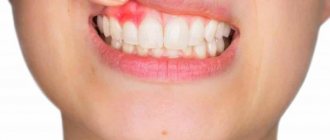
Among the pathological processes in the throat area, a burn of its mucous membrane . Dangerous injury that occurs as a result of inhalation or ingestion of chemicals or hot liquid. In severe cases, burn lesions affect not only the superficial layers of tissue, but also cartilage, muscle tissue, and ligaments. In this case, not only the oral cavity is often affected, but also the larynx, trachea, bronchi and esophagus. Severe pain and disruption of vital functions due to a burn injury require immediate consultation with specialists.
Photo 1. A burn to the throat is a reason to immediately seek medical help. Source: Flickr (Dumleedoo)
Causes and symptoms
Depending on the cause, a throat burn can be thermal or chemical.
Quite often, the cause of a burn is the improper use of medications when lubricating inflamed tonsils or sore throat. A highly concentrated product injures tissues. Burns to the throat can be caused by chemicals: iodine, alcohol, toxic steam, alkali, Lugol, concentrated acid. Throat injury is usually associated with ingestion or inhalation of these substances.
A burn to the mucous membrane of the throat can be caused by: consumption of hot food and drinks, boiling water, etc. This is usually observed in young children when their parents were unable to inspect them. Thermal burns, unlike chemical burns, are easier. This is due to short-term exposure to hot substances on the mucous membrane and neutralization with cool water.
The following symptoms may indicate that a burn has occurred to the mucous membrane of the throat:
Severe burning sensation Pain when swallowing Increased temperature Increased salivation Nausea
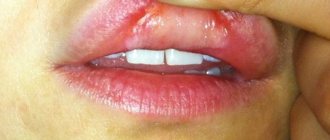
If the trachea and larynx are injured during a burn, a cough appears, the voice disappears, and there is a lack of oxygen. The throat cannot be burned on its own; usually the oral cavity is involved in the process. The mucous membrane is swollen and red, blisters appear, and the lymph nodes become enlarged. In severe cases, traumatic shock and respiratory arrest may develop.
Degree of burn to the throat mucosa
Burns of II-III degree are a threat to life!
Depending on the severity and damage to the mucous membrane, there are 4 degrees of burn:
1st degree. The surface epithelium is affected. Whitened areas appear on the mucous membrane, which begin to separate after a few days. The patient experiences a burning sensation and pain in the throat. 2nd degree. It is characterized by the formation of blisters on the mucous membrane, which burst over time. In place of the burst blisters, wounds appear. Scars can be observed on the surface, which are a consequence of wound healing. The pain syndrome intensifies and is accompanied by signs of intoxication. 3rd degree. The most severe burn of the throat mucosa. It is characterized by severe signs of intoxication and purulent sputum, which appears against the background of the death of inflamed tissues. In place of the scab, deep ulcers form, which after healing leave a scar. The process of swallowing with a 3rd degree burn of the mucous membrane is disrupted. In addition, the victim experiences acute pain, which can only be eliminated with painkillers. There are 4th degree burns of the throat mucosa. It occurs in rare cases and is not compatible with life. The fourth degree is characterized by damage not only to the mucous membrane of the throat, but also to the larynx and esophagus. The nerve endings are damaged and breathing stops.
For a local burn of the throat mucosa, no special treatment is required. Recovery of the affected area will take place within a week, so discomfort will continue to be felt for some time.
For more serious second and third degree injuries, specialist help is needed.
A chemical burn is very dangerous and can cause a lot of trouble, and treatment can take a long time. You will need to contact a specialist if there is damage to the throat of the trachea and bronchi. The patient develops a cough, changes in voice timbre and feels short of air. It is imperative to consult a doctor if the burn was caused by chemicals.
Symptoms of a throat burn
The severity of symptoms depends on the severity of the pathological process and the involvement of other gastrointestinal organs. Usually the victim tries to spit out the swallowed liquid; this prevents damage to the esophagus and stomach, but causes additional damage to the mucous membrane of the mouth, lips, and tongue. Because of this, a dense scab is formed on them, the color of which depends on the properties of the etiological factor. In case of thermal and chemical burns caused by acetic acid and alkalis, the scab is white, with nitric acid - yellow, with sulfuric or hydrochloric acid - black or dark brown.
The main complaint of the patient with any etiopathogenetic variant of a burn of the pharynx is pain of a burning and/or stabbing nature in the upper third of the neck, sometimes radiating to the lower part of the neck. In the combined form, pain also occurs behind the sternum and in the epigastrium, often combined with vomiting, which in the II-III degree of damage has the appearance of “coffee grounds”. There is increased salivation, cough, and taste disturbance. Another characteristic symptom is difficulty swallowing. In grade I, only solid food is affected; in grade II, solid food does not pass at all, and liquid food is accompanied by severe pain. III degree is manifested by the inability to swallow even liquids. Severe burns are accompanied by severe intoxication syndrome - an increase in body temperature to 39.0-40.0 °C, chills, dizziness, general malaise and weakness.
Drug treatment
Treatment of the throat mucosa depends on the cause and degree of the burn!
Depending on the degree of damage to the mucous membrane of the throat, treatment will be prescribed. For 1st degree burns, treatment can be carried out at home, but for 2nd and 3rd degree burns it must be carried out in a hospital setting.
