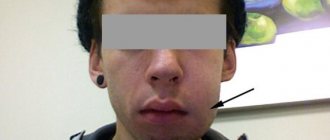
How to treat a hematoma after tooth extraction
Pain in the teeth is one of the most unbearable and can cause a person severe discomfort. If it is present, you need to contact a specialist as soon as possible, since you can lose your tooth, which can most likely be cured. In addition, you can start an inflammatory process with a wisdom tooth, which is quite problematic. In the future, undesirable consequences may develop, such as a hematoma after tooth extraction, and in addition, there may be swelling on the face or a bruise on the gum itself.
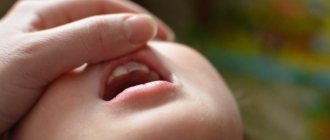
Hematoma during teething
Abundant accumulation of blood under the mucous membrane indicates a severe course of the process. This is due to many factors, here are the main ones:
- hereditary fragility of blood vessels;
- congenital pathology of blood clotting;
- rickets;
- poor nutrition;
- lack of vitamins.
Hematomas are manifested by the following symptoms:
- the gums become blue;
- swelling forms;
- changes, as a rule, occur over the molars and premolars, the teeth most intensively involved in chewing;
- the tumor is small, immobile and has a soft consistency.
The characteristic localization is associated with the anatomy of molars and premolars, designed for grinding food. Therefore, the mucous membrane above them is most severely injured.
Possible complications
Medical statistics say that in 75% of cases after the removal of a tooth or several teeth, most patients do not develop consequences. But unfortunately, 35% still have sensations after tooth extraction. These consequences are:
Painful sensations
During the tooth extraction operation, the specialist presses on the teeth located next to the diseased tooth in order to have a fulcrum. For this reason, the pain may bother the patient for a couple of days. In addition, soft tissues are damaged, which leads to discomfort. In such cases, specialists prescribe painkillers.
Swelling
This type of symptomatology appears some time after the manipulation. On day 3, the swelling develops quite strongly, and then begins to subside.
Hematoma
This type of complication often occurs after the removal of heavy teeth that have excessively elongated roots. When manipulation is carried out, the gum tissue has to be cut, otherwise the tooth cannot be removed. This type of removal does not go away without leaving a trace; blood leaks into the soft tissues. The specialist should prescribe specialized ointments and gels. Quite often a hematoma occurs after the removal of a wisdom tooth.
Increased body temperature
Usually occurs on the day of removal. The temperature does not rise to high levels and is low-grade.
Cheek swelling
If soft tissue is damaged, swelling may occur. The swelling begins to spread not only to the gums, but also to the adjacent tissues of the cheek. The swelling begins to subside on the third day after the manipulation.
Numbness
This type of complication does not appear immediately, since local anesthesia is still in effect in the first stages. But after 12 hours, you may notice a feeling of numbness. This is due to neuropathy of the nerve located in the socket. This type of complication is treated with physiotherapy, since numbness can accompany the patient from several days to several months. In some cases, medications are used.
Smell from the mouth
Most specialists, after performing a tooth extraction procedure, advise their patients not to perform oral hygiene. You can get rid of this type of unpleasant consequence with the help of special cleansing of the oral cavity with anesthetics in the doctor’s office. Also, decoctions of nettle and yarrow herbs can be used to sanitize the oral cavity.
Limited osteomyelitis
This type of pathological condition is characterized by the presence of acute pain of a strong nature in the area of the operation. In some cases, there is pain, the patient shudders, general weakness and headache occur. Body temperature rises to high levels, a putrid odor appears from the oral cavity. It is necessary to contact a specialist as soon as possible for appropriate treatment. Treatment at home is not recommended.
What are the complications after a tooth extraction procedure?
After completion of the operation, for 2-3 days the patient will experience pain in the socket, swelling of the gums or face, swelling may occur, difficulty speaking or eating - this is a normal reaction of the body to surgery, and the doctor will warn the patient about it before and after extraction. However, sometimes local complications develop after tooth extraction - some of them can lead to serious consequences. The photos accompanying the article will help you visually familiarize yourself with the symptoms of the most common complications after tooth extraction.
Prolonged bleeding
With a standard tooth extraction procedure, bleeding stops within 40-45 minutes after extraction. In some cases, external or hidden bleeding appears. The first will be easily noticed by the doctor when examining the hole, while the second may not make itself felt and lead to a large loss of blood. The development of prolonged hidden bleeding is indicated by the occurrence of hematomas - on the surface of the cheeks, gums, and sometimes on the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. If the case is advanced, the hematoma can spread to the patient’s entire neck and part of the chest.
