Editor
Anna Sandalova
Pulmonologist, doctor of the highest category
Mycobacterium tuberculosis can affect not only the bronchi and lungs. It happens that Koch's bacillus infects the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. In this case, oral tuberculosis develops, a rare form of the disease (1% of all cases of infection). It occurs as a result of a decrease in the tension of general and local immunity. Let's consider the causes of development, clinical symptoms, as well as methods of diagnosis and treatment of oral tuberculosis.
Reasons for development
The oral mucosa is not a favorable environment for the activation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Usually, Koch's bacillus dies in the mouth, but if there is damage on the surface of the mucous membrane, the mycobacterium penetrates deep into the tissue, causing the development of ulcers. We are talking about secondary tuberculosis of the oral cavity, since primary tuberculosis of this localization is extremely rare, mainly in children.
In patients with pulmonary tuberculosis, infection of the oral mucosa occurs as a result of the penetration of mycobacteria with sputum. The introduction of pathogenic microorganisms into the mucous membrane is facilitated by a general decrease in immunity, the presence of inflammation, microcracks and other injuries on the mucous membrane.
Oral tuberculosis
Oral tuberculosis is an infectious disease that, like other types of tuberculosis, is caused by mycobacteria. This pathology is classified as chronic.
As a rule, the inflammation characteristic of tuberculosis, affecting the lining of the mouth and the red border around the lips, is secondary: that is, it occurs as a consequence or the most characteristic manifestation of other forms of tuberculosis.
For example, these include tuberculous lesions of the lymph nodes and bones.
The mucous membrane of the oral cavity is far from the most favorable environment for the development and reproduction of mycobacteria that cause tuberculosis. As a rule, when entering this environment, mycobacteria die.
However, in the presence of favorable circumstances (microtraumas, mechanical damage in the oral cavity, opening the gates for infection), bacteria penetrate inside and provoke the formation of a tuberculous ulcer.
Oral tuberculosis is a relatively rare form of tuberculosis, usually diagnosed only in children. This is due to the characteristics of teething in children.
In an infant, such a disease can be extremely severe and includes the generalization of tuberculosis infection. Secondary tuberculosis infection begins to develop as tuberculous lupus or miliary ulcerative tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis is transmitted by airborne droplets. The incubation period lasts from eight to thirty days, and after this the formation of an uneven, blurred ulcer begins, which is severely painful. After a few days it begins to gradually increase. At the same time, the adjacent lymph nodes swell. There are no other signs of inflammation yet
Classification of types of oral tuberculosis
Oral tuberculosis is a disease that appears and develops mainly in patients with reduced immunity. The disease is caused by Koch's bacillus. The source of inflammation located in the patients' oral cavity is secondary in most cases.
It develops as a result of the spread of infection from the main focus, and spreads through the circulatory or lymphatic systems.
In the case when the patient is affected by the pulmonary form of tuberculosis, the infection spreads to the oral cavity due to the penetration of mycobacteria contained in the sputum.
There are four forms of oral tuberculosis. Among them:
- Primary tuberculosis of the oral cavity. Transmitted by the respiratory or fecal-oral route, this disease almost never occurs in adults. Most patients with this diagnosis are infants.
- Tuberculous lupus. It is the lupus form of oral tuberculosis that is most often encountered in dental practice. Erosive elements are localized on the mucous membrane of the gums. If treatment is not started on time, these tumors can develop into a malignant form.
- Miliary-ulcerative form. This form usually develops in patients who have already been weakened by tuberculosis. Along with their cough, they produce sputum, which is a source of bacteria that cause oral tuberculosis. The lesions are on the palate and tongue, in rare cases - in the area of marginal gums or on the side of the cheek.
- Scrofuloderma. This form of the disease is diagnosed in most cases in children. The clinical signs of scrofuloderma are somewhat different from those of other forms of oral tuberculosis. In the first stages - the appearance of not a tubercle, but a rather large nodule. After its softening and necrosis occurs, the stage of formation of fistula tracts begins. The healing process of the surface of the resulting ulcers takes a long time, and after it characteristic fringed scars form.
Treatment of oral tuberculosis
Treatment of this form, like all others, is carried out in specialized institutions - tuberculosis dispensaries. First of all, the underlying disease is treated. To prevent the bacterial infection from spreading further, antiseptic baths are prescribed.
After the acute condition has been relieved, it is necessary to take care of timely and high-quality sanitation of the oral cavity. It is important to promptly consult a specialist at the first symptoms: advanced oral tuberculosis leads to serious consequences for the patient’s health.
Source: https://best-stom.ru/articles/tuberkulez_polosti_rta/
Symptoms and stages
Symptoms of oral tuberculosis vary and depend on the location of the tuberculosis focus and the severity of the disease.
Disease of the mucous membrane
The course of the lupus process goes through several stages:
- The first is infiltrative , characterized by the formation of edema and redness of the tissues. Lupomas (tubercles) are not very pronounced.
