February 3, 2018
Agree that anesthesia makes our life much easier. The knees no longer shake at the mere thought of visiting the dentist, because anesthetics can relieve even the most severe pain. Anesthesia in dentistry makes it very comfortable to carry out procedures and manipulations of any complexity, from dental treatment to implantation and surgery. At the same time, the patient’s anxiety decreases and general tension subsides.
Local anesthesia
Modern anesthetics are also safe and do not cause significant harm to the body. But not everyone realizes that anesthesia can also be different. The editors of the UltraSmile.ru portal have prepared an overview of the types of such procedures that are used today in dental practice for tissue anesthesia.
Appliqué
Are you worried that your dentist appointment will be painful? Imagine what it was like for our ancestors. They dulled the feeling of pain with decoctions and infusions of herbs, dope, alcohol and ice. And in Italy, for example, more than 150 types of drugs were used for pain relief. The invention of cocaine brought relief to patients, but it was toxic and naturally addictive. And only in the 19th century novocaine was synthesized.
Application anesthesia is the simplest anesthesia, which does not require injections. Pain relief is carried out superficially using ointments, gels or sprays. But it is not very effective either - in dentistry it is used for oral hygiene, for removing tartar, and for treating gum inflammation.
Application anesthesia
Infiltration
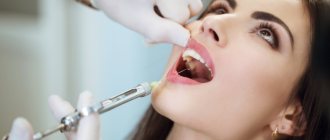
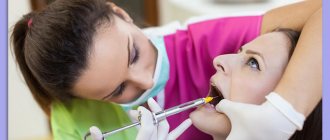
The most familiar method of anesthesia to all of us is what is called “freezing”, since it actually freezes a certain area of the jaw. If necessary, it can be combined with the previous one - superficial, which is carried out in order to numb the injection site.
The drug is injected using a syringe. Active substances begin to block nerve endings so that they do not transmit information about pain to the brain. Modern anesthetics begin to act very quickly - within 5-10 minutes the area begins to numb and a feeling of coldness appears. After the patient ceases to feel the cheek and lip, treatment can be carried out.
Infiltration anesthesia
The duration of such anesthesia is about 1-2 hours. It can be used both in the treatment of caries and during implantation, when cutting frenulums, and periodontal procedures. In general – for any dental procedures.
Classification
At this stage, all local anesthesia in dentistry is divided into two main types - injection and non-injection. Each of them has several separate specific techniques.
What all these methods have in common is that there is no need to inject or inject to achieve results.
- Application method. Also called chemical. Quite often used to relieve pain in the oral mucosa. In this case, the drug is applied or simply rubbed into the desired area.
- Physical. It is used very rarely due to its rather weak, superficial effect. Using this method, the desired area of tissue is frozen by spraying various substances that have a very low boiling point. Quickly evaporating, they cool the tissues, thereby blocking the nerve endings.
- Physico-chemical. The anesthetic is injected into the desired area of tissue using electrophoresis. In most cases, this technique is used for neuralgia.
The methods listed here show better results than pain relief without injections. In addition, the effect of painkillers in this case lasts much longer.
This is why doctors prefer injections for local anesthesia in dentistry.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Golden Crowns in Moscow, where to spend and do it best. Place gold crowns. All dentists in Moscow.
This type of pain relief can be divided into four types depending on the method and specific location of the injection. It is worth describing each of them in more detail.
Intraligamentous (intraglimentary)
There used to be a current joke among doctors that a patient well secured in a chair does not need anesthesia. Today, a trip to the dentist does not make us faint, and an anesthetic injection allows the doctor to better concentrate on his work, without being distracted by the patient’s trembling and tears.
This is the most “childish”, but far from the cheapest anesthesia in the range of dentists. It is injected into the periodontal fissures using injectors (they differ from conventional syringes, they are equipped with needles with different angles of inclination), and there is no numbness of the tongue, cheeks and lips, and the formation of hematomas is excluded. The injection is almost painless, and the effect is achieved within a minute. Dental treatment with this type of anesthesia is possible for children, people with a low pain threshold, pregnant and even lactating women.
Intraligamentous anesthesia
The spectrum of action of this anesthetic is quite wide: it is used in the treatment of pulpitis and all types of caries, in the extraction and restoration of teeth.
Instruments and preparations for carrying out
To achieve the desired result from local anesthesia, it is important to choose not only the drug, but also the instruments with which they will be administered.
Tools
The majority of clinics practice carpule anesthesia. The same methods and preparations are used for them as for other species.
The main difference is that the drug is not contained in ampoules, but in separate bottles. They are inserted into special injector syringes. When the needle is inserted, the capsule is pierced and the drug can be administered.
The advantage of this method is complete guaranteed sterility, since the capsules with the medicine are sealed. As well as a more gentle administration of the drug due to the very small thickness of the needle.
In addition, carpules (that is, capsules) may additionally contain a drug to constrict blood vessels (most often adrenaline) so that the effect of the anesthetic is longer.
However, regular syringes with needles are also used in dentistry. For the most part they are disposable, however, they can also be reusable. The effectiveness of these instruments is less compared to carpule injector syringes. This is due to some design and sizing flaws.
