Stomatitis is one of the most common diseases of the oral cavity. It can be traumatic, bacterial, viral, but the most common form of the disease is candidiasis. This is due to the fact that it is caused by opportunistic microorganisms that are contained in the healthy microflora of the oral cavity. A minor disruption in the body is enough for fungi to begin to actively multiply and lead to the development of fungal stomatitis.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis in adult patients and children consists of taking antifungal drugs, local treatment of the affected mucosa and increasing immunity. The therapeutic course should be supervised by a specialist.
Symptoms of candidal stomatitis in adults
Stomatitis is an inflammatory process in the mouth. If an opportunistic fungus becomes a provocateur of inflammation, doctors diagnose the candidiasis form of the disease, the second name of which is oral thrush. Young children and adults with weakened immune systems are most susceptible to the disease.
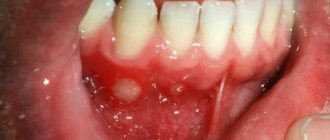
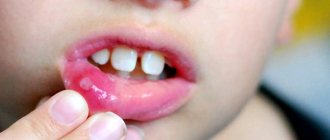
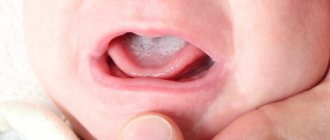
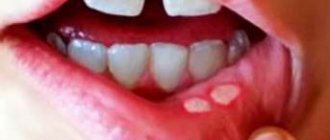
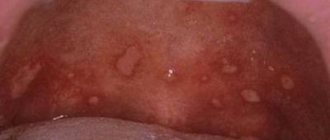
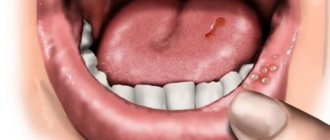
Photo: candidal stomatitis
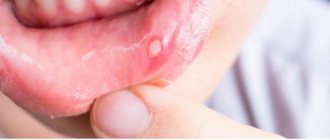
The first symptom of candidal stomatitis is the appearance of redness on the mucous membranes of the gums, the inner surface of the cheeks, palate and tongue. The lesions react to cold and hot, and when you touch them, a burning sensation and pain occurs. Gradually, the ulcers acquire a white border around the edges and become covered with a coating in the form of curdled flakes.
The patient faces the following problems:
- discomfort while eating;
- violation of taste perception;
- constant pain;
- signs of intoxication;
- bleeding
If treatment for candidal stomatitis is not started in time, the inflammation can spread to other tissues and organs. In adults, the fungal infection often spreads to the skin, larynx and genitals; in young children, the intestines and esophagus are affected.
Symptoms of candidal stomatitis largely depend on its form. The most common is acute pseudomembranous. With it, the mucous membranes of the mouth are covered with a whitish coating, similar to a film or plaques. At the beginning of the disease, they can be removed, then traces of hyperemia will remain on the damaged area, which heal quite quickly.
The severe form of the disease is characterized by a large number of plaque foci. They can merge and affect almost the entire oral mucosa. It is difficult to remove whitish spots on your own, but if the patient manages to do this, large bleeding erosions remain at the site of the plaque, causing serious discomfort.
If candidal stomatitis is not treated in time, the acute form of the disease can become chronic. With it, the characteristic whitish plaques are absent, but other unpleasant symptoms persist - the mucous membrane dries out, and noticeable pain appears when swallowing.
Risk factors influencing the development of fungal stomatitis
- Reduced body resistance to infections.
- Breastfed children.
- Elderly age. With age, the body's resistance becomes weaker, so fungal diseases develop more often.
- Development of AIDS with positive HIV status.
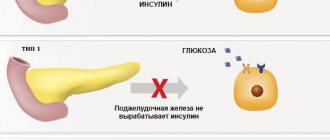
- Presence of diabetes mellitus. Fungal stomatitis develops in an acidic environment. In diabetes, the level of sugar in the blood is increased, which gives an acidic reaction in the body and the corresponding conditions for the growth of fungus.