- Tubercular stage . The formation of small tubercles is observed, connecting and resembling warty growths.
- Ulcerative stage , but in some cases it may be absent. It is characterized by the transformation of lumps into bleeding ulcers. Papillomas may also appear. A typical place for their localization is the soft and hard palate.
- In the final stage, scarring occurs . If the process of ulceration did not occur, then the scars are shiny and smooth, otherwise deforming dense scars are formed.
Miliary-ulcerative tuberculosis is characterized by the formation of small, multiple, painful nodules on the oral mucosa that quickly ulcerate. This type of disease and its vivid manifestation is observed in most cases in persons suffering from severe forms of tuberculosis of the lungs or larynx.
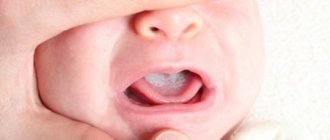
Scrofuloderma, or colliquative tuberculosis, is more common in children. It differs from other forms of oral tuberculosis in that it does not form a tubercle, but a large node in the subcutaneous tissue. The node becomes necrotic and disintegrates; a fistula is formed. You can see what damage to the oral cavity by mycobacteria looks like in the photo below.
Mouth ulcer
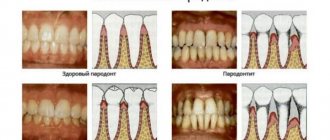
Ulcers can appear in any part of the mouth. If mycobacteria infects the gums, periodontitis quickly develops - inflammation of periodontal tissue, accompanied by destruction of the alveolar process of the jaw. As a result of the pathological process, the gums are unable to hold the teeth.
Disease of the tongue and lips
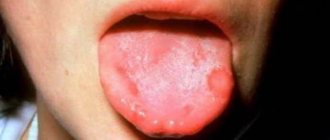
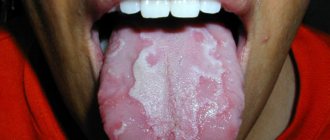
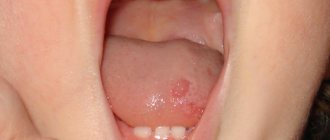
Such localization of mycobacterial infection is a rare occurrence. Occurs in patients with severe pulmonary tuberculosis. Characterized by the formation of painful lesions. Tuberculous ulcers are localized on the side surface, back or at the root of the tongue. They have a round shape or look like a slit with undermined edges, the bottom of which is covered with grayish-yellow granulations. Touching the granulations causes bleeding.
Tuberculous ulcers on the tongue can be either single or multiple; they cause significant discomfort to the patient, causing pain. You can see what tongue tuberculosis looks like in the photo below.
The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- difficulty chewing food;
- change in taste sensations;
- increased salivation;
- speech difficulties, difficulty pronouncing words.
Sometimes tuberculosis lesions are localized only on the red border of the lips. At the same time, it increases in volume due to edema. ulcers and cracks , covered with bloody purulent crusts,
on it
Tongue with tuberculosis photo
Oral tuberculosis is a fairly common pathology that affects the human body. The disease is quite scary, as it develops on the oral mucosa with the help of dangerous mycobacteria.
On the Internet you can find numerous photos of this disease in people of different ages. What kind of disease is this and how does it develop into tuberculosis of the tongue?
Characteristics of the disease
Oral tuberculosis is a pathology manifested by lesions of the mucous membrane located in the mouth. The manifestation of this disease is visible even to the naked eye.
In this case, the disease can occur as a tuberculous ulcer or as tuberculous lupus.
This disease enters the body of a healthy person not only through airborne droplets, but also through the spread of chronic periodontitis.
The hematogenous route facilitates the penetration of the pathogens of this disease - tuberculous mycobacteria - into the body.
Very often, in addition to the oral cavity, the infection also affects the nasal cavity. This is facilitated by the lymphogenous pathway, through which the process of infection of the nasal mucosa occurs.
Being in the mouth of a healthy person, tuberculosis pathogens affect not only the membranes located here, but also spread to:
- pharynx area;
- tongue area;
- surface of the tonsils;
- sky;
- mouth corners;
- gums;
- lips.
Tuberculous ulcers are more common among these infections. Despite this, this pathology is also quite dangerous and can cause a lot of inconvenience to the patient. Oral tuberculosis has several forms of organ damage.
A primary tuberculous ulcer is characterized by spread throughout the corresponding organ due to the presence of minor injuries on it.
It is through such through holes that violate the integrity of the tongue membrane that mycobacteria penetrate the body of a healthy person. In most cases, this pathology develops in the area of the lingual back or sides.
It is not for nothing that these areas are more susceptible to the occurrence of disease, since the greatest friction force is concentrated here.
Usually the disease progresses with the absence of acute inflammation, but with the presence of a small infiltrate at the base. Such a photo can also be found on the pages of medical websites. A peptic ulcer of a tuberculosis nature in the mouth occurs with enlargement of lymph nodes, thereby turning into a huge complex.
