carpule anesthesia in dentistry: what is it and how is it carried out?
659
The fact that modern methods of dental treatment are carried out almost painlessly is an undoubted achievement in dentistry and the use of effective drugs as an anesthetic.
Many patients, especially older people, are sincerely surprised by the options for freezing the working area, the bizarre shapes of syringes and disposable ampoules.
This article will discuss one of the innovative methods of performing pain relief procedures - carpule anesthesia.
General overview
The name of the technique is due to the design of the syringe, the contents of which sharply reduce the sensitivity threshold of the nerve tissues of the tooth.
The capsule in which the drug is placed is called carpula. Despite the specific packaging of the drug, the manipulation technology itself is standard.
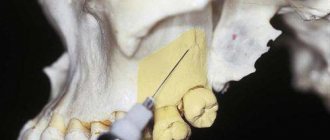
A carpule injection is a reusable syringe. This device is made of a medical metal alloy, and consists of a frame, a piston part and a needle. In this case, the piston cannot be completely removed from the housing, on the side of which there is a gap to accommodate the capsule.
It is a special ampoule containing an anesthetic composition. The capsule is hermetically sealed, has a rubber plug at one end, and a metal valve at the other.
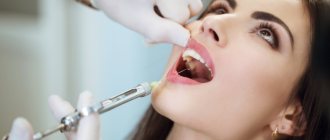
The device works on the following principle - after the cartridge with the necessary product is placed in the gap of the syringe, a needle is screwed into it and an injection is made.
In this case, the plug should be on the side opposite to the needle. When you press the piston, the medicine is injected into the organ cavity and reaches the target.
Advantages
According to practicing dentists, this type of anesthesia has the following advantages over analog painkillers:
- adherence to the dosage as accurately as possible. One carpool unit holds 1.7 ml contents;
- 100% sterility - each injection is performed with a disposable needle, and the contents of the capsule are pumped in strict accordance with antiseptic requirements. Compliance with sterility standards is especially important for those patients whose immune system is weakened by serious diseases, such as diabetes;
- good tolerance - the needle that comes with the device is so thin that inserting it into soft tissues causes virtually no pain. In addition, it simplifies the administration of the drug where the mucosa is close to the periosteal zone;
- comfortable working conditions for the dentist - the syringe is conveniently located in the doctor’s hand and, unlike standard syringes, is easily directed in different directions due to its design features. The needle is so flexible and durable that it can be bent without fear of it breaking and injuring the patient;
- impossibility of administering the wrong drug - the packaging contains a marking with the name and dosage of the composition located inside the capsule.
Flaws
As for the negative aspects of carpule anesthesia, practically none have been identified.
A number of patients note the high cost of the drug, which makes it limited to the category of citizens with low material income.
However, this is a controversial drawback, since the complexity of manufacturing the product and high efficiency are associated with additional manufacturing costs. A quality product cannot be cheap.
Another disadvantage is the inability to modify the composition. A vasoconstrictor cannot be added to it, but in some clinical cases this is necessary.
Injector contents
The use of the drug requires the dentist to know the composition of the anesthetic. This information is contained on the packaging; there is a detailed breakdown of the percentage of all its components.
Injector includes:
- An anesthetic is a substance that reduces the pain sensitivity threshold in the injection area to a minimum. These compounds are classified under the category of amides and their derivatives. These are mainly Lidocaine, Prilocaine, Articaine;
- vasoconstrictor – activates vasoconstrictor processes, which prolongs the relief of nerve endings and increases the effect of the drug. In addition, the substance prevents premature leaching of the drug from the working area. It has a serious limitation for use - the drug is prescribed with extreme caution to people with pathologies of the cardiovascular system, diabetes mellitus at any stage of the disease, and elderly patients. Vasoconstrictors include adrenaline, mesaton;
- antioxidants are mainly sodium sulfites or bisulfites. Their main function is to protect the vasoconstrictor from destructive processes that occur under the negative influence of an oxygen environment. They can provoke individual intolerance, including acute allergic reactions, since they contain sulfur fragments. Contraindicated for diseases affecting the lungs and bronchi;
- preservatives – ensure the safety of the composition until it is opened;
- EDTA – metal binder;
- parabens are fragments that ensure absolute sterility of the capsule contents. This is especially important when transporting to regions with hot climates.
Thanks to this balanced composition, the anesthetic is reliably protected from the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms.
