Degrees and clinical picture
Just one second is enough to damage the mucous membrane lining the oral cavity. Immediately after injury, symptoms of a palate burn appear. These include:
- feeling of unbearable burning sensation;
- edema;
- severe pain when touching the tongue;
- blisters;
- detachment of the mucous membrane;
- the presence of an unpleasant metallic taste in the mouth;
- pain while eating.
There are three degrees of palate burn:
- Characterized by mild symptoms. All clinical manifestations disappear on average within 4 days.
- The tissues become deformed and bleeding often develops. All this is accompanied by severe pain. Tissue restoration usually occurs after 2 weeks.
- Deep ulcers form on the mucous membrane, and the intoxication process progresses in the body. In this case, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Burns can be thermal, chemical, electrical and radiation. In the latter case, we are talking about methods of treating the respiratory tract. If you do not follow the rules of procedures and their duration, the likelihood of damage to the mucous membrane increases significantly.
As with any other burn, there are several stages of gum damage:
- At the first stage, there is slight redness and swelling of the damaged area, the pain is mild and intensifies with pressure.
- The second stage is accompanied by the formation of bubbles filled with liquid. They can have different shapes and sizes. After they burst, the patient experiences severe pain, burning and itching in their place. The pain is more intense.
- The third and most severe stage is characterized by the onset of tissue necrosis. There is multiple rupture of the bubbles, the pain is simply unbearable.
Each of these stages requires mandatory treatment, which is prescribed by a specialist. Independent measures taken in this regard can only aggravate the situation.
Treatment prognosis and possible consequences
Recovery time depends on how quickly first aid was provided, whether the treatment was chosen correctly and, of course, on the degree of damage.
Treatment results
Full recovery is possible if all rules are followed and the wound is properly cared for. We should also not forget that each case requires an individual approach and a full examination.
In a mild form, this takes about four days, and in a more severe form, up to two weeks, provided that all the recommendations received are followed.
Complications and consequences
Timely therapy and an established diagnosis in 80% of cases guarantee a complete recovery. If the damage is not treated in a timely manner, metastases may occur in 70% of cases.
Third-degree burns are especially difficult to treat, so their presence is fraught with some complications. Eg:
- general intoxication of the body (poisoning);
- tissue necrosis (death);
- the appearance of ulcers;
- presence of pus;
- bleeding
To prevent this kind of trouble, it is necessary to visit the dentist several times.
Drug therapy for severe burns
During the appointment, the doctor examines you and tells you how to treat a burned palate. The classic treatment regimen consists of the following points:
- Rinse the mouth with Miramistin 6 times a day.
- Treatment of the lesion with Lidocaine. You need to lubricate the sky no more than once every 8 hours.
- Spraying the mucous membrane with Chlorophyllipt spray. Repeat the procedure up to 5 times a day.
- Treat the burn with Methyluracil 5 times a day.
- Taking medications containing retinol, vitamins E and C.
Additionally, your doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures. The most effective are UV irradiation and electrophoresis.
Classification of oral cavity burns
Based on etiology, there are four forms of oral burns:
1. Thermal burn
. Occurs due to contact of hot drinks, steam or fire with the mucous membrane.
2. Electrical injury
. The main reason is a violation of the protocol for physiotherapeutic procedures.
3. Radiation burn of the oral cavity
. Develops as a result of exposure to ionizing radiation during radiation therapy of malignant neoplasms.
4. Chemical burn
. Occurs at the point of contact of the mucous membrane with chemical compounds: alkalis, acids, chlorine-containing substances.
How to relieve pain from a burn: tips and folk recipes
To relieve pain from a mouth burn:
- breathe through your mouth, the cold air will act as a distraction
- rinse your mouth with cold water
- eat ice cream or yogurt from the refrigerator
- If your tongue or lip is burned, sprinkle the damaged area with sugar and wait until it dissolves.
- suck a spoonful of honey in your mouth
- dissolve 5 drops of aloe juice in 0.5 teaspoon of water, dip a sterile bandage in the solution, apply a compress to the burned area
Ice cream can be used as a pain reliever for mouth burns.
Pharmacy medications help:
- Vitamin E capsules. Open the capsule and pour its contents onto the burn.
- Lidocaine 5%. Soak a sterile cotton swab in lidocaine ointment and treat the burns with the swab.
- Anestezin 5%. Dissolve it in a small amount of sea buckthorn oil.
- Novocaine 2% in ampoules. Use it in the same system as lidocaine.
Lidocaine ointment is used to relieve pain in mouth burns.
Traditional medicine recommends using the following remedies to treat this injury:
- Aloe. The aloe leaf is peeled and applied to the affected area. Good results can be achieved by simply chewing a piece of aloe several times a day. After this, you need to refrain from drinking and eating for about 15 minutes.
- It is recommended to treat the affected palate several times a day with a sterile cotton swab dipped in sea buckthorn oil or melted margarine. This procedure will relieve pain, speed up the healing process, and activate regeneration.
- Plantain is recommended for use on bleeding wounds. This plant has wound healing and antiseptic properties. The best effect can be achieved by chewing plantain leaves for several minutes.
- Rinsing with decoctions of chamomile, oak bark or sage will relieve inflammation, swelling, and speed up recovery.
A burn to the palate is considered a fairly minor injury, however, for a full recovery and to prevent unwanted consequences, it is important to carry out competent therapy. Recovery from this type of injury usually takes 1–2 weeks. You can avoid burns by following basic rules of caution when consuming hot foods and drinks!
Burn of the oral mucosa: causes and treatment
Burns
A burn is damage to the skin and mucous membranes that occurs when exposed to high temperatures or exposure to chemicals, radiation, or electricity. In everyday life, a burn to the palate occurs due to careless consumption of scalding tea or hot food. The mucous membrane is a delicate structure, it is easy to damage, but it quickly regenerates and is restored after a few days.
Causes and signs of palate burn
A burn to the oral mucosa occurs for a number of reasons:
- Drinking a hot drink (tea, coffee, cocoa).
- High temperature foods, abuse of garlic.
- Hot cutlery.
- You can get burned by inhalation fumes at high concentrations of medications.
- Contact with chemicals (acids, alkalis).
- Medicines if used incorrectly.
- In rare cases, a burn to the palate of the mouth is provoked by electric current or ionizing radiation.
Main features:
- An unpleasant burning sensation occurs.
- Intense pain appears.
- Blisters filled with liquid appear.
- The patient feels a metallic taste in the mouth.
Methods of treating burns of the mucous membrane and palate
An effective treatment for a burn on the palate is diet. The patient should receive liquid, pureed, pureed foods, cool or at room temperature. You should not eat sour or spicy foods. Fermented milk products (yogurt, kefir, sour cream) reduce inflammation and promote rapid cell recovery. It is advisable to use them daily.
Continue disinfecting procedures. Each meal should end with a chlorhexidine mouth rinse. Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic drug that accelerates wound healing and tissue regeneration.
The folk method is calendula solution. It has a similar effect (1 teaspoon per 200 ml of water). After rinsing, it is advisable to treat the burn area with a cotton swab with hydrogen peroxide.
This procedure should be carried out 2-3 times a day.
For severe pain, analgesics (aspirin, analgin) are used orally. Among medications, Cholisal has an effective analgesic and disinfecting effect.
Miramistin is suitable for rinsing the mouth. The popular drug tantum verde is a pain reliever. Aqualor is used to eliminate blisters. Panthenol ointment, derinat solution - restore mucous membranes. Vitamins with antioxidant properties A, C, E will help to heal the damage faster. Constantly lubricate the burn site, do not let the mucous membrane dry out.
