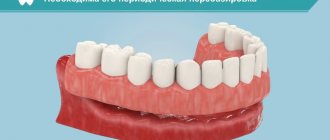
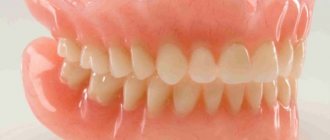
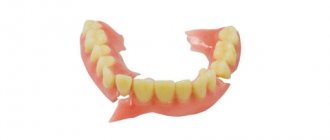
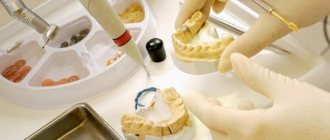
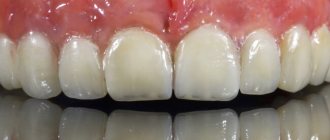
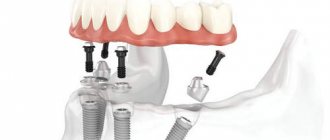
Denture – what is it?
Many people are scared by the very word “prosthesis,” but in vain. It is this device that makes your appearance more attractive, because artificial teeth can be made much more perfect than those that you naturally have. A denture is a dental structure that replaces natural teeth. When made correctly, all types of dentures do not cause discomfort, look beautiful and are perceived as your own. They are installed in case of complete or partial loss of teeth. Prosthetics are carried out in stages:
- prepare the oral cavity - treat, install fillings, remove plaque and tartar;
- make a cast;
- make a prosthesis;
- carry out a fitting - check the correctness of the bite and comfort;
- make a fixation.
Two main groups of dental structures
What dentures are best? Modern orthopedics has many different designs and materials for their manufacture. First of all, all designs are divided into two large groups:
- Removable – independently removed and installed by the patient in the oral cavity. Recommended for loss of a large number of teeth. A special corrector cream is used for fixation. Hygienic treatment is easy to carry out and only seems tedious when getting used to it.
- Fixed – used when one or more teeth are lost. They are firmly fixed and, if necessary, can only be removed by a dentist. Care is carried out in the same way as for your own teeth. This is the most suitable option when it is necessary to restore individual teeth.
When installing dentures, all factors are taken into account: the number of lost teeth, the condition of the gums, the location of the defect, the characteristics of the bite, and the cost.
Indications for the use of fixed structures
The essence of permanent prosthetics is to install a dental structure in place of a missing tooth fragment or to fill missing units for a long time.
This is interesting: Stamped crown: alloys, manufacturing and installation stages
When wearing a prosthesis, there is no need to periodically remove it from the jaw to perform hygienic procedures.
Experts have identified the following indications for the use of this method of dentition restoration:
- defects of the anterior or chewing units with the extent of the affected area exceeding 1/3 of the part;
- in case of partial destruction of the bone tissue of the tooth, when it is possible to preserve the root system;
- with the loss of one tooth or several located in a row;
- if teeth are completely missing.
Orthopedic dentist about fixed dentures:
Material for production
“What materials are dentures made from?” - patients who decide to have them are often interested. In ancient times, shells, pebbles, bones, wood, metal, pearls and gold were used for these purposes. An entire industry has now been created dedicated to the development of durable and safe materials. For this use:
- Nylon is a non-allergenic material, convenient for work, but sometimes the bone tissue underneath atrophies and gums rub.
- Ceramics - completely recreates the natural properties of tooth enamel, has strength and durability.
- Metal ceramics – a metal frame enhances the properties of ceramics and is used to restore chewing teeth.
- Surgical steel is a modern material, easy to install and use, and does not cause an allergic reaction.
- Plastic – mainly used for complete dentures when all teeth are lost. The material is light, has no contraindications, low prices.
- Titanium is a very durable and lightweight metal that does not cause discomfort.
- Gold – rarely used for people with oral diseases.
- Acrylic resin is often used for prosthetics in children. It is durable and fits well to the gums.
All materials differ in quality and price. The cheapest products are made from plastic, the most expensive ones from gold. For each patient, they are selected by the doctor depending on the individual characteristics, method of recovery, the client’s wishes and financial capabilities.