It is important to provide timely assistance to the patient:
In case of a thermal burn, the patient should be given still water to drink. Ice cubes are allowed. In case of a chemical burn, the agent that caused the damage to the mucous membrane should be neutralized. If the burn is caused by acid, then you need to gargle with a baking soda solution. In case of an alkaline burn, rinse is carried out with a not very concentrated solution of citric or acetic acid. After this, the victim should rinse his stomach, because the possibility of getting a burn to the esophagus and stomach is not excluded. Next, drink a tablespoon of vegetable oil and consult a doctor. At the clinic, the doctor will provide the necessary medical care. If necessary, Analgin, Lidocaine, etc., as well as narcotic analgesics in the form of Promedol, Fentanyl, Naltrexone, etc., can be prescribed to reduce pain. The use of sedatives is recommended: Valoserdin, Relanium, Afobazol, etc. These drugs are used if the victim is in shock and has psychological disorders due to the trauma. If the burn is deep, then detoxification therapy is carried out: Ringer's solution, glucose-saline solution, etc. To avoid secondary infection, antibiotics and sulfonamides are prescribed. Among antibacterial drugs, it is advisable to use fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and cephalosporins. They are prescribed for accompanying symptoms: fever, vomiting and nausea, etc. Glucocorticosteroids are used to relieve swelling: Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, etc. The throat must be gargled with antiseptic solutions: Miramistin, Anestezin, Tantum Verde, etc. To accelerate epithelization and tissue regeneration, Solcoseryl, Retinol, Aevit, Methyluracil, etc. are prescribed. If necessary, inhalations of drugs and herbal remedies are carried out.
Treatment of 2-3 degree burns should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, as the specialist prescribes drugs in a certain dosage.
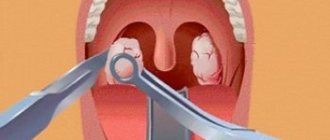
In more severe cases, surgical intervention is indicated for throat burns. The operation is performed for ulcers, scars and serious deformities.
During treatment, the patient should switch to a gentle diet.
It is recommended to eat soft, pureed food warm. In addition, you should exclude foods that irritate the inflamed mucous membrane. The victim should reduce conversations to a minimum to avoid painful sensations
Traditional methods of treatment
Gargling is first aid for mucous membrane burns!
For first-degree burns, you can use traditional methods:
To stimulate the restoration of the throat mucosa, oils and herbal decoctions are used. Oils used include sea buckthorn, peach, and olive. Soak a cotton swab in oil and lubricate the damaged mucous membrane several times a day. These oils have a soothing and regenerating effect, which allows you to restore the mucous membrane in a short time. It is necessary to regularly rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile, yarrow, and oak bark. You need to take a tablespoon of raw material and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Leave to infuse in a thermos. You need to rinse your mouth with a solution at room temperature. To speed up wound healing, it is useful to use a decoction of oak bark. However, before use, you should definitely consult your doctor, as this remedy may reduce the effectiveness of the medications. For burns, you can use beaten eggs to lubricate the throat.
A throat burn in children cannot be treated using alternative medicine, as this can lead to an allergic reaction, swelling of the mucous membrane and, as a result, suffocation.
Further treatment
Treatment at home. Treatment of such ailments in a mild form can be carried out at home, since there is no threat to the life and health of the victim, and the treatment is not complicated.
1st and 2nd degree burn injuries to the throat are not very dangerous and can be easily treated at home. It can be treated both with the use of medications and by resorting to folk remedies. Typically, rosehip oil is used, and when gargling, soothing, healing herbs are used. But still, before treating a burn in the throat, it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor.
Means for treating a burn of the larynx with boiling water.
In this case, drugs of the following types are used: almagel, phosphalugel, de-nol, rennie, methyluracil, motilium, gaviscon, vitamins A and E, lanza and nolpaza.
All these drugs are available, but consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Hospital treatment. The most dangerous injuries of this type are classified as third degree and are treated only under the close supervision of doctors and only in a hospital.
A laryngeal burn is damage to the walls of the larynx caused by inhalation of hot or caustic gases or suspended substances. This pathology is most often combined with burns of the lips, oral cavity, pharynx and esophagus.
Amphetamine often causes damage to the nasal mucosa. If the effect of the causative factor is too strong, the mucous membrane of the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles is also damaged. In this case, they speak of a combination of burns of the upper and lower respiratory tract.
Throat burn: what not to do
Important! Incorrect treatment can cause more serious consequences
Improper treatment can delay the recovery of the mucous membrane and the risk of infection increases. Victims must follow all doctor's instructions so as not to worsen the situation.
It is not recommended to eat hot foods or drink hot drinks. This is very irritating to the throat. It is prohibited to consume solid foods and alcoholic beverages. You should stop smoking, talk loudly, etc.
By following these measures, you can restore the mucous membrane of the throat after a burn in a short time. Mild burns heal quickly, as the mucous membrane can regenerate well.
If you do not provide timely assistance for second- and third-degree throat burns, this can lead to serious consequences.
Severe consequences of injury are:
Formation of large scars on the pharynx, larynx and esophagus Shock Collapse Asphyxia Respiratory arrest due to nerve damage
The resulting scars lead to dysfunction of the larynx, pharynx, and esophagus, but in more severe cases, the function may be completely lost.