Folk remedies cannot be ignored:
- Aloe. Its leaves are applied to the affected area of the body. Peel the sheet from the top layer and apply to the affected area. Chew aloe pieces throughout the day. After this procedure, do not eat or drink for 10-15 minutes.
- Tincture of calendula, chamomile, sage, oak bark will relieve inflammation and relieve pain.
- Treat the wound with sea buckthorn oil. It will reduce pain by activating healing and regeneration processes.
- Plantain leaves are used to heal wounds, for bleeding, and to disinfect the affected area of the body.
Further care and precautions
With proper care and adequate treatment, the first and second stage burns will go away in a couple of weeks. Damaged palatal tissue quickly recovers on its own, without outside intervention.
Third degree damage requires specialized care. Treatment in a hospital is mandatory. The sooner treatment begins, the less negative consequences there will be.
Inappropriately prescribed drug therapy can lead to intoxication of the body and sepsis.
Hot doesn't mean healthy. Burns to the palate occur in most cases due to inattention and carelessness. Here are a few simple rules for every day that will help you avoid it:
- Don't eat or drink while walking. Hot food and drinks cause injury and harm teeth and gums.
- Take only chilled food. 5 minutes will keep you healthy.
- Hide medications and household chemicals from children.
- Explain to your child the dangers of boiling water, hot objects, food, and drinks.
- Eliminate bad habits (smoking, alcohol). Vodka and tobacco smoke cause damage to the oral cavity.
It is always easier to prevent an unpleasant situation than to deal with its consequences later.
The article has been verified by the editors Link to the main publication
articles:
(2 5,00 of 5) Loading...
Didn't find suitable advice?
or see all questions...
Source: https://BezTravmy.ru/ozhogi/neba-rta.html
Rinsing the mouth with calendula tincture or decoction
Before treating a burn to the roof of your mouth, you need to make sure that it is first or second degree. As mentioned above, more serious injuries require medical attention.
Every first aid kit must have a drug such as Miramistin. This is a universal remedy that can help not only with burns. In addition, it is included in the treatment regimen for more serious mucosal damage.
Useful properties of "Miramistin":
- Anti-inflammatory. The active component stops the development of the pathological process and prevents the formation of exudate in the lesion.
- Healing. The process of tissue regeneration in burns is extremely long, the active substance helps to accelerate it.
- Antiseptic. The active component protects the mucous membrane, preventing infection.
Directions for use: point the nozzle at the sky and spray the product onto the burn twice. It is advisable to carry out the procedure after a meal.
The medicinal properties of the plant have long been recognized by traditional medicine. Calendula helps not only to eliminate painful sensations in a short time, but also to stop the inflammatory process.
If the palate is burned, adults are advised to rinse their mouths with a tincture based on this plant. To prepare, you need to take 100 g of pre-dried and crushed raw materials and pour it into a 0.5 liter jar. Fill the container with vodka without additives. Place the jar in a dark place for 2-3 days.
It is important to know that rinsing your mouth with undiluted product is unacceptable. This will inevitably provoke an even greater burn of the mucous membrane. How to dilute calendula for rinsing: add 1 tsp to 200 ml of water. tinctures, stir. Rinse your mouth with warm liquid as often as possible.
A decoction based on calendula is no less powerful. In addition, it can be used by children over three years of age. To prepare the decoction you need to take 1 tbsp. l. raw materials and fill it with 200 ml of water. Place the container on the fire. Cook for 10 minutes. After cooling, strain the product. Rinse your mouth as often as possible, preferably until the clinical manifestations disappear completely.
Drug treatment
Depending on the degree of damage to the mucous membrane of the throat, treatment will be prescribed. For 1st degree burns, treatment can be carried out at home, but for 2nd and 3rd degree burns it must be carried out in a hospital setting.
It is important to provide timely assistance to the patient:
- In case of a thermal burn, the patient should be given still water to drink. Ice cubes are allowed.
- In case of a chemical burn, the agent that caused the damage to the mucous membrane should be neutralized. If the burn is caused by acid, then you need to gargle with a baking soda solution. In case of an alkaline burn, rinse is carried out with a not very concentrated solution of citric or acetic acid.
- After this, the victim should rinse his stomach, because the possibility of getting a burn to the esophagus and stomach is not excluded. Next, drink a tablespoon of vegetable oil and consult a doctor. At the clinic, the doctor will provide the necessary medical care.
- If necessary, Analgin, Lidocaine, etc., as well as narcotic analgesics in the form of Promedol, Fentanyl, Naltrexone, etc., can be prescribed to reduce pain.
- It is recommended to use sedatives: Valoserdin, Relanium, Afobazol, etc. These drugs are used if the victim is in shock and has psychological disorders due to trauma.
- If the burn is deep, then detoxification therapy is carried out: Ringer's solution, glucose-saline solution, etc.
- To avoid secondary infection, antibiotics and sulfonamides are prescribed. Among antibacterial drugs, it is advisable to use fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and cephalosporins. They are prescribed for accompanying symptoms: fever, vomiting and nausea, etc.
- To relieve swelling, glucocorticosteroids are used: Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, etc.
- The throat must be gargled with antiseptic solutions: Anestezin, etc.
- To accelerate epithelization and tissue regeneration, Solcoseryl, Retinol, Aevit, Methyluracil, etc. are prescribed. If necessary, inhalations of drugs and herbal remedies are carried out.
Treatment of 2-3 degree burns should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, as the specialist prescribes drugs in a certain dosage.
In more severe cases, surgical intervention is indicated for throat burns. The operation is performed for ulcers, scars and serious deformities.
It is recommended to eat soft, pureed food warm. In addition, you should exclude foods that irritate the inflamed mucous membrane. The victim should reduce conversations to a minimum to avoid painful sensations
Traditional methods of treatment
For first-degree burns, you can use traditional methods:
- To stimulate the restoration of the throat mucosa, oils and herbal decoctions are used. Oils used include sea buckthorn, peach, and olive. Soak a cotton swab in oil and lubricate the damaged mucous membrane several times a day. These oils have a soothing and regenerating effect, which allows you to restore the mucous membrane in a short time.
- It is necessary to regularly rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile, yarrow, and oak bark. You need to take a tablespoon of raw material and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Leave to infuse in a thermos. You need to rinse your mouth with a solution at room temperature.
- To speed up wound healing, it is useful to use a decoction of oak bark. However, before use, you should definitely consult your doctor, as this remedy may reduce the effectiveness of the medications.
- For burns, you can use beaten eggs to lubricate the throat.
A throat burn in children cannot be treated using alternative medicine, as this can lead to an allergic reaction, swelling of the mucous membrane and, as a result, suffocation.
Who is most susceptible to burn injuries?
A burn in the palate can happen to anyone, but the following are more susceptible to it:
- cooks - they work with hot food, which can cause injury;
- automobile mechanics - such specialists are required to perform welding work; they may come into contact with heated parts;
- firefighters - come into direct contact with fire, which is always dangerous;
- people who smoke;
- children are extremely inquisitive and often do not understand what consequences certain actions may lead to;
- Busy people - due to a busy work schedule, they often eat in a hurry, which leads to injury.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the tubercles on the back wall of the throat
Classification
There are several types of burns:
- Thermal. Formed by close contact with hot liquid, boiling water, or hot appliances.
- Electrical. Quite often they occur under the influence of a lightning strike or when working with technical equipment.
- Chemical burns. It can be obtained by contacting with acid, alkali and other chemicals.
- Sunny. Formed when the skin is damaged. Most often this happens on the beach while sunbathing or in a solarium under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. They are similar to thermal burns.
There are 4 degrees of severity:
- Mild - accompanied by slight swelling and redness of the mucous membrane.
- Moderate - characterized by the appearance of blisters and gray plaque, burning acute pain and bleeding in the mouth.
