tilting the head, etc.
4.7.-3d 3D reconstruction. Both the perforation hole and the position of the implant are clearly visible.
4.7.-4 A rare case. The implant was in the sinus for more than 5 years without causing any discomfort or complaints from the patient, and was discovered during an x-ray examination.
4.7.-5 A few months after prosthetics, pronounced mobility of all implants appeared. This is probably a natural result if you look at the overall height of the orthopedic structure. Here, it was more appropriate to use a bone block on the alveolar process rather than a sinus lift.