The main requirement related to the specific composition of the anesthetic is to make sure before using the medicine that the patient is not allergic to its derivatives.
Neglect of this rule is fraught with anaphylactic shock, which can cause irreparable harm to human health.
The video provides a description of an innovative single-use carpule syringe.
Storage rules and periods
Any medicine needs proper storage. Capsules must be kept in a dark place. The optimal storage temperature is 23-25 degrees.
Failure to comply with basic conditions will shorten the shelf life of the composition, and improper transportation may compromise the structural integrity of the package.
Such drugs should not be used under any circumstances. Injectors should be stored in places inaccessible to children and pets.
Signs of loss of drug properties
You can understand that the medicinal effect of the drug has been neutralized and it has lost its main characteristics by a number of signs:
- the integrity of the packaging is compromised - most often this is due to careless transportation;
- An uncharacteristic sediment has appeared in the liquid or the shade of the composition has changed - this happens when the temperature regime is violated, causing overheating. The vasoconstrictor disintegrates and the agent changes its structural content;
- the appearance of gas bubbles larger than 0.2 cm. This is a consequence of freezing;
- the appearance of rust fragments on the outside of the ampoule.
Requirements for drugs
The main requirements put forward by specialists for drugs used as pain relief:
- predictability of the effect - the doctor must be sure that the result will be profound and the duration of its action will be enough to carry out treatment;
- safety - the medicine should not have allergic manifestations, not contain toxins, and have a minimum of side effects.
Popular means
The most popular option for carpule anesthesia is the products of French manufacturers, which are effective and affordable:
- Ultracaine is the most popular concentration for dental pain relief. The effect occurs after a couple of minutes and lasts for at least an hour;
- Ubistezin - the duration of pain relief does not exceed half an hour, this time is sufficient in most clinical cases. Indications for use: children, pregnant women;
- Scandonest – has a high concentration of adrenaline. Side effect is a long-term vasoconstrictor result. Prevents bleeding;
- Septanest - has a mild effect. The sensitivity threshold remains extremely low for 15-20 minutes. Indicated for people prone to allergies, with severe pathologies and serious chronic diseases, when the use of stronger drugs is not recommended.
Reasons for the lack of pain relief
In some cases, the effect of the product may be minimal or absent altogether, that is, tissue sensitivity remains almost at the same level.
There are reasons for this. If we exclude damage to the packaging and a violation of the properties of the composition, the lack of pain relief is explained by the following factors:
- fear of the upcoming procedure - fear blocks other reflexes, and anesthesia does not occur;
- production of adrenaline - it is intensely produced in moments of panic and enters the nerve cells, neutralizing the effect of the drug.
To exclude such manifestations, experts recommend that patients prone to panic fear of the dentist take a sedative half an hour before the procedure.
Chronic alcohol dependence, as well as the body’s addiction to the drug, can have an inhibitory effect.
Reviews
Carpule anesthesia is used almost everywhere in domestic clinics.
Its main purpose is to eliminate the fear of treatment and make it as comfortable as possible.
Source: https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/zubyi/karpulnaya-anesteziya-v-stomatologii-chto-eto-takoe.html
Carpule anesthesia in dentistry: advantages and disadvantages
- What is carpule anesthesia?
- Advantages of carpule anesthesia
- Disadvantages of carpule anesthesia
- Requirements applicable to local anesthetics
- What anesthetics are most often used
- Which anesthetic is better
The most important condition for modern treatment is the painlessness of all therapeutic and diagnostic procedures. Dentists are still trying to achieve better pain relief in order to smooth out the factors that traumatize the patient’s psyche and cause him to fear dentists.
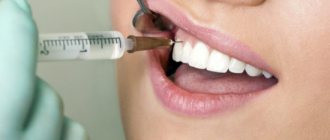
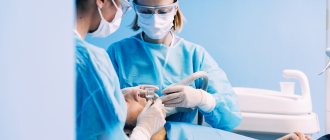
Carpule anesthesia is pain relief using a special syringe. It is used for comfortable and safe anesthesia.
Carpule syringe
A carpule syringe is a reusable metal device equipped with a piston, needle and body.
The piston in this case cannot be completely removed by moving backwards, like a disposable syringe; in addition, in the side of the syringe body there is a special recess for the carpule - a special ampoule containing an anesthetic, hermetically sealed and equipped with a rubber stopper at one end and a metal cap at the other end.
