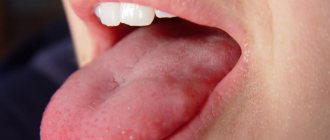
The glands of the mucous membranes of the nasal passages, as well as glands located in the throat, lower respiratory tract, and gastrointestinal tract, produce mucus, which helps moisturize these areas and protects them from the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms.
The mucous membranes in the nose produce about a quarter of the body's mucus every day. In most cases, this is not noticed, since it mixes with saliva and flows down the back wall of the throat. Then the person swallows it.
With increased mucus production, it becomes thicker and creates some discomfort. Why does mucus occur in the morning and when should you see a doctor?
Causes of mucus accumulation
One of the reasons for increased production and accumulation of mucus in the throat is the development of acute respiratory disease. Often this symptom occurs during an inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract, for example, with pharyngitis, laryngitis, sore throat, sinusitis, rhinitis, sinusitis.
The inflammatory process occurs with increased mucus production, which subsequently flows down the back wall of the pharynx or rises from the lungs. This exudate helps cleanse the respiratory tract of harmful microorganisms and goes away on its own after recovery.
Another reason for mucus in the throat is the development of a chronic process in the upper respiratory tract. If therapy for the corresponding diseases is not started in a timely manner, an intense accumulation of mucus occurs, which becomes permanent.
In this case, the symptom manifests itself under the influence of provoking factors throughout life.
Other sources of mucus accumulation in the throat include an allergic reaction to a certain irritant, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, poor diet, abuse of unhealthy foods, and bad habits, especially smoking.
Mucus in the morning
In the morning after waking up, the accumulation of exudate in the throat area is caused by an ENT disease that occurs with impaired functioning of the regional exocrine glands that are involved in the production of mucus.
Dysfunction and excessive production of mucous exudate are caused by the following factors:
- Development of an allergic reaction or infectious disease. In most cases, the appearance of a symptom in the morning is observed due to the development of viral, bacterial, allergic, fungal sinusitis, drug-induced, post-infectious, vasomotor rhinitis.
- The growth of adenoid vegetations, the development of the inflammatory process in this area - adenoiditis.
Less commonly, the accumulation of mucus in the throat in the morning occurs due to the development of pathologies of the digestive tract, in which gastric contents are thrown into the nasopharynx and oropharynx.
Appears after eating
Increased production of mucous exudate in the throat after eating food occurs for several reasons. The first is the inclusion of specific foods in the diet, especially those that are too spicy or salty.
Tablets for tinnitus and head noise: a review of the best drugs
This also includes foods with acid, such as vinegar or lemon juice. Such components of dishes irritate the mucous membranes of the throat, enhancing the process of formation of protective mucus.
The second reason for the appearance of exudate after eating is an ENT infection. With an inflammatory process in the throat, for example, caused by a cold, the slightest irritant (that is, food) further intensifies the symptoms, hyperproduction of mucus, which, when flowing down the back wall, provokes a cough.
In addition, the cause of the symptom that occurs after eating is also an allergic reaction. If you have an individual intolerance to a certain product, for example, chocolate or citrus fruits, their consumption may cause increased mucus production (a protective mechanism) and cough.
Causes of constant mucus
The main reason for the constant increase in mucus production is the presence of congenital or acquired anomalies in the structure of the upper respiratory tract. The classic form of mucus leakage is caused by the formation of a Thornwald cyst in the midline of the nasopharynx.
Often the symptom occurs against the background of a deviated nasal septum, bullous deformation of the conchae.
Provoking factors that contribute to the appearance of symptoms due to the presence of anomalies in the structure of the respiratory tract are: smoking, living in an unfavorable environmental environment, work requiring contact with harmful substances (for example, inhalation of vapors).
Recommended video:
Why doesn't mucus clear up?
In some cases, it is not possible to cough up mucus in the throat, for which there are reasons:
- increased body temperature;
- insufficient fluid content in the body;
- insufficient functioning of the ciliated epithelium, which occurs against the background of an inflammatory process;
- inhalation of dry or warm air.