- Pregnancy. During pregnancy, hormonal changes occur in a woman, accompanied by a weakening of local immunity. Most often, these changes lead to acidification of all environments of the body. If candida is present in the microflora of the oral cavity, it begins to grow.
- Doctor prescribing antibiotics or corticosteroids. Antibacterial drugs suppress not only pathogenic microorganisms, but also beneficial ones. Antibiotics, as a rule, have no activity against the fungus, and since nothing is now restraining its growth, it begins to multiply vigorously.
- Poor hygiene. Microbes living in dental plaque produce lactic acid, which shifts the pH of saliva to the acidic side.
- The presence of orthopedic structures in the mouth. The presence of removable, clasp, and extensive bridges in the mouth makes hygiene difficult.
- Incorrect use of rinse aids. Some rinses contain high concentrations of antiseptics (chlorhexidine). They are intended to prevent relapses of periodontitis and gingivitis. If they are used without a doctor’s recommendations and for longer than the prescribed time (usually more than 2 weeks), beneficial microflora may die, and any changes in it lead to increased growth of the fungus.
Fungal stomatitis can be contagious. Mostly infants who do not have this type of fungus are infected. If the disease develops for the first time, its course becomes acute. Subsequently, without appropriate therapy, fungal stomatitis in adults becomes chronic. In older people, a primarily chronic process occurs. The general condition changes slightly. The disease begins with the appearance of bright red spots on the mucous membrane of the tongue, cheeks and lips. A person feels pain and burning when eating.
Then tiny, white, pinpoint rashes appear on the surface of the mucous epithelium. Over time, they increase in size, merge with each other, and then a white, crumbly coating appears. These curdled masses are quite easily removed; the mucous membrane underneath has a glossy shine, red color and swelling. In older people, the atrophic form of candidiasis develops more often. In this form, the lesions are located on the tongue or in places of tissue contact with the orthopedic structure. The curdled coating is present in very small quantities. The mucous membrane is hyperemic and edematous. The papillae of the tongue are smoothed out, and grains of candidal plaque can be found in its folds. When a mycotic infection becomes chronic, plaque turns into films. Fungal cells penetrate deep into the tissues under the surface epithelium, so the film is difficult to separate when trying to remove it. After removing these masses, erosions open up, with uneven bleeding edges. The chronic course is typical for people with diabetes, HIV, and the elderly. To make a diagnosis, only clinical data and laboratory tests are sufficient. After examination by a dentist, you will need to take a scraping from the surface of the mucous membrane. Microscopy of the scraping should reveal not only mycotic cells of the yeast fungus, but also mycelium, which indicates that the microorganism is actively multiplying.
Treatment of fungal stomatitis primarily involves the following tasks:
- Identify and neutralize all risk factors for fungal growth
- Select the necessary medications to suppress the proliferation of candida
- Increasing local and general immunity
First of all, when a fungal infection occurs, it is necessary to determine the main cause of the development of the fungal infection. It is necessary to carry out professional hygiene, be sure to treat all carious teeth. Foci of chronic infection can harbor pathogenic microbes that disrupt the natural microbiocenosis in the oral cavity, which leads to a decrease in the number of those bacteria that inhibit the increase in the number of fungal cells. If you have removable laminar dentures, it is necessary to teach the patient how to properly care for them. The denture, like your own teeth, must be brushed at least twice a day after meals. Very often, oral candidiasis, especially its severe form with involvement of the tonsils and esophagus in the pathological process, is typical for people with immunodeficiency.
Fungal stomatitis in an adult on the tonsils
Immunodeficiency can be caused by HIV or other serious infectious diseases. In any case, the dentist, who sees large areas affected by the fungus in front of him, will send the patient for diagnosis of HIV infection or to an infectious disease specialist or immunologist. First of all, it is necessary to begin treatment of the disease that reduces immunity, then fight candidiasis. If candidiasis is not widespread, nutritional correction, vitamin therapy and, possibly, the prescription of immunomodulator drugs are sufficient. Eliminate sweets from your diet and add more fortified foods.
