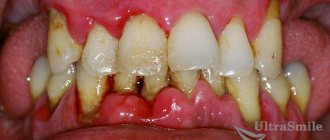
Gingival hyperplasia is a pathological increase in gum tissue that is most often found in adults. If fibromatosis or hyperplasia is hereditary, then in children the pathology can occur at an early age (1-10 years). Over time, the disease progresses and most of the surface of the crown of the teeth is covered by gum tissue. This causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient, so hyperplasia must be combated at an early stage of development.
Gum hyperplasia - what is it?
Types of gum hyperplasia
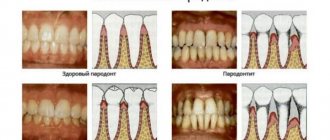
The disease can be focal or generalized depending on the nature of its spread. When the overgrown gum covers several teeth or the entire dentition, hyperplasia is called generalized. And if the pathological gum covers only one tooth, then this type of disease is called focal. According to statistics, focal hyperplasia occurs much less frequently than generalized hyperplasia.
There are several types of gum hyperplasia
The disease also varies depending on the causes of development. Hyperplasia can be fibrous or drug-induced:
- the fibrous form occurs very rarely and is classified as a hereditary pathology. The first symptoms are noticed in childhood, namely during the appearance of the first teeth. Over time, the disease develops, and at the same time the gums become larger. This form of hyperplasia is often confused with periodontitis due to a similar clinical manifestation (with thickening of the gums, the patient develops pockets, as with periodontitis);
- medicinal form of hyperplasia. It appears as a result of the use of medications, the side effects of which include an increase in gum tissue.
The disease is in an advanced stage
Forms
Depending on the location, there are 2 forms of periodontal fibromatosis: focal and generalized.
| Focal | Generalized |
| The damage to periodontal tissue is limited (in the area of 2–3 teeth). There are no uncomfortable feelings. Localization: alveolar processes of the upper jaw, lingual area of the molars and premolars of the lower jaw. | Extensive periodontal damage. Patients complain of pain, bleeding and bad breath. Localization: the entire periodontal area of the upper and lower jaw. |
Focal form
Focal gingival fibromatosis is much less common than generalized periodontal overgrowth. This type of pathological process is characterized by slow development, proliferation of soft tissues in the area of several teeth and overlap of the crown on ½ of the tooth.
Gum formations with a limited form have a rounded shape, dense consistency and shiny structure. In the absence of timely treatment, soft tissue hypertrophy provokes a loss of the gingival margin in the contact surfaces between the teeth.
Generalized form
This form of gum disease is characterized by the appearance of several lesions and their subsequent fusion. In advanced cases, the crown part of the teeth is completely covered with hypertrophied tissue.
Due to the impossibility of removing plaque, the following are observed: bad breath, mineralized dental plaque, multiple dental caries. In addition, the patient feels aesthetic discomfort and inconvenience in nutrition.
Causes
Despite the fact that gum hyperplasia is quite common, doctors cannot yet determine the exact causes of its occurrence. Often, the progression of the disease is caused by taking certain medications, for example, Phenytoin (used for epileptic seizures) or Cyclosporine (used in medicine for recovery after internal organ transplantation).
Fibromatosis
On a note! The likelihood of developing this disease increases when using a drug that blocks calcium channels in the body (Nifedipine, Diltizay, Verapamil and others).
Nifedipine tablets
The most common factors that can lead to the appearance of hyperplasia include:
- malocclusion;
- specific layering of tartar;
- puberty;
- genetic predisposition;
- pregnancy;
- the presence of diseases of the blood system, for example, leukemia.
Gum hyperplasia occurs for various reasons
Gum hyperplasia mainly affects adults, but in rare cases it can also occur in children. As a rule, this occurs due to the genetic characteristics of the organism. If we talk about the dosage form of the disease, it can affect a person of any age.
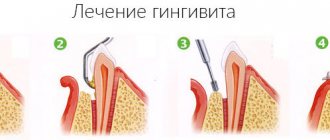
Diagnostics and therapy
Gum hyperplasia is not considered an inflammatory process in tissues, so drug treatment methods are not used. At the same time, the proliferation of connective tissue is not considered a tumor and does not create metastases. Bleeding gums, characteristic of hyperplasia, are often perceived as periodontitis or gingivitis, which is erroneous. Self-medication of periodontitis does not give the desired result, so it is better to consult a dentist to clarify the diagnosis.