It is difficult to cough up mucus when smoking constantly, so a person has to spit it out.
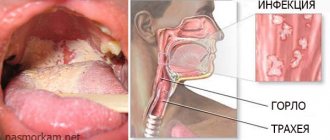
Sinusitis and rhinitis
Thick mucus is released without coughing in case of inflammation of the nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses. Copious sputum is expectorated in the following diseases:
- Rhinitis (runny nose). Inflammation of the nasal mucosa is accompanied by the secretion of viscous mucus. Its transparency and elasticity depend on the form of the disease. An infectious runny nose produces yellow or green mucus. In people with insufficient tone of blood vessels, vasomotor rhinitis occurs, in which a transparent secretion is formed. With atrophic rhinitis, foul-smelling green sputum occurs.
- Sinusitis. When the maxillary sinuses become inflamed, sinusitis occurs, the ethmoid sinuses - ethmoiditis, the sphenoid sinuses - sphenoiditis, and the frontal sinuses - frontal sinusitis. If you cough up white, thick mucus without coughing, the cause of the illness is a viral infection or allergy. With bacterial and fungal inflammation, it acquires a yellow or green tint and an unpleasant odor.
Expectoration of mucus without coughing occurs mainly in the morning, as during the night it flows down the back wall of the throat into the hypopharynx.
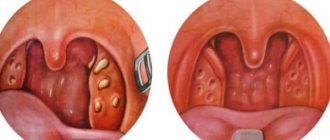
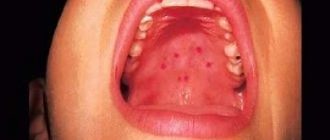
Phlegm in the throat without cough in children and adults occurs due to inflammation:
- palatine tonsils – tonsillitis;
- pharynx – pharyngitis;
- larynx - laryngitis.
If the secretion is transparent, this indicates the onset of the disease or the attenuation of inflammation. In the absence of complications, the cough does not bother you, and small amounts of sputum are expectorated. If it becomes thick and green, purulent inflammation is possible.
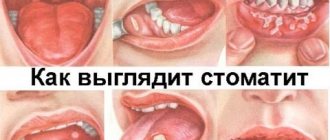
Symptoms of the pathological condition
Increased production and accumulation of mucus in the throat is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- soreness;
- a feeling of the presence of a foreign object that does not disappear when swallowing saliva;
- pain syndrome when eating solid food;
- nasal congestion;
- sneezing;
- enlargement of local lymph nodes;
- unpleasant sour odor from the mouth.
Some diseases of the upper respiratory tract are accompanied by other clinical manifestations, for example, body aches or increased general temperature.
The mucus that appears in the throat can have a different color, taking into account which the cause of its formation is indirectly determined:
| Sputum color | Cause | Peculiarities |
| Green | Abscess in the lung (purulent process). | Additional manifestations: pain behind the sternum, general malaise, discharge of mucus with bloody impurities. With a mild abscess, a favorable prognosis and complete recovery are observed. When the course is advanced, the process may become chronic. |
| White | Fungal infection, pulmonary tuberculosis. | The development of a fungal infection is possible after prolonged use of antibacterial drugs that weaken the immune system. If there are bloody streaks in the white sputum, we can talk about bleeding due to tuberculosis. |
| Brown | The presence of congenital bullae (cavities in the lung filled with air), when they ruptured, pulmonary tuberculosis, lung gangrene, cancer. | When the bulla ruptures, there is a feeling of lack of air. Tuberculosis is accompanied by general malaise and a dry cough. |
| Transparent | Previous viral infection, allergic reaction. | An allergic reaction occurs when inhaling harmful fumes, plant pollen, house dust, or contact with animal fur. |
What is Staphylococcus aureus and does it need to be treated?
Which doctor should I contact?