Construction and fastening of removable structures
The removable design of a denture consists of two main parts: the base and artificial teeth. If there are supporting teeth, it is attached to them; if there are none, implants can be placed. In this case, fastening is done using:
- Clasps - made of metal, fixed at the base of the tooth, secure the structure well and do not damage the enamel. A significant drawback is that they are visible when you smile.
- Locks - consist of two parts: one is located on the structure, and the other is on the supporting tooth or implant. They securely, easily and beautifully fix the prosthesis. It is believed that the lock has greater aesthetics and durability, in contrast to the clasp.
The fastening of complete removable dentures made of acrylic and nylon, carried out by suction to the hard palate and gums, is unreliable. For better fixation, it is recommended to use a special cream. It is applied to the inside of the denture and pressed tightly against the jaw, fixing it for 12 hours. It is especially recommended for individuals with excessive salivation. For people with little salivation, powders are suitable, which are poured in a thin layer onto the denture before being inserted into the oral cavity.
Fixation and stabilization of partial dentures
Methods for fixing partial removable dentures have remained unchanged over the past 10 to 20 years, i.e., since the advent of modern plate dentures.
| Fixation method | Description |
| Clasps | Metal or silicone hooks that fit around natural teeth and secure the denture in the mouth. |
| Attachmen | Micro-locks are installed on the supporting teeth, which snap into place upon contact with the structure. |
| Telescopic crowns | They are considered a very complex structure. The natural tooth is prepared and a special metal cap is put on it, after which a clasp prosthesis with grooves for fastening is installed. |
Clasp dentures: pros and cons
Such dentures have a comfortable orthopedic design and focus not only on the gums, but also on the existing teeth. A clasp is an arc that is made of cast metal based on titanium or precious metals. Artificial teeth with acrylic imitation gums are attached to it. This kind of prosthetics is quite popular. The main advantages of clasp dentures:
- Strong fixation.
- The minimal volume occupied in the mouth allows for easy movement of the tongue and lips.
- Durability – service life from 5 to 10 years.
- Even distribution of load across the jaw.
- Lightweight and easy to maintain - can be used around the clock. Once a month, remove and wash thoroughly.
- Aesthetics when fastening with a lock.
The disadvantages include the following:
- capable of breaking under heavy load;
- installed only if there are four supporting teeth on the jaw;
- quite high cost.
It should be noted that adaptation to this type of dentures occurs very quickly and takes several days. The patient does not suffer from changes in the taste of foods and speech distortion.
Metal-ceramics is a material used in dental orthopedics
This is a durable and wear-resistant composite material that is resistant to external influences. Metal-ceramic crowns consist of:
- Metal caps - are made from a special medical alloy, which includes gold, palladium and platinum.
- Ceramics, which are applied to metal in several layers, imitating the texture and color of healthy teeth.
Bridges are made on the basis of crowns and can replace from one to several teeth. The advantages of metal-ceramic dentures are as follows:
- Strength – teeth can withstand heavy loads as a result of their even distribution.
- Durability – proper operation guarantees a service life of up to 15 years.
- Aesthetics – the shape and color are chosen harmoniously with the natural teeth.
- Functionality – artificial teeth perform the same functions as real teeth.
- Biological compatibility - do not cause gum irritation or discomfort.
- Color fastness – there are no restrictions on the use of coloring products.
Metal-ceramics also have disadvantages: it is necessary to remove nerves from healthy teeth and sharply grind the latter to attach the prosthesis. The hardness of the material sometimes leads to abrasion of the natural tooth on the opposite jaw.
What is the basis for choosing prostheses?
The design is selected depending on the condition of the teeth, gums, qualifications of the orthopedist, financial capabilities and desires of the patient. Which dentures are best? The most commonly chosen are the following:
- Acrylic plastic is a budget option. Prostheses are light, quite dense, so they retain their shape well, but they lack the necessary plasticity, which contributes to breakage. Sometimes an allergic reaction occurs. Using acrylic structures, mini-implants are additionally installed to fix the prosthesis. This leads to increased fastening strength. Prosthetics with this material is possible with complete or partial absence of teeth, and it has no age restrictions. A complete denture covers the palate, so it can take a long time to get used to.