Useful video: what to do if your throat is burned with boiling water
A large number of injuries typically occur in the home, so it is important to reduce the risk of injury. If there are small children in the family, then you should not leave warm drinks and food within reach. Before feeding your baby, you should taste the food if it has been heated in the microwave. A restless child should be constantly monitored and cautionary conversations should be held. When working with chemicals, be sure to use a protective mask. They should only be stored out of the reach of children.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Share with your friends! Be healthy!
A throat burn is an injury to the mucous membrane of the throat caused by the destructive effects of chemical or thermal factors. The main cause of the pathology is simple carelessness. Burns occur accidentally in domestic or industrial conditions, as well as intentionally - during a suicide attempt. Industrial burns occur when inhaling vapors of chemical compounds while working without personal protective equipment, for example, without a respirator. Children are most susceptible to throat burns as a result of insufficient control over them, but they often occur in adults.
A burn of the larynx is a lesion of the epithelium, and in severe cases of deep-lying tissues: muscles, ligaments, cartilage. The consequences of such pathologies are very dangerous for humans.
Chemical or thermal damage to the larynx causes immediate pain and requires immediate medical attention and adequate correction.
Minor burns may not be treated, since the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract has the ability to quickly repair itself. Severe injuries can lead to disability and even death.
Depending on the type of etiopathogenetic factor involved, throat burns are classified into chemical and thermal. Symptoms and methods of providing first aid for these ailments are somewhat different.
Throat burn: how to treat it at home
A throat burn is a serious injury that can be either chemical or thermal in nature. What symptoms are observed in the victim and how to treat the burn?
Description and causes of injury
A laryngeal burn is damage to the mucous membranes that occurs as a result of exposure to high temperatures or aggressive chemicals.
This injury is quite widespread in everyday life, because a burn to the pharynx can be caused by consuming hot food and drinks. Damage from alcohol or acetic acid, Lugol, iodine, caustic alkalis, and concentrated steam is often found.
Experts consider a chemical burn to the throat to be the most difficult in terms of treatment and further recovery. Even a visit to the dentist can provoke injury, for example, if arsenic or other potent drugs come into contact with the mucous membranes of the larynx.
Young children are also susceptible to this type of damage and, due to their curiosity, may well try household chemicals. According to the international classification, burn injuries to the throat are divided by specialists into 3 degrees:
- The first degree is characterized by redness of the larynx and swelling of the mucous membranes.
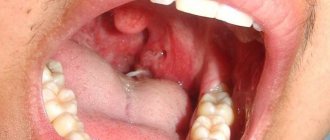
- The second degree - manifests itself with specific blisters and the formation of gray films on a red and swollen throat.
- Third degree - manifested by necrosis of the affected tissues. Muscle tissue, ligaments and cartilage tissue are affected.
Lesions of the larynx of the second and third degrees require competent and timely assistance to the victim. Otherwise, extremely serious consequences are possible in the form of an attack of suffocation, poisoning, scarring and even the death of the patient!
How does it manifest?
Doctors identify the following clinical symptoms that appear in a victim with a throat burn:
- Sharp pain in the throat, with a tendency to intensify when trying to swallow;
- Intense salivation;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Cough syndrome;
- Pain localized in the chest area;
- Voice changes;
- Feeling of lack of air;
- Swelling of the cervical lymph nodes;
- A strong burning sensation in the palate;
- Hiccups.
In severe cases, a state of shock may develop. Even minor injuries can cause respiratory problems and cause suffocation, especially when it comes to a child or an elderly person.
Therefore, having identified the first symptoms characteristic of this injury, you should urgently provide first aid to the victim, then take him to a medical facility and transfer him to the hands of professionals.
Possible consequences
With this injury, patients are highly likely to develop complications and adverse consequences, which include:
- Chemical intoxication, poisoning;
- Collapse;
- Reflex cessation of breathing associated with damage to nerve endings;
- Scarring of the larynx, pharynx and esophagus area.
Pre-hospital care measures
What to do if the larynx is burned? First of all, it is recommended to give the victim a drink of cold water, which will alleviate the general condition, relieve pain and swelling, but most importantly, prevent further spread of the burn into the depths of the tissue.
In this case, you need to drink water in small sips, holding it in the throat and mouth. A good effect is obtained by sucking crushed ice or rinsing the larynx with cool antiseptic solutions. In case of a chemical burn, it is necessary to neutralize the effect of the provoking factor. For these purposes, you need to examine the victim’s larynx.
With an alkaline lesion, a dry scab will be noticeable on the mucous membranes. In this situation, a weak solution of acetic or citric acid is used. If a jelly-like scab forms in the throat, then we are talking about exposure to acids, and the patient needs a soda solution to neutralize it.
After providing first aid and alleviating acute symptoms, you need to give the victim a gastric lavage, give him a glass of milk and a little sunflower oil, and then be sure to contact a specialist who will prescribe further treatment!
A burn of the mucous membrane of the throat of the first degree and sometimes the second is treated at home; in more severe cases, the victim is hospitalized. Successful treatment and recovery requires compliance with the following medical recommendations:
- Silence. The patient should talk as little as possible and avoid raising his voice.
- Rinse with chamomile decoction and antiseptic solutions.