Since phlegm often accumulates in the throat with a mild cold, you should first consult a physician. He is a general practitioner and can make a diagnosis on his own. If necessary, he will refer the patient to a specialist - an otolaryngologist. This doctor specializes in pathologies of the upper respiratory tract (sinusitis, sinusitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis).
If an examination by an otorhinolaryngologist turns out to be uninformative, the patient may be referred to a gastroenterologist. This doctor specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal pathologies.
If you suspect damage to the lower respiratory tract (pneumonia, lung cancer), the patient should consult a pulmonologist.
When a doctor's help is needed
It is recommended to visit a doctor if mucus in the throat is present for a long time (more than a week). First of all, the otolaryngologist examines the mucous membranes, collects information about the duration of the onset of the symptom, accompanying disturbing manifestations, and possible provoking factors.
To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental and laboratory measures are prescribed that will allow one to determine the source of the symptom and the method of its treatment.
The following diagnostic studies are carried out:
- Rhinoscopy. An external examination of the throat helps to identify swelling, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, and the presence of mucus.
- General blood analysis. If a viral infection is present in the body, neutropenia and lymphocytosis are detected, and eosinophilia is characteristic of an allergic reaction. Bacterial infections occur with leukocytosis. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases in almost every disease.
If an endoscopically negative picture is observed to detect damage to the paranasal sinuses, radiation diagnostic methods are used. This is an x-ray of the paranasal sinuses, computed tomography.
Methods for treating mucus in the throat
Treatment of mucus in the throat is determined taking into account the original source that contributed to its appearance. Most diseases that occur with a similar symptom require conservative therapy.
Surgical intervention is provided only for those cases when it is impossible to stop the source of mucus by other methods (drugs, physiotherapy, etc.).
Etiotropic treatment depends on the causative agent of the primary process. For example, for bacterial infections, antibiotics are used, for fungal infections, antifungals are used, and for viral infections, antivirals are used.
Symptomatic treatment consists of using agents that help reduce the severity of clinical manifestations. For example, for swelling of the mucous membrane, corticoids and antihistamines are used.
Surgical treatment consists of correction of a deviated septum, resection of bullous conchae, removal of cystic neoplasms, etc.
Rinse
Gargling with special preparations helps reduce the possibility of exudate and increase its production. For this purpose, ready-made preparations purchased at a pharmacy or folk formulations (infusions and decoctions and medicinal herbs) are used.
Among ready-made pharmaceutical products, preference is given to those such as Hexoral and Tantum-Verde.
Inhalations
Inhalation treatment has a gentle effect on the body, since the therapeutic effect is achieved in a certain area without entering the internal organs. At the same time, there is a rapid destruction of harmful microorganisms and a decrease in mucus production.
For steam inhalations, essential oils are used, which are added to water. It could be eucalyptus, mint, tea tree. It is recommended to consult a doctor before using them, as they may cause allergic reactions.
Inhalations with a nebulizer are carried out using ready-made formulations, for example, ACC, Sinupret, Pertussin.
Medicines
Taking into account the reason for the formation of mucus on the membranes of the throat, the doctor may prescribe the use of the following remedies:
- antibacterial;
- drugs that thin and remove mucus;
- antihistamines;
- antiseptic;
- immunomodulatory.
Unpleasant throat odor: main causes of the symptom
In some cases, medicinal solutions are used for washing in the form of a “cuckoo” procedure.
Features of treatment
It is possible that saliva becomes thick due to temporary hormonal imbalances. In such cases, medication is not required, and the natural secretion of saliva is restored after some time. To understand the causes of impaired salivation, an in-person consultation with a dentist is necessary.
The first thing that needs to be done is to stabilize the level of moisture in the oral mucosa. The following treatment procedures can help with this:
- Rinsing the mouth with anti-inflammatory herbal decoctions and soda-salt solution. To eliminate the symptoms of laryngitis, it is advisable to use antiseptics, for example, Hexoral.
- Use of artificial saliva. Used in the form of drops or spray.
