Indications and contraindications for topical anesthesia in dentistry
Indications for topical anesthesia include a variety of dental procedures in adults and children:
Uncomplicated caries - an anesthetic is applied to the tooth tissue and gums;- Increased sensitivity of teeth - the drug is rubbed into the bone base of the tooth;
- Treatment of pulpitis - a tampon soaked in an anesthetic is placed at the bottom of the carious defect;
- Preparation of adjacent teeth during prosthetics, as well as removal of splints, sutures, drainages;
- Extraction of baby teeth or molars with pathological mobility (for periodontal disease);
- Tartar removal - an anesthetic drug is applied to the gums and tooth enamel;
- Opening and drainage of purulent cavities under the mucous membrane;
- The presence of painful ulcerative and erosive lesions in the oral cavity - as a method of treatment;
- The planned further injection anesthesia is to relieve pain from the injection (preparatory stage).
In children, baby teeth respond well to the application of anesthetics due to their structure, therefore, in pediatric dentistry, terminal anesthesia is used for almost all types of treatment, as well as for tooth extraction. It does not frighten the baby and allows not only the little patient, but also the treating specialist to feel comfortable. The method is used in children after two years of age.
In addition to dentistry, topical anesthesia is used in general anesthesiology when installing an endotracheal tube, nasogastric tube, changing tracheostomies, while lidocaine remains the most popular agent.
Contraindications to superficial (terminal) anesthesia are cases of increased individual sensitivity to the components of the drugs, allergic reactions in the past to the active substance, and age under 2 years. Dicaine is not used in children under 10 years of age due to soy toxicity. These obstacles to the method are usually limited, since the drugs do not have any general adverse effects when the dosage is used correctly.
The safety of the method is high, but using it yourself, at home, is highly not recommended. Treatment of oral pathology with local anesthetics is possible only as prescribed by a doctor, under his supervision and in compliance with the exact dose of the drug used.
If there are contraindications to superficial anesthesia, specialists resort to infiltration or conduction techniques, injecting drugs directly into the tissue or into the nerve trunks during major interventions.
Side effects
Complications from the use of surface anesthetics are rare; they are possible if the rules of use are not followed. Most likely:
- local allergic reaction – itching, swelling. hyperemia;
- general allergic reaction - up to angioedema and anaphylactic shock (very rare);
- irritation of the respiratory tract - typical for sprays, aerosols, as well as when using anesthetics in dentistry;
- intoxication of the body when the dose is radically exceeded or the individual sensitivity of the body.
Attention! The physician is responsible for selecting and prescribing an appropriate surface pain reliever. It also regulates the use of the drug at home. Attempts to independently prescribe and use such compounds may provoke the above effects.
Preparations for terminal anesthesia
For topical anesthesia, the same substances are used as for other types of anesthesia, but they are enclosed in the form of a gel, ointment, spray and are contained in higher doses than in ampoules for injection.
Gel-based lidocaine, dicaine and promecaine, pyromecaine ointment, anesthesin in the form of a solution or ointment, which are widely available and not very expensive, are considered common. The drug of choice is lidocaine in spray form, which can be used in both adults and children. In some cases, the drug with anesthetic also contains antiseptic additives, flavorings, and dye. The latter are often added to anesthetics for children.
When placed on the surface of the mucosa, the drugs quickly penetrate 3-5 mm deep into the nerve endings and block the passage of nerve impulses through them, which is why sensitivity disappears after just a few minutes. Pain relief lasts about half an hour and affects both nerve trunks with blood vessels and dense bone tissue.
The agents used for topical anesthesia may differ in their mechanism of action:
- Anesthetic ointment, gel, spray eliminates the conduction of nerve impulses when applied locally (Platonov, Shinkarevsky, Hartmann liquid);
- Dehydration preparations remove water from the dentinal canals and thus eliminate sensitivity (carbonic acid salts);
- Preparations based on mineral components have a physiological effect , which eliminate the feeling of pain, fill the dentinal tubules and retain water in them, preventing its leakage (indicated for increased tooth sensitivity and pain);
- Cauterizing drugs are chemical compounds with acids that “glue” the dentinal tubules, but they are not used due to their strong damaging and toxic effects.
Cooling anesthetics, such as chloroethyl, are not currently used in dentistry due to the risk of their penetration into the respiratory system, as well as possible contact with overly sensitive teeth, which will cause severe pain.