Read also: Bleeding does not stop after wisdom tooth removal
Suppuration in the hole
If the tooth extraction technique was chosen incorrectly, an infection gets into the wound during the operation, or the patient neglects the doctor’s recommendations on the rules of oral care during the recovery period, suppuration may begin in the hole. You can suspect that the wound has festered if at least two of the following symptoms are present:
- the patient constantly has a severe headache;
- severe pain in the socket area, pain does not go away for more than 3 days;
- pus is released from the wound;
- unpleasant (purulent) odor from the mouth;
- fever and chills;
- weakness.
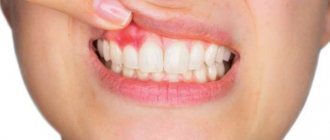
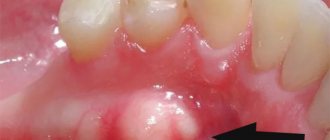
Hematoma on the gum
The appearance of a hematoma (or, more simply, a bruise) on the surface of the gum indicates hemorrhage in this area. A hematoma after tooth extraction can be an independent complication or indicates long-term hidden bleeding (we recommend reading: what to do if the wound bleeds after the removal of a wisdom tooth?). In the first case, the cause of a hematoma after tooth extraction is “brittle” and weak capillaries, increased blood pressure during surgery, or damage to a vessel during the administration of anesthesia. If the temperature rises, swelling and hardening appear at the site of hematoma formation, then symptomatic treatment will be required to eliminate it.
Damage to gum tissue
Sometimes it turns out that the gum tissue was damaged during the extraction process. In most cases, the reasons are haste or unprofessionalism of the doctor, improper administration of anesthesia, or surgery performed in insufficient lighting. This complication can be avoided if you choose a qualified, experienced specialist and a well-equipped clinic.
Jaw fracture
In rare cases, when a “wise” tooth is removed, a fracture of the lower jaw occurs. The main reason for such a complication after tooth extraction is a violation of the third molar extraction technique (using a Lecluse elevator, the dentist can apply too much force, and then a fracture will occur). The risk of a mandibular fracture during extraction increases if the chair is occupied by an elderly person or a patient suffering from osteoporosis or osteopenic syndrome. Also at risk are patients who have had a tooth removed at the location of the pathological process - neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature, chronic osteomyelitis, cysts - follicular or radicular.
Other problems
In addition to the complications that were discussed above, there are a number of injuries, as well as pathologies that arise as a result of tooth extraction surgery. Most often, complications appear after wisdom tooth extraction due to their complex, unpredictable root system and inaccessible location. However, a seemingly simple procedure for removing a canine or molar can provoke unpleasant and even dangerous consequences.
Sources:
https://stomaportal.ru/diagnostika/sinyak-shcheke-posle-udaleniya-zuba https://topdent.ru/vopros-otvet/sinyak-posle-udaleniya-zuba-eto-normalno.html https://www. pro-zuby.ru/hirurgiya/oslozhneniya/posle-udaleniya-zuba.html
Causes of hematoma
The hematoma that may appear after the manipulation is not similar to a hematoma from an ordinary blow. It looks like a formation of a solid nature, located between the gum itself and the cheek area. Hematoma occurs quite often after a wisdom tooth has been removed. Extraction of a wisdom tooth entails injury to small and larger vessels located in the soft tissues. The hematoma can rise higher, affecting the cheek area. A cheek hematoma after tooth extraction goes away without a trace after a few days, which cannot be said about a hematoma on the gum.
Symptoms of a bruise on the gum are an increase in body temperature and swelling.
It is customary to distinguish several factors that can lead to the occurrence of gum hematoma after tooth extraction:
- when performing anesthesia, there is a high probability that there may be hemorrhage from the damaged vessel;
- increased blood pressure due to the patient having hypertension or a restless state. A person may feel noticeably nervous while in the dentist's chair.
- hypersensitive blood vessels and their increased fragility.
Causes
All people have gum pain after an anesthetic injection; this is a natural reaction to tissue puncture. Pain sensations vary in intensity and time of manifestation. Each body is individual, so the discomfort from the injection lasts a couple of hours for some, and several days for others. Dentists consider both options to be normal, which does not require treatment or additional intervention.
In cases where the pain becomes unbearable, prevents you from returning to normal life, and prevents you from eating and resting properly, you can talk about the occurrence of complications. Let's consider the reasons why undesirable consequences from an injection appear and what are the main factors for the deterioration of a person’s condition.
Infectious process in soft tissues
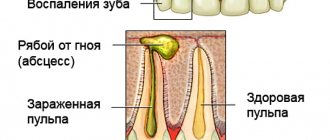
The mouth of any healthy person contains a large number of microorganisms and bacteria. In the presence of inflammation, their number rapidly increases. After an anesthetic injection, especially during a period of decreased human immunity, bacteria begin to penetrate inside through a small wound from the needle. This provokes the occurrence of an unwanted inflammatory process, the formation of pus or an abscess.
