Like any other, purulent inflammation is the body’s response to the influence of any irritant, aimed at limiting the pathological area, destroying provoking agents and restoring damage. The inflammatory response consists of three successive phases: damage, swelling, recovery. It is the nature of the edema that determines the type of inflammation.
Purulent inflammations develop when pathogenic pyogenic bacteria predominate in the edematous fluid (exudate). These can be Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, staphylo-, gono-, streptococci, Klebsiella, Proteus. The degree of bacterial contamination of the injury site determines the likelihood and nature of the inflammatory reaction.
Pus is a liquid medium containing dead blood cells (leukocytes, phagocytes, macrophages), microbes, enzymes (proteases), destroyed and dead tissue, fats, and protein fractions. It is proteases that are responsible for tissue dissolution (lysis) at the site of damage.
The following types of purulent inflammation are distinguished:
- empyema - accumulation of pus in the cavity represented by the walls of the organ;
- abscess - a cavity resulting from the melting of tissue, filled with purulent exudate;
- phlegmon is a diffuse purulent lesion of the subcutaneous tissue along the vessels, nerves, and fascia.
Inflammation of atheroma
One of the most common benign tumors in subcutaneous tissues is atheroma. It is formed in places where the sebaceous glands are most widespread: the head, tailbone area, face, neck. Atheroma has the appearance of a round formation; it is a cavity enclosed in a capsule containing fat, cholesterol, and skin cells.
It occurs as a result of the fact that the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland is clogged. Atheroma can be single, but in most cases there is multiple distribution of these formations of various sizes. This tumor is painless and, apart from cosmetic discomfort, does not cause inconvenience.
There are primary (congenital) and secondary atheromas that occur with seborrhea. On palpation they are dense, moderately painful, and have a bluish tint. Secondary tumors are localized on the face, chest, back, and neck. After opening them, ulcers with undermined edges are formed.
In outpatient surgery, atheroma inflammation is a common problem. Predisposing factors to this are the following conditions:
- insufficient hygiene;
- self-squeezing pimples, especially if antiseptic rules are not followed;
- microtraumas (scratches and cuts);
- pustular skin diseases;
- decreased local immunity;
- hormonal disorders;
- abuse of cosmetics.
Suppurating atheroma is characterized by pain, local redness and swelling. With large sizes, fluctuation may be observed - a sensation of fluid flowing in the elastic cavity. Sometimes the formation breaks out on its own and sebaceous pus is released.
Inflammation of atheroma can only be treated surgically. A skin incision is made, the contents are peeled out with the mandatory removal of the capsule. When it is not completely removed, relapse is possible after surgery. If atheroma re-forms, inflammation may develop in the same area.
Video: how to cure an internal pimple
Once and for all, special video materials will help you deal with the problem of subcutaneous rashes, in which this topic is covered in as much detail as possible. Experts talk about the main reasons for the appearance of such formations, provide photos of common types of rashes, explain how to deal with them and how to properly remove a pimple located in the deep layers of the epidermis.
Properly used ointment that draws out pus from a pimple helps to quickly break through the pimple and painlessly remove the contents. This treatment is much more effective than simply squeezing out pimples and damaging the skin. There are many remedies that allow you to get rid of purulent acne; a dermatologist will advise which one is suitable for a person in an individual case.
Suppuration of wounds
Wounds occur for numerous reasons: domestic, industrial, criminal, combat, after surgery. But wound inflammation is not always purulent. It depends on the nature and location of the damage, the condition of the tissues, age, and contamination with microbes.
Factors predisposing to inflammation of the wound surface are the following:
- injury from a contaminated object;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- use of steroid hormones and/or cytostatics;
- excess body weight;
- malnutrition;
- vitamin deficiency;
- elderly age;
- decreased local and general immunity;
- chronic skin diseases;
- severe somatic illnesses;
- hot, humid weather;
- insufficient wound drainage after surgery.
Typically, wound suppuration is characterized by the accumulation of purulent inflammatory exudate in the tissue defect. At the same time, hyperemia (redness) and “warm” swelling appears around the edges, caused by vasodilation. In the depths of the wound, “cold” swelling predominates, associated with impaired lymphatic outflow due to compression of blood vessels.