- Spray moisturizers and gel substitutes. Well-known manufacturers produce drugs in the form of gel and spray, which instantly help eliminate dry mouth. In addition, they contain antibacterial components designed to eliminate unpleasant odors.
- Mucolytics. A group of medications to increase the production and thinning of saliva. Bromlane and acetylsteine have proven themselves well.
- Inhalations. They help those who have problems with the lungs and bronchi. Both pharmaceutical preparations and herbal infusions, for example, St. John's wort or sage, are suitable for inhalation.
- Chewing gum with sugar substitute. Excellent stimulation of the salivary glands.
How to remove mucus using folk remedies
Along with the main treatment prescribed by the doctor, you can use folk remedies prepared on the basis of natural ingredients:
- from sea salt, baking soda or chamomile infusion: prepared solutions, infusions and decoctions of such ingredients are used for gargling, which helps remove pathogenic microorganisms from the mucous membranes;
- from black radish and honey: grate the fruit, mix with honey, take 1 tsp. three times a day, which helps relieve cough and quickly remove mucus from the mucous membranes;
- from aloe and honey: a mixture of plant juice and beekeeping product helps relieve the symptoms of an allergic reaction, helps remove exudate from the throat when consumed 1 tsp. twice a day;
- from calendula: grind the grass, mix 1 tsp. with honey in the same volume, take half a spoon orally before going to bed and after waking up;
- from potatoes: the tubers are boiled without waiting for the water to cool, and steam inhalation is carried out.
When you have a cold, warming your throat with warm compresses is helpful. This treatment helps prevent the infection from spreading and thus speeds up recovery. In some cases, it is enough to use the famous Zvezdochka balm, which is used to lubricate the neck, wrapping it with a warm scarf on top.
Folk remedies can cause adverse reactions, so you should consult your doctor before using them.
How to get rid of phlegm at home?
Getting rid of sputum is possible with the help of medications, effective folk recipes and auxiliary methods used during the treatment of children.
Treatment with drugs
Medicines used to treat the causes of sputum include mucolytics and expectorants, immunomodulators, antivirals, antifungals and antibacterials.
ACC Long is an effective drug for the treatment of sputum
| Group of drugs | Effect on sputum | Representatives |
| Mucolytics | It thins out excessively thick mucus, improving the process of coughing and clearing the throat of excess mucus. | Bromhexine, Ambroxol, ACC |
| Expectorants | Herbal or synthetic preparations that stimulate the outflow of mucus from the lungs and larynx. Used in the form of tablets and syrups. | Herbion, Althea, Gedelix |
| Antiseptic solutions | Topical disinfectants destroy bacterial accumulations, helping with bacterial infections. | Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Hexoral |
| Anti-inflammatory topical drugs | Lozenges, sprays and solutions act locally on the source of inflammation, eliminating the cause of mucus in the throat. | Cameton, Strepsils, Ingalipt |
| Local immunomodulators | Stimulate the restoration and strengthening of the immune system, help cope with viral and bacterial inflammatory diseases. | Lizobakt, Ribomunil |
| Antibiotics | Destroy pathogenic bacteria, stop the development of bacterial inflammatory diseases | Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin, Trifamox |
| Antiviral agents | They stop the reproduction and further spread of viral infection, eliminating viral diseases of DP. | Amantandine, Tamiflu |
| Antifungal drugs | Relieves oral candidiasis and other fungal diseases that cause sputum. | Nystatin, Fluconazole |
Read also: The most expensive pipe in the world
How to remove phlegm using folk remedies?
Proven folk recipes should be used in combination with drug treatment to increase effectiveness.
Herbal collection
A herbal mixture will help quickly remove phlegm from the throat: plantain, mint, marshmallow and coltsfoot. The drink is prepared from them like this:
- Take 40-50 g of each herb, chop and dry, if necessary, mix thoroughly.
- The mixture is poured into 1 liter of water and infused for 20 minutes in a water bath.
