Teeth of ancient people
The dentofacial apparatus of prehistoric and modern humans differs significantly. Ancient people had more than 36 teeth, protruding fangs and a massive jaw. This was explained by the need to chew rough food and raw meat. With the addition of thermally processed foods to the diet, the dentition began to change. The canines were the first to transform, becoming aligned with the bite line. Then the jaw arch narrowed, the interdental spaces disappeared, and the teeth themselves decreased in size. Currently, 32 teeth in humans are the norm, but third molars are considered to be an atavism.
Interesting fact!
The teeth of ancient man cannot be called aesthetic, but they were healthy. According to scientists, cavemen never suffered from caries and other oral diseases.
Age-related changes
Age affects the entire body, including teeth. Over the years, teeth are subject to an unpleasant process - wear. Tooth enamel becomes thinner and wears away, so many experienced dentists can determine a patient’s age by looking at the patient’s jaw. This is influenced by lifestyle, hygiene standards, daily diet and some physiological characteristics.
As a rule, by the age of 20, a slight smoothing of the enamel appears, which is quite natural for this age. After 30, a bone substance, dentin, forms on the edges of the incisors and fangs. By the age of 45, most teeth are covered with dentin, and crown wear is visible. By the age of 60, it is quite common for the enamel to completely wear out. And by the age of 70-80, only the roots and neck remain; at this age, most patients have artificial teeth.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Oral cavity sanitation – what is it and why is it needed? Indications for sanitation of the oral cavity. Sanitation of the oral cavity before dental implantation
Thus, the generally accepted norm of 32 teeth is not always met. Everyone can extend the life of natural teeth. The main thing is to follow the rules of hygiene, watch your diet and not put off going to the dentist. Remember that the beauty of your smile is in your hands.
Name of human teeth
Depending on the location and structure, dental units have their own functional characteristics and are called differently.
- Incisors.
On both jaws there are four front teeth in humans - medial and lateral incisors, which are used for biting food. - Fangs.
Sharp teeth designed for chewing hard foods. - Premolars.
"Fours" and "fives" on the left and right sides of each jaw arch grind soft or small pieces of food. - Molars.
Three large outer teeth in each row are aimed at grinding coarse substances. - The canines
and incisors are part of the anterior group, or the “smile zone,” and the human molars are part of the chewing segment.
In addition, teeth are divided into temporary and permanent. In the first case, we are talking about dairy products that appear in children from the fifth month of life to three years. The second refers to the final bite, which is formed between six and thirteen years of age. Milk teeth differ from permanent teeth only in size, but in structure they are identical.
Baby teeth
They are quite similar to the constants, but still have some differences. Firstly, the child has not 32, but only 20 teeth. They are missing premolars and one molar. The dental arch contains 8 incisors, 4 canines and eight molars. Their purpose is the same as in the permanent dentition.
The difference between temporary teeth and permanent teeth is as follows:
- the crown is smaller in size;
- the roots are massive, but highly branched;
- the enamel has a white-blue color;
- hard tissues are less durable and therefore more susceptible to carious destruction;
- deeper fissures;
- The tubercles and signs of crown curvature are more pronounced.
The replacement of baby teeth begins at 5-6 years of age. By the age of 14, the permanent dentition is usually fully formed. Deviation is allowed for one year. If the process of changing the bite is delayed, this can lead to abnormalities in the dental arch and the formation of the jaws themselves. Therefore, you should immediately contact your dentist to identify and correct the problem.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what to treat if you bite your tongue. I bit my tongue badly - how to provide first aid and how to treat it?
How many teeth does a person have?
The number of teeth a person has depends on age and anatomical features. The child has a set of 20 primary teeth, which are replaced by a permanent bite of 28 teeth. Third molars erupt, as a rule, after twenty years or do not grow at all, which is not a pathology.