- Intoxication - develops in the case of partial or complete necrosis of individual areas of soft tissue, accompanied by the formation of deep ulcers in the mouth, signs of intoxication.
- Heavy - expressed by charring of tissues. At stage 4, you cannot do without urgent medical care in intensive care conditions.
Taking into account the factor of impact on the skin, a burn of the mucous membrane in the mouth can be:
- thermal - when injured by steam, boiling water, hot tea, food,
- chemical - in case of contact with acid or alkali, which can cause serious damage to the respiratory tract.
Treatment with dental gels
Currently, the pharmaceutical market offers many products that accelerate the healing of damaged mucosa. One of the most effective medications for burns is Asepta gel. This is the drug most often prescribed by dentists. It is intended for the treatment of the oral mucosa. The active component of the gel is propolis, which has a number of healing properties.
The drug "Asepta" must be applied in a thin layer to the damaged areas of the mucous membrane. Immediately before treatment, it is recommended to dry the pathology site with a cotton swab. This significantly accelerates the penetration of the active component into the tissue. The drug should be applied three times a day.
Many mothers are concerned about the question - how to treat a burn of the palate in the mouth of young children? Most drugs are not recommended for use in children. An exception is the Cholisal gel. This is a universal remedy that can relieve painful sensations in a short time. This is especially important, since after receiving a burn the child experiences severe discomfort while eating.
According to the instructions for use, the “Cholisal” dental gel should be squeezed onto a clean finger. The strip of the product should be 0.5 cm long. Then the drug must be carefully rubbed into the area of damage to the mucous membrane.
Types of burns
The reasons for the appearance underlie the classification of gum burns. These include high temperatures and chemicals (alcohol, alkalis). A separate group is damage caused by medications - arsenic paste, phenol, formaldehyde, silver nitrate, some lotions with medications and analgesics. The cause of the condition may be improper resorption of antiseptics with an additional analgesic effect for sore throat or sore throat.
In pediatric practice, burns caused by accidental ingestion of household chemicals are common.
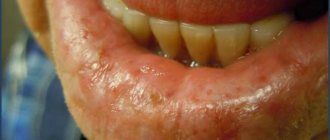
Thermal burn
This is the most common reason for visiting clinics, which is caused by hot coffee and tea or the first dish.
In this case it is observed:
- severe redness of the mucous membrane;
- burning;
- discomfort.
After some time, the burned area becomes rough, bursting blisters of different diameters appear on the gums, which turn into open, deep wounds. The whole process is accompanied by constant painful sensations, which intensify when the surface comes into contact with food or water.
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, swelling, darkening of the gums, bleeding, and necrosis occur.
Chemical burn
If this type of damage occurs, the help of a dentist is necessary.
A chemical burn occurs when potent substances enter the oral cavity:
- alkalis;
- acids;
- metal salts;
- kerosene;
- vinegar;
- homemade tinctures;
- technical alcohol and other substances.
Accidental contact may occur in the workplace. If parents do not comply with safety precautions, the baby may drink unknown lotion or household chemicals.
Another way of causing damage is when the dentist violates the dental treatment technique when using active chemicals (arsenic, phenol, bleaching agents).
This form of burn can lead to dangerous complications: the substances cause rapid development of tissue necrosis and the formation of deep wounds. They also enter the esophagus and stomach, where they can cause symptoms of poisoning, exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases, and internal bleeding.
Symptoms of chemical exposure to gums:
- itching;
- severe sharp pain;
- swelling and blackening of tissues;
- blisters (not always).
Alcohol burn
This is a type of chemical form of damage that occurs as a result of rinsing with alcohol solutions, using lotions, and drinking industrial alcohol. If it occurs, the help of a specialist and gastric lavage are required.
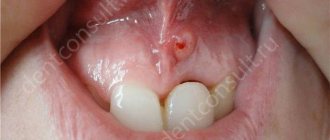
Arsenic burn to gums after dental treatment
If a tooth is filled carelessly or unprofessionally using arsenic, the substance may come out through the holes. As a result, arsenic causes gum burns and mucosal injury.
This creates:
- complaints of pain in the mouth;
- tissue death;
- subsequent destruction of bone cells.
This form of exposure does not always manifest itself immediately, so it is necessary not to neglect regular visits to the dentist to examine the oral cavity.
What does it come from?
A burn of the palate is damage to the mucous membrane, which can be caused by drinking hot liquids or eating high-temperature foods. Even hot cutlery or steam can burn if inhaled carelessly.
You can get injured if you carelessly handle alkalis, acids, or take some potent medications. In everyday situations, for example, if you burn yourself with hot tea or food, damage to the palate occurs 1 and 2, much less often, 3 degrees.
How does it manifest?
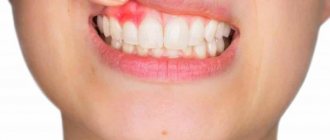
A burn on the palate causes sharp pain in the mouth and may be accompanied by the following clinical manifestations:
- Swelling;
- Burning;
- Redness of the mucous membrane;
- The appearance of a specific metallic taste.
The person has difficulty swallowing and has difficulty eating and drinking. More severe lesions are accompanied by detachment of the mucous membranes, the appearance of specific blisters, and pronounced pain. In such situations, it is necessary to take the victim to the hospital as soon as possible after first aid, where he will be prescribed an adequate, effective therapeutic course.
Classification of a burn to the palate in the mouth, how to treat it and traditional medicine
When a burn of the palate occurs in the mouth, how to treat it and how to relieve swelling, burning, and get rid of blisters, not everyone knows.
If first aid is provided correctly in a timely manner, this will help minimize complications and improve the condition of the victim.
For minor burns, the main treatment is the use of local regenerating ointments and gels; in severe cases, hospitalization is required.
Causes of burns and risk groups
Most often, a burn to the roof of the mouth occurs when consuming hot food or drinks.
Less popular reasons include:
- Damage from chemicals: acids, alkalis.
- Use of certain medications.
- Irradiation.
- Exposure to steam. This includes inhalations, for example, over boiled potatoes.
- Action of electric current.
Most susceptible to burns:
- Cooks. Since they have to constantly taste cooked food.
- Firemen.
- Smoking people.
- Children. They can either pull a hot cutlet into their mouth or a burning match.
Also at risk are people who always have breakfast in a hurry, which due to lack of time leads to drinking hot tea or coffee.
Classification of palate burns
- Thermal. More often they occur in everyday life when consuming hot foods and drinks.
- Chemical. Occur under the influence of acids and alkalis. Can be very dangerous.
- Obtained by quartzization.
Tube-quartz is common in pathologies of the upper respiratory tract. If the procedure is performed incorrectly or the heating time is exceeded, you can get a burn on the palate .
Separation by severity
Depending on the type of burning object or substance, as well as the time of exposure and aggressiveness of the provocateur, there are 3 degrees of severity of palate burns:
- In addition to swelling of the mucous membranes, a slight burning sensation is observed. The treatment is short-term, about 5 days.
- Plaque forms on the mucous surface, tissues are deformed, pain, severe swelling, bleeding, blisters are observed, and body temperature rises. Therapy may take from 10 to 20 days.
- Following intoxication of the body, large deep ulcers appear. Urgent medical attention is needed here.
In severe cases, the tissues become charred and can no longer be regenerated.
ethnoscience
Home treatment is indicated only after consultation with a dentist and stabilization of the patient’s condition. That is, traditional therapy is not suitable for first aid, but can be used at the stage of wound healing. 2nd and 3rd degree burns must be treated only in a hospital setting.
For mild damage, the following help relieve inflammation, swelling and heal tissue:
- Calendula infusion. 1 teaspoon of herb is poured into 250 ml of boiling water and left for 30-45 minutes. After straining, rinse the mouth up to 5 times a day.