Against the background of these signs, bursting, pressing pain appears, and the temperature in the affected area is locally elevated. A necrotic mass is determined under the layer of pus. Absorbed into the blood, decay products and toxins cause symptoms of intoxication: fever, weakness, headaches, loss of appetite. Therefore, if wound inflammation occurs, treatment should be immediate.
Tetracycline ointment
If pus appears in the eyes, most likely you have to deal with conjunctivitis. In this case, you cannot do without an external antibacterial agent. Tetracycline ointment shows good results. The active ingredient is tetracycline hydrochloride. This substance inhibits the activity of many pathogenic bacteria. Additionally, the drug contains sodium sulfite, petroleum jelly, and anhydrous lanolin. Positive results from using the drug are noticeable almost immediately. It is necessary to start using the medicine as soon as pus appears in the eyes.
Conjunctivitis is not the only indication for the use of the drug. The medication is widely used in the treatment of advanced forms of acne, furunculosis, eczema, and trophic ulcers. It is worth considering that addiction to an antibacterial agent can develop. If unpleasant symptoms do not go away within five days, you should consult your doctor again.
Suppuration of postoperative sutures
The process of inflammation of the postoperative suture usually occurs 3-6 days after surgical procedures. This is due to the entry of pyogenic microorganisms into the site of tissue damage. Bacteria can be introduced into a wound primarily (by a wounded object, poorly treated instruments, by the hands of medical personnel and/or the patient himself) and indirectly from a source of chronic infection: caries, tonsillitis, sinusitis.
Predisposing factors to the development of a pathological process in the suture area:
- insufficient disinfection of medical equipment;
- failure to comply with the rules of asepsis and antiseptics;
- reduced immunity;
- poor drainage of wound discharge;
- damage to subcutaneous tissue (hematomas, necrosis);
- poor quality suture material;
- lack of hygiene by the patient;
- areas of ischemia (lack of blood supply) due to clamping of blood vessels with a ligature.
If inflammation of the suture has developed, symptoms such as redness and swelling of the surrounding skin and pain will be observed. First, serous fluid mixed with blood may separate from the suture, and then suppuration occurs.
With a pronounced inflammation process, fever with chills, lethargy, and refusal to eat appear.
A festering surgical suture should be treated only under the supervision of a physician. Incorrect independent actions can lead to the spread of infection, deepening inflammation and the development of serious complications, including sepsis. This creates a rough, convoluted scar.
Syntomycin ointment
An effective and affordable remedy is widely used for purulent inflammation. The active ingredient is chloramphenicol. The substance suppresses the activity of pathogenic bacteria and prevents them from fully multiplying. Some viruses and pathogenic fungi are also at risk. Synthomycin ointment is widely used as part of complex therapy for purulent wounds. For preventive purposes, the medication is used in surgery after complex surgical interventions. The suture area is treated with ointment.
Purulent lesions of the skin and subcutaneous tissue
Pathological processes in the skin and underlying layers are very common in surgical practice. The skin and its appendages are the body’s first protective barrier from various adverse effects.
Negative factors that provoke the development of skin inflammation are:
- mechanical damage (scratches, abrasions and cuts, scratching);
- exposure to high and low temperatures (burn, frostbite);
- chemical agents (household alkalis, acids, abuse of antiseptics and detergents);
- excessive sweating and sebum secretion can cause purulent inflammation of the skin;
- poor hygiene (especially in obese people);
- diseases of internal organs (pathologies of the endocrine, digestive systems;
- ingrown nail.
Microbes introduced from outside and/or representatives of opportunistic flora can cause purulent inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Skin suppurations vary in location and clinical course.
Furuncle
Suppuration of the hair follicle and sebaceous gland - boil. It can be localized in areas of the skin where there is hair. Occurs at any age. Most common in patients with diabetes and/or obesity.
Clinical manifestations are expressed in typical inflammation: hyperemia, pain, increased local temperature, swelling. Sometimes this condition is accompanied by a reaction of nearby lymph nodes.
Complications of furunculosis can include lymphadenitis, abscess, thrombophlebitis (inflammation of the veins), phlegmon, reactive purulent arthritis, sepsis, and meningitis.
Carbuncle
Carbuncle is an acute infectious inflammation of several hair follicles with sebaceous glands simultaneously. It occurs more often in mature and elderly people. Endocrine disorders play a major role in the development of this inflammation. Typical localization is the back of the neck, back, abdomen, buttocks.