In dentistry, a single numbering of human teeth is adopted. Doctors classify teeth as lower and upper and distinguish the right and left segments of the jaws. Each of them includes two incisors, a canine, two premolars and three molars. The countdown starts from the first front tooth and ends, accordingly, with a figure eight. Sometimes a number is added to the serial number indicating the location zone. For example, the right canine of the top row is numbered 13. This order in the schematic representation is called the formula of human teeth.
Polyodontia
In rare cases, an anomaly such as polyodontia is observed - supernumerary, or extra teeth in a person. Dental units can appear in the primary and permanent dentition anywhere in the jaw, separate from or fused with the main teeth. The defect affects not only the aesthetics of the smile, but also leads to the formation of incorrect occlusion, impairs the quality of chewing food and diction. Most often, supernumerary teeth are removed in childhood or built into the dentition.
Edentia
There is also a deviation of the opposite meaning called edentia - congenital or acquired absence of dental units. The causes of the phenomenon include heredity or improper development of the embryo in the womb. People without teeth cannot fully eat and speak, have a deformed facial contour and weakened immunity.
Purpose of teeth
Teeth are hard tissue formations that are particularly durable. They have several purposes, based on their shape and location in a row. The main task of the teeth is to process food - chewing. This allows you to divide food into pieces that will be better digested and absorbed by our stomach.
No less important is the protective function of teeth. It is to protect the immune system and prevent viruses and bacteria from the environment from entering the body. Another function is the pronunciation of sounds. Without the presence of teeth, we will not be able to pronounce certain sounds correctly, so the appearance of baby teeth in humans is determined by evolution.
Dimensions of human teeth
The upper central incisors are twice as wide as their antagonists. The remaining dental units of the same name have approximately equal parameters. The size is determined using special tables with the optimal size and permissible deviations. Experienced doctors calculate proportions by dividing the length of a person’s teeth by the width. A result of about 0.75 millimeters is considered close to ideal. For more detailed diagnostics, other professional formulas and techniques are used.
Size deviations from the norm occur due to improper formation of the jaw, fusion of tooth buds, or genetic predisposition. Teeth that are too large are called macrodentia, and abnormally small teeth are called microdentia. Pathologies are accompanied by problems with bite and chewing functions, but can be successfully corrected by a dentist.
Interesting fact!
The longest tooth in the world belongs to an Indian teenager. The size of its crown is almost four centimeters. About a year ago, the tooth was removed, and the young man was included in the Guinness Book of Records.
Archive number No. 10 (1325) dated March 10, 2020 - Zdoroviechko
"EIGHTS" OF WISDOM
Remember the joke?
A man watches an advertisement: “Man: 32 teeth is the norm. Shark – 1000 teeth. Panda - 24 teeth." “Oh my, I’m a panda!” But seriously, it turns out that recently there are often cases when children do not even have the rudiments of “eights,” which are also called wisdom teeth. They just don't grow. Is this normal? [td]
As it turned out, many dentists do not consider the absence of “eights” to be a serious pathology, explaining that, rather, this is even good, since in most people these teeth still have to be removed over time.
As an orthodontist of the highest category, associate professor Irina Skripnik explains, the fact is that wisdom teeth usually erupt for a long time and painfully, and they are also very susceptible to caries. “Eights” are very large, so they are often the cause of crowded teeth and malocclusion. And this is already considered orthodontic disorders. If a person has crowded teeth and cannot clean them well, caries occurs. An incorrect bite leads to muscle-joint dysfunction.
– So, is it better to remove wisdom teeth?
– Yes, many experts recommend removing “eights” or even their beginnings in adolescence, if teeth have not erupted. They often grow at an angle, displacing the dentition. Adults, as a rule, do not want to part with damaged eighth teeth and ask for caries treatment. But it is very difficult to properly treat a wisdom tooth: access to it is difficult, its canals are usually crooked, and it is not possible to fill them perfectly. After a short time, the poorly treated tooth begins to hurt again and will still have to be removed.
– Why do children lack the rudiments of some teeth?