- Aloe juice. The fresh leaf is picked, washed and cut. At the site of juice release, apply to the affected area and hold for 10-15 minutes.
- Sea buckthorn oil. It is used only after the patient’s condition has been stabilized to improve tissue regeneration; it is contraindicated on the first day. They lubricate the sky up to 4 times a day.
- Egg white. It is drunk in small sips to cool tissues and relieve pain. You can only use eggs from healthy domestic chickens; it is better not to experiment with store-bought eggs.
Complications
The global nature of the consequences depends on the severity of the injury, the correctness and speed of first aid.
If the burn is more severe than second degree, the patient can expect:
- General intoxication.
- Temperature.
- Tissue necrosis.
- The appearance of ulcers.
- Bleeding in the affected area.
- Accumulation of pus at the site of the outbreak.
- Severe swelling. If the swelling progresses, affecting new tissues, then when the process reaches the larynx, the person may suffocate.
What not to do
If the palate is damaged, then for quick and high-quality healing it is necessary to exclude all provoking factors:
- Soda.
- Sour, salty and sweet dishes.
- Cold, hot dishes and drinks.
- Dry food: crackers, chips, cookies.
Under no circumstances should you:
- Scratch the affected area.
- Use home methods without consultation with your dentist.
- Putting any objects into the oral cavity. This may cause infection.
- Pop blisters.
- Treat the affected area with alcohol-containing mixtures.
Prevention
To avoid burns to the oral cavity, and in particular the palate, it is necessary to avoid hot foods and drinks, reduce the influence of chemicals, and eliminate bad habits. It is important to explain to your child the rules for handling flammable and traumatic objects. It is also advisable to lock up all household chemicals if there are small children in the house.
When taking medications, you must carefully study the instructions, as burns can occur if the medication is used incorrectly.
A burn to the palate is considered a common household injury. In this case, the lesion is shallow and goes away in a matter of days. Much less common are 2nd and 3rd degree burns, when a person cannot do without medical care.
To minimize the occurrence of complications, it is necessary to provide assistance to the victim correctly and in a timely manner.
To prevent burns, it is important to follow safety precautions when working with chemicals and not to consume hot food or drinks.
Source: https://mymedic.clinic/termicheskie/ozhogi/ozhog-neba-vo-rtu-chem-lechit.html
Preventive actions
To prevent palate burns, you must follow simple rules:
- Don't eat on the go. Rushing increases the risk of putting excessively hot food or drinks into your mouth.
- You should not eat freshly cooked food straight from the stove. It is better to wait 10-15 minutes until it cools to a comfortable temperature.
- Medicines and household chemicals should be kept in a safe place, out of reach of children.
- It is advisable to give up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol.
- It is imperative to conduct preventive conversations with children and explain to them the dangers of boiling water, fire and any hot objects.
With the right approach to treatment, a burn in the palate does not pose a serious danger. This type of injury responds well to treatment using pharmaceutical and folk remedies.
What to do if you are burned by tea
A burn to the palate is a common oral injury caused by high temperatures. What to do if the palate is burned, and what treatment does the victim need?
How to treat a burn in the palate of the mouth: folk and pharmacy remedies
A burn to the palate is one of the most common household injuries. Most often, children get it through negligence. Also at risk are adults who are accustomed to drinking and eating on the go due to a hectic schedule.
In most cases, people get burns to the palate from boiling water (too hot tea, coffee, etc.) and food.
Less commonly, injury is a consequence of contact of the mucous membrane with chemical compounds, aggressive components of medications and electric current.
Source: https://geraklionmed.ru/chto-delat-pri-ozhoge-chaem-neba/
Sea buckthorn oil against burns
This product has a number of useful properties. Sea buckthorn oil for burns helps relieve the inflammatory process and eliminate pain. In addition, the product has antimicrobial and biostimulating effects.
Sea buckthorn oil is used in almost all branches of medicine. This is due to its powerful healing properties. According to reviews, after using it, burn symptoms disappear after 2 days. To do this, you need to lubricate the affected area with a clean cotton pad three times a day.
Burn degrees
There are four degrees of burns. The approach to treatment depends on how severe the consequences of the injury are. With the first degree of damage (for example, a burn to the oral mucosa with tea), redness and slight swelling appear on the tissues. The pain is minor. This type of injury goes away on its own within 3-4 days.
In the second degree, small blisters appear on the mucous membrane. When they burst, the surface becomes ulcerated. The pain is severe, there is plaque and bleeding on the mucous membrane. Treatment is required for 2 weeks.
The third degree of burn is characterized by damage in the deep layers of tissue. Partial mucosal necrosis is diagnosed. Scabs and ulcers appear that bleed and hurt. This injury heals within 2 months.
In the fourth stage, the affected tissues die. This process also affects nerve endings. For this reason, the patient may not feel pain. This type of injury is extremely rare.
Prevention measures
Precautionary measures are very important, since most often getting burns occurs due to one’s own carelessness and haste. Particular attention must be paid to children, since due to their age they may not understand everything.
Explain to your child what he can do, what he can’t do, and what the consequences of his pranks are. You should also remove from sight all dangerous medications and chemicals that your baby might get their hands on.
When serving freshly prepared food and drinks, you should ensure they are safe. Eating food in a calm environment will not only keep you safe, but will also promote normal digestion.
Despite the fact that a burn to the palate is very common and occurs quite often, it can still be avoided. To do this, you just need to take precautions. But if it so happens that you have received damage, do not panic and try to remember what your actions should be.
More often than not, a burn to the palate is a simple carelessness caused by the consumption of hot foods and drinks. Prevention measures are simple:
- keep medicines, chemicals, hot foods away from children,
- explain how dangerous a burn from boiling water or hot food is and what consequences it can lead to.
The mucous membrane in the mouth is vulnerable and delicate, but quickly recovers if you approach therapy correctly and in a timely manner.
What not to do
If the palate is damaged, then for quick and high-quality healing it is necessary to exclude all provoking factors:
- Soda.
- Sour, salty and sweet dishes.
- Cold, hot dishes and drinks.
- Dry food: crackers, chips, cookies.
Under no circumstances should you:
- Scratch the affected area.
- Use home methods without consultation with your dentist.
- Putting any objects into the oral cavity. This may cause infection.
- Pop blisters.
- Treat the affected area with alcohol-containing mixtures.
Severity
Burns of the oral mucosa are divided into thermal and chemical injuries and are classified into 3 main groups:
- The mildest degree, accompanied by redness and slight swelling. The victim does not suffer from severe pain, there is a slight burning sensation and discomfort that lasts up to 4-5 days;
- In the second degree, a whitish coating appears and some skin defects are observed. In areas of intense contact, there may be bleeding and body temperature rises. General malaise, soreness and other symptoms last for about 14 days.
- The next degree is characterized by a more severe course of symptoms. In this case, a burn to the oral cavity is accompanied by severe intoxication of the body, deep scabs are formed that last up to 2 months. At the sites of contact with the irritant, ulcers form that constantly bleed.
The consequences of damage to the oral cavity can be diseases such as sepsis, laryngitis, pneumonia.
Experts distinguish several degrees of severity of mucosal burns:
- First. It is characterized by the development of mild swelling, accompanied by a slight burning sensation. With such a burn of the gums or palate, all unpleasant symptoms go away on their own within a few days.
- Second. A specific plaque appears in the oral cavity, the mucous membrane becomes deformed, and the victim complains of severe pain. Tissues bleed, body temperature decreases. Such burn injuries heal no earlier than in two weeks.
- Third. The oral cavity is particularly severely damaged, resulting in deep ulcers. Very often there is general intoxication of the body. These are the most severe injuries that necessarily require emergency care and special treatment in a hospital setting.