If fungal stomatitis begins while taking antibacterial drugs or hormonal therapy, a probiotic must be included in the treatment regimen. A probiotic is an auxiliary medication that contains bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, which restore the normal balance of microflora throughout the body. When purchasing these drugs, it is advisable to consult a doctor, since most of the bacteria of these drugs entering the digestive tract die in the acidic environment of the stomach. Treatment of fungal stomatitis depends on the extent of the fungal infection. In mild and acute cases, only local therapy in the form of irrigation of the oral cavity with solutions of soda 0.5-1% and borax in glycerin 10-20% concentration may be sufficient. These solutions are alkaline.
Popular probiotics
Candida fungus prefers an acidic environment, but dies in an alkaline environment. If the fungus penetrates deep into the tissues or occupies large areas of the oral cavity, it is necessary to use local antifungal drugs. Gels containing clotrimazole, nystatin, some herbal medicines and antiseptics, especially iodine-containing ones, are suitable for topical use. In case of a serious fungal disease, more often against the background of other serious viral or bacterial infections, antifungal drugs are prescribed orally. These drugs are mainly in tablet form and contain fluconazole, ketocanazole, nystatin, natamycin or levorin as active ingredients. They are usually prescribed by the doctor treating the underlying disease. They must be prescribed carefully because they are toxic to the liver. Below are the main groups of antifungal drugs.
Polyene antibiotics:
- nystatin
- levorin
Azole compounds:
- clotrimazole
Alylamine agents:
- lamisil
Biquaternary ammonium compounds:
- etonium solution
Herbal preparations:
- infusion of celandine
- tincture of calendula
- bay leaf tincture
- dill seed tincture
- propolis solution
Antiseptic solutions
- chlorhexidine bigluconate
- hexetidine
- Iodinol
Recovery can be considered to have occurred when the main manifestations of the disease disappear, microscopy of the scraping does not reveal mycelium threads, and the fungus is either absent or present in normal quantities.
Causes of candidal stomatitis in adults
Candida fungus is an opportunistic microorganism, that is, it lives in the mouth of even a healthy person. Each person has their own quantitative norm for the content of fungus in the microflora of the oral cavity. The disease begins only when the balance is disturbed due to the active proliferation of microorganisms.
It can be provoked by:
- Weakening of the immune system: “extra” fungus is destroyed by the body’s defenses if they are working at full strength. But small health problems are enough for control to cease.
- Wearing dentures: unsuitable dentures injure soft tissues, which provokes an inflammatory process.
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse.
- Age: most often children and the elderly suffer from stomatitis, since in children the immunity is at the stage of formation, and in adulthood it gradually begins to weaken.
- Long-term use of antibiotics: tablets kill not only harmful bacteria, but also beneficial ones. The usual composition of the microflora is disrupted, and dysbiosis often becomes the cause of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Hormonal problems: when hormones are imbalanced, both the natural microflora and the strength of the immune system are affected.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases: the greatest danger is diabetes mellitus, accompanied by a failure of carbohydrate metabolism, and diseases of the digestive system, leading to a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice.
- Poor hygiene: poor brushing of teeth or lack thereof leads to the activity of fungi and various bacteria that attack sensitive areas of the mucous membrane. If there are microdamages in the mouth, they become a source of infection.
If a pregnant woman is sick with genital candidiasis, during childbirth the pathology is transmitted to the child. Oral thrush in this case can begin in the first days of the baby’s life.
It is impossible to completely cure candidal stomatitis in the mouth without knowing the cause of its occurrence. If the predisposing factor is not eliminated, the risk of recurrent stomatitis is high, and then the treatment process will have to start all over again.
Symptoms of the disease
Every dentist can recognize the first symptoms of candidiasis of the oral mucosa. The main thing is that the patient seeks help in time for timely treatment. A couple of days after infection, the first signs appear, which may have a certain degree of severity depending on the characteristics of the patient’s body (in particular, on the state of the immune system and the drugs it takes if a drug is being treated for a disease).
