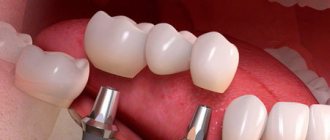
Bone deficiency in the alveolar process is the main obstacle to immediate dental implantation.
The problem can be solved by directed bone grafting (GBG), but this operation requires considerable time and certain conditions, and is not cheap.
Therefore, many patients treat it with distrust. Is it possible to implant teeth with narrow alveolar processes without performing GBR?
The essence of the technique
Bone deficiency is not an insurmountable obstacle to dental implantation. The method of installing artificial roots into narrow alveolar ridges without bone augmentation is somewhat different from the two-stage classical technology using bone augmentation.
But if you follow the treatment protocol and the professional actions of the doctor, you can get quite a good result.
Traditional implantation when there is a lack of bone is performed in 2 stages - bone grafting and the installation of the implant itself in the alveolar process.
When implanting without bone grafting, the first stage is absent. A titanium rod is inserted into the bone bed without prior augmentation.
There are three ways to install intraosseous implants in alveolar processes with low bone volume:
- Installation of zygomatic implants. The large length of these products (30-60 mm) allows them to achieve a dense and stable zygomatic bone, which remains unchanged even with significant atrophy of the cancellous bone of the alveolar process. As a result, high adhesion strength to the bone is achieved. But this operation is quite complicated and is applicable only to the upper jaw.
- Use of basal implants. The lower jaw bone consists of 3 layers. On top is the cortical plate, below it is the spongy layer, and even deeper is the basal layer, which is not subject to resorption. The implant embedded in it holds firmly and reliably, but this technology has the same drawback as the one described above.
- Implantation with splitting of the alveolar ridge. The method is relatively simple, low-traumatic, and can be used for both the lower and upper jaws. Therefore, when there is a lack of bone tissue in the alveolar process, it is used most often.
The essence of the operation is that the alveolar ridge is not drilled out, as is the case with classical technology, but is split (spread apart). An implant of a special design is installed into the gap formed, which provides relatively high adhesion strength to the bone.
The implant usually takes three to four months to heal, after which a crown is installed on the artificial root. Thus, it becomes possible not only to install an implant in a narrow alveolar ridge, but also to reduce the implantation time by eliminating the bone augmentation stage.
What problems can be solved with the help of an individual abutment and what are its advantages over standard products? Go here to learn more about the rationale behind plate implants.
At this address https://dr-zubov.ru/implantaciya/metodiki/komu-grozit-ottorzhenie.html we will talk about the first symptoms of implant rejection.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage is the ability to do without expensive and lengthy bone replacement. In addition, dentists highlight the following advantages of the technology:
- reduction of the rehabilitation period after surgery;
- the cost of treatment is lower than using sinus lift;
- installation on the artificial root of the prosthesis 3 months after implantation.
Also, splitting the alveolar ridge allows you to do without autoimplantation (there is no need to take bone from the patient).
Dentists call the disadvantages the lack of specialists capable of performing surgical intervention following this protocol and the inability to fill a row if more than 4 teeth are missing in a row.
Preparing for installation
Alveolar ridge splitting is a planned surgical procedure that requires an examination before implantation. Diagnostics include:
- taking anamnesis;
- taking urine tests;
- blood test (biochemistry, general, coagulability, syphilis, hepatitis);
- after examining the oral cavity, a CT scan or x-ray is done;
- sanitation of the oral cavity.
Important! If the doctor has suspicions about oncology, the dentist will advise you to take a test for tumor markers.
Installation
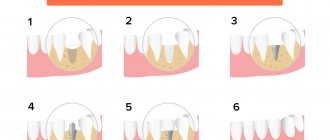
Surgery is performed under local anesthesia. Algorithm for performing work by a dentist:
- Opening access to the cortical plate.
- Detachment of a flap of soft gum tissue.
- Designation of the ridge cut line (two vertical and horizontal cuts each).
- Creating a deep hole using a fissure bur.
- Broken and pushed back bone.
- Drilling holes in the retracted segment.
- Installation of miniscrews.
- Filling the void with bone mass and blood.
- Screw clamp.
- Installation of a bioresorbable pad.
- Suturing.
Soft tissues heal quickly (10-15 days), osseointegration lasts more than 3 months. To speed up the healing process, you need to brush your teeth well and visit the dentist according to your schedule.
After the recovery period, the doctor installs the implant.
Complications
The first signs of complications appear after 2-3 days, so the patient should monitor the condition. If your condition worsens from the third day after surgery, you should immediately seek medical help.