- Abstinence from spicy, sour, hard salty foods.
- Following a diet with a predominance of liquid and puree foods. The patient's menu should include broth, sour cream, cheese, eggs.
For burn lesions of the throat, treatment involves mandatory drug therapy. A qualified specialist will advise you individually on how to treat a lesion in a particular case. Patients are usually prescribed analgesic and antibacterial drugs, and glucocorticosteroids are used to reduce swelling.
The mucous membranes of the larynx in the affected area are regularly treated with antiseptic and oil products - such procedures give a very good therapeutic effect! The surface of the larynx can also be lubricated with Vaseline, beaten chicken egg, using a sterile cotton swab.
Among the most common traditional medicines used to combat this disease are the use of peach, olive, sea buckthorn and rosehip oils.
These products can be used for oil inhalations and external treatment of burned areas.
Home treatment for thermal burns may include oil inhalations, sucking ice cubes, applying cold neck compresses, rinsing with sage and chamomile infusions.
Proper recovery also requires certain diet therapy. Products such as egg whites, vegetable and butter, cool drinks, and cream contribute to the speedy rehabilitation of the patient. For medicinal purposes, the oil is consumed in its pure form, 4 times a day.
Health care
Serious chemical burns are usually treated in a clinical setting, under the supervision of specialists. Often victims are completely unable to eat, so nutrient solutions are administered to them using droppers. The therapeutic course includes the use of strong painkillers, sedatives and antihistamines.
In order to prevent the development of infectious complications, a course of antibiotic therapy is expected. In particularly severe clinical cases, patients are administered intravenously Hemodez, glucose solutions, which eliminate signs of general intoxication of the body and alleviate the condition of the victim.
If scars form and laryngeal stenosis occurs, the patient requires surgical intervention.
A throat burn is an injury that requires careful attention and mandatory referral to specialists. Treatment includes taking medications, diet therapy, rinsing, inhalation, and external treatment of the affected areas.
Timely first aid and competent, comprehensive therapy will help avoid the development of adverse consequences and achieve full recovery. Depending on the severity of the burn, the rehabilitation process takes from 2 weeks to six months.
Source: https://lechimtravmy.ru/ozhogi/ozhog-gorla
Etiology
The causes of burns to the throat mucosa are divided into two large groups: chemical and thermal.
Chemical burns to the throat are a serious problem, the main cause of which in domestic conditions is alcohol or certain medications. Treatment of tonsillitis with iodine solution or alcohol tinctures can lead to a chemical burn of the throat mucosa. Iodine is an aggressive chemical that can cause serious tissue burns. "Lugol", "Yox" - medicines prepared on the basis of iodine. The use of these drugs in the presence of severe pharyngitis or tonsillitis can result in a burn of the mucous membrane. Specific substances that cause chemical burns include: citric acid, vinegar, ammonia, soda, acetone, acids and alkalis, ethyl alcohol. A burn of the larynx, accompanied by pain and burning, can be caused by the reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus during gastritis with high acidity. Acids cause coagulation of muscle proteins and the formation of a dry scab, which is an obstacle to further penetration of the chemical. Alkalis have a more aggressive effect on the laryngeal mucosa. They dissolve proteins. In this case, wet necrosis develops, allowing chemicals to penetrate inside. Thermal burn of the larynx occurs when consuming hot food and boiling water, as well as when inhaling hot air, for example, during fires. Many burn blisters appear on the oral mucosa. At the same time, the victim develops vision problems, general health worsens, and the functioning of internal organs is disrupted. This is a milder form of pathology compared to chemical damage to the laryngeal mucosa, which is associated with short-term exposure to hot substances and their rapid neutralization with cool water.
Causes
A chemical throat burn is caused by exposure to harmful or concentrated chemicals. It is possible in production and at home. Neglect of safety precautions often leads to work-related injuries. For example, this is working with chemical compounds without a respirator or protective mask, maintaining a conversation in an atmosphere saturated with hazardous substances.
In everyday life, a mistake leads to a burn. A person can simply confuse the bottle or vial and drink the technical liquid. A throat injury can occur as a result of drinking low-quality alcoholic beverages or homemade mixtures that replace alcohol.
Another reason is excessive zeal in treatment. The following situations are possible:
- gargling with a solution of soda and iodine in a very high concentration;
- increased lubrication of wounds and ulcers with iodine and iodine-containing preparations;
- exposure to alcohol or alcohol tinctures on the mucous membrane;
- prolonged or frequent inhalation;
- excessive consumption of vinegar and hot spices.
A thermal burn is the result of exposure to elevated temperatures. Sometimes it is caused by hot air or steam, but more often by hot food and drink. Unlike chemical damage, it immediately manifests itself as excruciating pain. Thanks to this, first aid is provided faster and the consequences are less severe.
Children often suffer from thermal burns. They lack the experience to correctly determine the temperature of food or drink. They have more sensitive mucous membranes and feel pain more strongly.
IMPORTANT: For burns, self-medication is unacceptable.
The degree of damage is determined by a doctor from the ambulance team; if necessary, he refers the victim to the hospital.
Symptoms
A burn to the throat is manifested by intense and excruciating pain when swallowing, burning and painful sensations in the nasopharynx, profuse salivation, dyspeptic disorders, fever, swelling and redness of the mucous membrane, the appearance of blisters and areas of whitening on it, enlarged and painful lymph nodes, changes in the timbre of the voice, cough , shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat.