Over time, ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane in children and adults greatly deepen with the appearance of suppurating and soft lymph nodes. The results of the Pirquet reaction are positive already after a month has passed from the moment the characteristic element appears.
Clinical picture of the pathology
Tuberculosis disease of the oral mucosa is characterized by the presence of certain symptoms. It is from them that you can understand that something is wrong in the body and you should immediately see your doctor.
The main signs of damage to the oral mucosa are:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- pain in the mouth;
- lymph nodes that are painful to the touch;
- pain when eating;
- discomfort when talking.
Such symptoms are further complemented by the appearance of small ulcers, many of which have scalloped soft edges. Typically, these ulcers on the mucous membrane are pale red in color and may externally resemble small cracks. The cavity of such cracks is filled with a mucopurulent yellowish coating.
If you carefully remove the indicated coating, then in its place a grainy bottom of an uneven shape becomes noticeable. It is not uncommon for this area to bleed profusely.
The emerging ulcers are accompanied by yellow-red tubercles, the so-called “Trill grains”. It is these “grains” that contribute to the spread and deepening of the existing ulcer.
Tuberculosis ulcers that appear on the surface of the mucous membrane of children and adults have a slow healing process.
How is this pathology detected and treated?
Like most tuberculosis pathologies, damage to the oral mucosa is treated. Its character is determined by correct diagnosis and a well-chosen treatment program.
Diagnosis of existing pathology is carried out based on the results obtained from:
- carrying out bacterioscopic studies;
- obtaining information from a cytological examination;
- clinical information.
The sooner a person with such a pathology goes to this medical institution, the greater his chances of getting rid of the disease as quickly as possible.
The histological picture of the disease is characterized by the appearance of a specific granuloma, the central area of which is occupied by typical necrosis.
Along the periphery of necrosis there are infiltrated lymphocytes, as well as a large number of Pirogov-Langhans cells, epithelioid and plasma formations.
Of all this “bouquet”, the most noticeable are the Pirogov-Langhans cells, since they have quite significant sizes.
Source: https://UziMaster.ru/jazyk-pri-tuberkuleze-foto/
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made on the basis of medical history, patient complaints and research results (clinical, cytological, bacterioscopic).
The dentist performs a physical examination. The discovery of small elevations on the surface of the mucosa, resembling tubercles in shape, testifies in favor of tuberculous lesions. Such formations are called lupomas.
On palpation they are painless, have a yellow-red color, and can merge with each other. At the site of their appearance, painful yellow-gray ulcers with ragged edges soon form. The lymph nodes are hard and lumpy, and the patient feels pain when palpating them. In addition, adhesions between the lymph nodes and surrounding tissues are palpated.
If tuberculous lupus is suspected, two additional clinical tests are performed. This is diascopy, in which the so-called “apple jelly” symptom appears: when pressure is applied to the tubercles, they become light brown. Another test is the Pospelov reaction. It is considered positive if, after touching the lupoma with a button probe, its top is destroyed and the tip of the instrument “falls” into it.
Diagnostic examinations include cytology: a scraping is taken from the surface of the formed ulcers. If Langhans giant cells are found in it, then the diagnosis of “oral tuberculosis” is confirmed.
Expert opinion
Anna Sandalova
Pulmonologist, doctor of the highest category
Ask a Question
Bacterioscopic examination shows the presence of Koch bacilli. In tuberculous lupus they may not be detected, but are always present in the miliary-ulcerative form of the disease.
Cytological and bacterioscopic examinations are decisive in making a diagnosis. It is important to differentiate tuberculosis of the oral mucosa from malignant neoplasms, actinomycosis, syphilis, decubital or gummous ulcers, and ulcerative necrotic stomatitis.
Treatment
Treatment of tuberculosis of the oral mucosa is carried out inpatiently, in an anti-tuberculosis dispensary.
Main directions of therapy:
- Local treatment. Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity with preparations based on chlorhexidine.
- Anesthesia. Local agents are used in the form of a spray or gel containing anesthesin or lidocaine.
- Systemic antibacterial drugs. Fluoroquinolones are prescribed, mainly Levofloxacin, Gatifloxacin or Moxifloxacin.
- Chemotherapy (Isoniazid, Streptomycin, Rifampicin, Ethambutol, Pyrazinamide).
- Strengthening the immune system by taking immunomodulators (Levamisole, Timalin, Taktivin).
Local treatment is carried out for ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane and secondary damage by nonspecific microflora. In these cases, aqueous solutions of aniline dyes are used: methylene blue or Fukortsin.
To eliminate the inflammatory process, they are treated with drugs based on 1% metronidazole. To accelerate tissue regeneration, a solution of zinc hyaluronate is used.
For tuberculous lupus, treatment includes physiotherapeutic procedures (ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis, UHF, inductothermy, etc.). Such therapy is aimed at stimulating skin regeneration processes, destroying mycobacteria, and preventing the development of complications.