Infection is accompanied not only by pain, but also by an increase in temperature both throughout the body and at the site of inflammation. A common symptom of inflammation is gum swelling. As the process progresses, the tumor moves from the gums to other parts of the face, which can lead to its asymmetry.
Nerve fiber damage
Even an experienced dentist can injure a nerve fiber with a needle when performing anesthesia. In this case, the gums will hurt for a long time, which is estimated at several months. The intensity of pain and its duration depends on how large the size of the nerve trunk injury is.
With conduction anesthesia, damage to a large nerve is possible, as a result of which the pain can spread to other parts of the oral cavity. It becomes difficult for a person to chew food or talk, and facial asymmetry may occur. When performing infiltration anesthesia, only small nerve endings can be damaged. In this case, a limited area hurts, and the discomfort lasts for several days.
Hematoma
When, during anesthesia, the dentist damages one of the small vessels that permeate the entire oral cavity, a small amount of blood accumulates in this place. It is this that contributes to the appearance of hematoma and swelling of the gums. The severity of pain will vary depending on the size of the tumor. The larger it is, the more noticeable its pressure on the soft tissues located nearby.
The pain from the hematoma goes away on its own within a week. To speed up the healing process, you can resort to folk remedies. There is a wide range of things you can use to rinse your mouth with a high degree of effectiveness. For example, a decoction of sage, chamomile, and St. John's wort are considered antiseptics and relieve swelling well.
Allergy to anesthetic
If a person is allergic to the substances that make up the anesthetic, this may result in swelling of the gums or part of the soft tissue. In this case, special medications must be used to relieve symptoms.
Radiation of pain from the site of dental surgery
When performing manipulations in the oral cavity, nerve endings or soft tissues may be injured. When the anesthesia wears off, aching pain appears. Pain has the ability to radiate to those parts of the mucosa that are located near the site of injury, but the person feels as if the puncture site hurts.
Necrosis
It means the death or death of mucosal tissue. As a result of anesthesia, this happens quite rarely, but if the patient develops a whitish or dark spot at the injection site, then this is a reason to urgently consult a dentist. Necrosis causes a number of reasons:
- A dentist's mistake, as a result of which alcohol or calcium chloride is used instead of an anesthetic.
- Rapid injection of an anesthetic leads to injury and excessive compression of blood vessels.
- Spasm becomes the cause of necrosis when the administered dose of adrenaline in combination with an anesthetic substance is calculated incorrectly.
- Poor circulation caused by diseases such as vasculitis or diabetes.
A characteristic feature of necrosis is throbbing severe pain, it quickly intensifies and requires immediate intervention from a doctor. Correctly selected treatment relieves discomfort, healing lasts for a month.
How to treat a hematoma on the gum
If it happens that a complication such as a gum hematoma develops after tooth extraction, treatment at home is strictly prohibited. The most correct decision in such a situation would be to immediately contact a specialist. And it’s even better if it’s the same doctor who performs the removal. After the doctor conducts an examination and consultation, several techniques will be proposed to eliminate the problem as soon as possible. First of all, it is necessary to remove the inflammatory process, swelling and pain. In this matter, healing herbs come to the rescue. You can use the following recipes for rinsing:
- Calendula flowers, pre-crushed, poured into 1 liter of boiling water and infused for an hour. It is necessary to carry out the rinsing procedure as often as possible, and especially after meals.
- Rinse using infused sage herb. This type of medicinal plant is crushed, poured with boiling water and infused for 15 minutes.
- Infusion of chamomile flowers. Preparing the infusion is not difficult, only the infusion time must be increased to 2 hours.
- In addition, you can use a decoction of St. John's wort in combination with pine needles. A similar decoction will help cope with hematoma, using it as a lotion.
Treatment options
The choice of one or another treatment method is made by the attending dentist based on the diagnosis and visual examination of the small patient.
Treatment of a bruise from an injury on the gum
If you are sure that the bruise on the child’s gum is the result of an injury, you can try to provide the child with first aid, which consists of using the following methods:
- applying cold compresses to the injured half of the jaw;
- rinsing the mouth with decoctions of chamomile, calendula and sage.
If the bruise does not resolve for a long time (more than 5 days), and the main symptom is accompanied by severe pain and a rise in temperature, then most likely an inflammatory process has begun deep in the gums. In this case, medical assistance is necessary , which may consist of both the use of medications and surgical intervention.
Treatment of a cyst on the gum of a child
Treatment of the cyst is prescribed by the dentist after examining the child. There are two ways to do this:
- if the cyst formed during teething . In this case, experts recommend using special teething toys that help break the tissue and speed up the process of tooth extraction. If this technique does not help, and temperature is added to the main symptoms, it is possible to use the technique of dissecting the upper layer of the mucosa;
- if the cyst is large and accompanied by pain . In this case, the surface of the “blue bump” is usually dissected and the bloody or purulent contents are removed. After which the wound is treated and washed. In some cases, complete healing may require several visits to the dentist.
