Features of dental x-rays for children
Previously (about 10-15 years ago), x-rays of baby teeth were not a common procedure. Some parents even believed in the myth that baby teeth have neither a root nor a nerve, so the causes of toothache must lie somewhere on the surface, that is, on the crown. This is absolutely not true, and childhood toothache can be caused by the same reasons as in an adult (more on this below).
When asked whether children undergo dental x-rays, we can confidently answer that yes, they do. Moreover, to accurately diagnose the problem and build the correct treatment plan, this is necessary. Another thing is that preference should be given to relatively safe types of x-ray examination, for example, digital.
There are several recommendations for parents to listen to when going for an x-ray with their child:
- You need to come to the clinic in advance so that you have time to psychologically prepare your child for the procedure. You need to tell him that the x-ray will not cause any pain, so you shouldn’t be afraid of it.
- The child's clothing should be loose, easily removable and without complex metal decorations.
- As for girls, you need to give them a simple hairstyle, without using metal pins, bobby pins, etc.
Are dental x-rays safe for human health?
In accordance with SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03, the maximum permissible annual radiation dose during diagnostic x-ray procedures is 1000 μSv (microsievert) for an adult and 300-400 μSv for a child.
To receive it, within a year you must complete:
- 500 targeted dental examinations using a radiovisiograph;
- 100 procedures of conventional x-rays with image output on film;
- 80 digital or 40 film orthopantomographies (obtaining a panoramic image).
Thus, dental X-rays for almost any purpose do not exceed the permissible doses. Therefore, it does not have a negative effect on health. Even when producing film OPTG, the radiation dose is a maximum of 30 μSv. If it is necessary to take a targeted X-ray of the teeth and use radiovisiography, you can even get several images during one appointment. Without any risk to health, since a single dose in this case is only 2-3 μSv.
Types of X-rays for children
Like adults, children may be prescribed different types of x-rays.
Sight radiograph
A targeted radiograph is performed using a special digital visiograph. A specific problematic tooth or several adjacent ones (maximum 4) are removed.
Panoramic radiograph
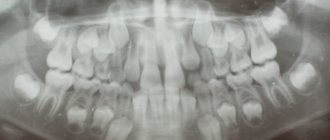
The panoramic image shows the entire oral cavity: the upper and lower dentition, teeth that have not yet erupted, and the jaws. It also affects the sinuses. An orthopantomogram (this is what a panoramic image is called) is often prescribed to young patients when it becomes noticeable that their teeth are erupting incorrectly: with an inclination, rotation, and so on. In this case, X-rays help to understand whether there is an anomaly in the development of the jaw bone. There are cases when, after the loss of baby teeth, permanent teeth do not appear for a long time. An x-ray will help identify the cause of this deviation.
Indications for testing
- To determine the extent of caries damage
Children's teeth are susceptible to caries. We cannot assume that caries of baby teeth is not dangerous, since they will fall out anyway. Pathology can spread to permanent teeth even before they erupt. Therefore, it is very important to identify caries and carry out effective treatment.
- To identify periodontitis and pulpitis
Periodontitis (tooth root pathology, pulpitis) is an inflammation of the pulp where the nerve is located. It is clear that such diseases cannot be detected during the initial examination, because they are hidden in the tooth itself or inside the gums. The child’s main complaint is pain in his baby teeth, and the ability to identify its cause is through an X-ray photo.
- When planning endodontic treatment
Endodontic treatment is a set of procedures aimed at preserving a tooth. When emerging caries causes complications, such as pulpitis or periodontitis, the doctor needs to perform therapeutic manipulations inside the tooth. To understand how much pathology has affected the tooth, what percentage of it is destroyed, you need to take an x-ray.
- To assess the condition of the permanent tooth buds
An assessment of the condition of the permanent tooth buds is also required before endodontic treatment. It is necessary in order to understand whether the permanent teeth have been affected by pathology and how close they have already descended to the milk teeth.
- To diagnose and determine treatment regimens for pathologies of occlusion or teething
At an early age, it is still relatively easy to correct an incorrectly formed bite or correct the position of erupted teeth. This can be done using braces or other special systems. However, to begin orthodontic intervention, you need to understand how serious the pathology is. X-rays help with this.
- To determine the reasons for the delay in the appearance of permanent teeth
If a child does not have baby teeth before one year of age, the doctor may order an X-ray to predict their appearance. Of course, such a developmental pathology as adentia (when there are simply no rudiments of baby teeth) is extremely rare, but it is still worth excluding it completely and understanding how soon the first tooth can appear.
Why is X-ray examination needed in dentistry?
X-ray examination (dental x-ray) is the basis of quality treatment with a good prognosis.
Without high-quality x-ray diagnostics, it is almost impossible to create a competent treatment plan. Our clinics have the best equipment, innovative software, and we use artificial intelligence for accurate diagnostics.
Dental x-rays can reveal:
- inflammatory process inside the tooth;
- presence, size and location of the cyst;
- presence of a tumor;
- quality of dental canal filling;
- how deep is the caries;
- abscess in periodontal elements;
- crack in the tooth;
- the presence of unerupted teeth (including wisdom teeth);
- various anomalies in the structure of bones;
Only after an adequate X-ray examination has been carried out can the doctor make a diagnosis with complete confidence and prescribe the correct treatment.
Dental X-rays are necessary during therapeutic treatment (especially during root canal treatment), prosthetics, implantation, and also before starting orthodontic treatment (bite correction).