- Nylon dentures are soft, lightweight and durable. They become especially relevant if the patient has an allergic reaction to metal and acrylic; they look good throughout the entire period of use.
Dentures can be left in place at night; they do not cause discomfort and are flexible. In the design, artificial teeth are visible through the base - this is a significant drawback. Prices for nylon prostheses are higher than for plastic models.
- Bugel - are very popular, are characterized by good strength and long service life. The load is distributed evenly on the jaw, which contributes to the long-term preservation of living teeth. Such prostheses are expensive.
Types of Removable Partial Dentures
There are several design options.
Lamellar. They are considered the most affordable prosthetic option. They are a plastic base that exactly follows the contours of the gums, with artificial teeth. They are attached to the supporting teeth using plastic hooks. The base is made of acrylic, nylon or modern hypoallergenic material Akri-Free.
Advantages of partial removable lamellar dentures: low price, easy installation, quick production, suitable for patients of all ages.
Disadvantages of plate products: poor fixation, partial restoration of chewing function, distortion of diction, poor aesthetics.
Partial plate denture
Bugelnye. They are presented with a base with artificial teeth on a metal frame (clasp). This gives additional strength and rigidity, so the products are reliable and durable. They are attached in different ways: hooks, attachments and telescopic crowns (the choice of attachment method depends on the characteristics of the clinical situation).
Advantages of the design: reliable fixation, completely restore chewing function, look natural in the oral cavity.
Disadvantages: more expensive, not suitable for patients with metal allergies.
Partial clasp denture
Immediate dentures. They are used as a temporary option for prosthetics after removal, as well as for the period of implant healing. Attaches with plastic hooks. They are used to restore both 1-2 teeth and multiple missing teeth. An immediate denture allows you to restore aesthetics, chewing function and prevent the displacement of other teeth into the space vacated after removal.
Advantages: reasonable price, quick installation, satisfactory aesthetics.
Disadvantages: suitable only for temporary use, does not withstand significant chewing loads.
Partial immediate prosthesis “butterfly”
Prosthetics of the upper jaw. How to make the right choice?
There is a significant difference in the prosthetics of the lower and upper dentition due to the structural features of the jaws. On the top there is much more space for supporting the prosthesis in the form of a palate, and the load on the supporting teeth, if present, is much less than on the bottom, but high aesthetic requirements are placed on the design, because the top row is visible when you smile.
Removable dentures for the upper jaw can be either partial or complete. Partial ones are used when there are several living teeth left on the jaw; a structure is fixed on them. In this case, any type of modern construction is suitable, but the most ideal option is considered to be a Quadrotti prosthesis or a clasp prosthesis that does not cover the palate.
In case of complete loss of teeth in the upper jaw, it is allowed to use any construction except the clasp one, since there is no support for the prosthesis. The most convenient and comfortable choice is the Quadrotti prosthesis, which is attached to the gums and is created without a palate. You can also use the following designs: Acry Free and acrylic, but they are less comfortable and have a palatal bridge. The doctor will tell you which prosthesis is best to choose, depending on the condition of the oral cavity.
Mechanical methods of fixing prostheses (clasps)
Currently, orthopedists have various designs of clasps that allow them to fix dentures in difficult conditions using natural teeth. But this is not enough when solving problems of attaching partial removable dentures. The main task is to use a system of clasps for fastening the prosthesis that would ensure fixation of the prosthesis and at the same time cause as little harm as possible to the supporting teeth. From this point of view, fixation of a removable partial denture is a complex biomechanical problem.
All existing varieties of clasps have both positive qualities and disadvantages. Knowing where and how to use a particular clasp is a science. It is comprehended by studying the clinical features of partial tooth loss, the functional characteristics of the tissues and organs of the oral cavity, as well as the mechanical properties of the clasps themselves and the method of their interaction.
Considering the different types of clasps, you can note the common details in them, which are an essential part of almost any of them. These parts are the shoulder, body, clasp extension and occlusal pad. In some clasps the listed parts may be presented in full, in others partially. There are more complex clasps, the design of which includes additional parts.