Experts include anesthetics based on Articaine among the most modern painkillers.
According to experts, the principle of operation of a carpule syringe is as follows: the required carpule is placed in the syringe, then a disposable needle is attached to it, after which the device is ready for use.
The cartridge must be inserted in such a way that the cap is on the side of the needle, since it must be pierced by its reverse end, and the plug must be located on the piston side.
Pushing the plug with a piston ensures that the anesthetic moves along the needle into the depths of the tissue.
At the moment, in modern dental institutions, specialists use carpule syringes, which are convenient and technically sophisticated.
Advantages of carpule anesthesia
According to experts, carpule anesthesia has the following advantages:
- Exact dosage of the amount of anesthetic. Each carpule contains 1.7 milliliters of anesthetic, which makes it easier to control the dose of anesthesia
- Sterility. A disposable needle is used for each individual patient, and the solution inside the capsule is sealed in compliance with aseptic standards. This is very important, especially when treating patients with low levels of immunity, for example, with immunodeficiencies or diabetes mellitus
Anesthesia
- Easy to tolerate for the patient. The needle of a carpule syringe is thinner than a disposable syringe, so its insertion into the tissue is practically not felt. Among other things, it can facilitate technical anesthesia for a specialist and subjective sensations for the patient during infiltration anesthesia from the lingual and palatal side of the jaw, where the mucous membrane has a very tight adhesion to the periosteum
- Convenience for the specialist. A carpule syringe is much easier to hold in the hand and point to the sides than a disposable syringe. This is possible thanks to its thoughtful design. The needle of such a syringe has great flexibility, which allows, if necessary, to bend it with almost no restrictions without fear of breaking off
- Completely eliminating the possibility of injecting a foreign substance or other anesthetic. Medicine knows of cases when, during the process of pain relief, a specialist administered the wrong anesthetic, and in some situations, a completely different substance was administered to the patient, for example, an antiseptic or alcohol. Carpule anesthesia eliminates the possibility of such an outcome, since each carpule indicates the name of the drug for pain relief, its concentration and quantity
Disadvantages of carpule anesthesia
Despite the existing minor drawbacks, carpule anesthesia has taken a strong place among modern options for pain relief. These disadvantages include:
- Price. This is mainly due to the complexity of the carpule syringe design. In addition, high-quality carpule syringes are more expensive than cheaper options
- Inability to modify the anesthetic. A specialist who uses carpule anesthesia does not have the opportunity to add a vasoconstrictor if necessary, because it is impossible to open the carpule before direct use
Requirements for local anesthetics
Classic requirements for local anesthetics:
- Minimal allergenicity and toxicity
- No damaging effects on nerves and tissues
- As low as possible the likelihood of side effects and complications
- Rapid absorption by the body
- However, in addition to the classical requirements for anesthetics, additional requirements must also be applied that will improve the quality of treatment
Additional requirements for local anesthetics:
- Deep and complete anesthesia of the pulp, hard tissues, oral mucosa and periapical tissues
- Quite fast onset of pain relief (no more than five minutes)
- Long-lasting effect - anesthesia should ensure complete painlessness throughout the entire treatment, including in the last stages of the operation. Thus, the duration of action of the anesthetic, especially for complex operations, should be about an hour
- Complete and rapid cessation of anesthesia after the end of the procedure, that is, after 2.5 - 2 hours
- Preservation of pharmacological properties and chemical stability during storage, that is, for 2-3 years
Carpule anesthesia
What anesthetics are most often used
Experts include anesthetics based on Articaine, the active substance used in anesthetics called Septanest, Ubistezin Ultracaine and many others, among the most modern painkillers. Anesthetics of the articaine series are distinguished by an effect that is 1.5-2 times more effective than lidocaine and 5-6 times more effective than novocaine.
An important advantage of articaine anesthetics over other painkillers is their effectiveness in anesthetizing the area of inflammation. For example, with purulent inflammation, Novocaine has practically no effect, and the activity of Lidocaine is greatly reduced.
At the moment, in modern dental institutions, specialists use carpule syringes, which are convenient and technically sophisticated.
Many anesthetics, in addition to the basic anesthetic component, for example, articaine, also contain vasoconstrictors such as epinephrine and adrenaline. Such substances, due to the constriction of blood vessels at the injection site, reduce the washout of the anesthetic, which increases the strength and duration of anesthesia.