Swelling, numbness of soft tissues, pain when touched, hyperthermia, the presence of a hematoma at the intervention site should not be considered a complication. This is a normal condition that lasts mostly no more than 7-10 days.
Possible complications:
- the seams are coming apart (the reason is mechanical damage or an inflammatory process);
- inflammation (occurs due to microbes entering the wound);
- peri-implantitis (complications in the absence of treatment of the inflammatory process).
Remember! Failure to promptly contact a dentist at the first signs of complications inevitably leads to a deterioration in general health and the removal of the implant from the oral cavity.
Indications and contraindications
The main indication for implantation by splitting the alveolar bone is a deficiency of bone tissue in the crest of the alveolar process. There may be a lack of volume for various reasons.
Most often this occurs as a result of bone resorption due to lack of load on the jaw after tooth extraction, or as a result of age-related changes.
Contraindications to the technique are basically the same factors as with the classic two-stage operation:
- Pathologies of the circulatory system (absolute contraindication).
- Immunodeficiency states.
- Tendency to allergies.
- Hereditary burden.
- Age up to 18 years (until bone formation is completed).
- Bruxism.
Implantation requires special attention:
- in people with age-related or systemic changes in bone structures;
- in women with osteoporosis (premenopausal and postmenstrual period);
- in heavy smokers, people who drink large quantities of alcohol or drugs, especially if all these abuses are accompanied by dysfunction of the pancreas and liver;
- in people with mental disorders.
If implantation is performed on the maxillary arch, the contraindications are:
- chronic runny nose and sinusitis;
- surgical operations performed in the maxillary sinuses.
There are extreme minimum bone sizes at which implantation without bone grafting is impossible, even when using splitting:
- The width of the alveolar ridge in its upper part should be at least 2.5-3 mm.
- The distance to the bottom of the maxillary sinus, inferior alveolar nerve, and mandibular canal should be at least 2 mm.
- The minimum distance to the chin hole is 5 mm.
- The distance between the adjacent tooth and the implant must be at least 3 mm.
What is alveolar ridge clefting?
Article navigation
- Ridge splitting surgery technology
- Care and recovery
Question for a specialist
Bone tissue atrophy manifests itself in the form of its deficiency, both in height and width. Narrow bone tissue can be either a congenital pathology or acquired as a result of tooth loss. But in any case, if it is necessary to restore lost teeth, it can become an obstacle to the reliable fixation of implants or metal artificial tooth roots. In this case, surgery to split the bone will be simple but effective.
Innovation! Implantation WITHOUT bone tissue augmentation.
A method of dental restoration in which implants are installed in deeper bone areas that are less susceptible to atrophy. Find out more >> Consultation with a doctor is free! Call now: +7 (495) 215-52-31
Ridge splitting surgery technology
The conditions for a positive outcome of the operation are the presence of a bone of a certain size:
- minimum width – not less than 2 mm,
- minimum height – not less than 10 mm,
- bone – medium in density.
Surgery to increase the width of the bone tissue can be performed in one or several stages, depending on the condition of the bone, the general physical health of the patient and other medical indications. The technology of the surgical operation is as follows:
- administration of anesthesia,
- the gums are cut and peeled off,
- the bone tissue is cut lengthwise (horizontally) using a laser or scalpel, then its edges are slightly moved apart,
- Under favorable conditions, an implant is placed inside the gap, the space around is sprinkled with synthetic materials, a protective membrane is installed, and the gums are tightly sutured. Under unfavorable conditions, implants are not installed, and the free space is filled only with artificial bone.
Both synthetic and natural tissues can be used as a material for bone augmentation In the second case, the rate of engraftment is higher, the likelihood of rejection is tens of times lower, since an allergy or the likelihood of the body not accepting its own bone is negligible.
The operation is generally painless and lasts no more than a couple of hours and can be performed in a dental clinic, unless a bone block is planned to be taken from the hip bone. The consequences of surgery may be associated with tissue swelling, pain, and suture dehiscence.
Care and recovery
The final stage of the operation is the restoration of the operated bone tissue. It is very important not to load it at first, since the installed implant is not secured very securely and may slightly change its position under pressure. At first, the patient will be offered only removable dentures to restore aesthetics, since at least 3-4 months are required to restore the built-up bone tissue. After this, the doctor will begin either direct implantation of the implants (if they were not installed simultaneously with the splitting of the ridge) or prosthetics. The patient must strictly follow all the recommendations of his attending physician to eliminate possible consequences of the operation, namely: mandatory hygiene procedures, avoidance of stress on the operated bone, refusal of physical activity and bad habits.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of the technique is the refusal to build up bone tissue. As a result, the time for tooth restoration is significantly reduced, the cost of the operation is reduced, and complications that sometimes accompany augmentation are eliminated.