The clasp arm is the springy part that covers the crown of the tooth. Its position is determined by the anatomical shape of the tooth. In practical dentistry, it is customary to divide the surface of the tooth crown into two parts - occlusal and cervical. The boundary between them is the equator of the tooth, that is, the line passing along the most convex part of the tooth (Fig. 125). In the front teeth, the equator on the labial side lies closer to the gum; on small and large molars, it runs in the middle, somewhat closer to the gingival edge.
When making a clasp arm, you need to remember the following requirements.
- 1. The shoulder should cover the tooth from the labial or buccal side, located directly behind the line of greatest convexity, i.e., between the equator and the gum.
- 2. The arm of the clasp, whether round or flat, should touch the surface of the tooth at as many points as possible. The fit at only one point leads to a sharp increase in pressure when the prosthesis moves and contributes to the occurrence of enamel necrosis.
- 3. The clasp arm should spring back when the prosthesis is displaced. Not all clasps have this quality: wire clasps are more elastic and cast clasps are less pliable, although the latter also have advantages. Unlike bent wire clasps, they more accurately follow the relief of the tooth, and therefore their harmful effect on tooth enamel is less pronounced.
- 4. The clasp arm should be passive, that is, it should not exert pressure on the covered tooth when the prosthesis is at rest. Otherwise, a constantly acting unusual stimulus arises, which is the cause of functional overload. Active clasp pressure, as noted above, can cause enamel necrosis if the tooth is not covered with a metal crown. Therefore, it is important that clasps are made from a material that has good elasticity and retain these qualities during heat treatment.
- 5. The clasp shoulder should be rounded and polished. Sharp ends, especially those of wire clasps, can damage the mucous membrane of the lips and cheeks when inserting and removing the prosthesis.
The body of the clasp is its stationary part, located above the equator of the abutment tooth on its proximal side. It should not be placed below the equator at the neck of the tooth. In this case, the clasp prevents the application of the prosthesis. On the front teeth, for aesthetic reasons, you can deviate from this rule by placing the body of the clasp closer to the gingival margin. But then a gap must be created between it and the tooth, facilitating the application of the prosthesis.
The extension is intended for attaching the clasp to the prosthesis. It is placed along the edentulous alveolar ridge under the artificial teeth. It is not recommended to place the process on the palatal or lingual side of the base, as this often leads to fracture of the prosthesis. The processes can be supplied with finely looped meshes, and in arched prostheses they are soldered to its frame.
Based on their function, they distinguish between holding, supported and support-holding (combined) clasps. The first ones are intended mainly to hold the prosthesis. Located below the equator on the lower teeth and above on the upper teeth, they slide along the surface of the tooth. The prosthesis, strengthened with their help, moves towards the mucous membrane under vertical pressure and sinks into it. In this case, the pressure is transferred not to the tooth, but to the mucous membrane. During lateral shifts of the prosthesis, the retaining clasps are included in the distribution of chewing pressure, transmitting it to the supporting teeth at an angle to the root, i.e., in a direction that has always been considered of little benefit to the periodontium.
Supported and combined clasps, in addition to the shoulder, usually have an occlusal pad located on the occlusal surface of the tooth. With its help, chewing pressure is transmitted to the supporting tooth along the length of the root, i.e. in the most favorable direction for the periodopt. Combined clasps are a combination of retaining (usually double-armed) clasps with supported ones. Thanks to this device, they take part in the distribution of both horizontal and vertical forces, thereby differing favorably from retaining clasps. By transferring part of the chewing forces to the supporting teeth, supported and combined clasps relieve the mucous membrane from chewing pressure, which is not physiological for it. Retaining clasps are made of metal (gold, stainless steel, gold-platinum alloy) or plastic. Metal clasps, in turn, can be wire or tape. If they are made manually (by bending), they are called bent; if they are cast, then cast.
There are many types of retaining clasps available. The most common are single-arm wire clasp, loop wire clasp, approximal clasp, single-arm band clasp, double-arm wire clasp, extended clasp, dento-alveolar clasp and gingival clasp.