Burn injuries often spread from the larynx to the lower parts of the respiratory system: the trachea and bronchi. At the same time, the general condition of the patients worsens significantly. Trauma to the esophagus is manifested by excruciating pain in the chest and epigastrium, prolonged hiccups, belching and heartburn. Simultaneous irritation of a large number of nerve endings leads to serious consequences - reflex cessation of breathing. In cases of severe burns, toxic shock occurs.
A local burn of the pharynx is manifested by internal discomfort and goes away on its own within a week. More serious injuries require consultation with a doctor and comprehensive treatment.
Thermal burn of the larynx occurs when drinking hot liquid, food or inhaling hot air. A burn from boiling water cannot be isolated. It usually spreads to the mucous membrane of the mouth, esophagus, and trachea. The symptoms of the pathology develop rapidly and cause a lot of trouble. The victim experiences sharp and excruciating pain, hypersalivation, reflex vomiting and other characteristic clinical signs. Chemical burns are less common than thermal burns, but are much more severe and less treatable. Throat burns from various chemicals are very dangerous for humans. Clinically, they manifest themselves with the same symptoms as thermal ones. When a chemical enters the respiratory tract, dysphagia and dysphonia occur, and respiratory functions are disrupted.
Based on the severity and severity of tissue damage, there are three types of throat burns:
A 1st degree burn is characterized by damage to the surface epithelium, on which whitened areas appear, and after 2-3 days they begin to separate. Patients feel a burning sensation and slight pain in the throat. A 2nd degree burn is characterized by more serious tissue damage and the formation of blisters with gray films on the mucosa. By the end of the second week, the plaque separates, the blisters burst, and erosions appear in their place - sores. They heal with the formation of small superficial scars that do not cause organ dysfunction. Intoxication is added to the pain syndrome. A 3rd degree burn is manifested by severe intoxication of the body and copious purulent sputum caused by the death of inflamed tissue. Scabs appear on the mucous membrane, which over time are rejected to form large and deep bleeding ulcers. After they heal, a scar remains, disrupting the swallowing process.
Second- and third-degree burns to the throat are dangerous injuries. In the absence of timely medical care, the victim may die due to suffocation or intoxication.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of a burn to the larynx largely depend on the cause of the injury, the degree of damage, the location of the pathological process and the general condition of the body.
Immediately after a burn injury to the larynx, a person may have the following complaints:
- unbearable, excruciating pain when swallowing;
- constant burning in the pharynx and pharynx, intensifying with inhalation;
- salivation;
- nausea, profuse vomiting;
- a sharp increase in body temperature to 38-38.5 degrees;
- swelling of the tissues of the pharynx and larynx;
- changes in voice, which becomes hoarse, muffled;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes;
- in case of a burn with a chemical substance – a characteristic chemical odor from the mouth;
- in severe cases - suffocation, bleeding, a sharp drop in blood pressure, shock, collapse, depression of consciousness, coma.
There are 3 degrees of burn reaction:
- The first degree is a superficial burn, there is no general reaction of the body. Tissue damage appears as uneven white and red swollen areas of the laryngeal mucosa. 2-3 days after the injury, they begin to be rejected, exposing the damaged pinkish-red mucosa, which is then covered with healthy cells.
- The second degree is a deeper damage, characterized by damage not only to the mucous, but also to the submucosal layers. Upon examination, the burn looks like redness and swelling of the laryngeal wall with areas of mucosal rejection, a white-gray coating and blisters.
Symptoms of intoxication are pronounced (fever, weakness, drowsiness, lack of appetite). After a few days, the damaged tissue peels off, revealing erosions and ulcers. With proper treatment, after 1-2 weeks they heal almost without scars.
- The third degree is a serious burn, during which necrosis (death) of the deep layers of the laryngeal wall occurs with the formation of ulcers and granulations. Symptoms of intoxication are very pronounced, the patient requires hospital treatment. During the healing of erosions, bleeding often occurs.
Isolated 1st and even 2nd degree burns of the larynx in adults do not pose a serious threat to health. The only thing that brings discomfort is severe pain when swallowing, which with proper treatment goes away after 4-5 days. Extensive and deep burn injuries to the respiratory and digestive systems are much more dangerous.
Urgent Care
The prognosis of the disease depends on the quality and speed of emergency care. First, it is necessary to establish the damage factor by inspecting the scene of the incident and interviewing witnesses. Then they move on to inspecting the affected area. With acid burns, there is a dry scab on the mucous membrane, and with alkaline burns, there is a wet, jelly-like scab.
First aid for thermal burns involves drinking cool water, crushed ice, or gargling with anesthetic solutions . Cold water will stop the burn from spreading into the tissue. You need to drink it in small sips, holding the water longer near the damaged area. Pieces of ice must be dissolved in the mouth. To reduce pain, you can take a solution of novocaine or lidocaine. In case of a chemical burn, first aid is aimed at neutralizing acids and alkalis that have entered the body. For acid burns, use a solution of soda, and for alkaline burns, use a solution of citric or acetic acid. The patient should rinse the stomach, give a glass of milk and a little vegetable oil, and then call an ambulance.
