1580
In modern dentistry, a new technology has appeared that allows you to return a tooth to its place.
That is, the organ that fell out as a result of injury is installed in its own alveolar bed.
Also, if an element of the dentition was removed for medical reasons for the treatment of severe oral pathologies.
Such manipulations in dentistry are called replantation.
General overview
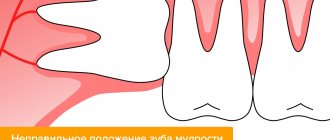
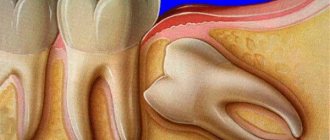
The operation is most often performed on the anterior units, which, having one root, are most susceptible to accidental falling out of the socket due to various injuries.
The success of the operation (i.e., the implantation of the tooth in the bone) directly depends on its integrity, the degree of damage to the socket, and the time that has passed since the loss.
It is noted that the less time has passed since the loss of the tooth, the more likely it is that the healing will be successful, its functionality will be fully restored, and the aesthetics of the smile will be higher.
Which implantation method best restores chewing teeth?
One-stage implantation with immediate loading
Most often used in cases of complete absence of teeth.
The one-stage method is preferable to the classical procedure, since load-bearing prosthetics are immediately possible, albeit with a temporary crown. And bone atrophy is not a hindrance. Implants can be installed at an angle or straight, fixed in dense layers of bone that are not subject to resorption (resorption).
Classic two-stage implantation
- a protocol with a half-century history. It ensures a high survival rate of implants and no complications. This method allows you to restore both single and multiple tooth loss of any location.
If the patient is missing 1-2 teeth, the doctor will suggest restoration with separate crowns. In case of multiple losses, prosthetic bridge construction is recommended.
However, the result in the form of permanent prosthetics will have to wait from 3 to 6 months.
Indications
In clinical practice, manipulations are performed very rarely and only in cases where preservation of the removed unit is impossible by any conservative or surgical method.
This usually occurs under the following conditions:
- chronic forms of granulating or granulomatous periodontitis lesions of the root unit, when standard therapy and resection of the upper part of the roots are not applicable for a number of reasons;
- the development of complications during drug treatment of periodontitis of a multi-rooted tooth, during which perforation of the roots occurs, breakage in the canals of the pulp extractor or dental needle;
- exacerbation of periodontitis in a single-root unit;
- severe injury, which is accompanied by accidental tooth loss or dislocation;
- acute form of odontogenic jaw periostitis;
- a fracture of the jaw bone in which a tooth has sunk into the fracture gap.
Important! In all of these cases, the return of a tooth is possible only under one important condition - the tooth should not have carious lesions, the crown part should be free of defects, and the roots should not have curvature or discrepancies.
What is the procedure for hemisection of a tooth, and the reasons for its implementation.
Come here if you are interested in the price of dental implant removal.
Follow the link https://zubovv.ru/hirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/posle-ostalsya-oskolok.html to find out what to do if a fragment remains after tooth extraction.
What are the health consequences of missing chewing teeth?
Large molars enable food processing. In their absence, rough food can cause inflammation of the gastric mucosa (gastritis). Also, gradual loss of bone tissue can further complicate implantation.
Removal of 1-2 teeth often leads to disruption of the growth of the remaining teeth, striving to take up the vacant space. And the loss of molars also changes the contours of the face - the cheeks may sink inwards, wrinkles appear, and this does not look very aesthetically pleasing, especially with one-sided defects.
Dentistry can offer patients with such problems removable prosthetics and implantation. Implantation has a number of obvious advantages.
Contraindications
Replantation as a surgical procedure has several limitations:
- extensive carious process;
- inflammation developing in periodontium and periodontal disease;
- multiple and significant cracking of enamel;
- twisted root system;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- diseases of the circulatory system and the blood itself;
- psychoneurological diseases in the active phase;
- malignant neoplasms of any organ;
- acute form of radiation sickness;
- acute infectious diseases.
The operation will also be refused if the results of the examination reveal conditions that have a depressing effect on the regeneration process. Such conditions include diabetes, drug addiction, chronic alcoholism, etc.