- Afterwards the drink should stand for 2-3 hours in a warm place.
Anti-mucus herbal drink as a means to combat phlegm
The collection should be consumed 2-3 times a day, on an empty stomach.
Pine decoction
Pine bark and needles are an effective anti-inflammatory agent for many respiratory diseases. The decoction is prepared as follows:
- 2 tbsp. l. Mix pine bark and pine needles and add 500 ml of hot water.
- Cook the mixture for 5 minutes over low heat.
- Leave the resulting broth for 2-3 hours, then strain.
Pine decoction is an effective anti-inflammatory agent
The decoction is taken orally, 50-60 ml, 2-3 times a day, on an empty stomach.
Pine buds
In addition to pine bark and pine needles, buds can also be used in combination with milk to get rid of phlegm. The mixture is made as follows:
- 1 tbsp. l. kidneys are mixed with 200 ml of warm milk.
- The drink is put in the refrigerator and infused for 12-15 hours.
- The mixture is carefully filtered and consumed internally.
For 1 dose you need to drink 50 ml of the product.
Black radish and honey
Honey is excellent for any inflammatory diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract. Black radish also has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Grate 1 medium radish on a fine grater; if the pieces are large, chop them almost into dust.
- Mix the resulting mass with 2 tablespoons of fresh honey, liquid or preheated to a liquid consistency.
- Drain the juice from the mixture and take it orally after meals, 1 tbsp. l.
Black radish and honey are an excellent antiseptic for fighting phlegm.
The mixture itself can be applied to the chest and throat as a compress.
Onion broth
Onions are an excellent remedy for the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases. To remove phlegm, it is taken orally as a decoction.
- Peel 2 large onions and place in a saucepan.
- Pour boiling water over, cook for 1-1.5 hours over low heat.
- Add 200 g of sugar to the broth.
The decoction should be consumed 3-4 times a day.
Aloe and honey
To remove mucus from the respiratory tract, aloe leaves can be added to honey as an additional component.
- Peel the leaf of a fresh plant and chop it thoroughly.
- Mix the resulting mixture with 1 tbsp. l. honey of liquid consistency and consume internally.
Aloe as an additional component to honey in the fight against phlegm
You can use this mixture 2 times a day: morning and evening. For each dose, it is necessary to prepare a new mixture, otherwise it will lose its beneficial properties during storage.
Banana pulp
Banana combined with sugar is an excellent folk recipe for better expectoration of mucus and speeding up recovery.
- Peel and grate 2-3 bananas.
- Add 2 times less sugar to them.
- Mix thoroughly and eat.
This recipe is harmless and very tasty, so it has no restrictions on use.
Propolis tincture
Propolis tincture can be used as a gargle, compress or lubricant for the throat to get rid of phlegm.
- For lubrication: mix 25 ml of propolis tincture with 50 ml of peach oil, lubricate the mucous membranes of the throat and nose 2 times a day.
- For rinsing: 2 tsp. Dilute the product in 200 ml of warm water, rinse 5-6 times a day.
- As a compress: mix 10 ml of propolis with 2 tsp. honey, cover with a sterile bandage, apply to the chest or throat for 2-3 hours.
Propolis for gargling, compressing or lubricating the throat with phlegm
Tea with herbs and berries
Adding anti-inflammatory herbs, berries and other components to regular tea will help quickly get rid of the inflammatory process and say goodbye to phlegm. As tea additives you should use:
Tea with added anti-inflammatory berries and herbs for phlegm
Tea with an anti-inflammatory effect should be drunk 5-6 times a day.
Calendula with honey
Fresh or dried calendula is perfect as a complement to honey: this herb copes well with inflammatory processes in the body.
- Peel and chop 2 tablespoons of calendula petals if necessary.
- Mix with 1 tsp. liquid honey, use 0.5 tsp. in one go.
Calendula with honey against inflammatory processes in the body
The product is used 2 times a day: morning and evening.