Ultracaine
Experts identify the following commonly used modern anesthetics:
- Ultracaine. This product is produced by a company from France called Sanofi Aventis in 3 variants, differing in the presence or absence of epinephrine and its concentration. Ultracain D does not contain epinephrine and preservatives, Ultracain DS has an epinephrine concentration of 1:200,000, Ultracain DS forte – 1:100,000
- Ubistezin. This product is produced by a company from Germany under the name ZM in 2 concentrations of epinephrine. Ubistezin has an epinephrine concentration of 1:200,000, Ubistezin forte – 1:100,000. The composition does not differ from the composition of Ultracaine
- Septanest. This product has been used in dentistry for many years and is available in 2 versions with adrenaline concentrations of 1:200,000 and 1:100,000. Septanest, unlike Ultracaine and Ubistezin, contains preservatives that can cause allergies
- Scandonest. This product is produced by a company from France called Septodont; Scandonest is based on Mepivacaine 3%. The anesthetic does not contain vasoconstrictor ingredients or preservatives. It is used in dentistry only for patients at risk, for whom anesthetics with epinephrine and adrenaline are not permitted, and for persons with bronchial asthma. Experts call the anesthetic Mepivastezin 3%, produced by the German company ZM, an analogue of the drug.
Which anesthetic is better
Many argue that almost all modern anesthetics act the same and reliably “freeze” the jaw.
Regular Ultracaine is suitable for almost everyone, but some prefer Ubistezin, although, in essence, they are no different in composition.
The main thing that both patients and doctors advise is to undergo allergy tests before administering the anesthetic in order to avoid unpleasant incidents.
It is also worth noting that pain relief depends not only on the anesthetic - anesthesia technique plays an important role. So if you felt pain during treatment, then the problem is most likely not in the anesthetic, but in how the doctor administered the anesthesia.
Useful article?
Save so you don't lose!
Disclaimer: This material is not intended to provide diagnosis, treatment, or medical advice. The information is provided for informational purposes only. Please consult your physician regarding any medical or health-related diagnoses or treatments. This information should not be considered a substitute for consultation with a physician.
Source: https://stom.32top.ru/stat/339/
Buy online
It is believed that performing an aspiration test is necessary to prevent the needle from entering a blood vessel and to avoid rapid intravascular injection of a local anesthetic solution, which can cause toxic complications [2]. Aspiration is an important safety factor for local anesthesia, which, according to the American Dental Association (1973) [7], is a desirable element of injection, and according to S. Malamed (2004) [8] - mandatory.
Intraligamentary anesthesia (ILA) has become widespread due to the advent of the non-aspiration pressor syringe. Aspiration with spongy methods of anesthesia cannot be carried out with a pressor syringe, since structurally there is no mechanical connection between the piston rod and the cartridge plug. However, S. Malamed (2002, 2004) [8, 9] believes that with normally performed IPA, intraosseous and intraseptal anesthesia, only a negative aspiration test occurs (!?). A.Zh. Petrikas et al. (1987, 2011) [4, 5, 10], on the contrary, showed that during spongy anesthesia - intraseptal and intraosseous - positive (!) aspiration is almost always observed, which is confirmed by the dissertation works of their colleagues [1, 3, 6].
This is one of the proofs of the vascular mechanism of intraosseous or additional anesthesia. The dentist does not take into account the dangers of vascular injection. We are not aware of studies of aspiration with these anesthetic techniques.
Assuming a vascular mechanism for intraligamentary injection, it is advisable to observe the relationship between positive or negative aspiration and the effectiveness of anesthesia. Of particular interest in this case are the lower lateral teeth - the most difficult for local anesthesia. The use of electrical testing is an important element for laboratory evaluation of pain management [11].
Our objectives were: 1) to investigate the frequency of aspiration test (AT) in IPA; 2) to study, using electrical testing, the depth of the ILA of the pulp of the lower molar with positive and negative aspiration.
Material and methods
A randomized, crossover study was performed on 36 volunteers - 17 men and 19 women - aged 19-24 years, practically healthy (ASA class I). After discussing the nature of the injection with each student, voluntary written consent to participate in the experiment was obtained. The study was approved by the ethics committee of the TGMA with further examination of the protocols.