Burns of the palate are also divided based on the causes of their occurrence:
- Thermal. This is the most common type of such injuries in everyday life. Damage can be caused by boiling water, hot drinks or food entering the oral cavity.
- Chemical. Occur after exposure of the mucous membrane to acids or alkalis. At home, such a burn can be caused by vinegar or ammonia. These injuries are very dangerous and require immediate medical attention.
- From using a quartz tube. This is a method that is used to treat respiratory diseases. If the procedure is not followed, there is a high probability of injury.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Tnch on the root of the tongue
Therapy
The doctor will tell you how to treat the burn in the future. Among the general measures, it is necessary to note the dietary requirements. Food should have gentle characteristics so as not to aggravate the condition: crushed, warm, without spicy, sour and salty foods
This is extremely important for rapid tissue healing. Medicines used:
- Local anesthetics (trimecaine, lidocaine, anesthesin).
- Antiseptics (chlorhexidine, furatsilin).
- Anti-inflammatory (Dimeskid, Citral).
- Regenerative (methyluracil, Solcoseryl, Cigerol).
- Proteolytic enzymes (trypsin, chymopsin).
- Oils (sea buckthorn, peach).
- Vitamins (Aevit, Carotilin).
As a rule, medications are used in the form of ointments, gels, rinses or applications. The patient's severe general condition requires infusion and detoxification therapy, and in case of pronounced local changes, surgical intervention is required. Necrotic tissue is excised and sutured. In case of extensive defects, oral plastic surgery is used.
Burns of the oral mucosa are a fairly common injury. They arise not only from hot food, but can develop upon contact with other aggressive substances and factors. Timely first aid and active qualified treatment are the main aspects that ensure recovery and recovery after burns.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The reason is the effect on the mucous membrane of high temperature during accidents at home and at work.
Thermal damage can occur due to careless use of the electrocoagulator, during electrophoresis, or ingestion of too hot food. The degree of damage depends on the temperature and duration of exposure; the burn can be limited or diffuse, accompanied by the formation of an area of hyperemia or blisters before the development of extensive deep tissue necrosis
Reactive inflammatory changes can spread beyond the damaged area. Secondary infection complicates the course and slows down epithelization.
Pain is felt at the moment of exposure to the stimulus, which quickly passes. Therefore, anamnesis is crucial in diagnosis. Then pain appears when exposed to any irritants, talking, eating, and even at rest. Hyperemia, edema, blisters or superficial painful erosions that form when the blisters are opened are objectively determined. In more severe cases, an area of necrosis is identified, which can range in color from gray-white to dark brown.
Diagnostics
Based on the collection of anamnesis and objective data.
Treatment of oral burns
Applications of painkillers (0.5-1% lidocaine solution, 0.5-1% novocaine solution, 2-4% pyromecaine solution or pyromecaine ointment), treatment with antiseptic agents of low concentrations and physiological temperature are used. Foam aerosols are widely used. Since the beginning of epithelization, keratoplasty applications have been used. If there is a focus of necrosis after its rejection, the same treatment is carried out as for a decubital ulcer.
For chemical burns
In case of careless contact with various household cleaning substances or medications, you must act strictly depending on the agent that caused the burn. We provide a list of effective measures to eliminate symptoms in the table.
| Substances | What to do? |
| Acids | The wound is treated with a 2% soda solution. After this, you can lubricate the surface with ammonia at a concentration of 0.5% |
| Hydrofluoric acid | It is necessary to wash the affected area with a special emulsion of magnesium oxide and water or glycerin |
| Alkaline compounds | Apply to the injured area with a 2% solution of acid (citric or acetic) |
| Lime (not slaked) | It is necessary to lubricate the palate with a generous layer of fat. It is strictly forbidden to treat it with water |
| Herbicides and pesticides | To clean the surface you need ethyl alcohol |
If in the case of a thermal burn in most situations you can cope with your own efforts and quickly restore the structure of the mucous membrane, then if you receive chemical injuries, you should definitely call an ambulance.
Etiology
The causes of burns to the throat mucosa are divided into two large groups: chemical and thermal.
- Chemical burns to the throat are a serious problem, the main cause of which in domestic conditions is alcohol or certain medications. Treatment of tonsillitis with iodine solution or alcohol tinctures can lead to a chemical burn of the throat mucosa. Iodine is an aggressive chemical that can cause serious tissue burns. "Lugol", "Yox" - medicines prepared on the basis of iodine. The use of these drugs in the presence of severe pharyngitis or tonsillitis can result in a burn of the mucous membrane. Specific substances that cause chemical burns include: citric acid, vinegar, ammonia, soda, acetone, acids and alkalis, ethyl alcohol. A burn of the larynx, accompanied by pain and burning, can be caused by the reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus during gastritis with high acidity. Acids cause coagulation of muscle proteins and the formation of a dry scab, which is an obstacle to further penetration of the chemical. Alkalis have a more aggressive effect on the laryngeal mucosa. They dissolve proteins. In this case, wet necrosis develops, allowing chemicals to penetrate inside.
- Thermal burn of the larynx occurs when consuming hot food and boiling water, as well as when inhaling hot air, for example, during fires. Many burn blisters appear on the oral mucosa. At the same time, the victim develops vision problems, general health worsens, and the functioning of internal organs is disrupted. This is a milder form of pathology compared to chemical damage to the laryngeal mucosa, which is associated with short-term exposure to hot substances and their rapid neutralization with cool water.
Possible reasons
There are many factors causing such damage:
- Hot food;
- Oral burn from boiling water;
- Vapors (hot, toxic);
- Medicines, mucosal burns with Chlorhexidine;
- Chemical reagents;
- Application in the treatment of liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction);
- Burn after dentist;
- Sometimes not only hot foods cause injury, but also excessively cold ones;
- Burns to the oral mucosa with alcohol or strong drinks.
There are quite a few reasons; by identifying a specific one, you can select an effective and high-quality treatment for the damage.
Thermal burn
According to statistics, thermal burns of the oral mucosa are common.
It occurs in both adults and children under the influence of high or low temperatures. Often the cause of such injury is contact with boiling water or hot objects. For example, a person may drink very hot tea. Thermal burns can range from mild to quite serious. The consequences of exposure to high temperatures can manifest as redness, swelling, and hyperemia. In some cases, ulcers and erosions appear. Moreover, similar consequences occur when contacting cold objects. In most cases, children suffer this type of injury. In winter, they touch the icy metal with their lips or tongue. This leads to burns.
Serious consequences of thermal damage to the oral mucosa can include superficial tissue necrosis and hemorrhages. Dystrophic changes may also appear. To reduce pain and prevent the development of negative consequences, a person needs to provide first aid.
Emergency help
Diagnosis of gum burns is differential. It is important to determine the type of lesion, on which subsequent prescriptions of therapeutic procedures will depend.
First aid:
- In case of thermal injury, it is necessary to give the person an anesthetic (Analgin, Tantum Verde) or cold water, which he should drink in small sips to relieve pain.
- For chemical treatment, you need to clean the affected area, rinse with warm soda solution (1 teaspoon per glass).
- In case of damage caused by alkali or ammonia, you should rinse your mouth to neutralize the substance with vinegar (7%) diluted in water and lemon juice in a ratio of 1:7.
- If you are burned by sulfuric or hydrochloric acid, you need to rinse your mouth with a soda solution (a teaspoon of soda per glass of water).
- If you are affected by alcohol (ethyl, medical), you need to rinse your mouth with warm, clean water or an isotonic solution (sodium chloride).