What to do if your child has phlegm?
Due to anatomical and physiological characteristics, children of preschool and primary school age do not cough up sputum as easily and simply as it happens in adults and adolescent children.
In order not to cause stagnation of mucus and not to provoke complications, when getting rid of sputum from a child, you should follow these recommendations:
- For an expectorant effect, syrups and sprays of plant origin with natural ingredients should be used.
- Mucolytics should be used in the form of inhalation with a nebulizer or steam inhaler. There are special solutions for these purposes: Ambrobene, Lazolvan.
- It is necessary to do special massage and gymnastics: this method stimulates the outflow of mucus from the lungs and larynx.
- In addition to drug therapy, it is worth using traditional methods: gargling, nasal rinsing, various compresses with a hypoallergenic composition.
- Drug treatment should be supplemented with physiotherapy: UHF therapy, laser therapy and galvanization stimulate the immune system, improve microcirculation and help the body quickly overcome the disease.
Preventing mucus formation
It is easier to prevent any disease than to quickly deal with its unpleasant symptoms and negative consequences. This also applies to those pathologies that occur with the formation of mucus in the throat.
Preventive measures include:
- giving up bad habits, especially smoking and drinking alcohol;
- correction of the diet with the exception of hot spices, salty foods, and foods that have an irritating effect;
- correction of the drinking regime: it is recommended to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day;
- avoiding contact with carriers of infectious diseases;
- restriction of visiting public places during the epidemic;
- timely treatment of chronic infectious processes in the oral cavity - caries, gingivitis, etc.;
- strengthening the immune system by maintaining an active lifestyle, taking vitamins, visiting places with clean air - the sea, forests, etc.
In any case, only a doctor can determine why mucous exudate accumulates in the throat. Based on the results of diagnostic measures, he makes a diagnosis and prescribes the most effective treatment.
Recommended video:
Self-medication rarely leads to recovery. In addition, with improper therapy, not only does recovery slow down, but additional health problems arise.
Comments (4)
Anya
07/18/2019 at 23:12 |
To be honest, this article really scared me; it talks about some kind of lung abscess if green mucus appears. I have this kind of mucus often, what could it be?Answer
Expert Marina Rusetskaya
07/19/2019 at 10:49 |
Anya, there are several reasons why mucus forms and coughs up in the morning.
Let's take a closer look.
First of all, a lung abscess does not appear on its own out of nowhere. This is a serious complication of severe pneumonia.
In case of a lung abscess, the patient is initially treated for pneumonia with high body temperature, and only after the formation of an abscess and then its opening does purulent discharge appear in the bronchus.
The most common causes of colored sputum (mucus) in the morning when coughing are:
1. Smoker's bronchitis or chronic bronchitis.
2. Traffic jams in the tonsils (and you may not even suspect their presence). The disease is accompanied by bad breath, periodic sore throat with bouts of dry cough, foreign body sensation and rare passage of dense light-colored lumps.
3. Diverticulum of the esophagus (a sac is formed from the wall of the organ in which food remains. Then it ferments, and when there is a lot of content, it flows into the oral cavity).
4. Neck cyst.
Listed above are only the most common reasons; in order to understand your situation specifically, see an ENT doctor and therapist. After a comprehensive examination, you will find out exactly the cause and receive adequate treatment.
Answer
Nina
03.11.2019 at 23:48 |
Tell me why in the morning yellowish mucus sometimes appears in the throat, and there is also an unpleasant odor, which in turn also comes from the nose. What could this even indicate and who should I contact?
Answer
Expert Marina Rusetskaya
11/10/2019 at 21:50 |
Nina, if your symptoms indicate the presence of a bacterial infection in the upper respiratory tract.
Yellow color and unpleasant odor are symptoms of the presence of pathogens.
Regarding treatment, you need to contact an ENT doctor and submit the material for examination.
During the process, the type of bacteria and their sensitivity to antibiotics will be determined. Then the doctor will choose the best antibiotic for you.