For ILA, 4% solutions of articaine with adrenaline 1:100,000 and 1:200,000 were used.
ILA was performed on each subject by 1 operator (M.D.V.) using a QuickSleeper computer injector (Dental Hi Tec Cholet, France). Special intraligamentary needles with a length of 9 mm and a diameter of 0.3 mm Intralig-S (Dental Hi Tec) were used. The test object was the mandibular first molar (H6). Teeth with gingivitis, large restorations and endodontic treatment were excluded. The injector provided a constant injection rate of 1.0 ml MA≈102 s. Anesthesia was achieved using 2 classic injections - on the mesial and distal sides of the tooth, and in case of their insufficiency - another 1-3 additional injections [3].
Aspiration was created by reversing the syringe plunger for 5 s. Electroodontometry (EOM) was performed before anesthesia and after each injection. The effectiveness of anesthesia was assessed by the value of the pain sensitivity threshold of the pulp using an IVN-98 Pulpotest-Pro apparatus for electroodontodiagnostics (Kaskad, Russia) on an intact lower first molar. The threshold of pain sensitivity was determined in microamperes (μA) until the sensation of pain appeared. The criterion for the onset of pulpal analgesia was a threshold value of 100 μA, recognized in Russian endodontics as an indicator of pulp death or switching off its sensitivity [2]. Additionally, the second indicator of the depth of anesthesia was taken into account - maximum analgesia (complete anesthesia) - 200 μA.
Statistical analysis of the results was carried out using t and χ2 tests.
Results and discussion
ILA was successful on all 36 mandibular molars. It was achieved by several injections - from 1 to 5 (on average - 3.2), as well as by increasing the administered dose of anesthetic from 0.4 to 1.2 ml (on average - 0.7 ml). In 2 cases, anesthesia was achieved with 1 injection. With each effective anesthesia, 1 of the injections, and sometimes 2, were accompanied by positive aspiration. A positive aspiration was indicated by a thin stream of blood or pink coloration of the anesthetic solution in the cartridge (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Positive AT for IPA, carried out using a SleepеrOne computer syringe (“Dental Hi Tec”).
As a result, 34 (94.4%) of 36 successful IPAs had positive aspirations. Positive AT was observed in 50 (43.9%) of 114 injections, negative - in 64 (56.1%) injections (see table).
With positive aspiration (50 injections), pulpal analgesia developed in 42 (84%) cases, and in 35 (70%) - with a maximum EOM of 200 μA (complete switching off of sensitivity) and in 7 (14%) - with reduced thresholds - from 102 to 180 µA. When performing 8 (16%) injections, EOM indicators did not reach the level of pulpal analgesia, although they were relatively high - from 60 to 90 μA.
With negative aspiration (64 injections), EOM indicators in 96.9% of cases were below 100 μA. In 2 (3.1%) cases, however, after 3-5 minutes, pulpal analgesia was observed with EOM indicators of 100 and 110 μA.
In 2 cases out of 36 ILA, when pulpal analgesia occurred immediately after a single injection with a positive aspiration test, the EOM indicator was maximum - 200 μA.
Changes in average EOM indicators with the results of statistical processing depending on positive or negative aspiration are presented in Fig. 2.
Figure 2. Average pain threshold values (μA) with confidence limits (p=0.05) for EOM of the lower first molar before and after ILA in cases of positive or negative aspiration with 114 injections of 4% articaine with adrenaline.
The average EOM indicators with 36 ILA after 50 injections with positive aspiration were 171.6±7.9 μA, with negative AT after 64 injections - 38.2±3.4 μA (the differences between all EOM indicators are highly significant; p<0.001). EOM indicators during injections with negative aspiration significantly increased compared to the initial ones (before anesthesia), during injections with positive aspiration - compared to indicators before anesthesia and with indicators with negative aspiration.
In 34 (94.4%) of 36 cases, ILA of the lower first molar was almost always achieved with several injections (114 in total), at least one of which was with positive aspiration. The absolute positive success of the injections was achieved both through several injections and an increased dose of ILA (on average - 0.7 ml). Only in 2 (5.6%) of 36 anesthesia procedures in all injections was aspiration negative. This is contrary to S. Malamed's findings, repeated in several ADA guidelines. Positive aspiration during intraseptal anesthesia was observed by A.Zh. Petrikas in 1987, with intraosseous (Stabident Technic) - L.A. Yakupova in 2006 and with intraseptal - O.E. Efimov in 2011, which is reflected in their dissertation works [1, 4, 6].