At the site of infection, dense diffuse swelling occurs, the skin becomes purple and painful. Necrotic melting of tissue occurs. The carbuncle opens in several places and creamy pus is released. The lesion with such inflammation of the skin has the appearance of a honeycomb.
Hidradenitis
Inflammation of the sweat glands occurs mainly due to uncleanliness, diaper rash, and scratching. Shaving the armpits ranks first among the provoking factors. Microtraumas of the skin occur, and the use of deodorant contributes to blockage of the excretory ducts of the glands.
A dense, painful lump forms in the armpit area, and the skin becomes purple-bluish. As inflammation develops, the pain intensifies and interferes with movements. A fluctuation occurs, the skin in the center becomes thinner, and thick pus breaks out.
When inflammation spreads to other areas, due to the abundance of lymphatic tissue, a conglomerate of nodes with protruding skin papillae is formed - a “bitch udder”. If treatment is not carried out, the process can spread - an abscess or phlegmon forms. A serious complication of hidradenitis is sepsis.
Abscess
A purulent-necrotic cavity limited by a capsule is an abscess. More often it occurs as a complication of inflammation, pustular diseases on the skin.
The cause of the development of a purulent cavity can be inflammation of a puncture wound or injection site when the outflow of pus is impaired.
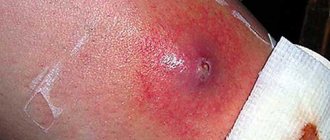
Clinically, an abscess is manifested by swelling and hyperemia of the skin in the affected area. A dense, elastic, painful formation is palpated deep in the tissues. The skin over the abscess is hot to the touch. Symptoms of intoxication appear.
When an abscess is opened and is not completely emptied or there is a foreign body in the cavity, the walls of the capsule do not close completely and a fistula is formed. A breakthrough of pus can occur on the skin, into surrounding tissues, and into organ cavities.
Phlegmon
A purulent-necrotic process of inflammation, located in the cellular space, without clear boundaries. The causes of phlegmon are the same as for an abscess.
In connection with the development of aesthetic medicine, the formation of phlegmon can be provoked by corrective procedures: liposuction, the introduction of various gels. The location can be any, but the areas of the abdomen, back, buttocks, and neck are more likely to become inflamed. Damage to leg tissue is not uncommon.
Gradually melting the tissue, phlegmon spreads through the fiber and fascial spaces, destroying blood vessels and provoking necrosis. Often phlegmon is complicated by an abscess, hidradenitis, or boil.
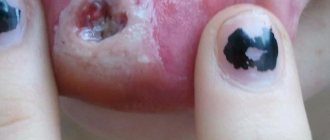
Paronychia and felon
Panaritium is an inflammation of soft tissues, bones and joints of the fingers, and less commonly the foot. The pain of felon can be unbearable and deprive you of sleep. At the site of inflammation there is hyperemia and swelling. As the process develops, the function of the finger is impaired.
Depending on the location of the lesion, felon can be of different types:
- cutaneous – the formation of suppuration between the epidermis and the next layers of skin with the formation of a “bubble”;
- subungual - pus flows under the nail plate;
- subcutaneous – purulent-necrotic process of soft tissues of the finger;
- articular – damage to the phalangeal joint;
- tendon - suppuration of the tendon (tenosynovitis);
- bone - the transition of a purulent process to the bone, proceeding as osteomyelitis.
Paronychia is damage to the ridge around the nail. The nail bed can become inflamed after a manicure or cuticle trimming. In this condition, throbbing pain, redness, and discharge of pus are noted.
Traditional methods of treatment
Minor inflamed cuts and scratches can be treated at home; folk remedies are often used for this.
A hypertonic saline solution (sodium chloride 10%) is suitable for rinsing at the first stage. It can be made at home by adding 90 g of salt to a liter of clean water and straining through sterile gauze. The product draws back and adsorbs exudate without damaging surrounding tissue.
For this purpose, decoctions of chamomile and calendula are also used. A tablespoon of raw material is poured into a glass of water, heated in a water bath for 15 minutes, and filtered thoroughly. Wash the wounds twice a day.
An aloe leaf from an adult plant (at least 2-3 years old) is used as a regenerating and anti-inflammatory agent. It is cut off and placed in the refrigerator for a day. Then they cut it in half lengthwise and tie the inside to the wound.