Aerosols are not widely used due to the large spray area and difficulties with precise dosing. High doses of these drugs can cause intoxication if rapidly absorbed into the blood. With a prolonged freezing effect, children may bite the tissues of their cheeks or tongue, and adults most often experience subjective discomfort from prolonged anesthesia.
Anesthetics used through application contain lidocaine, tetracaine, benzocaine and other substances, but they can be produced under different names - perylene ultra, xylonor, kamistad and others. Spray with lidocaine for children has a fruity (banana, pineapple) taste.
Among the local anesthetics is propolis, which is a beekeeping product, but its widespread use does not allow its strong allergenic effect.
Diplene-LH
is considered a very popular means of local anesthesia in dentistry - a special film with analgesic and antiseptic properties for gluing to the mucous membrane. Contains chlorhexidine and lidocaine. The resorption of the film lasts up to 12 hours, so it can be left in the mouth after treatment.
Topex is a gel containing the anesthetic benzocaine. It is applied to the desired area for 1-2 minutes, after which anesthesia is achieved. Disilane is a benzocaine spray that provides pain relief for no longer than a quarter of an hour. It can be used in children under 5 years of age.
The listed drugs can be used not only in dentistry or for anesthesia of mucous membranes. More than a decade ago, the drug ESMA , capable of penetrating the skin and combining water solubility with lipid solubility, began to be used. The product contains lidocaine and prilocaine, mixed in equal proportions in a water-oil emulsion.
ESMA can be used in surgery, cosmetology and anesthesiology. The cream is applied to the skin under compress paper, left for 45-60 minutes, after which pain relief occurs to a depth of up to half a centimeter. The duration of such application anesthesia is 1-2 hours.
ESMA cream can be used for puncture and catheterization of blood vessels, circumcision, collection of skin flaps for transplantation and other operations. For pain relief, use up to 2 grams of cream for every 10 square centimeters of skin.
This drug should not be applied to mucous membranes, damaged skin, or to children under one month of age, and as a side effect, swelling, redness or blanching of the skin, and itching are possible.
In addition to the dentist, a cosmetologist can also offer this type of pain relief for a variety of cosmetic procedures. It does not lose its relevance in general surgery when carrying out some unpleasant procedures during general anesthesia.
Varieties
Today, there are many drugs for topical anesthesia, with effects of different nature and mechanism. Let us list the main groups of such funds.
Dehydration
The dehydration method, or dehydration, is a pain relief method, the effect of which is achieved by removing water molecules from the enamel and dentin, which are conductors of nerve impulses.
To implement this method, carbonates or bicarbonates of sodium, potassium, magnesium, as well as other salts with dehydration properties are used. This method is often used during professional teeth cleaning, as well as other minor manipulations affecting only enamel and dentin.
The disadvantage of this method is the low intensity of pain relief , but it is sufficient for superficial manipulations.
Cauterization
Cauterization is one of the first methods of superficial anesthesia. Cauterization is used to relieve pain in periodontal and dentin areas.
Cauterization preparations block tissue pores, thereby stopping the impact of the environment on the nerve endings.
Despite the rather good effect, the effect of cauterizing drugs did not last long. Subsequently, their use was abandoned due to the high toxicity and damaging effect that the drugs have on the enamel.
The main representatives of cauterizing anesthetics are nitric and carbolic acids, zinc chloride, and silver nitrate.
Preparations of physiological action
The principle of operation of physiological drugs is to block the transmission of impulses to nerve endings due to the specific properties of the composition.
In addition to the analgesic effect, such drugs have a therapeutic effect, which expands the possibilities of their use in treatment.
This group of drugs includes glycerophosphate, sulfidine, strontium and aspirin pastes. Their regular use for appropriate indications can reduce tooth sensitivity and restore enamel.
Local anesthesia
Local anesthetics can eliminate the conduction of peripheral nerve fibers. This is the most common type of local anesthesia and works quickly, effectively and predictably.
Lidocaine, Benzocaine, Tetracaine, and other concentrated anesthetics are used as drugs for the procedure.
Indications and restrictions
The technique is used mainly due to the patient’s high anxiety due to the injection for pain relief. This is especially true for young children.
In some clinics, topical anesthesia is used before injection anesthesia to increase patient comfort - this has a positive effect on the dentist’s work.
In addition, the technique is used in cases where the intervention occurs very superficially, or when the injection may be dangerous (for example, when opening purulent capsules, this type of anesthesia avoids the risk of spreading infection).
Other cases of application of topical anesthesia may include:
- treatment of gingivitis or stomatitis;
- removal of the neurovascular bundle of the pulp;
- professional teeth cleaning;
- fixation of orthodontic appliances or prostheses;
- pronounced gag reflex when taking impressions.