Important! The doctor makes the decision to perform or refuse surgery based on all the indications and limitations the patient has at the time of seeking medical help.
What are the requirements for implantation of chewing teeth?
Restoring large molars using dentures on implants has a number of features:
- These teeth are constantly under heavy stress
. Therefore, you need to choose an implant that will provide reliable support for the prosthesis. - The number and type of implants are selected individually
. There is no single universal treatment method. The procedure will be different for each patient. - The implantation method is selected based on the available capabilities and wishes of the patient
. The final decision is made by the attending physician.
Undoubtedly, classical implantation is the good old method that has helped many over the 50 years of its existence. However, its main disadvantages - traumatic nature and long-term outcome - contribute to the choice in favor of modern implantation protocols.
Intervention methods
Replantation is carried out using two technologies - devital and vital. The first method is applicable in cases where one of the pathological conditions is being treated (chronic periodontitis, exacerbation of periostitis, etc.), when traditional treatment methods do not give a positive result.
In this case, the dentist first carefully removes the tooth, without stretching or damaging the surrounding tissue, and then:
- treats with antiseptics;
- removes all deposits;
- removes nerves;
- places fillings in root canals;
- cuts off the top part of one or all roots at once.
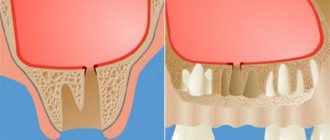
Then the doctor cleans the hole from tissues affected by the pathology, rinses it with an antiseptic and returns the unit to the alveolus.
The second (vital) technology is applicable in case of tooth loss due to severe injuries. In this case, the fallen unit is not filled, the nerves are not removed from the pulp (it remains “alive”).
The specialist only treats the tooth itself and the socket with antiseptics, and then puts it in its place. With this method, the functionality of the unit is fully preserved for 10 years or more.
The sequence of complex wisdom tooth extraction and possible risks.
In this publication we will talk about the technique of resection of the apex of the tooth root and complications after the operation.
Here https://zubovv.ru/hirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/stoit-li-boyatsy-retinirovannogo-mudrosti.html reviews about the removal of impacted wisdom teeth are presented.
Installation steps
Before the implantation procedure, a long preparation is carried out, during which it is important to exclude possible contraindications and create all the conditions for normal engraftment of the pin. If problems appear at the initial stage, the dentist considers other recovery options. Stages of implantation:
- Diagnostics. The doctor prescribes laboratory tests, x-rays and examination by specialized specialists.
- Preoperative preparation. The oral cavity is sanitized, existing foci of inflammation and caries are eliminated, old fillings and crowns are replaced.
- Operational stage. Includes antiseptic treatment, anesthesia, formation of a bone bed and fixation of the pin itself.
- Orthopedic stage. Impressions are taken and structures are prepared for subsequent prosthetics after the bone has healed.
- Installation of the prosthesis. Artificial teeth are placed on implants after a few months.
Simply it looks like this:
In case of immediate implantation, the pin is installed a few days after tooth extraction. The patient must visit the dentist every few months to monitor tissue healing.
Preparation
Before proceeding with replantation, the doctor must carefully examine the causative unit.
If it was lost as a result of injury, then the degree of damage to the organ and alveolar walls must be clarified, and the condition of the surrounding tissues and adjacent teeth is determined. The doctor receives this information based on the results of radiography.
If replantation is planned and removal is part of a comprehensive treatment of periodontal pathologies, then a set of therapeutic measures is performed to improve the health of the oral cavity and prevent the development of other dental problems, i.e., complete sanitation is carried out. Manipulation includes:
- removal of various types of deposits;
- elimination of caries;
- restoration of the coronal parts of those units in which developmental pathologies or defects were identified (cracks, hypoplasia, chips, etc.);
- anti-inflammatory therapy;
- removal of those teeth that cannot be restored.
Important! Since sanitation can solve several problems at once, its duration will directly depend on the condition of the patient’s oral cavity.
Only after such preparation can the dentist begin to implant the tooth in its original place.