In addition, X-ray diagnostics allows the doctor to confirm the effectiveness of the treatment.
How is research conducted?
Panoramic dental x-rays are done for children, just like for adults:
- The child stands inside the orthopantomograph.
- He clamps the plastic tube between his teeth and keeps his lips closed.
- The device blade is moved as close to the patient as possible.
- A picture is taken (while the device rotates around the child’s head). This takes no more than 20-30 seconds, during which you cannot move or breathe.
A targeted photograph is taken as follows: the child sits on a chair and approaches the device. Next, he wraps his mouth around the digital sensor and clenches his teeth. A picture is taken (takes a few seconds); during this process you cannot move or breathe.
To protect the body from exposure to x-rays, a special apron is worn.
Is it harmful to take x-rays?
An X-ray is an invisible electromagnetic wave that has the ability to penetrate any substance. As a result of exposure to radiation, photographic material darkens. Thanks to this effect, the structure of the human body is displayed on photographic film, after which a number of conclusions can be drawn about the state of health of the patient’s internal organs and bones.
Despite the wide range of applications of X-ray radiation in such branches of medicine as traumatology, pulmonology, gastroenterology, etc., this research method has a significant drawback. It has been established that the maximum dose of X-ray radiation allowed for an adult is 150 mSv (millisievert) per year. For a child under 16 years of age, the maximum radiation dose using various methods is no more than 50 mSv, and research is carried out only in emergency cases.
When carrying out standard X-ray examination procedures that must be done annually (in particular, fluorography), an adult patient receives a radiation dose not exceeding 20 mSv.
The main contraindication to x-ray examination is exceeding the safe and recommended by experts radiation dose. The consequences of exposure to electromagnetic rays on the human body can be different: from skin burns (erythema) to infertility, the appearance of tumors and even radiation sickness.
The negative impact of X-ray radiation on the human condition exists, however, if precautions are taken, exposure to electromagnetic radiation during X-ray examinations can be reduced.
Contraindications
- If there is bleeding
Bleeding in the mouth, caused, for example, by problem gums, can affect the quality of the X-ray image. First, the doctor must prescribe hygiene procedures that can stop the bleeding, and only then send for x-rays.
- If you feel unwell
If your child is sick, has a fever, or simply feels unwell, you should not take him for an x-ray. It is better to postpone this procedure until complete recovery.
- In the presence of serious pathologies of the thyroid gland
The thyroid gland is very sensitive to external factors, so dental x-rays are contraindicated for children with pathology of this organ.
Category Children Published by Mister stomatolog
Classification of dental X-ray machines
Here are the main types of x-ray machines:
- Digital devices. Radiovisiographs, which are the most modern and effective diagnostic method, are most often considered digital devices. All radiovisiographs are equipped with extremely highly sensitive sensors, which not only allow you to obtain accurate and informative images, but also significantly reduce radiation exposure, that is, the danger to the human body.
- Film devices. Film is what the radiography method has always been associated with; such devices are usually attributed to the previous outdated generation. The fact is that they take a long time to produce images, and the radiation exposure is relatively high.
- Universal systems. Quite recently, equipment has appeared that can conduct X-rays of both film and digital nature; this can be selected in the device settings. Such systems, unfortunately, are practically not widespread.
Let's take a closer look at the main device options.
A radiovisiograph is a device that allows you to take images of teeth using a special sensor that transmits the image to a computer.
Radiovisiographs
Visiographs are special sensors that convert the rays of an X-ray machine passing through the human body into a digital image. Such equipment is quite large, because you need to install both a personal computer and a high-frequency X-ray machine.
The principle of operation of such a device is similar to many other similar devices, that is, the information is analyzed not on film, everything happens immediately in the sensor, which sends this information to the doctor’s personal computer.
But radiovisiographs can also differ significantly from each other, firstly, in design (you can find not only wired, but also wireless equipment). Wireless options provide for the transfer of information through a scanning device, into which the sensor is placed after the study. As you might guess, in another version of the device everything happens via wire.
In any case, the main advantage of radiovisiographs is considered to be low radiation exposure, associated with the high sensitivity of the already described sensors. Such devices are even allowed to be placed in ordinary premises, next to which there are residential apartments! The fact is that this will not compromise radiation safety.
Unlike other x-ray methods, intraoral x-rays allow you to get a complete picture of a local area of the jaw.
Devices for intraoral radiography
It is also worth mentioning about devices that imply the possibility of intraoral radiography, and not only equipment that is fixed in the office is found. Portable portable devices have also appeared that can be confused with an old camera.
Note! Such devices are characterized by ease of operation and low radiation exposure. Unfortunately, for obvious reasons, the quality of the images in this case will be lower.
Orthopantomography (OPTG) can be digital or film.
Orthopantomographs
The last type of radiography device that needs to be considered is orthopantomographs. Such installations enable the doctor to obtain not only a two-dimensional image of the jaw, but also a full-fledged three-dimensional system that provides complete information about the structural features in the oral cavity. Orthopantomographs are not too expensive, and are also easy to use and functional, so they often become the best choice for most dental clinics.
Important! In any case, the choice of diagnostic procedure and treatment method in the future should be determined only by a qualified and experienced specialist. Don’t even try to self-medicate, because this will definitely not lead to anything good, and time will be lost, which will complicate therapy and can pose a serious danger to health.