To alleviate the patient’s condition, it is necessary to provide an influx of fresh air, maintain a silent regime, and exclude from the diet foods that irritate the affected mucous membrane and interfere with regeneration.
First aid
The first thing to do is to determine what exactly the child (or adult) burned his throat with. Look around the room, try to identify the product by smell. If the damage is thermal, you should immediately give cold water (you can use ice cubes).
The next action is to induce vomiting. But this is not always effective and even dangerous.
If acid gets into the larynx, rinse the stomach with soda. You need 2 grams per liter of water. If alkali is to blame, rinse your throat and stomach with citric acid (weak solution). If potassium permanganate is to blame, you need to drink vitamin C. These measures must be taken within the first two hours. Next you need to give warm milk (0.5 l) and butter. If there is a burn, give alcoholic water in small sips.
Treatment
It is necessary to treat 2nd and 3rd degree throat burns in a hospital setting. First degree burns are treated at home under medical supervision.
In the hospital, patients are prescribed the following groups of drugs:
Painkillers - “Lidocaine”, “Trimecaine”, “Analgin”, painkillers pastes, narcotic analgesics “Fentanyl”, “Naltrexone”, “Promedol”. Sedatives - Relanium, Persen, Valoserdin, Afobazol. Detoxification therapy is carried out for deep burns - intravenous administration of glucose-saline solutions, Ringer's solution, Lasix. Broad-spectrum antibiotics and sulfonamides are used to prevent secondary infection. Typically, patients are prescribed drugs from the group of fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and the latest generation cephalosporins. Glucocorticosteroids to reduce swelling and relieve shock - Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone. Antiseptic solutions for rinsing - “Anestezin”, “Miramistin”, “Tantum Verde”, “Aqualor”. Antihistamines - Diphenhydramine, Calcium Chloride, Suprastin. Drugs that accelerate epithelization and tissue regeneration - “Aaevit”, “Retinol”, “Aekol”, “Solcoseryl”, “Methyluracil”.
Experts transfer patients with a burn to the larynx to a gentle diet and recommend eating only soft, cool food in pureed form.
To treat first-degree burns, traditional medicine, topical medications, and physiotherapeutic procedures are used:
Gargling with decoctions of medicinal herbs, Cold compresses on the neck, Irrigation of affected tissues with peach or rosehip oil, Oil inhalations, Lubricating a sore throat with olive or sea buckthorn oil.
In severe cases, surgical methods are used to treat burns. Operations are performed when scars, ulcers, or serious deformities form, which lead to dysfunction of the affected organ.
Treatment of local burns gives a good result: the mucous membrane quickly regenerates. With 2nd and 3rd degree burns, tragic consequences may develop that can lead to disability and death of the victim.
Popular remedies for treating a burn of the larynx with boiling water
In case of a burn to the throat with boiling water, therapy with medications is prescribed, which are also suitable for home treatment:
Alginates are antacid drugs that protect the mucous membranes by forming a film on them, stimulating the formation of prostaglandin to produce protective mucus:
- almagel;
- Maalox;
- de-nol;
- gaviscon;
- Rennie;
- phosphalugel;
Metabolism and regeneration accelerators:
- motilium;
- domperidone;
- methyluracil;
- vitamins A, E;
Reducers of acidity levels in the stomach:
- nolpaza;
- Lanza.
Despite the availability of all the listed medications in pharmacies, if the larynx and adjacent organs are burned with boiling water, the victim needs immediate hospitalization - to save his life and prevent serious health consequences.
Source: BezTravmy.ru
Prevention
It is known that burn diseases of the larynx are usually the result of simple carelessness. To prevent this, you need to pay a lot of attention to preventive measures, be vigilant and extremely attentive.
Small children should not be left unattended. Before giving your baby a bottle of formula, try it. Do not leave hot drinks, household chemicals and other chemicals within reach. Hazardous substances should be stored in specially designated areas out of the reach of children. People who are interested in alternative medicine can use prescriptions only after consultation with a specialist. It is necessary to follow safety precautions and know the rules of first aid.
A throat burn is a traumatic injury to the mucous membrane of the larynx. Depending on the cause of the injury, thermal and chemical burns of the throat are distinguished. This type of injury is more common in children, but can also occur in adults. Often such a burn is accompanied by damage to the oral cavity and esophagus, and in some cases to the trachea and bronchi. Damage can spread deeper and affect cartilage, muscle tissue, and ligaments. Thermal burn occurs when swallowing hot food or drinks, inhaling steam, chemical burn - can be caused by alcohol, iodine, acids and alkalis.
Treatment for the injury depends on the type of injury. It is important to provide timely qualified first aid. A throat burn can be treated with folk remedies that have a healing effect on the mucous membrane and promote rapid tissue restoration.
Causes of injury Degrees of burn Symptoms of pathology Burn treatment First aid Traditional treatment Diet Prognosis and prevention
Types of burns
The mucous epithelium is the most sensitive tissue in the body. That is why it is vulnerable to factors that may be indifferent to the skin. A burn of the larynx is damage to the mucous membranes by harmful substances in a gaseous or liquid state.
Depending on the damaging factor, thermal and chemical burns are distinguished. Not only the throat is affected, but also the larynx, trachea and bronchi. The injury is combined with damage to the lips and esophagus.