Why is dental implantation better than other methods?
Prosthetics on implants has a number of significant advantages:
- There is no need to injure healthy teeth by using them as a support for a prosthesis.
- It is possible to restore 100% tooth function. The implant is made of durable titanium and can withstand chewing loads.
- There is no atrophy, since the load on the bone is the same as from your own teeth.
- Normal bite and growth of adjacent teeth. Maintaining normal diction.
- Convenience of prosthetics. According to the subjective feelings of most patients, a new tooth supported by an implant is no different from others.
- Long service life. This type of prosthetics can serve a person for decades. Good stabilization of the implant and high-quality materials are the key to this.
Order of conduct
The operation begins with anesthesia. To do this, conduction anesthesia is performed, and as soon as it begins to take effect, the dentist begins extraction. The manipulation is performed with minimal trauma to the tissue in the alveolus.
After:
- The chewing organ is placed in a warm (not higher than 37 ⁰ C) physiological solution with the obligatory addition of one of the antibiotics - Penicillin or Gentamicin. This is done to prevent the development of infection and eliminate pathogenic microflora in the root system.
- The dentist prepares the hole for replantation. To do this, he treats the entire oral cavity and alveolar area with an antiseptic (usually 0.2% Chlorhexidine is used).
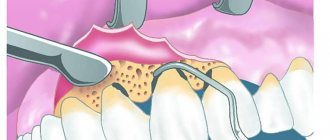
- The hole is very carefully cleaned of granulations and small loose bone fragments using a curettage spoon , treated with a solution of sodium chloride or Furacilin, and covered with a tampon.
- Afterwards, the specialist treats the tooth. All large deposits are removed from the crown with tweezers, small deposits are washed off with saline solution from a syringe. Holding the tooth by its crown with dental forceps or a fixing device, its cavity is opened and the pulp is removed.
- The root canals and the tooth cavity itself are filled with filling material . The apex of the tooth root is resected using a special bur.
If for some reason it is impossible to remove the pulp and fill the tooth cavity and its root canals with a filling mass, after sawing off the root tips, retrograde filling with silver amalgam . The tooth treated in this way is again placed in saline solution.
At this time, the blood clot is carefully washed out of the hole with a stream of antiseptic solution and a curettage spoon, and it is re-irrigated with antibiotics. The prepared tooth is inserted into the alveolus and strengthened by the doctor with a splint (left for 3-4 weeks).
The video shows a diagram of tooth replantation after injury.
Price
The price of replantation is quite affordable, and depends on the number of roots of a dental unit.
The average cost of the necessary manipulations is presented in the table.
Replantation means transplanting an extracted tooth into its own alveolus.
There are immediate and delayed replantation.
Indications and contraindications for direct replantation are the same as for resection of the apex of the tooth root. Replantation of mainly multi-rooted teeth is performed.
Operation technique:
The tooth is carefully removed, trying not to injure the walls of the alveoli and adjacent soft tissues. The extracted tooth is immersed in a warm (+ 37 degrees) isotonic sodium chloride solution with the addition of an antibiotic. Granulation growths or granuloma are removed, trying to preserve periodontal tissue, the lateral walls of the alveoli and the circular ligament, and the socket is washed with an antibiotic solution. Under aseptic conditions, the canals and carious cavity of the tooth are mechanically cleaned, filled with phosphate cement or quick-hardening plastic, and the apexes of the roots are resected. After toileting the socket, the tooth is placed in the socket and fixed with a wire splint made of quick-hardening plastic for 2-3 weeks and removed from occlusion. Multi-rooted teeth may not require fixation.
There are three types of fusion of the transplanted tooth with the alveolus: periodontal - occurs with complete preservation of the alveolar periosteum and periodontal remnants on the roots of the tooth; periodontal fibrous - with partial preservation of the alveolar periosteum and periodontal remnants on the tooth root; osteoid - with complete destruction or death of the alveolar periosteum and periodontal tooth root. The prognosis for the viability of a replanted tooth is most favorable with periodontal and least favorable with osteoid type of engraftment. In acute inflammatory processes (acute and aggravated chronic periodontitis, periostitis, osteomyelitis), delayed replantation is performed. The extracted tooth is placed in an isotonic solution.