If the pain is severe, you can give the victim a drink of raw egg white. In case of a chemical burn, do not hesitate to call an ambulance and see a doctor. A particularly dangerous condition is considered to be one in which there is a putrid odor from the mouth, bloody vomit, and pain that does not go away for 2-3 days.
Burn of the palate of the mouth: how to treat the mucous membrane - folk and pharmacy remedies
A burn injury to the oral cavity leads to swelling, burning, and the formation of painful red blisters. The integrity of tissues is compromised. It is better to prevent a burn to the roof of your mouth than to treat its consequences.
To do this, you need to avoid exposing soft tissue to provoking factors - hot food and drinks. The main treatment is local (gels, ointments), although in severe cases the process may drag on indefinitely.
Clinical manifestations
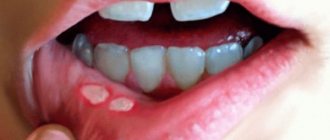
Just one second is enough to damage the mucous membrane lining the oral cavity. Immediately after injury, symptoms of a palate burn appear. These include:
- feeling of unbearable burning sensation;
- edema;
- severe pain when touching the tongue;
- blisters;
- detachment of the mucous membrane;
- the presence of an unpleasant metallic taste in the mouth;
- pain while eating.
There are three degrees of palate burn:
- Characterized by mild symptoms. All clinical manifestations disappear on average within 4 days.
- The tissues become deformed and bleeding often develops. All this is accompanied by severe pain. Tissue restoration usually occurs after 2 weeks.
- Deep ulcers form on the mucous membrane, and the intoxication process progresses in the body. In this case, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Burns can be thermal, chemical, electrical and radiation. In the latter case, we are talking about methods of treating the respiratory tract. If you do not follow the rules of procedures and their duration, the likelihood of damage to the mucous membrane increases significantly.
Who is most susceptible to injury?
Most often this type of injury occurs:
- Cooks . The work involves direct contact with hot dishes, tasting them and quickly completing them.
- Car mechanics . Sometimes this profession requires handling welding, hot parts and other equally dangerous objects.
- Firemen . When going out on calls, you are always exposed to danger.
- Smokers . Damage from cigarettes is possible.
- Children . Due to ignorance of some things, they do not understand what consequences their actions may have.
- People with busy schedules. They eat food in a hurry due to lack of time.
First aid
If you experience symptoms of a first or second degree injury, there is no need to panic. In such situations, you can do without medical intervention. But information on how to treat a third-degree burn of the palate in the mouth should be provided exclusively by a specialist (combustiologist or dentist).
If you receive an injury of any severity, you must provide first aid to yourself or the victim. The duration and success of treatment directly depends on the timeliness of these activities.
First aid algorithm:
- The wound must be disinfected. To do this, apply a cotton pad generously soaked in hydrogen peroxide to the palate.
- Take cold water into your mouth and hold it until it warms up. It is advisable to repeat this action until the burning sensation is completely relieved. Contrary to popular belief, it is strictly forbidden to use food as a cooling agent. This is fraught with infection.
Further actions directly depend on the type of burn. In case of thermal injury, you must take an analgin tablet. In case of a chemical burn, the affected area should be washed with a soda solution (1 tsp per 200 ml of warm water).
If the mucous membrane is damaged by ammonia or alkali, it is necessary to rinse the oral cavity with a weak solution based on vinegar and water, prepared in a ratio of 1 to 7, respectively.
If the injury is caused by medical or ethyl alcohol, you need to wash the lesion with an isotonic solution.
Preventive actions
To prevent palate burns, you must follow simple rules:
- Don't eat on the go. Rushing increases the risk of putting excessively hot food or drinks into your mouth.
- You should not eat freshly cooked food straight from the stove. It is better to wait 10-15 minutes until it cools to a comfortable temperature.
- Medicines and household chemicals should be kept in a safe place, out of reach of children.
- It is advisable to give up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol.
- It is imperative to conduct preventive conversations with children and explain to them the dangers of boiling water, fire and any hot objects.
With the right approach to treatment, a burn in the palate does not pose a serious danger. This type of injury responds well to treatment using pharmaceutical and folk remedies.
Drug therapy for severe burns
During the appointment, the doctor examines you and tells you how to treat a burned palate. The classic treatment regimen consists of the following points:
- Rinse the mouth with Miramistin 6 times a day.
- Treatment of the lesion with Lidocaine. You need to lubricate the sky no more than once every 8 hours.
- Spraying the mucous membrane with Chlorophyllipt spray. Repeat the procedure up to 5 times a day.
- Treat the burn with Methyluracil 5 times a day.
- Taking medications containing retinol, vitamins E and C.
Additionally, your doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures. The most effective are UV irradiation and electrophoresis.
Types and degrees
In medical practice, there are several degrees of thermal damage to the oral mucosa, in particular the palate:
Source: https://osp-sakhalin.ru/rotovaya-polost/ozhog-neba.html
Classification
There are 4 degrees of severity:
- Mild - accompanied by slight swelling and redness of the mucous membrane.
- Moderate - characterized by the appearance of blisters and gray plaque, burning sharp pain and bleeding in the mouth.
- Intoxication - develops in the case of partial or complete necrosis of individual areas of soft tissue, accompanied by the formation of deep ulcers in the mouth, signs of intoxication.
- Heavy - expressed by charring of tissues. At stage 4, you cannot do without urgent medical care in intensive care conditions.
Taking into account the factor of impact on the skin, a burn of the mucous membrane in the mouth can be:
- thermal - when injured by steam, boiling water, hot tea, food,
- chemical - in case of contact with acid or alkali, which can cause serious damage to the respiratory tract.
Who is susceptible to injury?
Typically, a burn to the palate is diagnosed in children when they inappropriately eat hot food in a hurry, on the go. The oral mucosa is vulnerable and can be injured even by an adult after eating food or water that is not too hot.
It is difficult to independently determine how injured the oral cavity is. If the cause of the damage is alcohol, alkali, or acid, then it is better to refuse self-medication and seek help.
Emergency help
Diagnosis of gum burns is differential. It is important to determine the type of lesion, on which subsequent prescriptions of therapeutic procedures will depend. If the burn condition is caused by a chemical, then it is necessary to determine the nature of the substance that led to the injury .
First aid:
- In case of thermal injury, it is necessary to give the person an anesthetic (Analgin, Tantum Verde) or cold water, which he should drink in small sips to relieve pain.
- For chemical treatment, you need to clean the affected area, rinse with warm soda solution (1 teaspoon per glass).
- In case of damage caused by alkali or ammonia, you should rinse your mouth to neutralize the substance with vinegar (7%) diluted in water and lemon juice in a ratio of 1:7.
- If you are burned by sulfuric or hydrochloric acid, you need to rinse your mouth with a soda solution (a teaspoon of soda per glass of water).
- If you are affected by alcohol (ethyl, medical), you need to rinse your mouth with warm, clean water or an isotonic solution (sodium chloride).
Even the usual rinsing of the mouth with cold water will help relieve the burning sensation.
If the pain is severe, you can give the victim a drink of raw egg white. In case of a chemical burn, do not hesitate to call an ambulance and see a doctor. A particularly dangerous condition is considered to be one in which there is a putrid odor from the mouth, bloody vomit, and pain that does not go away for 2-3 days.
Treatment options
Primary measures for severe burns of the oral cavity:
- treatment of affected areas with antiseptics, painkillers,
- sanitation, elimination of damaged necrotic tissues, exfoliated crusts in the affected areas,
- rinsing with herbal infusions,
- treating wounds with ointments, gels, isotonic, bactericidal, analgesic solutions,
- prescribing systemic medications to relieve signs of intoxication.
Additional measures when treating a burn:
- physiotherapy,
- ultraviolet irradiation,
- electrophoresis with the application of an electromagnetic field of a certain frequency to damaged nerve tissue.