Other advantages of this technology include:
- Strong connection of the implant with the bone of the alveolar process. Direct contact of the titanium rod with “living”, autogenous bone ensures high-quality osseointegration.
- Less traumatic surgery with minimal swelling and hematoma.
- The ability to install an implant almost anywhere (with rare exceptions).
Flaws:
- There are restrictions regarding the size of bone tissue. Implantation without bone grafting using the splitting method is possible in most cases of bone deficiency, but not always (see “Contraindications”).
- High demands on the professionalism of a dental surgeon, the need for experience.
Bone grafting: complications
Bone grafting during dental implantation - reviews will depend on the surgeon’s precise execution of the surgical technique. Any deviation from the surgical technology most likely leads to failure and even rejection of the transplanted bone. In addition, in most cases, a lot depends on the quality of the bone material used, the membrane.
With both surgical techniques, the membrane may be exposed through the suture line, which in many cases leads to purulent inflammation of the wound. The use of a bone block grafting technique with insufficient vascularization rate can lead to sequestration (rejection) of sections of the bone block or its entirety.
In addition, when using bone blocks, there is a loss of volume of the bone block during the process of integrating it into the tissue - sometimes up to 50%, which can be critical and require repeated surgery. It is also possible for the implanted bone block to tear off (during screwing in the implant at the second stage), which is due to insufficient integration of the block into the jaw’s own bone tissue.
Important for smokers: jaw bone grafting (as well as the installation of implants itself) is a relative contraindication in smoking patients, especially heavy smokers. The fact is that nicotine leads to a sharp narrowing of the lumen of blood capillaries in the tissues of the oral cavity, which sharply reduces blood flow to the bone graft or implant.
If you want bone tissue augmentation for dental implantation to proceed without complications, you must stop smoking at least 2 weeks before bone grafting surgery and for 4 months after surgery. If the implants are not installed simultaneously with bone grafting, but at the second stage, you will have to quit smoking again at the same time.
Applied systems
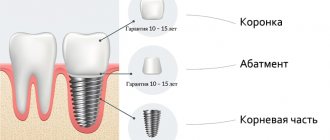
Carrying out implantation with a narrow alveolar ridge requires the use of special implants, which differ in appearance and design from standard systems.
They are characterized by:
- Pronounced conical shape for easier entry into the bone gap.
- Increased ratio of the outer diameter of the spiral to the inner diameter (thin solid rod and wide thread). This design provides a large area of contact between the implant and the bone tissue and sufficient space for the formation of new bone.
- Short length. This is a necessity in conditions of bone tissue deficiency. The strength of the connection is achieved due to the developed thread, which compensates for the short length.
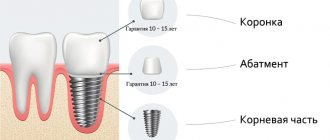
Implants are made from titanium or its alloys, which have good biocompatibility with autoimmune tissues.
Key points to remember after dental implantation, regardless of the technique used. In this publication we will discuss what can affect the healing time of dental implants.
Here https://dr-zubov.ru/implantaciya/metodiki/lazernaya-peredovaya-texnologiya.html we will consider the price of laser dental implantation.
What can replace bone grafting?
Implantation in conditions of bone tissue atrophy is not practical in the classical version, however, there is an alternative method of basal fixation of implants. In any case, replenishing the deficit in the width or height of the alveolar ridge is more physiological and effective, but in a situation where such an operation is impossible, specific implantation is performed in the presence of resorption.
Basal implantation involves the use of small and differently shaped implants. They are attached to those layers of the jaw bone where resorption does not occur. In addition, it is possible to install an artificial root at an angle or in the tissue of the zygomatic bone. Such implants are immediately covered with crowns, after which they can be used like regular teeth. Immediate loading will stimulate the growth process of your own bone tissue. However, the aesthetics of such structures is not very high, which is why they prefer to perform bone grafting.
Preparing for surgery
Before the operation, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, including the study of all factors that, one way or another, influence the indications, contraindications and result of the operation:
- The condition of the teeth, bite, and mucous membrane of the oral cavity is assessed. Rehabilitation of the RP is mandatory.