- 5. Materials for student activation during lecture presentation
- 1. A 31-year-old patient has chronic granulomatous periodontitis of the 11th tooth. On the radiograph, there is a granuloma up to 4.5 mm at the apex of the 11th tooth. in diameter. The filling mass is not brought to the root apex by 2-3 cm. What type of treatment should be carried out for this patient?
- 2. A 42-year-old patient consulted a dentist about a defect in the crown of the 46th tooth. There is a large carious cavity on the distal approximal surface of the 46th tooth. On the radiograph, the medial root is filled to the apex, there are no periapical changes.
The crown defect reaches the bifurcation. At the distal root there is a rounded bone tissue resorption with clear boundaries with a diameter of up to 4 mm. with a sclerotic rim along the periphery. Choose the most appropriate type of treatment.
TOOTH REPLANTATION
Replantation is the return of an extracted tooth to its alveolus. Tooth replantation is carried out for: 1) chronic granulating and granulomatous periodontitis of multi-rooted teeth, when, due to certain circumstances, neither conservative therapy nor a root apex resection operation can be used; 2) complications that arose during conservative treatment of chronic periodontitis of multi-rooted teeth (root perforation, fracture in the root canal of the pulp extractor, root needle); 3) trauma accompanied by tooth dislocation, or accidental tooth extraction; 4) acute odontogenic periostitis of the jaws, exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, which is not subject to conservative treatment (in these cases, delayed tooth replantation is performed).
The tooth to be replanted must have a well-preserved crown and not have significantly divergent or crooked roots. The method of tooth replantation is as follows. Under general anesthesia, the tooth is carefully removed with minimal trauma to the soft and hard tissues in the alveolar area. The extracted tooth is immersed in a warm (37 °C) isotonic sodium chloride solution with the addition of antibiotics. The alveolus of the extracted tooth is carefully cleaned of granulations with a sharp curettage spoon and washed from a syringe with an isotonic solution of sodium chloride with antibiotics or furatsilin and covered with a sterile gauze swab. Then the tooth is treated, which consists of mechanical cleaning of the root canals and carious cavity. During tooth processing, the rules of asepsis are strictly observed. The tooth is held in a sterile gauze moistened with an isotonic solution of sodium chloride with antibiotics. The drill tip and bur must also be sterile. Periodontal remains on the tooth root are not removed. The root canals are filled with phosphate cement or quick-hardening plastic. After filling the canal, the root apex should be resected, since in the area of the root apex there is a large number of deltoid branches of the canal with necrotic content. Penetration of infection from these branches beyond the apex of the root of the replanted tooth leads to relapse of chronic periodontitis.
The tooth prepared for replantation is inserted into the alveolus after the blood clot is removed from it and irrigated with an antibiotic solution. Single-rooted teeth should be fixed for 2-3 weeks using a wire splint or a pre-made plastic splint. Multi-rooted teeth, as a rule, are well retained in the alveolus, and no additional fixation is required. At first, it is necessary to create resting conditions for the replanted tooth—to turn it off from articulation. A gentle diet, analgesics, and sulfonamides are prescribed. 3-4 sessions of UHF therapy can be recommended.
With exacerbation of chronic periodontitis and acute periostitis of the jaw, delayed replantation is possible. The operation differs from the one described above in that it is a two-stage process. The first stage consists of removing the tooth and preserving it in an antibiotic solution at a temperature of 4°C. The second stage is carried out 14 days after the signs of acute inflammation disappear. The tooth is treated and replanted using the usual method. The healing process of the replanted tooth is greatly influenced by the preserved periodontium and alveolar periosteum. Healing during tooth replantation lasts from 4 to 6 weeks, which depends on the type of fusion. There are three types of fusion of the transplanted tooth with the alveolus: 1) with complete preservation of the periosteum of the alveolus and periodontal remains on the roots of the tooth - periodontal; 2) with partial preservation of the alveolar periosteum and periodontal remains on the tooth root - periodontal fibrous; 3) with complete removal of the periosteum from the alveolus and periodontium of the tooth root - osteoid.