There may be an acute or chronic form of the disease. The main symptoms are as follows:
- There is discomfort when eating or brushing your teeth. A burning sensation appears;
- The mucous membrane becomes irritated, sensitive and dries out, turns red and swells;
- Redness of the corners of the lips and peeling are noted;
- Possible increase in body temperature;
- Swallowing becomes difficult, a feeling of a “lump” appears in the throat;
- The mucous membrane “overgrows” with a white cottage cheese-like coating, under which there is irritation.
If the above-described plaque is not removed by the patient, and the mucous membrane is not disinfected with special compounds, then a kind of dried out crust is formed, under which inflammatory processes begin. This can lead to the formation of erosions and ulcers.
How is fungal stomatitis of the oral cavity diagnosed?
The first task of diagnosis is to examine the patient and exclude other diseases of the oral cavity. An accurate diagnosis can be made based on the following points:
- Patient complaints;
- Dermatological examination;
- Biochemical and routine blood tests.
Only after going through all stages of the examination will it be possible to accurately exclude other diseases, as well as identify diseases that provoked candidiasis, if they were not detected earlier.
Medicines for the treatment of candidal stomatitis
If in the initial stages of the disease you can limit yourself to local treatment of rashes, advanced candidal stomatitis needs to be treated with more serious pharmaceutical agents. Taking antibiotics for this disease is useless; general antifungal drugs are used to fight fungi.
Diflucan
Diflucan is a capsule for oral use whose active ingredient is fluconazole. They are used to treat any fungal diseases, including oral candidiasis. After using the drug, fluconazole penetrates into all liquids and protects the entire body from fungus.
The dosage is determined individually, depending on the patient’s age and general clinical picture. Noticeable relief often occurs after the first day of treatment, but stopping the medication prematurely is prohibited: the disappearance of symptoms does not indicate the cessation of the inflammatory process.
Nizoral
Nizoral is an antifungal drug with ketoconazole. It stops the synthesis of the fungus and prevents its reproduction. After use, ketoconazole is quickly absorbed and distributed throughout the tissues of the body.
The dosage depends on the age and weight of the patient. Children over three years old weighing up to 30 kg can take half a tablet once a day. For adults weighing more than 30 kg, a whole tablet is prescribed per day. To cure candidiasis, you need to take Nizoral for at least a week.
The product is not suitable for people suffering from liver problems or individual intolerance to the components. Possible side effects are nausea, vomiting, stool disturbances, signs of allergies and dizziness.
Itracon
Itracon is a capsule based on itraconazole, an antifungal component. It destroys the fungus and eliminates the symptoms of candidal stomatitis in adults. With long-term use of the drug, its therapeutic concentration remains in the tissues and nail keratin.
The duration of therapy is 15 days, during which you need to drink one capsule per day after meals. Itracon is prohibited in case of acute heart failure; it is used with caution in case of problems with the kidneys and liver. In case of an allergic reaction, further use is cancelled.
What is fungal stomatitis
This is the name for damage to the oral mucosa by fungi of the genus Candida. Other names for the disease are candidiasis or oral thrush, candidal stomatitis (fungal). The oral cavity is poorly protected from the effects of adverse external factors. It is easily damaged, and bacteria, viruses and fungi enter the mouth and live there almost constantly, causing inflammatory processes. Young children who are breastfed are especially susceptible to fungal infections, including stomatitis, since milk creates favorable conditions for fungal growth.
Local medicinal treatment for stomatitis
For local action on the fungus, local agents are used - gels, ointments and solutions. They are designed to alleviate the course of the disease, stop the proliferation of microorganisms, disinfect the oral cavity and promote the speedy healing of injured areas.
Eludril
Eludril is a local solution that has anti-inflammatory, antifungal and bactericidal effects and is a mild anesthetic. When used correctly, the product is non-toxic and quickly removes white plaque and other signs of infection.