- The presence of facial disproportions is determined, the width and height of the alveolar processes are measured, and the location of the mental foramen and mandibular canal is determined.
- X-ray examinations are carried out, that is, photographs of individual teeth, orthopantomograms.
If necessary and possible, CT and teleradiography (images of teeth from the frontal side) are performed. Three-dimensional visualization (cone-beam and computed tomography) and visiography are very visual, allowing one to obtain a detailed image of all elements of the dental system.
Important! An assessment of the patient’s general health is required, taking into account the presence of serious systemic diseases, age, and the state of the immune system.
Features of the event
The main stages of installing an implant using the splitting method:
- Anesthesia. This is usually done under local anesthesia, but in rare cases general anesthesia may be necessary.
- An incision in the gum mucosa to access the bone, detachment of the flap.
- An incision (expansion) of the ridge with a scalpel or chisel.
- Screwing into the implant slot.
- Formation of supra-alveolar soft tissues around the implant, suturing the supragingival mucosa.
- Control radiography.
In the video, see the diagram of implantation without bone grafting.
Actions and recommendations for the post-implantation period
- “Cold” for 2 hours after surgery (applying ice in a plastic bag).
- Rinsing the mouth with antiseptic drugs (chlorhexidine).
- High-quality hygiene of the RP. When brushing your teeth, you should avoid touching the operating area.
- If necessary, take painkillers and antibiotic therapy for a week.
- Liquid food for 1-2 weeks.
- Monitoring the condition of the mucosa in the implant area (inside and supra-alveolar area). Normally, fibrous tissue should form in this area, and there should be no gingival pocket.
- Dressings and examination by a doctor within 3 weeks.
- Monthly medical supervision.
After the final restoration of the tooth, it is necessary to visit a doctor for examination every 3-4 months.
Engraftment period
The main thing in the postoperative and rehabilitation period is the interaction of the implant with the alveolar bone. Typically, osseointegration and healing of soft tissues ends after 3-4 months, after which restoration of the coronal part is carried out.
There are two types of implant healing, which determine the functionality and durability of the restored tooth. The best option is osseointegration, direct fusion of the implant with the bone.
It is also possible for a titanium rod to connect to the bone due to the formation of fibrous tissue – fibrointegration. This is considered a relative failure as it may cause the implant to move. A mixed type of engraftment is also possible - fibro-osseointegration.
The path the fusion takes depends on many factors:
- biocompatibility of the implant material with tissues;
- its chemical composition and type of surface treatment;
- the nature of the load when chewing;
- quality of RP care.
The result of implantation is assessed according to the following criteria:
- absence of inflammation, pain and bleeding in the implant-gingival junction;
- structural stability;
- absence of destruction in the bone tissue surrounding the implant neck.
Statistics show that 5 years after surgery, 95% of implantation cases are considered successful, and after 10 years – 80%.
Tunnel plastic surgery of the alveolar ridge in the area of 3 teeth in Moscow
Plastic elimination of insufficient bone tissue height. Dentists quite often encounter situations where, before implant treatment, patients need to undergo plastic surgery of bone and soft tissues.
Such operations have been carried out for more than half a century. Initially, their goal was to eliminate the consequences of various types of jaw injuries. But with the development of implantology, the acquired clinical experience began to be actively and successfully used to eliminate the deficiency of tissue (both bone and soft), which should serve as a support for implanted implants.
On the need for tunnel grafting of the alveolar ridge
Surgical restoration of bone tissue of insufficient height or volume can be performed before implantation. And if there are indications, then simultaneously with the installation of dental implants or augmentation (a treatment process that stimulates tissue regeneration). There are several popular methods of tissue grafting: apical displacement, grafts, pedicled flaps, and the roll method. Their detailed description will be of interest only to a specialist. It is more important for the patient to understand that the doctor has a huge number of treatment options at his disposal. The dentist’s task is to choose the most gentle and optimal method, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body. And most importantly, it is necessary to carefully plan in advance all further actions for installing implants.
Before starting the process of dental prosthetics, you need to determine how and on what the implant will be fixed. The teeth of the upper jaw row are attached to the alveolar process, the lower row on the alveolar part.
The deficiency of these tissues is compensated for by transplanted material, which can be taken from various areas of the patient’s oral cavity, donor tissues, as well as tissues of animal and artificial origin can be used.