The prognosis for the viability of a replanted tooth is most favorable with periodontal and least favorable with osteoid type of engraftment. The function of the transplanted tooth is preserved from 2 to 10 years or more. The longest periods are observed when transplanting a healthy tooth that was accidentally removed or dislocated from its socket.
Transplantation—transplanting a tooth into another alveolus—is rarely used. This operation is undertaken in cases where it is possible to transplant a healthy supernumerary or impacted tooth into the alveolus of a tooth removed due to chronic periodontitis or crown destruction due to acute trauma. The surgical technique is the same as for replantation. Particular difficulties during this operation lie in the formation of an alveolus for transplanting another tooth, since there is a significant difference in the size of not only the crown, but also the roots of the extracted and replanted teeth. Formation of the alveoli in accordance with the transplanted tooth often leads to additional trauma to the alveoli and removal of its periosteum, which adversely affects the healing process.
Implantation is the intraosseous introduction of artificial roots made of metal or other material. The purpose of the operation is to use materials implanted into the bone tissue to fix individual crowns or abutment crowns for bridges. Currently, this operation is at the stage of experimental study and cannot be recommended for use as a therapeutic intervention.
Tooth replantation
- a procedure that represents the return of an extracted tooth to its own alveolar bed.
It is possible only if the tooth does not have an overly branched root. The operation will be more successful if there are teeth adjacent to the replanted tooth. In this case, the use of conduction anesthesia is indicated. The use of local is fraught with vasoconstriction, which prevents the normal filling of the alveolar bed with blood.
Tooth replantation: indications
Indications for dental replantation are the following situations:
- chronic periodontitis, not amenable to conservative treatment methods;
- periodontitis in chronic form, in which resection of the root apex cannot be performed;
- perforation of the tooth root;
- odontogenic periostitis of the jaw in acute form;
- preservation of a healthy accidentally removed (for example, during complex procedures with neighboring teeth affected by disease) or dislocated teeth.
Tooth replantation: stages of surgery
The first stage of the procedure is tooth extraction. It should be carried out as carefully as possible; in no case should hard or soft tissues be damaged.
The extracted tooth is placed in a saline solution of sodium chloride, the temperature of which should correspond to body temperature. The solution also contains antibiotics, usually streptomycin or penicillin.
Then it is necessary to clean the alveoli from granulations characteristic of chronic periodontitis. To do this, use a special sharp spoon. After cleansing, the alveolus should be rinsed with warm saline from the syringe from which the needle has been removed. After this, mechanical and chemical treatment of the replanned tooth begins, and the alveolus is first covered with sterile tampons, however, avoiding dense tamponing. The root canals are cleaned, and then, after wrapping the tooth in sterile gauze soaked in saline solution, they begin filling the roots and crown. In this case, a quick-hardening mass is used, less often cement.
Having done this work, you can begin resection of the root tips. This step is required because the apexes are deltoid branches of the canals. The latter contain necrotic tissue. If you neglect the resection procedure, the likelihood of relapse of periodontitis increases. Such replantation is called devital.
Vital view of dental replantation
There is another type of replantation - vital, which does not involve canal filling. With this operation, the pulp of the tooth is preserved, and the indication for it is the replantation of a healthy tooth, for example, after a dislocation.
After carrying out these procedures, you can place the tooth in the alveolus. This process is fraught with difficulties, especially if the tooth has complex multi-channel branches or the alveolar walls are not mobile. The best effect can be achieved by using wire or styracrylic tires.
If there is an acute inflammatory process in the alveolus, then placing the tooth in it is postponed for 1-2 weeks. The alveolus itself is covered with a bandage soaked in an antibiotic solution. The tooth is stored in a solution of sodium chloride and antibiotics, the temperature of which is 40 degrees.