The holding properties of a metal clasp depend on the material from which it is made (gold, steel), its heat treatment, cross-sectional profile and arm length. Clasps made of an alloy of gold and platinum have the best springing properties. Increasing the platinum content in the alloy makes it possible to enhance the elastic properties of the clasp wire.
The length and diameter of the cross section also affect the elasticity of the clasp. A long shoulder is more elastic than a short one. With an equal cross-section, the elasticity of the clasp on the premolar and molar will be different. In order for clasps on different teeth to have the same elasticity, wires of different cross sections should be used.
For clasps, wire with a diameter of 0.6 to 1.5 mm is produced. In addition, 750 gold alloy wire is produced, the diameter of which also varies.
New generation dentures
Modern dentures are functional and comfortable. You can install any one: removable or non-removable, restore partial or complete loss of your teeth. They are made from modern synthetic materials and have the following advantages:
- have antibacterial properties;
- do not absorb odors;
- soft and light;
- comfortable to wear and does not cause discomfort;
- most of the oral cavity is not covered by the prosthesis;
- the appearance is as close as possible to natural teeth.
It should be noted that all prostheses have reliable fixation, but more and more models are appearing that are not removed at night.
Modern dentures for complete loss of teeth
In the absence of teeth, the entire load from the prosthesis is transferred to the gum, which often leads to a decrease in its height. As a result, dentures need to be replaced at least every three years. In addition, there is a problem with fixation, especially of structures on the lower jaw. The most popular new generation complete dentures include the following:
- Acry-free – have high aesthetic characteristics; the prosthesis material is similar in color to the oral mucosa. The products are soft and elastic, do not rub the gums, and suggest the presence of a bridge in the palate. Service life up to 10 years.
- Quadrotti - the base part and fastenings are made of modern material, soft and pleasant to the touch, which is easy to process, withstands significant loads, does not corrode and does not cause allergic reactions. The design lacks a massive sky cover. Full dentures are comfortable and durable.
- Acrylic - made of acrylic plastic and is an economical option. The advantage of acrylic is a wide palette of colors, which allows you to accurately match the natural color of your teeth.
But these models partially block the palate, therefore causing some discomfort and leading to a distortion of taste. In addition, the material has a porous structure and is quite fragile.
- Nylon dentures are losing their relevance and are gradually leaving the market. When used, nylon stretches greatly and leads to bone tissue atrophy, so after a short time the structure no longer stays in the oral cavity and begins to fall out. And the upper jaw prosthesis covers the palate.
In case of complete absence of teeth, acry-free and quadrotti dentures are considered the most comfortable. Their designs are comfortable, safe and aesthetically pleasing. Acrylic plastic devices come next, and nylon systems come last.
In case of complete loss of teeth, the main method of orthopedic treatment is still the production of complete removable dentures. With the active development of dentistry, the introduction of new materials and technologies, little attention is paid to the manufacture of complete removable dentures, and the method remains the most conservative and practically did not change with the advent of acrylic plastics.
Every dentist in his practice has encountered the difficulties associated with each stage of prosthetics, as well as the inability to achieve stabilization and fixation of dentures in the oral cavity (especially in the lower jaw) after completion of treatment. This leads not only to the inability to fully restore chewing efficiency, but also to speech impairment, in addition to dissatisfaction with appearance. What to do with such patients? The easiest way, as many do, is to get rid of them by sending them to another clinic, or simply refuse them. But you can explain everything to the patient, make him your ally and try to make prosthetics that will at least somehow satisfy him.
Using a clinical example, we will try to trace all the stages of making dentures and dwell on some of the features of manufacturing complete removable dentures on the basis of the State Unitary Enterprise RO "OHSP".
Patient K., 64 years old, came to our clinic with complaints of the inability to eat a full meal, an aesthetic defect in appearance, and speech impairment.
An external examination of the patient revealed characteristic signs of complete edentia: a decrease in the lower part of the face, recession of the cheeks and lips, as a result of which the nasolabial and chin folds are sharply expressed, the chin stands sharply forward, the corners of the mouth are drooping (senile face).
Photo 1. Patient's appearance.