– Each tooth has its own function. Some bite off food, others chew, grind, crush. But most people switched to softer foods a long time ago, so changes occur at the genetic level. A person should regularly eat solid foods: apples, carrots. Such food, by the way, not only provides the necessary stress to the teeth and gums, but also cleanses the enamel well. Many mothers today feed their babies ground food, even when they have teeth. As a result, children develop orthodontic problems. After all, teeth do not carry the load. Accordingly, the chewing muscles do not work properly, and the temporomandibular joints do not receive the necessary load.
Modern children often lack “eights.” It is considered almost normal if an adult develops 28 teeth instead of the required 32.
Share link:
Read the latest news from “For Each Other” on social networks:
VKontakte, Odnoklassniki, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram.
facty.ua
The structure of the human tooth
Anatomy
From an anatomical point of view, a human tooth consists of three parts.
- Crown.
The visible part protruding above the gum. It has four sides: the occlusal, or cutting edge, in contact with the antagonist teeth; contact wall adjacent to adjacent dental units; vestibular and lingual surfaces facing the lips and tongue, respectively. - Root.
Fixed in the socket by connective tissue, located in the recess of the jaw. As a rule, premolars have two roots, and molars have three, four or even five. The remaining dental units have one root canal. - Neck.
It is located between the coronal part and the root of a human tooth, surrounded by periodontium.
Histology
What are human teeth made of? Let's look at the cross-section of the structure of a human tooth.
- Enamel.
A transparent protective coating of the crown, almost entirely consisting of inorganic microelements. - Dentine.
The hard base of the tooth, containing 80% mineral components and 20% organic substances. The shade of dentin is responsible for the color of dental units, as it shines through the enamel. - Cement.
The bone tissue covering the tooth root. Plays the role of a fastening element connecting the tooth to the alveolus. - Pulp.
Soft tissue filled with bundles of nerves and capillaries. Painful sensations during caries are explained precisely by the presence of nerve endings.
Types by shape and location
The human oral cavity has not always been what it is today. Millions of years of evolution have transformed the body beyond recognition. The reason lies in changes in living conditions, including diet. Over time, human food became increasingly soft, so the jaw became smaller and the teeth became less developed compared to the distant ancestors of Homo Sapiens.
- Incisors located in the front central part of the jaw.
- Fangs located on the sides of the incisors.
- Premolars are the two teeth next to the canines.
- Molars located at the very edge of the jaw.
The number of incisors in the body of any person is “fixed” - eight units.
Four are located on the upper jaw, four more on the lower jaw. The thin cutting edge of these teeth is designed for biting food. It is quite fragile and does not withstand shock or strong pressure. That is why most cases of tooth breakage occur in the incisors.
If the incisors cannot cope with some particularly stubborn piece of food, then the fangs come to the rescue. There are four of them. They have a thickened edge and a developed tubercle. The purpose of the fangs is to tear off or chip away dense and strong pieces of food. It is not surprising that these are the strongest teeth a person has.
The next type of teeth in the human mouth are premolars. They are adapted for both biting food and chewing it. They are very similar to fangs in their structure, but have a large working surface equipped with two tubercles. Despite single roots, premolars sit firmly in the jaw and are difficult to lose.
The outermost teeth are molars. As the name suggests, their job is to grind up pieces of food before swallowing. They are distinguished by deep roots and a large working surface, equipped with three and sometimes five tubercles. Another feature of molars is that the further they are located from the center of the jaw, the less developed their root system is. Their number may vary from person to person.
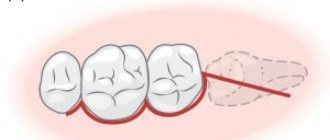
The outermost molars are known as wisdom teeth. In some people they do not appear at all, in others only two or three units grow. Thus, the number of wisdom teeth (eights) may vary from person to person.
You should not try to crack food that is too hard, such as nuts, using incisors. This weakens the enamel and leads to destruction of the cutting edge.