Positive aspiration, as a rule, was combined with pulpal analgesia and, conversely, negative aspiration was almost always associated with insufficient pain relief.
The hypothesis according to which positive aspiration during IPA is a guarantee of an analgesic effect is confirmed by convincing data from the mathematical processing of the results of this study (χ2=7.75; p<0.01 and t test, p<0.001 - see Fig. 2).
This hypothesis indicates the presence of a leading vascular component in the mechanism of IPA, although not in all cases. The results of the observation carried out on 36 subjects are reliable; they cover 114 aspiration samples and are supported by electrical testing. These studies indicate a significant, but apparently virtual misconception S. Malamed [8, 9] made in assessing aspiration during intraosseous anesthesia. The consequences arising from this error are beyond the scope of this study and require serious discussion.
In 2 cases, pulpal analgesia developed in the absence of blood in the syringe (AT - negative) only due to injection pressure and diffusion (infiltration) of the anesthetic, i.e. without obvious vascular component. Conversely, in the other 2 cases, complete anesthesia almost under the needle was achieved with positive aspiration with 1 vascular injection. In other cases, there was a mixed mechanism of anesthesia: vascular plus diffuse. Nevertheless, the vascular component prevailed over the diffuse one: 84% versus 3%.
This logical explanation must take into account the anatomy of the anesthetized lower first molar, which consists of 2 roots with different sources of blood supply.
The absence of pulpal analgesia with a positive aspiration test in 8 (16%) of 50 injections in the presence of fairly high pain thresholds when exposed to electric current is probably due to the anesthetic reaching only 1 of the 2 roots of the first molar.
The use of EOM has proven to be a useful manipulation for obtaining reliable, controlled analgesia. In the clinic, when electrically tested anesthesia was insufficient, additional injections always solved the problem [3].
So, in the present study, the phenomenon of aspiration during intraligamentary injection was studied for the first time. Positive aspiration was observed in 94.4% of cases during PLA and is an indicator of effective pain relief; provides clear evidence for the vascular mechanism of IPA in the form of positive aspiration upon injection, which is directly related to its analgesic effect; with ILA performed with negative aspiration, in some rare cases it is possible to develop anesthesia of the dental pulp with some delay (3-5 minutes) of this effect and its decrease.
Carpule anesthesia in dentistry - what is it and features of the injector
4026
Anesthesia has become an integral part of dental treatment.
It is used not only for the peace and comfort of the patient, but also to facilitate the doctor’s work.
The process of improvement in dentistry concerns not only treatment and prosthetics, but also types of anesthesia. This article is devoted to this type of pain relief, carpule anesthesia - what it is and what is the principle of its action.
Signs of loss of drug properties
An anesthetic drug may become unusable not only due to expiration, but also due to non-compliance with storage conditions.
There are several signs that the drug has lost its properties and cannot be used:
- Damage to the integrity of the ampoule. Small cracks may occur due to improper transportation. Using carpules with defects can lead to their destruction at the time of injection;
- The solution has changed color or a precipitate has appeared. Ideally, the solution should be transparent. The appearance of impurities indicates a change in its chemical composition. This may occur due to the breakdown of the vasoconstrictor under the influence of heat;
- Presence of large bubbles. Small bubbles are always present in the solution due to the removal of oxygen during the manufacturing process. If the ampoules are strongly cooled during storage or transportation, bubbles larger than 2 mm in size appear and the rubber stopper may even be slightly pushed out. Such ampoules must be returned to the manufacturer;
- The appearance of rust on the carpule indicates a change in its chemical composition or an incorrect disinfection procedure.
If such signs are detected, it is strictly forbidden to use the carpule, since in addition to the lack of effect, an unexpected side effect may occur.
Carpule anesthesia in dentistry - drugs, technique
Today, carpule anesthesia in dentistry is used more often than any other, because it is convenient and safe. Both patients and doctors like this method of local anesthesia because it has numerous advantages. What is it, what are its features, and does carpule anesthesia have any disadvantages?
Description of the method
The method gets its name from one of the components of the kit required for anesthesia. A carpule is an ampoule containing an anesthetic solution. It is sealed and closed on one side with a metal lid, and on the other with a rubber stopper (piston). The carpula easily fits into a special syringe, which has a composite design:
- a hollow body into which the carpule is placed;
- a rod that produces pressure on the piston;
- adapter with thread for screwing on a disposable needle.
