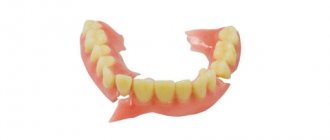
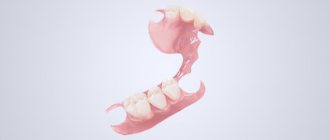
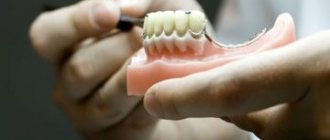
For prosthetics
Materials used for various procedures in dental clinics are divided into several types.
Consumables are classified into various areas in the field of dentistry, for example, materials for prosthetics, surgical, orthodontic and other areas.
This separation of types allows dental clinics to quickly make purchases and determine the necessary consumables that are acceptable in their properties and cost.
The group of prosthetics includes means that make it possible to maximize the quality of the manipulations performed to solve problems associated with the dentofacial apparatus with the subsequent installation of orthopedic systems.
To determine the bite
To register a bite, dentists use impression materials from different manufacturers, the most popular of which are the following:
- O-Bite, presented by a German company. This brand of impression material is considered an impression material with 12 mixing tips per package.
The advantages include high strength and hardness of the material, minimal resistance to bite, precision in the transfer of contours, registration of both dentitions in one procedure. In addition, the mass hardens quickly and has a pleasant citrus aroma. Cost: 3800-4000 rubles. - Greenbite apple is produced in Germany by the company. The basis of the registration material is A-silicone, which has a thin viscosity and is characterized by medium fluidity and thixotropy.
The mass is not able to penetrate into the interdental space and is easily removed from the oral cavity. Polymerization occurs in 1 minute, which primarily distinguishes the material from its analogues. The set includes 12 pieces of mixing cannulas and contour tips. Price: 2500 rubles. - Elite HD+ Light Body Normal from the Italian corporation Zhermack . This product is considered a Class A hydrocompatible dental silicone impression material.
Has a runny consistency. Includes 12 mixing tips. The advantages of the mass include high biocompatibility, maximum precision in reproducing parts, increased dimensional stability, tensile strength, the ability to form a model after disinfection, and a long warranty period. Cost: 1300 rubles.
To form a dental stump
As a rule, clinics use both standard radiopaque unfilled composites with remineralizing properties and nanocomposites characterized by double and triple curing.
The following representatives of this group are widely used:
- Bis-Core. Dual-curing composite from the American manufacturer Bisco. Today it is recognized as the most durable material. Dentists prefer the material for its highest conversion rate and unprecedented strength. Price: 3200-3500 rubles.
- Jen LC-Core. The material is made in the USA and belongs to the category of highly filled, light-cured composite materials. It is most often used to restore the coronal part of teeth and build up a stump. The product has a blue color or a dentin tint. Cost: 700-800 rubles.
- RESIGLASS F. The material is manufactured in Brazil by the leading company Biodinamica.
It is considered a light-curing glass ionomer core material. This cement is capable of releasing fluoride, which is very important in modern dentistry. The advantages include aesthetic, mechanical features and anti-caries effects. In orthopedics it is used as a cushioning material when restoring a dental stump. Price: 3500-3700 rubles.
What is deep caries and what does it look like on an x-ray? We will discuss here the causes of an abscess after wisdom tooth removal.
At this address https://dr-zubov.ru/lechenie/zuby/kompyuternaya-tomografiya-sovremennyj-podxod-k-sverxtochnoj-diagnostike.html we’ll talk about cone-beam computed tomography of teeth.
For making temporary crowns
To perform these tasks, specialists more often use acrylic composites, however, as a good replacement, you can resort to using plastic masses or one-step cements.
As an example, consider several materials from well-known manufacturers:
- Q-Crown. The composite was created by JM Laboratories in Israel and is intended for the manufacture of temporary orthopedic structures. The material is strong in compression and bending, does not increase the internal temperature during polymerization, is elastic and easy to polish. Price: 3500 rubles.
- SUCCESS CD. The composite material is presented by a German company. It is characterized by high strength and withstand strong functional loads. It polishes well, retains its original shade, and cures quickly. Cost: 3500-4000 rubles.
- TempSpan C&B Material. This composite system for the rapid production of orthopedic replacements was manufactured by Pentron in the USA.
The possibility of double curing provides the material with unique technical characteristics, and thanks to the matrix of the substance, the finished product can easily be adjusted or refined with a fluid. Price 4000-4700 rubles.
Pins
Pins are usually called rods that a specialist uses to strengthen a damaged crown.
The design is used by a specialist when it becomes impossible to solve the problem in any other way, that is, when the crown cannot be restored without extension to the pin.
Pins are made from various materials, which differ in technical characteristics and quality.
Let's consider several popular models that can be purchased in online stores:
- A set of Unimetric titanium posts presented by the Swiss company Dentsply Maillefer. The set includes 145 pins with different crown heights, as well as penetration, calibration drills and cross-shaped keys. The design lasts about 3-4 years, and the quality of installation depends entirely on the qualifications of the specialist. Cost: 10,000–12,000 rubles.
- Set of gold plated anchor pins. Manufactured by various brands. Sold 12 pieces per pack. High quality brass products are widely used in dentistry. The thickness of the gold coating is 3 microns. Price for 1 piece. size S1 is 150-180 rubles.
- Dental Screw Post. These gold-plated anchor pins were released onto the dental market by the Swiss company Nordin. Each pin in the set is equipped with a shank, which makes screwing much easier without putting pressure on the dentin. The cost ranges from 350-800 rubles.