A limitation to the use of topical anesthesia is increased sensitivity to the drug (allergic reaction). In addition, drugs containing lidocaine are not used in patients under 10 years of age.
Application anesthesia in cosmetology
Cosmetology has been actively developing in recent years, and some methods of fighting for beauty, health and youth are being replaced by others, which are possible only under conditions of anesthesia, so the application of an anesthetic is often an excellent solution for both clients and specialists in beauty salons.
The anesthetic must penetrate intact skin, so it is important to create the correct concentration at the site of manipulation. The most popular topical drug is EMLA (ESMA), containing lidocaine and prilocaine.
An hour before the cosmetic procedure, cream is applied to the skin, during which time it numbs up to 3 mm of the skin depth. If deeper anesthesia is necessary (maximum half a centimeter), the effect of the cream can be increased. A prerequisite for the application of EMLA is an occlusive dressing that prevents the evaporation of liquid from the drug.
This cream is usually well tolerated and produces a minimum of adverse reactions. It is indicated for injection mesotherapy, correction of age-related changes in the skin of the face and body, contouring, administration of drugs based on botulinum toxin, and hair removal.
In addition to ESMA, Anestol, containing lidocaine, tetracaine and benzocaine, is also used in cosmetology. The anesthetic is quickly absorbed and provides a long-lasting analgesic effect (up to 2 hours). It should be applied a quarter of an hour before the procedure; no bandage is required. Anestol is indicated for tattooing, permanent makeup, mesotherapy, hair removal, etc.
The most powerful application of anesthetics in cosmetology is considered to be the drug Ane stop, containing amecon, lidocaine, prilocaine, benzyl alcohol and other components. The gel is applied for 15-20 minutes, after which it is removed, but is effective for up to 1 hour and penetrates to a depth of 5 mm. Indications for its use include injection facial plastic surgery.
In cases where a very rapid onset of anesthesia is required, xylocaine in an aerosol can be used, applied to the skin and giving an anesthetic effect after just a few minutes.
Which painkiller to buy
Release forms:
- In tablet form.
- Using special capsules.
- Suppositories.
- Injections and solutions for introduction into the circulatory system.
- Ointments.
- Gels.
- Sprays.
All drugs of this type can be divided into several types:
- Non-narcotic. The safest for the body. These include all analgesics. The main advantage was the insignificant effect on the nervous system in comparison with other group of drugs. In addition to eliminating pain, they can reduce the degree of inflammation of the damaged area.
- Narcotic.
Their main target becomes the central nervous system. The substances contained in such medications replace the feeling of discomfort with a state of euphoria. The effect occurs only on the receptors responsible for pain, without interfering with the activity of other mechanisms in the body. A person can continue to live in a given lifestyle, but with some degree of inhibition. With a long period of use of such drugs, due to the influence of the substances included in its composition, dependence may occur. - Antispasmodics are placed in a separate category due to the impossibility of classifying them either into the first group or into the second.
Their main goal is to combat spasms of various origins:
- In smooth muscles.
- When localized in the gastrointestinal tract.
- For genitourinary pain.
- And the biliary system.
When used appropriately, antispasmodics will prove to be more effective.
This drug group is most effective in the form of anesthetic injections. The most potent drugs are Ketorolac, Ketanov, Ketorol. Their active substances act directly on the source of pain. Medicines eliminate the inflammatory process, reduce swelling in the affected area, as a result of which the nerve fibers are released from the pressure of the soft tissues.
The most effective means:
- Ketorolac. It has antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. It is prescribed intramuscularly. The drug reduces pain and inflammation after surgery for a short period of time. The remedy is most often used for inflammation of the joints, pinched nerve roots, muscle pain, and to relieve pain in cancer.
- Ketanov. It is characterized by rapid pain relief, lowering body temperature and relieving inflammation. Most often, such pain-relieving injections are given after surgery, injuries, damage to bones and tissues. The duration of treatment should not exceed 5 days. The drug is administered intramuscularly only. The medication is contraindicated for bronchospasm, dehydration, problems with the digestive system, pregnancy, and peptic ulcers.
- Ketorol. The solution is administered intramuscularly for severe pain caused by the inflammatory process. In addition, a drug is prescribed to reduce swelling and hyperemia, as well as reduce high body temperature. The medication effectively relieves postoperative and post-traumatic pain, helps with neuralgia and myalgia. The drug is contraindicated for hemophilia, dehydration, severe renal and liver failure, and pregnancy. Can be purchased in pharmacies without a prescription.