The severity of the course depends on the depth of the damage and the extent of the burn. Exposure to harmful substances can impair a person's ability to speak and swallow.
Thermal burn
In everyday life, a throat injury can occur due to a careless sip of hot food or tea. This often happens to children when their parents neglect them.
Important! Throat injury can occur when treated with herbal inhalations. Burns occur when victims inhale hot air during a fire.
Depending on the duration of exposure to temperature, the airways or esophagus are damaged to varying degrees of severity. In mild cases, there is redness of the walls or blisters in the throat. Thermal damage occurs more easily due to the short duration of exposure to temperature.
Chemical burn to the throat
In everyday life, this problem occurs when drinking strong alcoholic beverages. Alcohol burns to the throat and esophagus occur when a strong drink is used internally. Alcohol 70–96° is a chemically active substance.
After its consumption, a white coating of dead tissue forms on the mucous membranes of the esophagus, which in appearance resembles egg white. No special treatment is required to restore the mucosa. Over the course of a week, the tissues spontaneously regenerate.
Burns of the pharynx and esophagus occur when exposed to damaging substances - acetic or inorganic acid, caustic soda, battery fluid, and various adhesives. Such injuries are combined with a burn to the stomach.
Attention! Toxic liquids and their vapors, even in minute quantities, corrode the mucous membranes. Poisoning is manifested by spasm and stenosis of the esophagus. When the substance is absorbed, shock or collapse develops.
Toxic manifestations are especially pronounced when exposed to acetic acid. Dissolution of blood cells occurs, damage to the liver and kidneys.
Chemical burns to the larynx can occur if lubricants or gargles are used incorrectly. Treatment of inflamed tonsils with alcohol tinctures or iodine leads to a burn of the throat epithelium.
Medicines created on their basis often damage the walls of the pharynx and tonsils.
Such drugs include Lugol's or Yox's solution. Iodine itself is an aggressive substance. The epithelium affected by the inflammatory process during pharyngitis or sore throat becomes even more sensitive. After lubrication, a burn of the mucous membranes occurs.
Causes of injury
The causes of damage to the mucous membrane may be different. A burn to the larynx occurs in adults at home and at work due to negligence, an accident, while intoxicated or by mistake.
A chemical burn of the laryngeal mucosa develops when ingesting concentrated alkalis, acids, and alcohol infusions. In this case, tissue damage will occur until the agent is neutralized.
The most common causes of chemical damage to the mucous membrane are entry into the larynx:
alcohol tinctures or alcohol itself; iodine; ammonia; concentrated citric, acetic, sulfuric, hydrochloric acid; alkalis, in particular caustic soda.
In everyday life, a chemical burn to the larynx can occur when trying to lubricate or rinse the tonsils with iodine in the case of a sore throat. In this case, people do not dilute the alcohol tincture to an acceptable concentration, and mucosal injury occurs. If there were ulcers or wounds on the mucous membrane, then even diluted iodine can cause damage.
Thermal burn of the throat occurs when swallowing too hot drink or food. Another cause of injury is inhaling too hot steam during inhalation to treat a sore throat. Such a burn is often accompanied by damage to the mucous membranes of the trachea and bronchi.
Description and reasons
According to the type of origin, a burn of the larynx can be chemical or thermal in nature:
- The chemical is formed when swallowing concentrated acid-base or alcohol-containing compounds - iodine, acids (citric, acetic, hydrochloric), alkali (caustic soda), ammonia. Tissue damage continues until the aggressive substance is neutralized .
- Thermal burn occurs from too hot drink or food, steam during inhalation. Characterized by injury to the mucous membrane of the throat. Blisters appear in the mouth, and the victim’s health worsens. Cool water helps stop further tissue destruction.
Manifestations of a burn to the pharynx are distinguished by severity:
- First. Only the outer layer of the mucosa is affected, redness with slight swelling is observed.
- Second. A more serious lesion, accompanied by the appearance of blisters, a grayish film, and severe swelling.
- Third. Deep layers are involved, necrotic changes in the mucous membrane and nearby tissues are possible.
In everyday life, 1st degree burns most often occur, which do not pose a threat to life.
Burn degrees
There are three degrees of throat burns:
First degree. Only the surface layers are affected. A person experiences redness and slight swelling of the laryngeal mucosa. Second degree. Deeper tissue damage occurs. Bubbles or grayish films appear. Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane are also noted. Third degree. The damage extends deeper. Necrosis of the mucous membrane and other tissues may occur.
Most often, adults experience first- or second-degree burns, which do not pose a serious danger. Symptoms of such an injury will decrease as the mucous membrane recovers. In total, treatment takes up to one week.
However, in some cases, more serious burns may occur, damaging other tissues and spreading to the esophagus, trachea and bronchi. In this case, there may be serious consequences and longer treatment.
Symptoms of pathology
The following symptoms of a throat burn are distinguished:
severe acute pain, which only intensifies when swallowing; swelling of the oral mucosa and larynx; nausea, vomiting; increased body temperature; enlarged and painful lymph nodes; characteristic odor (acid or alkali) of vomit or exhaled air;
If a person suffers a severe burn to the larynx, it can cause severe swelling and suffocation.
If the burn damages the airways, additional symptoms occur:
cough, difficulty breathing; chest pain; change in voice, hoarseness.