The primary goal in case of a burn in the mouth is to relieve pain, prevent the mucous membrane from drying out, speed up the healing process of wounds and ulcers, and avoid secondary infection.
You need to disinfect the oral cavity with antiseptics regularly, every 3-4 hours, especially after eating.
Drug therapy
The safest antiseptics for mouth rinses: Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Aqualor, calendula tincture.
Treatment of thermal burns is carried out with the following medications:
- Miramistin solution - rinse up to 6 times a day,
- Lidocaine (10%) is an analgesic for local application to the affected areas, the manipulation must be repeated every 7-8 hours,
- Chlorophyllipt spray - for treating wounds in the mouth up to 4-5 times a day, until the unpleasant symptoms go away completely, the average course of treatment is 10 days,
- Methyluracil (aerosol) - it is necessary to cover damaged mucous areas with foam, leaving the product for 10-15 minutes up to 5 times a day, the course of treatment is 14 days.
The victim needs to take vitamin complexes:
- Retinol - to restore damaged tissues, accelerate the regeneration of epithelial structures,
- vitamin E - antioxidant, stimulator of cellular metabolism processes,
- vitamin C (ascorbic acid) - for renewal of connective tissue, nutrition and restoration of collagen fibers.
Folk remedies
At home, it is recommended to rinse a burned mouth:
- calendula: pour 1 small spoon of herb into a glass of boiling water, leave for 40 minutes, filter, rinse up to 4-5 times a day,
- aloe: apply the juicy side of the leaf to the affected areas to relieve pain, inflammation,
- sea buckthorn oil: lubricate burned areas 3-4 times a day.
Folk remedies can alleviate the condition only with a minor, mild form of burn.
You can chew a leaf of Kalanchoe, plantain, or nettle if the tissues bleed. Drink a glass of cool milk or egg white in small sips to cool the palate.
Treatment prognosis and possible consequences
The prognosis depends on the severity of the lesion and the speed of providing correct assistance at an early stage . If the burn is mild, the mucous membrane in the mouth will begin to heal after 4-5 days. If the damage is severe, then recovery will take 2-3 weeks and only if all the doctor’s recommendations are fully followed.
Third and fourth degree burns are fraught with complications:
- intoxication of the body,
- death (necrosis) of tissues,
- bleeding, suppuration in the mouth.
What not to do
In case of a burn it is prohibited:
- drink cold water, carbonated drinks, eat ice cream to avoid infection of wounds and increased irritation of injured areas,
- take folk remedies without a doctor’s prescription,
- apply cooling objects to avoid introducing additional infection into the mouth,
- pop blisters with dirty hands in unsterile conditions,
- treat the affected areas with solutions of iodine and alcohol.
Prevention measures
It's always easier to prevent a burn. This is a specific injury that leads to exfoliation and destruction of mucosal tissue in the mouth. It can be difficult even for doctors to immediately identify the depth and severity of the lesion.
More often than not, a burn to the palate is a simple carelessness caused by the consumption of hot foods and drinks. Prevention measures are simple:
- keep medicines, chemicals, hot foods away from children,
- explain how dangerous a burn from boiling water or hot food is and what consequences it can lead to.
The mucous membrane in the mouth is vulnerable and delicate, but quickly recovers if you approach therapy correctly and in a timely manner.
Assess your chances against coronavirus. Take our test
Attention!
The site administration advises you not to self-medicate, and in any controversial situations, consult a doctor.
Source: https://fr-dc.ru/kozhnye-zabolevaniya/travmy-kozhi/chem-lechit-ozhog-neba-vo-rtu-pervaya-pomoshh-lekarstva-narodnye-sredstva
Treatment options
To treat mouth burns, it is necessary to approach this process comprehensively. Experts have developed a number of recommendations that make therapy as effective as possible.
To avoid infection of injured areas, it is recommended to treat the mucous membrane with antiseptic solutions after each meal. For this purpose, you can use the following drugs:
- Chlorhexidine;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- Miramistin;
- Dekasan.
Folk remedies
The following traditional medicines are used to treat injured mucous membranes:
- Aloe leaves are cut lengthwise and applied to the problem area. Pieces of the plant can be chewed. After the procedure, you must refrain from eating and drinking water for 15 minutes.
- Traditionally, decoctions of medicinal herbs are used - chamomile, calendula, oak bark. To prepare them, add 200 ml of boiling water to a tablespoon of plant material. The resulting liquid must be cooled and used for rinsing.
- It is allowed to use sea buckthorn oil to treat burned mucous membranes. It helps relieve inflammation, accelerates tissue regeneration, and reduces pain.
Primary measures for severe burns of the oral cavity:
- treatment of affected areas with antiseptics, painkillers,
- sanitation, elimination of damaged necrotic tissues, exfoliated crusts in the affected areas,
- rinsing with herbal infusions,
- treating wounds with ointments, gels, isotonic, bactericidal, analgesic solutions,
- prescribing systemic medications to relieve signs of intoxication.
Additional measures when treating a burn:
- physiotherapy,
- ultraviolet irradiation,
- electrophoresis with the application of an electromagnetic field of a certain frequency to damaged nerve tissue.
The primary goal in case of a burn in the mouth is to relieve pain, prevent the mucous membrane from drying out, speed up the healing process of wounds and ulcers, and avoid secondary infection.
Treatment methods?
How to treat burn lesions of the palate? First of all, it is recommended to pay attention to nutrition. The patient should be fed liquid, pureed, pureed foods at room or cool temperature. It is necessary to temporarily exclude spicy and sour foods from the diet.
Drinking cool fermented milk drinks will help stop the inflammatory process and speed up recovery, so they should definitely be included in the daily menu. After each meal, it is recommended to rinse the oral cavity with Chlorhexidine or calendula solution (a teaspoon of tincture in a glass of water) for the purpose of disinfection and accelerated healing.
Recovery is also facilitated by treating the affected areas with a sterile cotton swab soaked in peroxide. Such procedures are recommended to be carried out after rinsing the mouth, 2-3 times a day. For medicinal purposes, you can use analgesic, anti-burn ointments and sprays.
I severely burned my tongue, palate, lips, throat: what should I do?
It is important to differentiate them, since the type of burn directly determines what first aid should be provided to the victim.
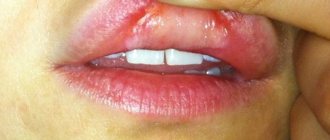
Lip burn.
- If an adult or child drinks boiling water or a very hot liquid, inhales steam, comes into contact with a very hot object (a piping hot cutlet, a hot spoon), he will receive a thermal burn of the lips, mucous membranes of the mouth and throat. The degree of the burn and the severity of the symptoms depend on the temperature Thus, hot tea can cause irritation of the mucous membrane, accompanied by slight swelling and short-term moderate pain, while boiling water leads to ulceration of the mucous membrane and pain that requires special medications to relieve it.
- A chemical burn occurs due to contact with the lips, mouth or throat of strong chemicals - alkalis, acids, chlorine-containing household chemicals, etc. It is dangerous because the destructive effect on tissue will continue until the chemical is neutralized.
Tongue burn.
But let’s say a everyday situation arose - I was in a hurry to go to work, grabbed a cup of coffee, took a sip, but the drink turned out to be too hot, it burned my lips, tongue, palate and even my throat. What to do? Don't panic! Try to pull yourself together and determine what temperature the drink was. If it has already cooled down to a temperature of 50-70 degrees, most likely the burn is of the first degree of severity, the mucous membrane is only superficially damaged by the temperature. To relieve swelling and inflammation, do the following:
- Apply an ice cube to the burn on the outside of your lip. Contact time is 2-3 seconds. Take a break, then apply the cube again. Panthenol, Bepanten and other products based on pantothenic acid help very well with this type of burn. As a folk remedy, you can use chilled cucumber juice.