Medicines are usually not prescribed for blue gums. The only exceptions are those cases when the hematoma is accompanied by the formation of an abscess and an increase in body temperature.
Teether toy
Treatment of gingivitis
In this case, experts recommend resorting to plaque removal and prescribing anti-inflammatory rinses. In some cases, antibiotics are used as a rinse solution.
Painkillers
If the blueness is accompanied by severe pain, the child can be given painkillers. The most popular are “Ibuklin”, “Ibufen”, “Nurofen” and many others. In addition, you can use analgesics in the form of suppositories, for example “Viferon” - suppositories that, in addition to pain relief, have an antiviral effect. In addition, you can use special dental gels:
- "Holisal";
- "Kamistad";
- "Baby Doctor"
Treatment at home
It is worth understanding that any home therapy must be fully agreed with the attending dentist . In addition, sometimes experts themselves recommend supplementing the basic treatment with some folk recipes.
Mouth rinses
If the child is already quite independent and knows how to rinse his mouth, then this method will help to significantly speed up the process of relieving swelling and pain. The best options for preparing infusions are chamomile and calendula, which have an antibacterial effect.
To prepare the mixture you need:
- take 1 tablespoon of dried chamomile or calendula flowers;
- pour a glass of boiling water and leave for about an hour;
- Cool the infusion and strain.
You can rinse your mouth 4-5 times a day or after each meal.
Infusion of chamomile.
Teether toys
Such toys are sold in all pharmacies and children's stores. The teether contains distilled water inside, which allows you to significantly cool the toy by putting it in the refrigerator for a few minutes. This teether not only speeds up the process of teeth appearing, but also relieves swelling due to the cooling effect.
Applying compresses
Cold compresses help relieve swelling and inflammation. They have a special effect in the case of hematoma formation during dental surgery. To do this, you can take several lud cubes wrapped in a clean cloth and apply them for a while to the cheek or lip located above the injury.
How to avoid hematoma
After the tooth extraction procedure has been carried out, it is necessary to adhere to generally accepted rules, with the help of which it is possible to reduce the risk of hematoma to a minimum. These rules are:
- After the manipulation, it is necessary to remove the gauze or cotton swab after 20 minutes. This period of time is quite enough to stop the bleeding.
- After a tooth has been removed, it is not recommended to eat for 3 hours. During this time, the blood around the wound surface thickens, the wound heals, which prevents food particles from penetrating into the wound. It must be remembered that food and drinks should not be hot or too cold. Spicy, sour and spicy foods should be avoided. The fact is that the types of food described above can irritate the wound surface and also contribute to the destruction of the blood clot.
- A cold compress applied to the cheek on the side from which the tooth was pulled out helps reduce the risk of hematoma or bleeding. Between applications it is necessary to take a break of 5-15 minutes, thereby avoiding frostbite of the tissues.
- For several days after tooth extraction, you should avoid playing sports and other types of physical activity. You should not go to the sauna.
- It is important to follow the instructions of your treating specialist and take medications prescribed by your doctor.
You need to refrain from bad habits for several days after the manipulation.
It is important to remember that it is necessary to follow the instructions, as this will avoid possible complications. If a hematoma forms, you can rinse your mouth with a decoction of medicinal herbs, and you should also consult a doctor.
source
Causes of the problem
Hematoma after wisdom tooth removal is a consequence:
- development of the inflammatory process;
- mechanical damage to soft tissues during surgery;
- complex extraction requiring retination or dystopia of the corresponding unit;
- removal of an abscess (ulcer on the gum);
- individual characteristics of the patient’s body (for example, a bruise on the cheek or even under the eye after tooth extraction may appear in a hypertensive patient, a diabetic, or a patient with weak blood vessels).
Signs
The appearance of a bruise on the gum is accompanied by a host of other unpleasant symptoms: the formation of a compaction (nodule), swelling of the soft tissues, increased body temperature, and weakness. The patient may experience pain directly at the site of the surgical intervention, but the pain can also radiate to neighboring teeth and radiate into the jaw.
Hematoma after extraction of a wisdom tooth is a common phenomenon due to the “inconvenient” location and, accordingly, difficult medical access to this unit, as well as the high risk of damage to soft tissues during surgery. In an empty socket, there is often a feeling of tingling, pressure, tightness, and numbness.
When no treatment is required
In dentistry, there are a number of signs that allow us to say that in this case, swelling, puffiness, and cyanosis of the gums (cheeks) are normal:
- the soft tissues are slightly swollen immediately after the end of the operation, the swelling does not increase or, on the contrary, gradually subsides;
- body temperature does not increase;
- the pain syndrome is either absent altogether or mildly expressed; on the 4th day after extraction all unpleasant sensations disappear;
- The gums after tooth extraction are slightly hyperemic, there are no signs of inflammation around the empty socket.