An X-ray of the gums is used to make an accurate diagnosis. To exclude other forms of gum pathology, an additional histological analysis is performed.
In the medicinal form of the pathology, treatment is not required: the gingival tissues return to their original form after discontinuation of the drug that caused the disease.
In other cases, the overgrown tissue is surgically excised down to the periosteum, under local anesthesia. Therapy can also be carried out bloodlessly using a laser. The advantage of laser intervention is:
- avoidance of injury;
- high accuracy of tumor removal;
- incidental destruction of bacteria;
- rapid tissue healing.
The advantage of laser treatment is obvious. Firstly, the method eliminates bleeding: the laser immediately seals the blood vessels. Secondly, the high precision of removal of affected tissue eliminates trauma to neighboring areas. In addition to removing overgrown connective tissue, the laser destroys any type of bacteria and sanitizes the oral cavity.
Is it possible for tissue growth to recur? There is such a possibility; it does not depend on the quality of the operation performed. Spontaneous proliferation of connective tissue may occur again, and the patient will require repeated removal of the tumor. This pathology can be partially prevented by careful sanitation of the oral cavity and regular visits to the dental office for check-ups.
Characteristic symptoms
The main symptom of this disease has already been mentioned earlier - gum overgrowth. But it is worth familiarizing yourself with the clinical picture of gum hyperplasia in more detail:
- Gum tissue swells and increases in volume. This applies to the interdental gingival papillae and gingival margin;
- overgrowth of interdental spaces;
- the affected gum area becomes much denser than the healthy one;
- the patient’s gums have a uniform color – pink;
- The surface of dental crowns is covered by more than half.
Gingival hyperplasia in adults
If you notice any of the above symptoms, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Otherwise, the disease may progress and cause complications.
Symptoms
The pathology may not manifest itself in any way for some time: there will be no changes in the tissues and mucous membrane of the gums, or pain. It is important to always pay attention to the condition of the mucous membrane in the mouth and its color.
The first and main manifestation of the disease is a significant increase in the size of the tissue on the gums. The process of development of fibromatosis is usually divided into 3 degrees. Each of them has its own characteristics:
- I degree - the edges of the gums and interdental papillae begin to grow.
A thickening forms that resembles a roller in appearance. It grows throughout the affected area and reaches 1/3 of the height of the tooth crowns. Clinical signs of inflammation and pain are completely absent. - II degree - the thickening continues to increase in size and covers ½ of the height of the teeth.
Performing all hygienic procedures and eating solid food provoke bleeding from swollen affected areas. - III degree - the crowns of the teeth are almost completely covered by an overgrown thickening.
In advanced forms of the disease, the cutting edges and chewing surface of the teeth can completely overlap. Granulations form on top of the affected areas.
The enlarged affected areas are divided into segments corresponding to the original shape of the gum. Outwardly, they look like a bunch of rollers.
In isolated cases, such areas look papillomous, that is, they consist of several small growths.
Diagnostics
Gum hyperplasia is diagnosed by a periodontist or dentist. Initially, the patient is offered to undergo an X-ray examination. This allows you to diagnose the disease more accurately. In addition, a sample of the enlarged gum tissue is sent for histological analysis.
Diagnosis of the disease
More research is being done to differentiate generalized hyperplasia from other diseases, such as periodontitis or gingivitis. These include differential diagnosis of gingival cysts. After the doctor makes a diagnosis, he prescribes treatment for the patient.
Causes
The main cause of the development of gum fibromatosis is considered to be a hereditary predisposition. The disease develops against the background of a mutation in the SOS1 gene. This disruption causes fibroblast growth to occur more slowly. These cells are responsible for the production of collagen. Exceeding the level of the latter provokes active growth of fibrous tissue.
The pathogenesis of the disease is not fully understood today. It is believed that genetic predisposition is the main provoking factor. Fibromatosis is first detected in young children.
However, their clinical picture of the disease is mild. In the future, the intensity of symptoms increases under the influence of hormonal changes in the body. It can also be affected by certain medical conditions and pregnancy.
On this topic
- Gum inflammation
All about tooth root inflammation
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- September 3, 2020
The second theory states that the inflammatory process, in which fibrous tissue grows, is caused by drugs. The latter include:
- drugs against epilepsy;
- immunosuppressants;
- calcium blockers ;
- medications prescribed after transplantation;
- hormonal contraceptives (they contain a lot of estrogen).
It has been established that long-term use of these drugs causes hypertrophy of gum tissue in approximately 30% of patients. The disease caused by drugs is characterized by rapid development, and the affected area turns red.