- Diclofenac. The solution contains diclofenac sodium. The drug has antipyretic and analgesic effects. The medication by injection is prescribed for back pain, acute attacks of rheumatic diseases, osteochondrosis, arthritis and radiculitis. It is often used for diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which are accompanied by severe pain. Diclofenac is prohibited for bronchial asthma, gastric ulcers caused by helicobacter, hemophilia, pregnancy, individual intolerance.
Central action:
- Derivatives from glycerol: Meprotan, Prenderol, Isoprotan.
- On benzimidazole - "Flexin"
- Combined action – “Mydocalm”, “Baclofen”.
Such drugs, by affecting interneurons in the spinal cord (reducing their activity), reduce muscle hyperactivity, which allows them to be used not only for relaxation, but also for a wider range of functions.
Also, medications of this type can relieve spasms without stopping the body’s ability to breathe - this is a big advantage compared to other drugs.
Peripheral impact:
- Of an underpolarizing nature – “Arduan”, “Diplacin”, “Melliktin”.
- Depolarizing – “Ditilin”.
- Mixed type - "Dexonium".
They are able to influence cholinergic receptors located in the muscles, which helps with spasms and pain syndromes.
Applicable:
- Paralysis caused by tetanus.
- Convulsive muscle contractions.
- For anesthesia during surgical interventions.
Benefits of muscle relaxants:
- Complete immobilization and relaxation of the patient’s muscles - this allows operations of any complexity and duration.
- Thanks to such medications, artificial ventilation of the lungs became possible.
- The intubation procedure has been simplified.
- With artificial hypothermia, it prevents the occurrence of seizures, this is especially true for tetanus and rabies.
- It is used in therapy in the treatment of neurological diseases that are accompanied by muscle hyperactivity.
- Relieves pain in the lumbar region.
- Before abdominal surgery.
- When carrying out complex diagnostics.
- During electroconvulsive therapy.
- During anesthesia without disconnection from the natural respiratory process.
- During the recovery period after injury.
- Rehabilitation in the postoperative period following spinal surgery.
- For relief from intervertebral hernia.
Minuses:
- Decreased level of attention and concentration.
- Decreased blood pressure readings.
- Excessive excitability of the nervous system.
- Urinary incontinence at night.
- Reactions of allergic etiology.
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Conditions accompanied by seizures.
Large list of contraindications:
- Parkinson's disease.
- Kidney diseases.
- Alcoholism.
- Children under 1 year.
- Myasthenia.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Allergies and intolerance to the components included in the composition.
- Epilepsy.
- Psychological disorders.
- Pregnant and nursing mothers.
- Chondroprotectors
Drugs whose action is aimed at relieving inflammatory processes in joints and restoring cartilage tissues contain a combination of sulfate substances - chondroitin, hyaluronic acid and glucosamine.
These medications restore joint fluid, nourish the joint, preventing it from deteriorating, relieve pain and stop the development of the inflammatory process. The cartilage returns to a healthy state.
List of chondroprotectors:
- “Liquid prostheses” – intra-articular. The injection is injected directly into the joint. The most effective are “Giastat” and “Ostenil”. Even one procedure per year can provide improvement. “Argelon” and “Sinokrom” have not bad results. However, products of this type are used only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Intramuscular injection - "Alflutop" or "Glucosamine". 20 injections are enough and this will make the patient’s life easier. Read about which is better Rumalon or Alflutop here.
- In tablets, drugs are cumulative in nature and their effect becomes noticeable only after 6 months of taking the drug - these are “Teraflex”, “Dona”, “Arthra”, “Structrum”, Chondroitin Akos”, etc.
- In the form of lotions and creams. Their main action is aimed at reducing pain and relaxing muscles. For example, “Toad Stone” shows good results and has a natural composition. Chondroxide is very good.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that have a chondroprotective effect - “Chondrosamine”, “Chondartron”, “Stop Arthritis”, etc. They fight inflammation and joint stiffness in the morning.
Advantages:
- Reduced pain.
- Nourishes damaged cartilage and prevents its destruction.
- The tissue is restored.
- Swelling is relieved.
- Made from natural ingredients.
- There are almost no contraindications.
- Safety of use.
Flaws:
- High price.
- Low recovery and treatment speed.
- Long course.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
An effective treatment method without harmful effects on the body is the use of NSAIDs.
They come in three types depending on the purpose of use:
- Painkillers.
- Relieving fever.
- Reducing inflammation.
