Repairing a removable denture is a technical manipulation aimed at restoring its appearance, integrity and functionality. It is carried out in dental clinics or denture laboratories. According to statistics, breakage of prostheses is a common phenomenon, which is encountered by 10% of patients treated by an orthopedist. The reasons that led to this can be of various origins, and even the most expensive and high-quality products are not immune from problems. It is not always necessary to make a new prosthesis; it is quite likely that it can be repaired without incurring significant material costs.
Common causes of removable denture malfunctions
The most common causes of removable denture failures:
- A manufacturing defect.
- Failure to comply with or violation of prosthesis installation technology.
- Improper or careless care of the prosthesis.
- Increased chewing load on the structure.
- Injury due to impact with a hard surface.
- Poor quality material.
- Changes in the structure of supporting teeth (looseness, destruction).
- Use of a prosthesis after its service life has expired.
All this causes the need for restoration of a removable denture. It must be performed by qualified dental technicians.
Repair, correction, relining of full-arch removable dentures
All inaccurately made full dentures can cause various lesions of the oral mucosa and inflammatory growth, so repairing, adjusting and relining dentures in such cases is very important.
Repair
A fracture of the prosthesis can occur either during its use or when it hits a hard surface. Thus, the key point of repair will be the exact matching and connection of the broken parts in the original position.
Median fractures
Causes
- Absence or insufficient relief in the midline
- Resorption of alveolar ridges
Procedure
The broken parts are matched and fixed with sticky wax on the polished surface
- The matching of parts can be strengthened using pins or plastic sticks
- Any undercuts on the contacting surfaces are isolated with wax or plaster
- Gypsum is poured onto the contacting surface. After the plaster has cured, the prosthesis is removed from the model and cleaned of wax residues.
- The edges of the fracture are excised, expanded by 8-10 mm along the fracture line and beveled towards the polished surface to expand the adhesion area
- For a more durable bond, dovetail cuts can be applied to the fracture line.
- The model is painted with the middle part demarcated, then the prosthesis is attached to the model using rubber clamps
- Self-curing resin is applied to the modified fracture line until all voids are filled. The area of the median palatal suture is unloaded.
- If necessary, make corrections
- Rework in some situations
Breakdowns in various parts
Main reasons
Hitting the ground or sink when cleaning
Types
- Floor without defects (repair as described above)
- Floor with part missing
Procedure
- An impression is taken when the prosthesis is inserted into the oral cavity.
- After casting the model, the defect is filled with wax or self-hardening plastic, restoring the lost part. This is followed by packing, replacement, curing, grinding and polishing.
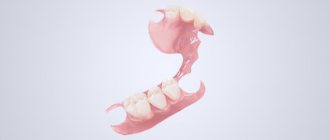
Breakage with fracture or loss of teeth
- Broken teeth are cut with burs
- A sufficient amount of plastic is removed from the lingual side and dovetail cuts are made.
- Teeth of similar shape, size and shade are placed in the correct position and fixed with base wax
- A “key” is made from plaster to register and maintain the position of teeth
- Teeth to be repaired are removed with all surrounding wax
- Subsequently, the teeth are set according to the plaster “key”
- Self-hardening resin is applied from the lingual side until the defect area is completely filled. The surface is covered with thin foil
- After curing, the “key” is removed, the prosthesis is ground and polished
Correction of a complete removable denture
Prosthesis correction refers to manipulations that lead to greater tissue adaptation to the prosthesis by adding new material to the contacting surface without changing the occlusal relationship.
It is used in cases where the prosthesis loses good fixation or adaptation to the underlying tissues, while all other factors, such as occlusion, aesthetics, centric relation, and the basis of the prosthesis remain satisfactory.
- Loss of retention
- Instability
- Food under the denture
- Damaged mucosa
General terms
- Optimal condition of the underlying tissues
- Correctly installed lateral and central occlusion
- Adequate peripheral expansion
Procedure
The patient is forced not to wear the prosthesis for 48 hours to allow the mucous membrane to recover and reduce inflammation due to improper fit of the structure.