For example, the needle diameter of conventional syringes is about 0.7–0.8 mm. The tissues in the oral cavity are very saturated with blood vessels, and when using such needles, hematomas and other unpleasant complications may occur.
Also, during the procedure for drawing an anesthetic from an ampoule, a violation of sterility may occur, which is unacceptable.
There are several of the most effective and common drugs that are used in dental practice for local anesthesia.
- Ultracaine. Produced by a French company based on articaine. There are three main forms, which differ in the presence and concentration of an additional vasoconstrictor component, epinephrine. The drug is produced with the labels “D”, “DS” and “DS Forte”. In the first case, epinephrine and preservatives are not added to it.
- Ubistezin. An analogue of ultracaine, produced in Germany. It has two release forms with different concentrations of components.
- Septanest. It is a proven and high-quality anesthetic, but it contains a high concentration of preservatives, so there is a high probability of allergies in patients prone to this.
- Skadonest. Produced in France. The drug is based on three percent Mepivacaine. Does not contain preservatives or various vasoconstrictor additives. Suitable for patients at risk.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with how and where wisdom teeth grow from.
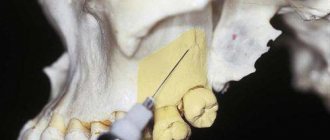
Intraosseous
The injection is made directly into the bone tissue. First, part of the gum is numbed, and then an anesthetic is injected into the deep layers of the jaw bone. Intraosseous anesthesia is used for complex tooth extraction, dental implantation and other surgical procedures.
Intraosseous dental anesthesia
Stem
A special and very serious type of anesthesia, applicable only in a hospital setting, and when very complex and serious operations are required. For example, surgical correction of bite and jaw abnormalities, for injuries and neuralgia. The anesthetic is injected directly into the beginning of the cranial nerve, which is located at the base of the skull. In this way, the sensitivity of the upper and lower jaws is relieved simultaneously.
Anesthesia at the base of the skull
The widespread use of anesthesia allows for a wide variety of treatment procedures. Most patients are happy to undergo local anesthesia to avoid pain and discomfort.
Share your impressions of the use of anesthesia - do you agree to an injection for dental treatment or do you try to endure the unpleasant sensations?
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
anesthesia
Consulting specialist
Gomzin Andrey Sergeevich
Doctor rating: 9.5 out of 10 (4) Specialization: Dentist-therapist, surgeon, orthopedist Experience: 13 years
Epidural anesthesia kits
Set for epidural anesthesia - intended for puncture and subsequent catheterization of the epidural space for the purpose of administering an anesthetic. Prolonged epidural anesthesia creates
complete analgesia in the surgical area, visceral peace and improvement of peripheral circulation, ensures rapid normalization of gas exchange, stabilizes hemodynamics, which sharply reduces the number of postoperative complications. The use of epidural anesthesia makes it possible to maintain effective pain relief in the postoperative period in the most severe patients (urological and obstetric-gynecological operations, operations on the abdominal organs, perineum, chest, lower extremities, etc.)
The kit includes: - Tuohy needle G-16 or G-18, 8 cm long with mandrel , has international color coding and a protective cap, 1 cm markings along the entire working part of the needle, Luer-Lock connector, needle cut direction indicator and plate - a clamp to facilitate the doctor’s tactile sensations. The transparent Tuohy needle pavilion allows for rapid visualization of cerebrospinal fluid during dural injury. — Epidural catheter G-19 or G21, at least 70 cm long, made of radiopaque nylon with a rounded closed end, minimizing the possibility of trauma during insertion. The catheter has: three lateral perforations at the distal end of the catheter, ensuring rapid delivery of the anesthetic with its uniform distribution and
hydroseparation of the epidural space, black clear lines marking the depth of the catheter and a catheter guide to facilitate its insertion into the needle. — Connector for the catheter with a protective cover, allowing it to be securely fixed with a Luer-Lock connector. — Epidural flat filter 0.22 microns, surface 7 cm², providing reliable antibacterial protection with Luer-Lock connector. — Scarifier needle G-16 for puncturing the skin before placement. — Loss of Resistance (LOR) syringe is a three-piece syringe with a sealed piston and a soft, sensitive stroke for clear identification of the epidural space. Volume 5 or 10 ml with Luer-Lock connector. The epidural kit is intended for one-time use for no more than 60 minutes. Non-pyrogenic. Free from heavy metals. Pressure resistance 6 bar. Sterilization: Ethylene oxide (EO). Packaging: individual in the form of a durable tray, packed in a blister with instructions in Russian. 10 pieces in a cardboard box. Shelf life: 5 years.
, India Set for extended epidural anesthesia (with Tuohy needle: G18 / G16 x 80 mm, epidural catheter 1000 mm, flat filter 0.2 µm.) Price:
Set for epidural anesthesia "SURU", India Set for epidural anesthesia "SURU": Tuohy needle G-18 (10 mm long), mandrel, epidural catheter G-21, bacterioviral filter 0.20 micron. , Luer syringe “loss of resistance” -10 ml, Price: 742.00 rub.