NSAIDs are not hormonal drugs, so the effect on the body is not so significant.
The mechanism of their functioning works in such a way that they block the production of a substance such as prostaglandin by stopping the release of the enzymes COX-1 and COX-2.
The anti-inflammatory effect is determined by:
- Reduced vascular permeability and, as a consequence, improved microcirculatory activity.
- Reducing the amount of inflammatory mediators - the main culprits in the occurrence of a destructive process.
Types and list of medications:
- Salicylates are the first representatives of this group. In modern practice, only Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid, is used from this class.
- Derivatives of propionic acid – “Ibuprofen”, “naproxen”, “ketoprofen” and others.
- Produced on the basis of acetic acid - “indomethacin”, “ketorolac”, “diclofenac”, “aceclofenac”, etc.
- COX inhibitors – 2 selective actions. Only two drugs are registered in Russia: celecoxib and rofecoxib. There are 5 of them in the world.
- Others are “meloxicam”, “piroxicam”, medications based on nimesulide, “mefenamic acid”.
- "Lysine monoacetylsalicylate."
- "Etodolac."
- Flurbiprofen.
- "Phenacetin".
- "Saridon".
- "Reoperine."
- "Baralgin."
- "Citramon - P".
- “Amidopyrine.”
- “Bystrumgel.”
- “Upsarin UPSA.”
- "Nise."
- "Nurofen".
- "Movalis".
- "Thrombo ACC".
- "Fastum."
- "Finalgel".
- "Ketorol".
Pros:
- High level of security.
- The toxicity level is lower than others.
- Does not cause addiction or dependence.
- When used in large dosages, there is a low likelihood of complications and side effects.
- Helps quickly.
Minuses:
- Due to the blocking of COX-1, the production of protective substances to eliminate the harmful effects of hydrochloric acid on the walls of the stomach stops. Because of this, gastrointestinal ailments and peptic ulcers may develop.
- Long-term use of NSAIDs can lead to impotence in men.
- Renal dysfunction.
- Long-term use develops photosensitivity, especially for piroxicam and diclofenac.
- Allergic reactions, bronchospasms, drowsiness, headache and weakness.
- Impossibility of use during pregnancy.
Technique of application anesthesia, its advantages and disadvantages
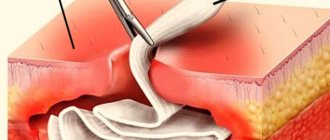
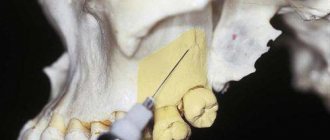
The technique of surface anesthesia is extremely simple: the product is applied to the surface of the mucous membrane or skin (ointment, gel, paste) or the tissue is treated with a spray. If it is necessary to numb the soft tissues of the tooth (pulp) or dentin during caries, apply a cotton or gauze swab with the drug to the desired area after drilling out the pathologically altered bone tissue of the tooth.
Before application, dry the anesthesia area as much as possible with a swab or cotton swab. To ensure the highest effectiveness of pain relief, the saliva drainage sites are covered with cotton swabs, and the tooth is covered with a latex sheet secured with a metal clip.
The effect of application anesthesia for large molars is lower than after injection infiltration of soft tissues, but the depth of anesthesia allows for comfortable treatment. In addition, one should take into account the different sensitivity of different teeth to the drug, which requires the use of different amounts of anesthetics.
The advantages of topical anesthesia include:
- Rapid onset of analgesic effect;
- Safety;
- No general toxic effect;
- Minimal number of adverse reactions and possibility of use in pediatric dentistry.
The disadvantages of the method include difficulties with dosing the drug, especially if it is in the form of a spray or solution, as well as a potential toxic effect when excess drug is absorbed through the mucous membrane. Insufficient depth of anesthesia does not allow the use of anesthetics for prolonged and too painful manipulations.
General instructions for performing superficial anesthesia
- ointment, cream or anesthetic solution must be applied to the desired area in several portions;
- for topical anesthesia, the total dose of the drug should be less than the dose used for infiltration anesthesia;
- when using the cream, there is no need to apply an occlusive dressing, although its use increases absorption and reduces the time for the onset of the effect;
- viscous lidocaine can be used as a stand-alone anesthetic or as part of a mouthwash solution (for rinsing and then spitting out);
- Iontophoresis enhances the effect of drugs for surface anesthesia, but the equipment for carrying out such a procedure is quite cumbersome and expensive. In addition, some patients reported discomfort associated with the effect of electrical current on tissue.