Indications for emergency medical care
If, after a day, severe swelling appears at the site of the extracted tooth, but there is no pain in the socket area, this may indicate the development of a cystic or inflammatory process. When rapidly growing swelling of the cheek (lip, gum, tongue) is accompanied by shortness of breath, these are clear signs of an allergic reaction.
Constant throbbing, aching pain in the empty socket or “neighboring” lesions in combination with elevated body temperature, general weakness, apathy, nausea and dizziness are symptoms of intoxication of the body. Discomfort, unpleasant sensations (pain) when opening the mouth, moving the head, while eating, a swollen cheek 3-4 days after extraction are classic signs of alveolitis (inflammation of the alveolar ridge).
Solution
Treatment of hematomas, swelling and associated complications after surgery depends on the causes and severity of the pathological process. So, with extensive destruction of the coronal part of the tooth, the dentist has to make an incision in the gums in order to extract the remaining part of the root using an instrument.
It is the soft tissue injury that in this case leads to the appearance of swelling (hematoma). Local painkillers, antiseptics, cold compresses, and rinsing the mouth with a soda-salt solution help to cope with the problem. Concomitant gum and periodontal diseases are indications for antibacterial treatment. Decoctions of chamomile flowers, calendula, and other medicinal herbs (they are used for rinsing) help speed up the healing process of a postoperative wound.
As a rule, extraction of wisdom teeth is associated with a number of difficulties and therefore entails unpleasant complications, including the appearance of hematomas. Treatment is the same as in the previous case - the use of local antiseptic compounds, painkillers, and, if indicated, antibiotics. To ensure that the swelling goes down as quickly as possible, cold compresses are applied to the “affected” area.
How to distinguish cyanosis during teething from diseases?
Gums can change color due to various pathologies.
Here are the main ones:
- gingivitis;
- stomatitis;
- anemia.
With stomatitis, the gums do not have a pronounced blue color, but only a tint against the background of redness. This disease can be distinguished by accompanying symptoms:
- pain;
- the mucous membrane changes throughout the entire oral cavity, and not just on the gums;
- there may be yellow fibrin deposits.
Gingivitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the gums. Blue gums in a child during teething differ in size from signs of gingivitis. This gum disease is characterized by local changes, that is, the gums change color in limited areas near the teeth.
As in the previous case, the mucous membrane has a reddish-blue color. It should be noted that both pathologies usually occur in weakened children with low reactivity of the immune system.
Anemia is characterized by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in red blood cells, and due to this, a change in the color of the blood. Therefore, the skin and mucous membranes acquire a pale blue color. This is especially visible on the gums, skin, white of the eye and earlobes.
Anemia can be distinguished by additional symptoms:
- lethargy, apathy;
- cracks in the corners of the mouth;
- hair fragility;
- peeling of the skin.
Home methods
You can speed up the subsidence of edema in the absence of other complications using folk remedies. So, 2–5 g of propolis are crushed and diluted in clean warm water. The resulting mass is applied directly to the lesion and left for 10 minutes. Treatment is carried out three times a day until the hematoma (swelling) disappears.
A few grains of potassium permanganate (manganese) are diluted in a glass of water (you should get a light pink liquid). Rinse your mouth with the prepared product 1 time/2 hours during the first 3 days after extraction. So, 2-3 tablespoons of dry crushed chamomile flowers are steamed with boiling water and left to infuse for 1 hour. The medicine is used for therapeutic rinses (the procedure is carried out 2-3 times a day).
What to do if you have a hematoma during tooth eruption?
In most cases, this process does not require intervention and the pathological changes go away on their own over time.
During this period, the child can be given carrots in small pieces or other dense foods, which will promote rupture of the mucous membrane and help teething. Small accumulations of blood resolve on their own.
You should definitely see a doctor when:
- the hematoma does not go away within 3 days or more;
- high and prolonged temperature;
- severe pain;
- The general condition worsens, that is, weakness and loss of appetite occur.
In other cases, you can get by with a preventive examination. Treatment depends on the complication - the contents of large hematomas are released through a small incision in the gum. Abscesses are also removed surgically.
All children go through an unpleasant period when they are teething. Special teething gels do an excellent job of relieving discomfort.
Another remedy that helps a child survive the difficult period of the appearance of his first teeth is candles. You can read how to use them and which products are recommended more than others here.
Precautionary measures
To avoid the appearance of hematoma, swelling and other complications, you should not practice active physical activity or lift heavy objects for 2-3 days after tooth extraction. You cannot intensively impact the soft tissues of the oral cavity with a toothbrush and “aggressive” toothpaste with a large number of abrasive particles. It is better to give preference to dental floss and mouthwash with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties for the entire healing period.
Excessively cold and hot foods are also prohibited for several days after surgery. It is recommended to drink drinks through a straw to reduce the risk of bacteria or irritants getting into the wound. During the first 3 hours after extraction, food (drinks) are prohibited. The cotton swab is removed from the empty hole no earlier than 20 minutes after completion of the surgical intervention.