When replanting an accidentally pulled out or dislocated tooth, it must be cleaned of scraps of gum and periodontal tissue. After placing the tooth in warm milk, you should rush to the doctor. If a tooth is not susceptible to caries and does not have other non-carious pathologies, then there is a high probability that it is ready for replantation. However, the final decision is made by the doctor. Otherwise, the replantation procedure is performed in the same way as replantation for periodontitis.
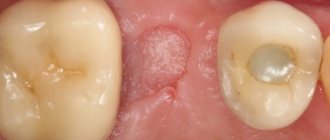
Healing of the tooth takes 3-4 weeks. To ensure rest, the cusps of the replanted tooth or its antagonist can be ground. In the first 5-7 days, a special diet is indicated, including liquid food at room temperature.
The healing process is painful. This syndrome is relieved by taking analgesics.
Even with an impeccably performed operation and strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions in the postoperative period, the average service life of a transplanted tooth is 5 years. Then it will begin to loosen and the question of removal and further prosthetics will arise. However, in some cases replantation is justified.
A tooth whose transplant was caused by dislocation or accidental removal can cope with its functions a little longer, up to 10 years.
Replantation: types of fusions
There are 3 types of fusion of the transplanted tooth:
- periodontal (the most favorable, possible when the alveolar periosteum is preserved in full and part of the periodontium on the roots of the tooth);
- periodontal fibrous (in which there is partial preservation of the alveolar periosteum and periodontium);
- osteoid (the least favorable type, characterized by complete removal of the periosteum and the absence of periodontal particles on the roots).
Recovery period
Important! Proper execution of the operation and strict adherence by the patient to all prescriptions and recommendations of the specialist guarantees a successful outcome of the implantation.
The patient must be observed by a dental surgeon throughout the entire postoperative period. According to his recommendation, the replanted unit should be kept in conditions of absolute rest and be excluded from articulation. To do this, doctors often grind off the cusps of the implanted tooth or antagonist teeth.
Also, all this time it is necessary to take analgesics to relieve pain symptoms and antibiotics (usually from the sulfonamide group). In some cases (usually if replantation was carried out to relieve inflammation), 3-4 sessions of UHF (ultra-high frequency) therapy may be prescribed.
It is very important for a person to change his diet for the first few days - all food taken should be liquid. Spicy, fried, smoked, and salty foods should be completely excluded.
Hygiene procedures should be carried out with caution. It is forbidden:
- press the brush onto the operated area;
- rinse your mouth intensively with any solutions;
- use an irrigator;
- touch and loosen the tooth with your tongue.
On average, the postoperative period (tooth healing) lasts from 4 to 6 weeks. This period is influenced by the type of fusion and the reason why the unit was removed from the alveolus.
How does dental implantation proceed? What are the main stages and deadlines?
Regardless of the technique chosen to restore lost teeth, there are a number of generally accepted steps:
- Preparation:
Sanitation of the oral cavity, hygienic cleaning and thorough diagnostics are carried out. The doctor determines the method of implantation, type of design and placement of implants. - Bone grafting
is not always required. Modern methods make it possible to do without it, making implantation less traumatic, costly and time-consuming. Time frame: bone growth 4-6 months. - Implantation
Involves the insertion of an implant. In the case of the classical technique, a bed is made in the bone where the implant is placed. In case of simultaneous tooth extraction, it is implanted into the tooth socket. If an implant is implanted using the express method into an area of bone where there is no longer a tooth, the doctor makes a puncture with a thin instrument and carefully screws the implant inside. Time frame: procedure - 40-90 minutes, fusion with bone - from 3 to 6 months. - Gum formation
This stage is only necessary for the classic two-stage procedure. Duration: 2-3 weeks. - Temporary prosthetics
With load-bearing prosthetics, a temporary prosthesis is put on immediately after implantation (1-7 days). It allows you to provide a load on the bone for its active blood supply. Blood flow promotes rapid fusion of the implant. Duration: 2 weeks-4 months. In the classical procedure, the prosthesis is removable. Time frame: 3-6 months. - Permanent prosthetics
A temporary prosthesis made of metal-plastic, used for load-bearing temporary prosthetics, can last up to 5 years.