Eludril is used to rinse the mouth: 2–4 teaspoons of the product are diluted in half a glass of boiled water at room temperature. The procedure must be repeated 2-3 times a day.
The Eludril solution contains ethyl alcohol, so the drug is not recommended for the treatment of children. If it is used, care must be taken to ensure that the baby does not swallow it.
Daktarin
Candidal stomatitis in adult patients and adolescents can be treated with Daktarin oral gel, an antibacterial and antifungal drug for local and external use. The active ingredient of the drug is miconazole. The drug is suitable for prophylactic use.
Treatment of mucous membranes with gel is carried out 3-4 times a day; half a teaspoon of the product is needed for one application. It is applied to problem areas of the mucous membrane using a soft swab made of bandage or cotton wool. It is recommended to keep the gel in your mouth for some time; do not immediately swallow or spit it.
Contraindications to the use of Daktarin are renal or liver failure, diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, lactation and age under 12 years. With prolonged use (more than two weeks), stool disorders and allergic skin reactions are possible.
Traditional medicine tips
Herbal infusions and decoctions, pharmaceutical sea buckthorn oil, a mixture of fresh aloe juice and white cabbage in equal parts will provide effective help.
A proven method is soaking the affected areas with chamomile infusion. To prepare the medicine, take a tablespoon of chamomile flowers. Pour boiling water and leave in a container under a lid, wrapped in cloth for 20-30 minutes. Strain. Cool. Treat all affected areas several times a day until cured.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis in the mouth in adults with folk remedies
Treatment of candidal stomatitis with folk remedies is most effective in the initial stages of the disease. It is recommended to use them in combination with traditional methods of therapy. Various decoctions and solutions are well suited for local treatment of ulcers. The simplest option is to rinse your mouth with a solution of soda and salt, for the preparation of which you take a teaspoon of each substance in a glass of warm water. The liquid is thoroughly mixed and applied at least once an hour. With its help, you can quickly relieve inflammation, relieve pain and destroy bacteria that multiply on the mucous membrane.
Chamomile decoction has an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect. A tablespoon of dry herb is poured into a glass of boiling water and brought to a boil. When the liquid has cooled, it needs to be strained. You should rinse your mouth with chamomile decoction as often as possible.
For local treatment of plaque, a special ointment is prepared. It includes:
- 50 g olive oil;
- 20 g calendula flowers.
The oil is heated in a water bath, then calendula is added to it, and the mixture simmers for another 15 minutes. The mixture is removed from the stove and infused for at least four hours. Ready-made calendula oil is applied to the plaques using a cotton swab; during the procedure, care must be taken not to remove the plaque.
Types of disease
In most cases, infants suffer from candidal stomatitis. This is due to the imperfection of their immune system. In adults, the problem more often appears against the background of exacerbation of chronic problems or taking antimicrobial agents.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to quickly cure stomatitis in the mouth in an adult and a child: how to get rid of the disease, quick treatment
Depending on the extent of spread, pathology is classified into several types:
- Glossitis is inflammation of the tongue. This form is the initial stage of development of candidal stomatitis. When sick, the speaking organ looks as if it has been polished. With atrophic glossitis, there is a decrease in the papillae on the surface of the speaking organ and a loss of their sensitivity. The hypertrophic type of disorder, on the contrary, is associated with the proliferation of papillary tongues.
- Cheilitis is a fungal infection of the inside of the lips, their corners and surface.
According to the nature of the course, stomatitis is divided into acute and chronic. The clinical picture in the first case will be more pronounced, but the acute form of the pathology is easier to treat, unlike the chronic one. In the second case, the pathology occurs in waves with periods of subsidence and exacerbation of the fungal infection.
According to clinical and morphological characteristics, the disease is divided into:
- Pseudomembranous type. Children who have had infectious diseases (sore throat, bronchitis, pneumonia) are susceptible to the disorder.
- Erosive type. Distinctive symptoms are the appearance of small ulcers on the surface of the mucous membranes, which are accompanied by pain and burning during eating.