So, hematoma (bruise, bruise) and accompanying swelling are a common consequence of tooth extraction. The causes of this complication can be both medical errors and the characteristics of the patient’s body. The fight against postoperative hematoma is carried out based on why it occurred. As a rule, in the absence of concomitant dental problems, cold compresses and rinsing with antiseptic, anti-inflammatory solutions (homemade or pharmacy) are sufficient.
source
Hematoma due to tooth extraction
Toothache is considered one of the most severe and can bring a lot of inconvenience . When it appears, you should immediately consult a doctor, because you can lose a healthy tooth that could be cured or trigger a situation with a problematic wisdom tooth. Complications may occur, most often a hematoma occurs after tooth extraction, as well as swelling or bruising on the gums.
Treatment of bruises on the gums during teething
The appearance of a bruise on the gum when teeth are cutting in 90% of cases does not require treatment. The coloring of the gums can last up to 2-3 weeks until the tooth appears. In most cases, the hematoma or hemorrhage resolves over time. You should consult a doctor in the following cases:
- the presence of a large hematoma more than 2 cm in diameter;
- long-term existence of blue gums (more than 3 weeks);
- hematoma suppuration;
- in case of acute pain;
- The baby's body temperature is more than 38 degrees.
To eliminate pain and speed up the appearance of teeth, use:
- anesthetic gels (for example, Cholisal);
- teethers;
- massage;
- medications;
- traditional medicine.
If there are formations on the gums, do not try to open them or burst them yourself, as there is a high probability of introducing microbes and developing further complications.
Complications after a bruise on the gum of a baby
The most serious and undesirable consequence of a bruise is gum suppuration. This happens with a long-term existence of a hematoma, severe inflammation and infection.
Infection can occur when the child’s immunity is reduced and pathogenic microorganisms enter the oral cavity. If a purulent focus occurs:
- the gums become very swollen, become red in color and yellow in the presence of pus;
- the child experiences high body temperature and acute pain;
- the baby refuses to eat and needs urgent treatment.
After examination and diagnosis, two treatment options may be offered:
- Conservative - appropriate for minor hematomas and no complications. In this case, the doctor prescribes special gels, ointments and medications for oral administration, and gives recommendations on gum care.
- Surgical - in case of suppuration, the presence of a large hematoma or the impossibility of tooth eruption. Under anesthesia, the mucous membrane is dissected and the hematoma is removed or washed with antiseptic solutions. After this, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs are prescribed.
If you are cutting teeth and bruising occurs, do not be afraid. You just need to monitor the complication, and in case of suppuration or infection, immediately consult a doctor.
Liana Mokhtari, dentist, especially for Mirmam.pro
mirmam.pro
Possible complications
70% of cases of tooth extraction (removal) proceed without complications, and many people may not even remember about this procedure after a couple of days. But in the remaining 30% of cases, patients are exposed to a number of unpleasant postoperative sensations. These include:
- Pain. During the removal process, the dental surgeon often has to put pressure on adjacent teeth to provide support. Because of this, they may bother you for several days. And damage to soft tissue also brings painful discomfort. If you don’t have the patience to endure such a consequence, then you need to take painkillers.
- Edema. This symptom appears the day after surgery. On the third day, gum swelling reaches its maximum, and then gradually declines.
- Bruise. This consequence can occur after the removal of complex teeth that have long roots. During the procedure, the gum is cut, since it is not possible to remove the tooth using the usual method. And due to this, blood enters the soft tissues. It can be removed with special ointments and gels.
- Fever. It is acceptable to have a low-grade fever on the day of extraction.
- Swollen cheek. Due to damage to soft tissues, not only the gums, but also the cheek can swell. The swelling usually goes away within three days.
- Numbness. Such a complication cannot be immediately noticed, because the patient thinks that this is a simple effect of anesthesia. But after 12 hours, you can notice the resulting neuropathy of the alveolar nerve. This condition can last from a couple of days to a month, it should be treated with physiotherapy, and sometimes medications are used.
- Unpleasant smell. In the first days, dentists do not advise performing oral hygiene, so this may occur. You can get rid of it by cleansing with antiseptics in the dentist's office, as well as using a decoction of nettle or yarrow.
- Limited osteomyelitis. Severe acute pain begins at the site of the extracted tooth, which may be accompanied by chills, weakness, and headache. There is a temperature of more than 38 degrees, pus, and an odor from the wound. You should immediately go to the hospital and do not self-medicate.
But the most common complication is a hematoma. There are certain reasons why it may appear.