Ideally, as soon as good stabilization of the implant in the bone is achieved, prosthetics can be installed. On the lower jaw after 3 months, on the upper jaw after half a year.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
The main advantages of replantation are the following characteristics:
- preservation and complete restoration of the tooth;
- performing all surgical procedures in one visit to the dentist;
- almost 100% survival rate of the tooth, even if it was outside the mouth for a day;
- return of aesthetics and functionality to the replanted unit for a period of 10 years;
- the manipulation is completely safe for the patient’s general condition, and the likelihood of adverse consequences is reduced to a minimum;
- absence of pain due to high-quality anesthesia.
Disadvantages include the following:
- there is a possibility that the replanted unit will not engraft, when after some time the roots begin to dissolve and the unit itself becomes mobile;
- the entire postoperative period, diet must be combined with treatment with antibiotics and analgesics;
- there are significant restrictions on the operation related to the general condition of the body;
- due to damage to the coronal part, the operation will also be denied.
The most significant drawback, according to patients, is the inability to predict the result of the operation and how the tooth will behave in the future, even if the person strictly followed all the rules and medical prescriptions in the postoperative period.
Story
The first successful replantation is considered to be an operation performed in 1962 by a group of doctors led by Dr. Ronald Malt from the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston (Massachusetts, USA) to restore the hand of a 12-year-old child. In 1963, hand replantation was successfully performed by the Chinese doctor Chen at the 6th Hospital in Shanghai; in 1965, the Japanese Komatsu and Tamai completed the first successful replantation of a finger.
There are indications in the literature that for the first time in medical practice, the operation of replantation of the upper and lower extremities was developed and performed by the Russian surgeon Platon Tikhov[1].
Price
Replantation is not considered an expensive dental service even though this technique is new. The cost of its implementation depends on how many roots there are in the tooth.
Thus, the average cost of implanting a single-root unit is from 800 rubles. up to 1000 rub. A multi-rooted tooth will cost a little more - about 1,400 rubles.
The patient will have to pay separately:
- examination and consultation – from 300 rub. (in many large dental centers this service is free);
- extraction (if necessary for medical reasons) - from 1200 rubles;
- anesthesia - from 1 thousand rubles. (depending on the type of anesthesia and the volume of the drug administered);
- radiography - about 800 rub.
The stated cost of replantation and all additional manipulations is approximate and may vary up or down. The final price can only be found out at the clinic where the operation will take place.
Is there a guarantee for implantation of chewing teeth?
In our clinic, we have achieved 99.5% success with implantation, so the clinic provides a 5-year warranty on all implants installed in the clinic. However, how long the implant will last depends not only on the talent and experience of the doctor, but also on the patient himself. Your new teeth will last for decades if you:
- you will follow all the recommendations of the treating specialist in the postoperative and rehabilitation period;
- you will not overload your new teeth with work unusual for them (gnawing nuts, seeds);
- give up bad habits and, most importantly, smoking, as nicotine impairs microcirculation in tissues;
- You will regularly come for preventive examination, removal and hygienic cleaning of implants and prosthesis.
Come to our clinic for a consultation to learn more about treatment. We are ready to do whatever it takes to help restore the beauty of your smile!
Reviews
Replantation is a new dental technology that allows you to save an avulsed or fallen tooth and completely restore its functionality for a fairly long period.
In most cases, the outcome of the operation is favorable if two conditions are met - if the manipulation itself was carried out in accordance with the protocol, and the patient followed all medical recommendations.
You can share your impressions and experience of replantation by leaving a review in the comments to this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags tooth replantation surgery
Did you like the article? stay tuned
What is dental replantation?
Replantation is a procedure that allows you to restore the dentition after the loss of one or more teeth. The main difference between this operation and standard implantation is that a tooth that has fallen out of the alveolus is returned to its original position.
This method of restoring the dentition helps to keep the bite unchanged - it prevents the movement of neighboring teeth, which deforms the jaw. Most often used to restore front teeth - they have less strong fixation due to the presence of one root. Remember, the operation is performed only when saving the lost tooth - saline solution is used for this.