In addition, drink more warm liquid and gargle.
Answer
Causes of thick saliva
Saliva may become thick for the following reasons:
- Sinusitis. Chronic sinus disease makes itself felt by thick mucus and bad breath. The mucus produced by the sinuses continuously moves from the mouth to the throat. The nasal cavity swells and saliva thickens. Patients make efforts to clear the throat of sticky mucus and then spit out the clot. The chronic form of the disease is complicated by headache and, less commonly, fever. If you suspect sinusitis, you should immediately make an appointment with an otolaryngologist.
- Xerostomia. Sudden disruption of the salivary glands, complicated by severe dryness. The saliva becomes very viscous. The surface of the tongue thickens, the functioning of the receptors is disrupted, and there is a burning sensation in the mouth. Sometimes the throat feels sore and sore.
- Fungal candidiasis. An infectious disease that develops due to impaired immune function after long-term use of antibiotics and corticosteroids. It can also be triggered by contact routes of infection and personal hygiene items. Candidiasis can be a symptom of much more serious diseases: diabetes, tuberculosis, AIDS. With thrush, you may experience a metallic taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing food, itching and burning of the mucous membranes.
- Sore throat, pharyngitis, laryngitis. Diseases affect the tonsil area. Infection causes the formation of purulent blisters, and their spontaneous rupture creates discomfort in the mouth. The inflammatory process is accompanied by elevated temperature, which deprives the body of water and inhibits the function of the salivary glands.
- Periodontitis and periodontal disease. Due to damaged gum tissue, the amount of saliva produced decreases. Elements of epithelial tissue penetrate the salivary fluid, which makes it viscous and white.
- Infectious diseases of an acute nature: dysentery, typhoid fever, hepatitis.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). With this pathology, gastric juice rises into the oral cavity. In this case, additional saliva production is necessary to neutralize stomach acid.
- Endocrine disruptions. Changes in hormonal levels occur during pregnancy, puberty and menopause. These reasons can also cause thick saliva.
- Autoimmune diseases. A serious disease that is practically untreatable. Pathology manifests itself in damage to the exocrine glands, including the salivary glands.
- Dehydration. Water is the main component of saliva. A lack of fluid in the human diet leads to an increase in saliva viscosity. A person needs 1.5–2 liters of water per day to avoid dehydration. This is the minimum dose that ensures the proper functioning of all body systems.
- Dry air. Often saliva becomes foamy and viscous due to the negative effects of dry air on the respiratory system. In a poorly ventilated room, where air humidity does not meet standards, the oral mucosa instantly dries out. As the mucus thickens, it forms crusts around the perimeter of the inside of the throat, which is manifested by soreness and a dry cough. Thus, air masses, moving along the respiratory tract, receive the necessary moisture due to the moisture of the mucous membranes. The mouth and throat are not responsible for humidifying the air. The nasal cavity is intended for this purpose, in which a special muconasal secretion is produced. When a person cannot breathe normally through his nose, he uses his mouth to do this, so the saliva immediately begins to thicken.
- Smoking. Tobacco smoke causes irritation of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, and an increase in the volume of mucus occurs. Many smokers complain of the feeling of a foreign object in their throat.
- Action of allergens. Thick saliva observed in certain months indicates a seasonal allergy to pollen.
- Taking medications. There are categories of medications that cause such side effects as thickening of saliva. These can be hormonal pills, antidepressants and antihistamines.
- Diabetes. Dry oral mucosa and thick saliva are often observed against the background of hyperglycemic conditions.
We suggest you read: If the root of a tooth has rotted, what to do?
In addition to a sharp reduction in the volume of secreted saliva and, as a result, an increase in viscosity, patients may experience additional symptoms:
- Impaired taste perception
- Sore throat
- Foul odor from the mouth
- Cracks on the lips and corners of the mouth, dry mucous membranes
- Burning sensation in the palate and tongue
- Hardening of the muscle fibers of the tongue