How to treat a hematoma on the gum
If you have to deal with such a nuisance as a hematoma after tooth extraction, you should not self-medicate. It is better to consult a doctor for advice, optimally if it is a specialist who performed the surgery. After his consultation, you can apply some techniques that will solve the problem in the shortest possible time. First you need to eliminate inflammation, swelling and pain, herbs will help with this. For treatment, you can use products that are available at home.
- Calendula flowers must first be crushed, then pour one liter of boiling water and let it brew for an hour. Rinse at least 5 times, especially thoroughly after meals.
- Rinsing with sage infusion will help relieve swelling. The dry herb should be slightly mashed, then poured with hot water and left for 15 minutes. Then you can rinse - the more often the better.
- An infusion of chamomile flowers will also have an antiseptic effect. It is prepared according to the same principle as the first two options, only you need to insist longer: two hours.
- An excellent option that is used to treat dental hematoma is a combination of calendula and sage. Herbs need to be boiled using a water bath. The process should continue for four hours. Next, the resulting decoction should be filtered and the mouth should be rinsed with it often.
- You can use oregano for rinsing. The flowers of this plant should be poured with boiling water and wait until the broth cools down, then you can rinse.
- An effective remedy is to lubricate the injured area with a decoction of St. John's wort (4 tablespoons) and pine needles (1 tablespoon). They can be pureed using a blender or knife and then allowed to simmer for up to five minutes. Then make lotions using gauze or cotton wool.
But if such measures do not help and the hematoma does not decrease within three to four days, you should immediately consult a dentist. At the site of inflammation, pus can form, which, if it enters the bloodstream, will cause terrible complications, including death.
Hematoma on the gum: reasons for its appearance, how to remove it, photo | All about gums
Most people diligently take care of their teeth, completely forgetting to monitor the health of their gums.
Dentists say that the beauty of a smile depends on the condition of the soft tissues in the mouth, so any disease brings serious consequences. The appearance of a dark bruise on the mucous membrane is always alarming and confusing.
This may be a consequence of injury or tooth extraction, but in any case it requires careful consideration and full treatment.
Cause of hematoma on the gums in adults
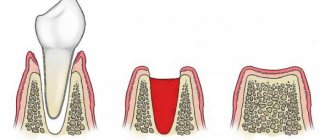
A bruise on the gum itself is not a separate disease. This is a hemorrhage into the soft tissue of the mucosa due to the destruction of small capillaries.
Despite its small size, this problem sometimes provokes serious inflammation in the periosteum and may well cause the loss of healthy teeth.
If it is accompanied by swelling and other painful symptoms (bumps, growths), treatment under the supervision of a dentist is required.
The most likely causes of the formation of a dark spot on the gums in an adult patient:
- The doctor performs manipulations with soft tissues or teeth: removal, filling or cleaning of dental canals, cutting to remove drainage, installation of a prosthesis. The larger the area where such procedures are performed, the more noticeable the bruise on the jaw.
- Problems with blood pressure, which provokes sudden surges and changes in the circulatory system.
- Congenital diseases associated with blood clotting disorders in the body. In such people, a hematoma on the gum is formed from a slight scratch, biting or injection.
- Consequences of injury and impact.
In adult patients, a common cause of bruising on the mucous membrane is improper growth of wisdom teeth. As a rule, they come to the surface in adulthood, when the jaw is fully formed.
They do not have enough space in the row, they move to the side and damage the periosteum. In this case, swelling accumulates around the dark spot, causing swelling and severe redness.
The process is accompanied by aching pain, a slight increase in temperature and loss of performance.
Why does a bruise appear on a baby’s gum?
Many parents are perplexed when they discover a characteristic bruise in the child’s mouth. It can be a consequence of injury during active play, chewing on toys or biting on a pacifier. But most often, a small black-blue spot forms in the upper part of the gum.
Dentists warn that teeth sometimes cut through this way. Primary molars and incisors lack the sharpness to pierce the dense tissue of the periosteum. Damage to the smallest capillaries and slight bleeding into the gum occurs.
From the outside, the picture looks unpleasant and worries parents, but in most cases the lump resolves on its own and does not require special treatment.
The doctor may recommend light gels with an analgesic so that the baby is not overly restless and can more easily endure the teething process.
Symptoms of bruises in the mouth
Depending on the reason why a hematoma appeared on the gum of an adult, it has different sizes. Dentists divide them into two groups according to the complexity and severity of the consequences:
- Blood pours into the dental pockets and accumulates around the tooth, surrounding it with a dark bluish area. Usually the mucous membrane increases in volume, the patient feels discomfort and cannot completely close the jaw. He finds it difficult to chew and pronounce certain sounds.
- Hemorrhage occurs inside the roots of the teeth, resulting in a rounded swelling affecting the inner surface of the cheek. Outwardly, it resembles flux in the acute stage: a person complains of aching pain, irritability, and slight facial asymmetry appears. The gums become swollen and there is a feeling of tightness, chills, general weakness and fever.