Researchers suggest that gum fibromatosis develops against the background of certain diseases of the endocrine system. In addition, many patients with Down syndrome have a generalized form of the pathology.
Treatment of gum fibromatosis
Modern medicine provides for the treatment of gum hyperplasia only with surgical methods. A special procedure is performed - gingivectomy, during which the doctor makes an incision into the enlarged gingival margin. The operation lasts 30 minutes and requires local anesthesia. The dentist applies a special periodontal bandage to the damaged area, which protects the wound from infection. In parallel with this, sanitation of the oral cavity is performed, including the elimination of tissue defects and the treatment of dental caries. If the disease affects temporary teeth, the doctor is forced to remove them.
Treatment of gum fibromatosis
It is not uncommon for fibromatosis to return after treatment. In such cases, the doctor is forced to perform another surgical operation. If hyperplasia has a medicinal form, then during treatment the doctor recommends replacing the previously used drug with another. Such a replacement often leads to positive changes, namely to the gum tissue regaining its previous appearance.
With repeated use of drugs that provoked the occurrence of gum hyperplasia, the chances of recurrence of the pathology increase significantly. If replacing the medications does not help, the doctor removes the pathological gum tissue surgically. Regular removal of tartar helps slow down the progression of the disease.
At the dentist
ethnoscience
Folk remedies will not help get rid of hyperplasia, but they can be used as an addition to the main therapy. Due to the antibacterial effect, various infusions of medicinal herbs are used for rinsing the mouth. Below are the most effective recipes for folk remedies used in the treatment of oral diseases.
Table. Folk remedies for gum hyperplasia.
| Product name, photo | Application |
| Horseradish tincture | Pour 500 ml boiling water 3 tbsp. l. chopped horseradish and leave for 50-60 minutes. After straining the finished tincture, use it to rinse your mouth 2 times a day - morning and evening. This will cleanse the blood vessels, relieve inflammation and destroy bacteria in the oral cavity. |
| Propolis chewing gum | Dissolve 60-80 g of propolis in a water bath, then mix it with 5 g of lemon juice, 5 g of lemon balm essential oil and 1 tsp. honey Cut the hardened mass into small pieces. Cooked chewing gum can kill bacteria, which is why it is often used to treat colds. |
| Beetroot compress | Mix 1 tbsp. l. sea buckthorn oil with fresh beets chopped on a fine grater, so that the result is a homogeneous substance. Apply a compress from the prepared composition to the gums 2 times a day. The duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. |
| Oak bark balm | Grind 2 tbsp. l. oak bark and mix it with 1 tbsp. l. linden flowers. Pour 300 ml of boiling water over it and leave for 40 minutes. After straining the prepared balm, use it to rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day. |
| Chamomile decoction | In medicine, chamomile is used for its wound healing and anti-inflammatory properties. To prepare the decoction, pour 200 ml of boiling water into 4 tbsp. l. dried chamomile flowers. Leave for 1-1.5 hours. Rinse your mouth with this decoction 5-6 times a day or every few hours. |
On a note! Refusal to seek medical help, as well as self-medication for gum fibromatosis can lead to serious problems. Eliminating such consequences will be much more difficult than curing hyperplasia.
Traditional medicine: will it help or not?
Gum hyperplasia has nothing to do with the inflammatory process, so its independent treatment with folk remedies will not give positive results. A person will only waste precious time, and the mucous membrane will continue to grow. However, traditional medicine can alleviate the condition and speed up the rehabilitation period after professional intervention is initiated and carried out.
You can simply perform the well-known rinses from a decoction of chamomile, sage, and oak bark herbs. Or you can use more unconventional methods:
- beets and sea buckthorn: if you mix pureed fresh vegetables with sea buckthorn oil, you can apply similar applications to sore gums. Exposure time – no more than 20 minutes,
- propolis: melt the wax in a water bath, then add lemon juice and a little honey to the resulting mass. Leave to harden - use by chewing the pieces thoroughly in the mouth,
- horseradish: grate it, pour boiling water over it. Next, you need to leave the broth for an hour and rinse your mouth with it.
Possible complications
Often, hyperplasia can provoke the development of other, no less dangerous diseases. An increase in the volume of gum tissue leads to disruption of the functioning of the patient's oral cavity.
Example of possible complications
Complications of this pathology include:
- loss of one or more teeth;
- the appearance of loose teeth;
- bone tissue atrophy;
- spread of tartar.