Wax materials
Wax materials are wax-based auxiliary dental materials used in orthopedic dentistry for the purpose of manufacturing an intermediate version of a therapeutic orthopedic apparatus.
Properties of wax materials
1. Chemical properties:
In terms of chemical composition, waxes are the highest saturated hydrocarbons of the fatty series, their monohydric alcohols and monobasic acids.
Waxes can contain all of these substances in a free state, but more often in the form of compounds called esters. Esters are formed as a result of the interaction of alcohols with acids with the loss of a water molecule.
2. Mechanical properties.
a) waxes dissolve well in gasoline, chloroform, benzene and essential oils; b) their relative density is less than unity, i.e. they are lighter than water;
c) with low heating they soften well, acquiring a high degree of plasticity; with a further increase in temperature, they easily turn into a liquid state, and then burn almost without a residue, with minimal ash content, which is important in casting processes;
In dental practice, as a rule, waxes are not used in their pure form, but mixtures of various waxes are used.
Dental wax mixtures are used mainly as modeling materials. To give dental wax mixtures certain properties, compositions are created from natural waxes, synthetic waxes and modifiers.
In dentistry, natural waxes (of natural origin) are mainly used. Synthetic waxes belong to the group of polymer compounds.
The physicochemical properties of synthetic waxes differ in many ways from natural waxes, and therefore their use in dental practice is limited. They are included in some wax compositions, but have not yet found widespread use.
Wax classification:
1. Natural waxes (contain mainly two groups of organic compounds: hydrocarbons and esters of higher fatty acids and higher monohydric, less often dihydric alcohols) are divided into:
a) mineral waxes, the main component of mineral waxes are hydrocarbons.
Paraffin is a solid, crystalline, colorless mass, odorless and tasteless. It is obtained by distilling high-paraffin grades of oil and coal. The chemical composition is a mixture of higher hydrocarbons. Density - 0.907-0.915 g/cm, melting point - 42-7 °C, volumetric shrinkage - 11-15%, soluble in ether, gasoline and partially in alcohol. It can be used to make phantoms of artificial teeth, but is most often used as a component of dental waxes and thermoplastic impression masses.
Ozokerite (earth wax) is a solid resinous substance with a faint odor of kerosene. Depending on the nature of the resinous impurities, it has a light or dark green color, sometimes brown. Density - 0.85-0.93 g/cm, melts at a temperature of 65°C. It is used in orthopedic dentistry as a component of some wax mixtures and thermoplastic masses.
Ceresin is a white or yellow solid. Melting point - 60-80°C, density - 0.91-0.94 g/cm. It is obtained by heat treatment of ozokerite in the presence of sulfuric acid. It dissolves well in many organic and mineral solvents (kerosene, gasoline, chloroform, acetone, etc.).
In its pure form it is not used in dental practice, but is included in many wax compositions and thermoplastic masses, increasing their melting point,
hardness and viscosity.
Montan wax is an extract from dissolved brown coal. Contains esters of higher alcohols. It is characterized by significant hardness and a high melting point of 73-80°C. Used as additives in dental wax mixtures to increase their melting point and hardness.
b) animal waxes, contain significant quantities of esters, acids, hydrocarbons and resins.
Beeswax has the greatest practical value among animal waxes. It appears yellow in color, but after exposure to hydrogen peroxide it becomes hard and loses its color. It softens at a temperature of 36-38°C, the melting point is 62-64°C, the coefficient of linear expansion when heated to 30°C is 0.0003. It dissolves well in gasoline, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide and essential oils. Improves the plasticity and modeling properties of dental waxes.
Stearin is a fine-grained, translucent, white solid with a greasy feel. Obtained by processing (hydrolysis) of beef or lamb fat. Chemically, it is stearic acid with an admixture of palmitic, hydroxystearic and isooleic acids. Density - 0.93-0.94 g/cm, melting point 68-7 °C. Dissolves in gasoline and chloroform. In dental practice it can be used for modeling teeth. It is introduced into wax compositions and impression thermoplastic masses in order to reduce their plasticity. Stearin is the basis for obtaining various polishing pastes.
Wax of animal origin also includes Chinese wax, spermaceti, and lanolin.
c) vegetable waxes, contain significant quantities of esters, acids, hydrocarbons and resins.
Carnauba wax is made from the leaves of palm trees growing in Brazil. The purified wax is yellow-green in color. The smell is reminiscent of hay. It does not knead in the hands, cannot be cut with a knife and is distinguished by resin-like fragility. Density - 0.999 g/cm, softens at a temperature of 40-45°C, melts at a temperature of 80-96°C, soluble in ether and boiling alcohol. In dental practice it is used as a modeling material. Included in dental wax compositions to increase their hardness and melting point. The plasticity of the compositions decreases when carnauba wax is added (Lavax wax mixture).
Japanese wax (fruit wax) is made from the fruits of wax trees growing in Japan and other countries. Under normal conditions it is a hard, brittle substance, but when heated it is very sticky and yellow-green in color. When left outdoors for a long time, it turns brown. Consists mainly of palmitic, stearic, butyric acids and glycerin. Density - 0.99 g/cm, softens at a temperature of 34-36°C, melting point - 52-53°C. Included in dental wax mixtures to increase their hardness and melting point. In this case, the plasticity of the mixture decreases.
Candelilla waxes - consist of 40-60% paraffin hydrocarbons, as well as free alcohols, esters, acids and lactones. Melting point - 68-73°C. They are used to increase the hardness of dental waxes.