Prosthesis correction
- Any undercuts on the base are removed
- Side edges are checked and adjusted
- The edges are rounded and smoothed, and the space is also prepared for filling with new material.
- A hole is made on the palatal side so that excess impression material can come out through it.
- A new impression is taken in centric occlusion and correct occlusal relationship
- A plaster model is cast using the new impression.
- The denture is removed, the old base is carefully cleaned
- The new plastic is packaged and the prosthesis is cured in a setting with water at 45 degrees for 20 minutes. This mode prevents the porosity of the material and its deterioration (releasing internal stress)
- Manual grinding and polishing of the prosthesis is carried out
Relocation
This is the process of readapting the prosthesis to the underlying tissues by replacing the base without changing the occlusal relationship
Indications
When the existing base is of unsatisfactory quality, damaged or has pores
Procedure
- An impression is made using the existing prosthesis, then the model is cast
- Occlusal and incisal indices are established using a duplicator, areas duplicating the lower teeth are attached to the upper teeth to obtain an accurate jaw relationship
- The denture with impression material is removed from the model
- The artificial teeth are separated from the denture and all base material is removed (porcelain teeth are removed under high temperature)
- The teeth are placed and held in the correct position in the index model using adhesive wax on the labial and buccal surfaces
- A sheet of base wax is placed along the edge of the model
- The top of the duplicator closes and the artificial teeth are positioned in the correct position
- The model is deleted and cleared
- After cleaning, the model is attached to the top of the duplicator to check the occlusal relationship
- The occlusion of the relined prosthesis is subsequently corrected in the oral cavity
Author: Dr. Jaouadi Jamila
Repairing removable dentures
Of course, you can find a lot of advice on how to repair removable dentures yourself, but there are negative aspects to this. You can completely damage the product, making it unsuitable for restoration. Or there are defects that cannot be detected visually, but are noticeable when worn. Therefore, it is wiser to turn to qualified specialists - this will save your money and time.
Clasp dentures
The clasp design is used when at least several supporting teeth are present. It is characterized by high strength due to the presence of a metal arc. But, nevertheless, the service life of the clasps is not very long; they may periodically require repairs. However, if the arch or frame is fractured, it is not possible to repair them; new ones must be ordered. The cost and duration of restoration of the prosthetic system depend on the complexity of the breakdown. On average, repairs take no more than 3 hours. What can happen to clasp removable dentures:
- appearance of cracks or fracture of the base plate.
The technician glues the damaged parts and brings it into proper condition. The work is carried out within a couple of hours; - The clasp
(a device for attaching the prosthesis to the supporting tooth) has broken. The defect can be simple or complex. It can be eliminated by welding or replacing bushings. Time costs – from 2 to 4 hours; - loss of crowns.
The cost of eliminating this problem is affected by the possibility of installing an existing element or whether a new crown needs to be fixed; - the base has darkened.
In this situation, the aesthetic factor suffers - the structure becomes clearly visible in the oral cavity, which patients may not like. The issue is resolved within one hour.
Fracture of clasp (metal hook)
In the dental office, the doctor takes an impression of the patient’s mouth along with the prosthesis and sends it to the dental technician in the laboratory. A plaster model is cast along with the prosthesis. The technician removes the broken clasp from the inside of the denture and bends a new one along the supporting tooth. After polymerization of the plastic, it is applied first to the site of the sawn hook, then to the outside of the prosthesis. After a short period of time, excess plastic is removed with a cutter on an electric motor, and the repair area is processed and polished, if necessary.
Repairing nylon dentures
The restoration process of nylon artificial elements is quite labor-intensive. They should be handled by good technicians from a laboratory or prosthetic repair shop. Patients often present with the following problems:
- crown loss.
Product repair involves the use of special dental adhesives or resins. After gluing is completed, the treated area is polished; - damage to the fasteners.
Dental laboratory workers use adhesives that securely hold the components that hold the prosthesis on the teeth; - failure of the base.