Gradually, with proper treatment, all unpleasant symptoms go away, and a spot with a yellowish tint remains at the site of the hematoma. It gradually dissolves and disappears completely. This process may take several weeks.
Methods of treatment for bruises on the gums
Patients mistakenly believe that a bruise should go away without treatment.
But a hematoma on the gum after a blow or tooth extraction requires special attention: harmful bacteria that are present in the oral cavity easily penetrate into the open wound.
This is fraught with extensive abscesses, fistulas on the mucous membrane and accumulation of suppuration in the roots of the teeth. Therefore, if the temperature rises and discomfort, it is better to seek help.
The dentist may open the gum to allow any accumulated fluid to escape. If necessary, a small drainage is left in the wound to accelerate the outflow of ichor. Through a miniature incision, the doctor washes the damaged area with antiseptics, which eliminates the formation of infection. At home, the patient is recommended to continue therapy:
- Use broad-spectrum antibiotics (Lincomycin, Tetracycline or Gentamicin). As a rule, this is more of a preventive measure, which is necessary if there are teeth destroyed by caries in the oral cavity.
- Nurofen, Paracetamol or Nise are suitable for relieving fever and pain. If a person cannot tolerate discomfort, feels pulsation and twitching at the root of the tooth, you can drink Nimesil.
- The mouth should be rinsed at least 3 times daily with special antiseptics: Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt or Fukortsin diluted in water.
- To relieve discomfort, the gums are lightly lubricated with Metragil Denta, Kamistad or Cholisal ointment. They will improve blood circulation and swelling will go away faster.
To heal the incision and speed up the resorption of the bruise, dentists recommend using compresses with Solcoseryl healing ointment. After a few days, your gums will become firmer and the dark area will be less sensitive.
Traditional methods of eliminating hematomas on the gums
To improve the health of the mucous membrane, you can use recipes with natural ingredients. Their healing properties help to quickly deal with bruises and restore the beauty of your smile.
To prepare natural preparations, plants with wound healing and anti-inflammatory properties are used.
Tannins and beneficial compounds promote rapid resorption of hematoma and restore soft periodontal tissue:
- Several calendula inflorescences (fresh or dried) are infused in a glass of boiling water, and the teeth are rinsed 4-5 times a day.
- A decoction of common sage effectively relieves puffiness. It is used warm and try to keep it in the mouth for 5-7 minutes.
- Brewed dry chamomile flowers in combination with St. John's wort will replace the antiseptic and improve the microflora.
- A bruise on the gum is lubricated with fir, bay leaf, sea buckthorn or tea tree oil.
- A paste of aloe or Kalanchoe will speed up wound healing after removing the drainage.
- To reduce pain and swelling, apply an ice cube made with the addition of propolis tincture.
The combination of effective homeopathic recipes and drug treatment will help you quickly get rid of the problem, while avoiding complications that are unpleasant for the patient.
Previous article
Hole in the gum: possible causes, treatment, photo
Next article
Nevus on the gum: causes, treatment, photos
Source: https://vdesnah.com/gematoma-na-desne.html
How to avoid hematoma
After removing a wisdom tooth or other tooth, you should follow simple rules that will reduce the risk of hematoma, as well as other complications. They are to:
- 20 minutes after surgery, the gauze or cotton swab should be removed. This period of time will be quite enough for the bleeding to stop. If this is done very early or late, the likelihood that a clot may not form increases. In this case, the bleeding continues, and stopping it can be very problematic.
- After removal, you should not eat any food for at least three hours. During this time, the blood will be able to thicken around the wound, which will prevent food particles from getting there. It is worth remembering that food and drinks should not be very hot or cold, or spicy, hot or sour. All this will serve as additional irritants or contribute to the destruction of the formed clot.
- Cold, which should be applied to the cheek on the side of the pulled out tooth every half hour, will help reduce the risk of not only hematoma, but also bleeding. Be sure to take a break for 5-10 minutes to avoid frostbite of the soft tissues.
- On the day of surgery, rinsing is prohibited, as there is a risk of leaving the socket unprotected, washing out the formed clot.
- For hygiene purposes, you should only use a toothbrush with soft bristles, avoiding the area of the extracted tooth.
- For three days, it is strictly forbidden to work out in the gym or have other physical activities, as well as go to the sauna or bathhouse.
- You should follow the instructions of your treating dental surgeon and take medications if prescribed. Most often these are painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs or hemostatic agents.
- You should refrain from smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages on the day of tooth extraction.
Thus, after removing a wisdom tooth or another patient, you need to follow certain recommendations. Of course, no one is immune from complications, but it’s still worth adhering to safety measures. If a hematoma has formed, you should rinse your mouth every two hours with a decoction of chamomile, sage, St. John's wort or calendula. And if such measures do not help, you should immediately contact your dentist. You must always remember that self-medication will only worsen the situation, and delay in the matter can cost your health and life.
source