- Hyperplastic type. It is characterized by increased dryness of the oral mucosa and the appearance of roughness on the inside of the cheeks and the back of the tongue.
- Atrophic. The tongue becomes covered with a thin film due to long-term use of antibiotics and corticosteroid drugs.
Diet
Throughout the treatment, it is advisable to adhere to a certain nutritional system. Some foods, for example, carbohydrates and sweets, promote the growth of fungus - they create an environment in the mouth that is favorable for the activity of dangerous microorganisms.
You will have to exclude from the diet:
- simple carbohydrates;
- semi-finished products;
- fast food;
- snacks;
- salty;
- fat;
- spices;
- spices and seasonings;
- White bread;
- any sweets.
The basis of the diet should be fresh and boiled vegetables, cereals and legumes, crackers, boiled meat, non-acidic fruits and vegetables. A prerequisite is the consumption of fiber. It is advisable not to use oil when cooking.
Candidal ulcers are very sensitive to temperature changes, so food should not be cold or hot. Also, during the period of illness, it is better to refrain from eating too harsh foods, which can further injure the mucous membranes.
Treatment
For candidal stomatitis, complex treatment is required, which includes taking systemic medications, using local remedies, and sometimes prescribing a therapeutic diet.
How to treat with systemic drugs
Medicines are used for any form and type of candidiasis. In the form of tablets or capsules the following is prescribed:
- Fluconazole;
- Intraconazole;
- Nystatin;
- Ketoconazole.
To increase the body's defenses, it is recommended to combine antifungal drugs with vitamins B, C and PP.
The duration of the course depends on the degree of damage, usually 5-10 days. To prevent dry mouth, it is additionally recommended to treat with a solution of potassium iodide in a 2-3% concentration. The drug stimulates saliva production and reduces the formation of new fungal colonies.
Topical products
In most cases, it is impossible to get rid of the problem without using medications for external use. They may be in the form of mouth rinses, ointments, or gels. For children, medications are available in the form of chewable tablets or candies. The most famous topical agents:
- Levorin;
- Amphotericin;
- Econazole;
- Clotrimazole;
- Miconazole;
- Nystatin.
It is advisable to use gels and ointments for candidal stomatitis in the form of applications. The course of treatment with such drugs is always long – up to one month.
To reduce the fungus, rinsing with antiseptic solutions - potassium permanganate, boric acid, iodine water - is often prescribed. Less commonly used are chlorhexidine or Hexoral. Procedures should be regular and carried out exclusively after meals.
Nutrition
Diet during illness allows you to quickly cope with infection, since a number of foods can enhance the growth and development of the fungus. When preparing therapeutic nutrition, we are guided by the following principles:
- reduce as much as possible the amount of foods high in simple carbohydrates;
- Avoid eating fast food, alcoholic beverages, salty and smoked foods;
- exclude products containing yeast (baked goods, bread, beer);
- increase the amount of fermented milk products; they should be present in all meals;
- Most of the diet should consist of foods rich in fiber, fresh vegetables, cereals and boiled meat (poultry, rabbit or veal).
It should be understood that diet is not a complete treatment for candidal stomatitis, but following simple nutritional rules can speed up the healing process and enhance the effect of medications.
Prevention
To protect yourself from stomatitis, you need to monitor your health. A proper balanced diet rich in vitamins and microelements will help support the immune system. During the cold season, when access to fresh vegetables and fruits is limited, it is recommended to take vitamin-mineral complexes and immunomodulators.
It is important to carefully follow all the rules of oral hygiene - brush your teeth at least twice a day, and after eating, rinse your mouth with a balm-rinse or at least running water. Once every six months you should visit the dentist for preventive purposes, even if nothing bothers you.
Despite the fact that Candida fungus remains in the body forever, stomatitis is curable. With the right approach to therapy, the recovery process will take only a few days. In the future, you just need to adhere to preventive health care to prevent a relapse.