Here it is not enough to simply connect parts of the structure; it needs to be strengthened. For this, a metal mesh is used; - weakening of the fixing properties of the prosthesis.
In order to restore fastening abilities, a special procedure is prescribed - relining the removable denture. This is quite a difficult and painstaking work; it takes from one day (in a clinical setting) or more time (in a laboratory transfer).
Any problem in the prosthetic structure requires an individual approach and high professionalism on the part of the dental technician.
Repairing plastic dentures
Fractures and cracks in plastic dentures can be caused by various reasons. They are often caused by falling prostheses, biting hard food, etc. But most often the causes of fractures remain unclear. There is, however, no doubt that the basis for repeated fractures and cracks in the same place is the incomplete correspondence between the relief of the prosthesis base and the prosthetic field. During chewing movements, due to uneven pressure, the plastic ruptures in the area where the prosthesis balances.
Understanding the mechanism of cracks and fractures in dentures that occur during eating is very important. This is what can help the doctor choose the most rational method of repairing the prosthesis and prevent recurrence of the fracture.
We must strongly condemn the unfortunately widespread practice when prostheses are accepted for repair and returned to patients through registrars or other persons, without the participation of doctors. At the same time, the deadlines set for repairing dentures, according to “tradition,” are still unreasonably long (a day or even more). After all, one cannot help but take into account that the patient, deprived of a prosthesis for this time, experiences very great inconvenience, and sometimes suffering.
In recent years, there have been attempts to streamline the way dentures are repaired. They consisted in the fact that the authors shortened one of the stages of work - casting models, placing the glued prostheses directly into the ditch. However, these proposals do not solve the problem of repairing dentures within a period of 15-30 minutes to 2 hours.
The emergence of new materials always causes the need to change existing technological processes. Thus, in dental prosthetics, a radical change in technological processes was associated with the replacement of porcelain teeth and rubber with plastic, and gold and other precious metals with steel.
Currently, thanks to the availability of fast-hardening plastics with high strength, the technology for repairing prostheses must change.
All types of repairs to removable dentures can be divided into two groups: simple and complex. Simple repairs include:
- 1) adding 1-2 teeth if there is artificial gum in the prosthesis,
- 2) eliminating the crack,
- 3) adding a clasp to the prosthesis (without taking an impression),
- 4) connection of parts of the prosthesis when it is completely fractured.
Complex repairs include all others when you have to add missing teeth or other parts (wings) to dentures without artificial gums, rearrange the clasps, and sometimes combine all these works at the same time.
Such repairs are made, as a rule, after receiving an impression of the jaw along with the prosthesis put on it. Often it is also necessary to obtain impressions of the antagonists' teeth using wax rollers.
The difference between working with fast-hardening plastics is that all aspects of repair are completed without immersing the prostheses in ditches with all the accompanying processes, which, as is known, take a lot of time.
The variety of different types of repairs does not allow us to give a detailed description of each of them. Therefore, we will present the most typical ones.
Measures to prevent breakdowns
Breakage of a denture is a big nuisance. To avoid it, you need to carefully care for the structure, handle it carefully and regularly visit an orthopedic doctor to monitor its condition. What to do at home:
- remove and thoroughly clean any stuck pieces of food;
- do not use toothpastes with a strong abrasive effect;
- buy a toothbrush with soft bristles;
- rinse after every meal, no matter whether it was a full meal or a tasting;
- remove dentures over a towel or cup of water - this reduces the risk of hitting a hard surface and, as a result, severe mechanical damage.
Even though the material used in removable denture systems is quite smooth, bacteria can also accumulate and multiply on it. To ensure optimal disinfection, special pharmaceutical products should be used. Your doctor will tell you which ones exactly.
Unfortunately, many people are now forced to resort to prosthetics. The development of dental technologies makes it possible to produce removable elements that are practically indistinguishable from natural teeth in appearance and quality. Our clinic’s specialists are highly qualified, they are always up to date with innovative developments and use only high-quality materials. Do not worry about the breakdown of the prosthetic structure - with us you can get prompt assistance from an orthopedic dentist at an affordable price.