- For burns on the inside of the lips and the oral cavity (inner surface of the cheeks, palate, tongue, gums), rinse your mouth with cool water or milk (even better, as it creates an enveloping, greasy film). If it hurts a lot, take ibuprofen or paracetamol.
If you burn your mouth, rinse it with cold water or milk.
When in contact with liquids, products and objects with a temperature above 70 degrees, burns of the mucous membrane of the second degree occur on the lips and mouth. Along with pain and swelling, vesicles appear on the damaged surfaces - bubbles from swollen skin filled with liquid. Since it is impossible not to touch them, the vesicles burst very quickly, exposing wounds that are very painful.
Contact with boiling water may cause a third-degree burn of the mucous membrane, characterized by deep thermal damage to the tissue, accompanied by ulceration and necrosis. Here you cannot help yourself qualitatively; you need to call an ambulance and go to the hospital.
Diagnostics and first aid
If symptoms of a first or second degree burn are detected, a visit to a specialist is not necessary. But with the third, be sure to go to the dentist or combustiologist. Only they will be able to prescribe the correct treatment and prescribe the necessary medications.
First aid sequence
First, the wound is disinfected using hydrogen peroxide lotions and a cotton pad. Next, it is recommended to hold cool water in your mouth. It is best to perform these actions until the burning sensation subsides.
The sequence of actions for diagnosis and first aid to the victim:
- treatment of the palate with analgesics and bactericidal preparations for disinfection and acceleration of healing;
- removal of exfoliated mucous membrane and crust formed;
- prescription of treatment, ultraviolet therapy is possible.
What not to do if your palate is burned
In order not to aggravate the situation, it is strictly prohibited:
- use food as a cooling object, since this way you can introduce an infection;
- If you have severe burns, self-medicate; it is more correct and beneficial to consult a doctor.
First aid if a child burns his tongue, palate, lips, throat with boiling water or hot tea
Cases of burns of the lips, tongue and palate in children from boiling water, hot liquids or foods most often occur due to the carelessness of adults - they did not notice, did not control. But what happened happened. You will blame yourself and work on your mistakes later. Give your child first aid immediately:
- Be sure to call a doctor. It is difficult to determine the degree of burn yourself; let a specialist do it. For first- and sometimes second-degree burns, the child will not be taken to the hospital, but they will tell him what to do. If the injury is of the third degree of severity, the child needs specialist help, it will be provided in a hospital.
- Before the doctor arrives, try to reduce the pain your child is experiencing. Give him a piece of ice or frozen berry to suck on. If you have ice cream, that will work too.
- If your child knows how to rinse his mouth, let him rinse with water or milk from the refrigerator.
- You can also use honey as a folk pain reliever and anti-inflammatory remedy, but only if the child is over 1 year old and is not allergic.
- At your own discretion, never use anesthetics with a “freezing” effect - lidocaine, novocaine, etc. Firstly, it will be difficult for you to calculate the dose based on the child’s age. Secondly, the child may bite the numb cheeks and tongue. Thirdly, if used incorrectly, the throat and larynx may become numb, and the child will have breathing problems.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with how stomatitis in the mouth is treated in children
Burn of the oral cavity in a child.
Treatment of mouth burns with traditional methods
This type of treatment can be effective for minor burns of the palate and tongue, or can be used as restorative measures following severe burns of the mucous membrane.
- Dried flowers, leaves and stems of common chamomile are boiled for 10 minutes in boiling water. The broth should cool and brew for 2 hours. After this, you can start rinsing your mouth. Ingredient ratio: 1 liter of water per 50 grams. medicinal plant.
- Alcohol tincture of calendula dissolves in a glass of warm water and the patient can begin rinsing the mouth. To achieve a positive therapeutic effect, it is enough to add 10 drops of tincture.
- Take 100 grams of fresh honey and two small aloe leaves. The plant is ground in a meat grinder into a pulp. Then it must be mixed with honey and left for 1 day to infuse. The resulting mixture is applied to the burn-affected mucous membrane of the tongue and palate as a compress. Treatment continues until symptoms disappear.
To avoid burning your mouth, you should always first test the container with liquid with the tip of your little finger. This finger is considered the most sensitive and will always give a signal if the contents of the cup or plate are too hot. You should also be careful when working with chemicals to prevent acid or alkaline burns of the mucous membrane.
Burns of the oral cavity occur due to traumatic effects on soft tissues of aggressive environments or high temperatures. Due to the large number of receptors in the oral cavity, they always cause pain and discomfort. You can burn the palate, tip, body or root of the tongue, the inner surface of the cheeks, and gums. A traumatic lesion should be treated in the dentist’s office, who will select therapy based on the cause, nature and extent of the damage.
Symptoms
A burn to the oral mucosa is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain when swallowing;
- burning in the throat;
- heavy salivation;
- swelling in the mouth;
- nausea and vomiting;
- pain and swollen lymph nodes;
- chills and fever;
- suffocation;
- weakness and drowsiness.
Knowing how to treat a burn and provide first aid to a patient can help him avoid complications associated with an increase in the extent of the injury and its consequences.
Kinds
In medicine, there are two types of household or industrial burn injuries:
- thermal;
- chemical.
The impact of significant temperatures on mucous tissues causes thermal burns, and the consumption of corrosive aggressive components is considered a chemical injury. A thermal burn in the mouth occurs when consuming hot food and drinks, exposure to steam, and a chemical burn occurs when acids, alkalis, ammonia and other chemical compounds penetrate inside.
First aid
Burns of the oral mucosa require urgent assistance, regardless of the temperature of the affected element and the duration of contact with it. For thermal burns, rinsing with cold water is appropriate. This will stop the mucous membrane from contacting the high temperature, which continues to heat up for some time and causes severe burning pain to the patient. With cooling, tissue damage stops and the pain gradually subsides. For minor burns, symptoms will disappear within 5 days.
With a chemical burn to the oral cavity, you need to be more careful and put more effort into the healing process. It occurs when taking unfamiliar medications, alcohol-containing products, etc. It is the most dangerous and painful injury, causing a large number of erosions and ulcers, regardless of its severity. In some cases, rinsing with cold water for a long time is also good for chemical burns of the mucous membrane.
Symptoms of a burn to the mouth
With a thermal burn of the oral cavity, the mucous membrane first becomes red and swollen. With short-term exposure to low temperatures, signs of focal maceration of the epithelium appear. In the case of prolonged contact of the physical factor with the mucosa, rejection of the surface layer is observed, resulting in painful erosive surfaces. In case of electrical injury that occurs during the electrophoresis procedure, a whitish zone is identified on the mucous membrane in the projection of the application of the active electrode, the shape corresponding to the size of the electrode. Soon the mucous membrane in this area is rejected, which leads to the appearance of ulcerations.
A radiation burn of the oral cavity manifests itself in the form of filmy radiomucositis. The areas of the mucosa covered with non-keratinizing epithelium are most susceptible to the effects of high doses of ionizing radiation. At first, the affected area has a hyperemic tint; over a short period of time, the mucous membrane loses its former elasticity, becomes cloudy and dense, and acquires a folded relief. In the case of further radiation therapy, erosions appear in the oral cavity, covered with necrotic masses. Hyposalivation is observed. With an acid chemical burn of the oral cavity, a shallow area of coagulation necrosis is formed, delimited from healthy tissue. Liquation necrosis occurs when alkali comes into contact with the mucosa. During the examination, the affected area is identified, which can cover all layers of the mucosa. At the same time, it is not possible to draw a clear line between necrotic and healthy tissues.