Photo 2. Prosthetic bed of the upper jaw.
Photo 3. Prosthetic bed of the lower jaw.
Stabilization and fixation of dentures depends not only on anatomical and topographical features, which will not be considered in this article, but also on the quality of impressions and the correct choice of the boundaries of future dentures.
We divide impressions into primary and secondary. Primary impressions are made with standard toothless trays using alginate mass for casting models with regular plaster, on which individual trays (photos 5, 6) and bite wax templates are made, and diagnostic models are used to study the prosthetic bed of both jaws. Secondary impressions (functional) are used to obtain models from super plaster and to carry out the final stages in the manufacture of prostheses.
Stages of obtaining primary and secondary (functional) impressions.
1) Alginate impressions (photo 4).
2) Fitting and forming the sides of individual spoons (photo 7, 8, 9).
3) Obtaining stabilization impressions (photo 10, 11).
4) Obtaining decompression functional impressions (photo 12, 13, 14).
Fitting individual trays (photos 5, 6) in the oral cavity consists of precise fitting along the border of the proposed dentures, achieving stabilization, and then reducing the sides of the trays by 1-1.5 mm. Lubricate the spoons with Polyether Adhesive 3M ESPE, let them dry for 5 minutes, and begin to form the boundaries of the dentures. The optimal material for forming borders is Functional impression Detaseal or Orthogum Zhermack. In this work, we use Orthogum, which is applied to the edge of the spoon with wet hands in the form of a roller, and we form the boundaries of the denture in the oral cavity for 1.5-2.0 minutes (photo 8, 9). Having formed and obtained a valve zone on the trays, which will create good suction for the dentures, we begin to take impressions from the stabilization zones. The stabilization zone on the upper jaw is the border running along the crest of the alveolar process, covering the entire area of the hard palate, not reaching line A by 3 mm. On the lower jaw, the stabilization zone runs through the center of the alveolar process, descends to the transitional fold, not reaching 2-3 mm. Therefore, with pronounced atrophy of the alveolar processes, the stabilization zone of the dentures sharply decreases, and in the lower jaw it may be completely absent.
A stabilization impression is obtained using Elite HD+ Monophase.
Express Ultra-Light Body impression material (photo 4).
To reduce pressure on the mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed and compensate for the pliability of the mucous membrane, we perforate the stabilization layer together with the tray or make decompression grooves in the impression (photo 10, 11).
At the next stage, we make models from superplaster (photo 15, 16), wax bite templates (photo 17, 18) and determine the central occlusion (photo 19).
Central occlusion is characterized by the following main features: the muscles that elevate the mandible contract symmetrically, evenly, the articular heads are located at the base of the slopes of the articular tubercles, at the depth of the articular fossae. When trying on wax reproductions of dentures (photos 20, 21, 22), we evaluate the patient’s appearance visually, take repeated anthropometric measurements of the face, in the oral cavity we pay special attention to the boundaries of the dentures, especially in the area of the frenulum and mucous-muscular cords, and check the occlusal planes (closing teeth ). Already on wax bases it is possible to assess the degree of stabilization and fixation of future dentures. We check the relationship of the dentition in the phase of physiological rest (the separation of the dentition should not exceed 2-3 mm), and also carry out an aesthetic examination together with the patient. The transfer of the wax reproduction into finished prostheses is carried out in the laboratory by injection molding using Re-fine Bright thermally cured plastic (photo 23, 24, 25).
The last stage of prosthetics is the application of finished dentures (photo 26) and correction in the oral cavity. For the initial correction we use a paste - Pressure Indicator Paste Sultan (USA), which, when applying prostheses, will show the presence and localization of areas of excessive pressure of the prostheses on the prosthetic bed. Adaptation to dentures usually takes from 2 to 4 weeks, depending on the complexity of the case. During the adaptation period, we evaluate the quality of orthopedic treatment, carry out psychological work with the patient, and teach him how to use prostheses correctly. The service life of plate dentures is limited to 2-3 years, and only with proper care. If necessary, during the period of operation it is necessary to carry out correction of the prostheses in the form of relining, which significantly improves the fixation and stabilization of the prostheses.