Causes of defeat
The causes of throat burns are varied:
- Carelessness, inattention. Caustic alcohols, acids, and vinegar are indistinguishable from water in appearance; they are mistaken for a safe liquid and drunk.
- Alcohol or alcohol damage.
- Parental neglect. A child under 3-4 years old, unattended, tastes everything he can reach.
- Burns caused by smoke when inhaling a hookah.
- Failure to comply with safety regulations at work. We are talking about industrial burns of the nasopharynx and esophagus caused by inhalation of toxic fumes.
- Damage by quartz during the quartzing procedure.
- As a result of self-medication.
- Intentionally consuming dangerous liquids or substances in an attempt to commit suicide.
Depending on the influencing factor, burns, according to the International Classification of Diseases, are divided into two groups:
- thermal (ICD code T28.1);
- chemical (ICD code T28.6).
In the first case, people can injure their mouth, palate, throat, trachea, esophagus (sometimes nasopharynx) with too hot food, spicy foods and seasonings (hot peppers), boiling water or very heated steam.
In the second, the list of chemical agents that can cause burns is much wider:
- alcohol containing poisonous corrosive alcohols;
- ethanol;
- ammonia;
- ammonia;
- iodine;
- acetone;
- sulfuric, hydrochloric acids, their vapors;
- lemon acid;
- vinegar;
- bleach, chlorine vapor;
- caustic soda.
According to statistics, most often people get alcohol and alcohol burns to the throat.
Alcohol and alcohol
Alcohol burn occurs when swallowing medical alcohol 70-96% and vodka-based tinctures. The victim loses his sense of taste, experiences weakness, pain in the chest, neck, and stomach. A white fibrin coating of dead tissue forms on the walls of the esophagus, resembling the white of a boiled egg.
Burn treatment
A distinction is made between first aid and subsequent treatment for throat burns. You can treat a first- or second-degree throat burn at home using folk remedies. The mucous membrane is characterized by a high regenerative potential and quickly recovers from damage.
First aid
First aid is very important. The degree of damage and subsequent treatment depend on how quickly and effectively it was provided. If the burn is thermal, then first aid is to give the person cool, still water to drink in small sips. You can swallow small pieces of ice and snow.
If the damage is chemical in nature, then first aid is to neutralize the agent that caused the damage. If it is an acid, then treatment involves gargling with a weak solution of baking soda (1 teaspoon of soda per 200 ml of water). If the injury is caused by alkali, then you need to gargle with a weak solution of citric acid (0.1 g acid in 100 ml of water) or acetic acid (2 teaspoons of 9% vinegar per 1 liter of water). If the burn is caused by alcohol or alcohol tinctures, you need to drink a large amount of water in small sips. Also, in case of chemical damage, it is necessary to rinse the stomach with a large volume of boiled water.
Traditional treatment
Traditional treatment for such a laryngeal injury involves the use of folk remedies that prevent the development of bacteria in the damaged area and stimulate the restoration of the mucous membrane.
Oils. Sea buckthorn, olive, peach oil, and rosehip oil are also useful in treatment. These oils are used to lubricate damaged mucous membranes several times a day. Herbal decoctions. Carry out regular rinsing with decoctions of chamomile, calendula, oak bark, and yarrow. To prepare decoctions, steam 1 tbsp in 200 ml of boiling water. l. dried herbs, leave in a thermos for 1 hour. Before infusion, oak bark must be boiled over low heat for 5 minutes, then the infusion is filtered and used to gargle 3 times a day. Rinse with a solution at room temperature. Solutions of different herbs are alternated.
Diet
In addition to taking folk remedies, in some cases the patient has to follow a diet. Adequate nutrition for such people is difficult due to pain in the larynx. It is recommended to consume liquid and pureed foods at moderate temperatures. Sunflower oil, which is consumed 1 tsp, is also useful for treatment. 4 times a day.
First aid for burns of the throat and trachea
The quality and speed of emergency assistance to the victim determines the prognosis of the disease.
The affected area (visible) is examined. A dry scab indicates an acid burn, a moist, jelly-like surface of the mucous membranes indicates an alkaline burn.
- Give the victim cool water (drink in small sips, holding it in the damaged area).
- Rinse your mouth and throat with solutions of anesthetic drugs.
- If it is acidic, neutralize the effect of the acid by drinking a solution of baking soda (2 g per 1 liter of water).
- If alkaline, give diluted acetic or citric acid (3-4 g per 1 l).
- You can cleanse the body of aggressive substances with a small amount of vegetable oil or a glass of milk. Then induce vomiting.
- Open the windows and provide air flow.
- Call an ambulance.
Prognosis and prevention
First- and second-degree burns usually heal well without leaving marks. Third degree injuries to the larynx pose a real danger to human life. In this case, the patient may develop swelling, which will lead to suffocation. Choking can also occur due to damage to the nerves innervating the respiratory organs. Severe chemical burns of the larynx are usually accompanied by the entry of chemical agents into the digestive system, which can lead to poisoning. After healing, third-degree burns can lead to scarring of the mucous membrane.
Preventing burns involves following safety measures, especially for young children. It is necessary to ensure that they do not have access to hot drinks and food, dangerous chemical agents.
Write in the comments about your experience in treating diseases, help other readers of the site! Share the material on social networks and help your friends and family!