Human wisdom teeth
A “wisdom tooth” is the third outer molar with three to five roots. In structure it is no different from its “neighbors”. To the question “How many wisdom teeth does a person have?” cannot be answered unambiguously. They erupt around the age of twenty, one on each side of both jaws. However, there are people without wisdom teeth. This is a variant of the norm, since in the process of human evolution the need for the “eight” disappeared, and the structure of the jaws underwent corresponding changes. Today, third molars are considered a vestigial organ.
Types of teeth
The upper and lower jaws have a symmetrical composition, although they differ somewhat in shape. A complete set of teeth has been developed as a result of evolution; each has its own, irreplaceable function.
The front teeth are incisors. There are eight of them, they have cutting edges and allow you to bite off food.
Behind the incisors are fangs - these are strong, sharp-shaped teeth that tear food into pieces.
Behind the fangs there are 4 small molars - premolars, and behind them are large molars - molars . Their task is to chew food and prepare it for the digestive process.
“ Wisdom teeth ” are located along the edges of the jaw. Many dentists consider them an atavism.
Dental health and human health
The connection between teeth and human organs is not obvious at first glance, but oral health directly affects the functioning of the entire body.
- Gastrointestinal tract.
Dental pathologies reduce the quality of chewing food, disrupting digestion. - The immune system.
Oral diseases weaken the overall immune system. As a result, it is difficult for the body to resist bacteria and viruses, which are especially active during epidemics. - Heart and blood vessels.
Inflammation of the tissues of the oral cavity can be accompanied by suppuration, which, in turn, causes intoxication, causing heart failure and angina attacks.
The health of the dentition itself is affected by nutrition, stress, environment and bad habits. The teeth of a smoker, for example, have a yellow coating and are prone to early loss.
Eating sweets provokes the development of caries - the destruction of hard dental tissues, starting with demineralization of the enamel. Poor dental care and untimely treatment contribute to the appearance of inflammatory complications of this disease such as pulpitis, periodontitis or dental cysts.
Healthy human teeth ensure not only the coordinated functioning of the whole organism, but also external attractiveness. A responsible attitude towards oral hygiene, quitting smoking and regular visits to the dentist for preventive examinations will help you maintain a perfect smile for many years.
Formation of tooth buds in a child before birth
The formation of primordia occurs in the prenatal period. Their first symptoms were recorded at 6-7 weeks of pregnancy. It is during this period that the fetus begins to form and develop, its future features and characteristics are laid in it, including teeth (the approximate timing of teething).
READ ALSO: What are the main signs of teething in children?
At the end of the first – beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy, certain formations of enamel begin to divide into separate sections. These are the embryos. They can be clearly seen in the photographs.
During the formation of the rudiments, the mother’s unbalanced diet and bad habits (passion for sweets, carbonated drinks), as well as calcium deficiency in the body, can negatively affect the quality of the unborn baby’s future teeth, as well as affect the timing of teething.
Why do not all of the four possible wisdom teeth grow?
Quite often 1 wisdom tooth erupts, sometimes 2, very rarely 3 or 4. So why does this happen? It all depends on the availability of free space on the jaw where the 8th tooth is going to appear. Normally, one wisdom tooth is placed on each jaw on each edge. In total, one person can erupt up to 4 third molars. It should be noted that this occurs very rarely due to the limited space for tooth development.
The lower jaw is physiologically slightly larger than the upper jaw, there is a little more space on it, and the risk of an 8th tooth appearing there is much higher. Therefore, under normal conditions, in people without pathology of the maxillofacial apparatus, teeth erupt more often in the lower jaw in the amount of 1-2 pieces.
If a person suffers from malocclusion, progeny of the upper jaw (congenital enlargement), then the probability of the appearance of 3 molars in the upper jaw increases significantly, as a result, from 2 to 4 wisdom teeth can erupt: 1-2 on the lower jaw and another 1-2 on upper jaw.