The process of tunnel grafting of the alveolar ridge
The most well-established procedure, which proceeds practically without subsequent inflammation and with excellent results, is considered to be plastic surgery of the upper jaw (alveolar process) with grafts borrowed from bone blocks of the lower jaw. It sounds scary, but in fact, an experienced doctor performs such an operation quickly, and it is relatively inexpensive for the patient. The only negative is that it is impossible to introduce the implants themselves at the same time.
The patient should also be aware that in situations where implantation is performed almost simultaneously with tissue plastic surgery, the implant must be hidden by the graft by at least 1-1.5 mm. This, of course, does not look very aesthetically pleasing at first, but it eliminates the possibility of exposing the implant in the future.
It is necessary to ensure that temporary crowns do not come into contact with the grafts. Otherwise, pressure on the transplanted tissue can provoke atrophy, and as a result, the implanted implant will lose reliable support and may be lost. Based on the specific surgical and orthopedic task, the implantologist decides what the graft will be, where to collect it, and how to attach it.
The price of tunnel plastic surgery of the alveolar ridge in the area of 3 teeth in Moscow
Today we offer patients one of the most advanced methods of bone grafting - 3D reconstruction. The capabilities of modern medicine are increasing every day; there are already new progressive solutions to the problem, in addition to those described above.
The cost of tunnel plastic surgery of the alveolar ridge in the area of 3 teeth in Moscow at Partner Dentistry, excluding the cost of taking a bone block, ranges from 15,000 rubles.
Possible complications
One of the main complications is a decrease in the stability of the implant due to an increase in bone tissue deficiency. Its volume is already insufficient, and for some reason it may become critical.
The result is mobility or even loss of the artificial tooth. This can be avoided only by strictly following the implantation technology and taking into account all contraindications related to the volume of bone tissue.
Other complications are possible:
- Damage to blood vessels and nerves passing through the canals of the jaw.
- Violation of the maxillary sinus due to a deficiency of bone height.
- Implant rejection.
- The development of peri-implantitis due to overload of the artificial tooth, poor oral care or due to other reasons.
As a precaution against complications, it is recommended to constantly monitor the condition of the artificial tooth and the mucous membrane around it, taking timely measures depending on the clinical picture.
Bone grafting of the alveolar process
It is not always possible to install a dental implant immediately after tooth extraction; in such cases, alveolar bone grafting is used. The ridge graft fills the void left by an extracted tooth and holds the volume of that space, while natural bone can fill the space with high quality living bone. Depending on the size of the tooth, a ridge graft requires 3 to six months before the implant can be placed. Watch the video of the procedure.
The material most commonly used for alveolar bone graft is bovine bone xenograft. The empty socket is filled with a graft immediately after the tooth is removed and secured with collagen and a pair of sutures.
Price
The cost of implantation without bone grafting includes consultation, diagnostics, sanitation of the oral cavity, anesthesia and the operation itself.
The last stage includes the cost of the implantation system (implant, abutment), which depends on the manufacturing technology and brand. The final cost for a turnkey operation varies from 50 to 100 thousand rubles.
It is important to know that when you slowly and carefully search for a more economical option, you always find one at which prices are significantly lower than market ones. So the lower price limit is 50,000 rubles. can be considered conditional.
Types of grafts for bone grafting
Natural bone material for bone grafting in modern medicine is not used as often as it seems. Innovative technologies for the production of artificial transplants make it possible to avoid many of the disadvantages and risks of using natural materials.
There are four types of grafts for bone grafting:
- Autogenous material. Transplants that are taken from different parts of the jaw, chin or hard palate from the patient himself. It takes root the fastest and most successfully, since it does not have antigens to which the human immune system will react. However, the installation of such grafts requires additional intervention. During the recovery period, multiple surgical approaches will need to be monitored and cared for.
- Allogeneic material. Natural bone material that is taken from another person. As a rule, corpses are used, that is, the use of such transplants requires special laws that allow the removal of any body parts from deceased people. Allogeneic material takes root less well, but is also absolutely safe, as it undergoes a number of treatments and quality controls.
- Xenogeneic transplant. Materials of animal origin are enjoying great success in modern technologies. They are made from bovine tissue and carefully modified into a human-fit structural design or shavings. By filling the space with such material, the doctor increases the likelihood of increased regeneration of the patient’s own bone.
- Synthetic material. Artificial structures are widely used for several reasons. The main one is the low cost of the material. In addition, the patient can have 100% no doubt about the safety of a synthetically created graft.
The patient is involved in the selection of material for bone grafting, since the financial side of the issue is not in last place. The dentist is obliged to explain to the person in detail all the features of natural and synthetic transplants, as well as recommend the most optimal options.