Needles for carpule anesthesia are very thin, but durable. These two properties make it possible to reduce pain in the patient during a puncture, and it is convenient for the doctor to manipulate the syringe if he suddenly needs to change the direction of the needle to cover a larger area of anesthesia.
The principle of operation of a carpule syringe is simple. An ampoule is placed in its body. The rod is set to the retracted position.
On the other side, a needle is screwed on, which simultaneously pierces the rubber stopper.
Pushing the plug with the help of a piston ensures the movement of the anesthetic along the needle to penetrate it into the depths of the tissue. As soon as the doctor stops pressing on the rod, the supply of solution stops.
Advantages and disadvantages
Young patients did not see the time when anesthetic solutions were prepared separately.
The doctor assessed the need for the presence of each component (anesthetic itself, vasoconstrictor, antioxidant) and mixed them in certain proportions. Then the solution was drawn into a regular disposable syringe, and an injection was made into the gum.
This required a lot of time, and the risks of mixing something incorrectly were high. And the needle was too thick, which caused pain to the patient.
Today everyone knows about carpule anesthesia in dentistry, because... We saw that this is a special device for performing local dental anesthesia quickly and safely. What advantages does this method have?
- No need to prepare an anesthetic . The doctor has a set of capsules with various compositions indicated on the label. Therefore, the dentist calmly selects the desired drug and injects it.
- Exact dosage . There are marks on the syringe rod that show the dentist how many ml of solution have already been injected.
- Sterility. The needle is disposable, and the solution for carpule anesthesia is enclosed in a sealed ampoule, so it is almost impossible to infect the patient.
- Minimum pain. The needle is also very thin, which allows for pain relief with minimal discomfort for the patient.
- Convenience for the doctor . The dentist can easily hold the carpule syringe and manipulate it freely, thanks to its ergonomics.
Carpule local anesthesia has only one drawback - its cost. The clinic spends a lot of money on purchasing cartridges, as well as on disinfecting syringes, so the patient has to pay for pain relief. But it’s not so expensive that you have to give up anesthesia altogether. The average cost is 200 rubles.
Types of syringes
For carpule anesthesia, initially only reusable metal injectors were used.
Surely many patients have seen these terrible syringes with three rings to support the dentist’s fingers: one at the end of the rod and two at the end of the body. Each injector is designed to provide carpule anesthesia for one patient.
After the procedure, the syringe is sent for disinfection, where it undergoes a number of mandatory steps: disassembly, cleaning, sterilization, etc.
Today, reusable metal injectors have been replaced by disposable plastic ones. They are produced in sealed bags, which are opened in front of the patient immediately before carpule anesthesia. The design of the plastic injector is exactly the same, but it is smaller in size and lighter in weight.
The peculiarity and advantage of disposable carpule syringes is their safety for medical staff. When working with a metal injector, the following often happens: the dentist removes the cap from the needle, administers anesthesia, then, when putting the cap on, misses and pricks.
Curious! A dentist who accidentally pricks his finger on a needle that he has just used for local anesthesia can instantly become infected with various infectious diseases: from hepatitis to HIV.
For plastic injectors, special needles are produced with an additional cap that protects the doctor from accidental microtrauma. This cap is easily pulled out after anesthesia and allows you to remove and then dispose of the needle without the risk of pricking yourself and becoming infected.
What is carpule anesthesia?
The name of carpule anesthesia is based on the principle of a syringe used to relieve sensitivity. The technique of pain relief remained unchanged.
A carpule syringe is a reusable metal device that has a body, a piston and a needle. The piston, unlike its disposable counterpart, cannot be completely removed backwards, and in the side of the body there is a recess for placing the cartridge. The carpula is a kind of ampoule with an anesthetic, hermetically sealed and having a metal cap at one end and a rubber stopper at the other.
The principle of operation is as follows: after placing the desired cartridge in the syringe, a disposable needle is screwed onto it, and the device is ready for use. The cartridge is inserted so that the metal plug is on the needle side, since it is pierced by its reverse end, and the rubber plug should be on the piston side. The movement of the rubber stopper by the piston ensures the movement of the anesthetic along the needle into the tissue.
Currently, the vast majority of modern dental clinics use such devices.