At the healing stage, mumiyo is used to prevent the formation of a rough scar. 1.5 g of this substance is dissolved in 50 ml of warm water and mixed with a tube of baby cream. Apply once a day. Sea buckthorn oil also helps, it simultaneously softens the skin and stimulates healing.
Remember that traditional methods are applicable only for minor injuries or as an addition to traditional therapy.
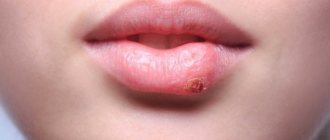
Effective acne medications
Salicylic acid
This is an effective medicine that is good for removing acne and purulent pimple. The main task of the drug is to disinfect the inflamed area and destroy the bacterial infection. The drug first softens the skin, allowing deeper penetration into the pores. Before applying salicylic acid to the inflamed area, the skin must be treated with Chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide. After this, you need to anoint the pimple with the product. This medicine is used at least 3 times a day, the course of therapy lasts until the rash completely goes away.
Ichthyol ointment
This is an effective drug that helps to quickly remove the purulent contents from abscesses. The ointment is recommended to treat subcutaneous acne on the face and other parts of the body. Penetrating through the upper layer of the epithelium, the drug destroys bacterial microflora. The auxiliary components included in the composition have an irritating effect. Thanks to this, blood circulation is activated at the site of the rash, which, in turn, helps the pus to come out faster, and the abscess will soon heal.
How to cure acne with iodine?
If it becomes noticeable that a pimple is breaking out, you can treat it with iodine at night. This drug is an antiseptic and also has a drying effect, making the rashes disappear faster. If pimples with pus appear on your face, you need to spot treat the inflamed areas with a cotton swab dipped in the preparation. By the morning, the purulent lump decreases in size, and the skin looks less inflamed.
It is forbidden to make compresses and lotions based on iodine. This product contains alcohol, which causes burns if it comes into contact with the skin for a long time.
Badyaga treatment
To make pimples more active, it is recommended to spot-smear the affected areas with badyagi. This is a natural remedy that helps not only remove the rash, but also accelerate skin regeneration and prevent the appearance of new rashes. After applying badyagi, irritation appears on the skin, due to which blood circulation is activated. A deep pimple matures faster and is better to pull it out from the inside.
Liniment Vishnevsky
This is an ointment that effectively sucks out pus and quickly deals with an abscess. The antiseptic components included in the medicine penetrate deeply into the subcutaneous structures, destroying pathogenic microflora and eliminating inflammation. Apply a cotton swab with ointment to the area where the pimple appears and secure it well. Overnight, the drug almost completely sucks out the green pus, due to which the internal pimple on the forehead, nose, cheeks or chin disappears.
Gel "Skinoren"
This drug is mainly used to tighten pores, but in addition, the product effectively fights purulent acne. The active components included in the composition block the increased production of subcutaneous fat, due to which the number of rashes decreases. In addition, Skinoren has an excellent antibacterial effect, and if you apply the gel to a pimple that has yellow pus inside, the inflammation goes away faster and the pimple is much easier to remove.
Local antibiotics
Antibacterial ointment or cream does not draw pus out of a pimple. The main task of the drug is to destroy the bacterial infection and stop inflammation. After the pimple becomes hard and without pus, it must be squeezed out correctly. Popular local antibiotics are:
Levomekol helps get rid of acne, which, when applied to a spot, draws pus from the pimple and promotes healing.
- "Zinerite". The medicine additionally contains zinc, which promotes accelerated skin regeneration. The course of therapy is 10 days, after application the product is not washed off.
- "Levomekol". This is an effective ointment that has a powerful bactericidal effect. But, in addition, the product helps to quickly draw pus out of the pimple, which speeds up the healing of the skin. Therapy lasts an average of a week, the ointment is applied pointwise in the morning and evening.
- "Baziron AS". This is a powerful antibacterial agent that, in addition to destroying infection, normalizes the production of subcutaneous fat. The drug is applied twice a day to cleansed skin. The course of treatment is 10-14 days.
- Streptocide ointment. Prescribed for extensive purulent rashes. The product is applied in a thin layer to the entire inflamed area, but if there are only a few acne, the ointment is applied pointwise and covered with a cotton pad on top. Already on the 2-3rd day of therapy, the purulent contents mature, after which they are pulled out.