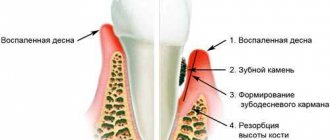
Gum pockets gradually enlarge as the connective tissue of the gums increases. The development of fibromatosis significantly complicates the process of cleaning the oral cavity, so small food particles often accumulate in the resulting pockets. All this leads to the development of bacteria, the appearance of plaque, resulting in the formation of tartar.
Gum hyperplasia during pregnancy (22nd week)
In severe stages of the pathology, the patient experiences bone tissue atrophy. As a rule, it extends only to the upper jaw. The interdental septa are resorbed, as is the alveolar process (the anatomical part of the upper and lower jaw on which the teeth are located). Over time, the gum tissue becomes looser, which is why it cannot perform its main function - to hold teeth. As a result, the patient loses one or more teeth. In rare cases, he may lose his entire row of teeth.
Prognosis and complications of gum hypertrophy
Hyperplasia leads to other serious problems in the oral cavity. The consequences of the pathology include:
- pathological enlargement of the periodontal pocket;
- loss of teeth or the appearance of their looseness;
- deformation of bone tissue;
- formation of tartar.
Timely treatment and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations will help cope with the pathology of gum growth and avoid serious complications.
Bibliography
- Murovyannikova Zh.G. – Dental diseases and their prevention, Rostov n/a: Phoenix, 2011.
- Dmitrieva L.A. — Modern aspects of clinical periodontology, M., 2001.
- Tsepov L.M., Kamanin E.I., Morozov V.G. — Periodontitis: problems of complex therapy, Smolensk, 1992.
- Gaurav, Solanki and Renu Solanki - Dental Plaque Forming Bacteria's Characterization and Stress Responses - M.: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, 2012.
- Leontyev V.K., Pakhomov G.N. — Prevention of dental diseases, M., 2006.
- Afanasyev V.V. — Surgical dentistry: textbook, M.: Geotar—Media, 2011
- T. G. Robustova, V. V. Afanasyev [and others] - Surgical dentistry / 4th ed., M.: Medicine, 2010.
- G. M. Barer, E. V. Zoryan. — Rational pharmacotherapy in dentistry, M.: Litterra, 2006.
Read related posts:
Prevention measures
Among all the possible reasons contributing to the development of gum hyperplasia, insufficient oral hygiene is far from the least important. To prevent the occurrence of an inflammatory process, it is necessary, first of all, to limit the amount of sweets consumed, as they negatively affect the condition of the teeth and oral cavity. After each meal you need to rinse your mouth with a special solution or brush your teeth. It is also advisable to give up bad habits that have a detrimental effect on the condition of the gums and teeth.
Disease prevention
Smoking not only weakens the patient's immune system, but also impairs blood circulation in the gums. Therefore, if you or your relatives have had gum hyperplasia before, try to get rid of this bad habit.
On a note! If you have dentures that do not adhere well to the surface of the gums, replace them with better ones. Otherwise, harmful bacteria will accumulate in the space between the gum and the product.
Dentures
Regular snacking can cause the formation of tartar, which can lead to gum tissue disease. To prevent this phenomenon, you need to use dental floss after each such snack or abandon them altogether. Dental chewing gum can help clean your mouth, but it is not recommended to chew it on an empty stomach.
Whether you have any dental disease or not, it is important to visit your doctor's office regularly for dental checkups. Many oral pathologies do not appear in the initial stages, so only an experienced specialist can identify them in a timely manner. Visit your dentist twice a year and you can avoid many oral diseases.
Teeth cleaning
You can have your teeth professionally cleaned periodically when you visit your dentist's office. This will remove all plaque from the surface of the teeth that cannot be removed with a regular toothbrush. Also, do not forget about the therapeutic diet. Proper nutrition also helps prevent many oral diseases, including hyperplasia. It is better to consult a specialist regarding the preparation of your diet, but in most cases it includes daily consumption of vitamin-containing foods (fresh fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and so on). Following such a diet will not only protect the body, but also lose extra pounds.
Treatment
Treatment of fibroma is carried out surgically: pathological tissue is removed using laser or radio wave exposure. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis and lasts 20-40 minutes. If the fibroma is large, the wound formed after removal is covered with a V-shaped flap from adjacent tissues. This helps prevent deformation of the mucous membrane.
In cases where the appearance of a tumor is caused by permanent damage to the mucosa, it is sometimes possible to do without surgery. Fibroma may decrease or completely disappear after eliminating the provoking factor: re-filling the tooth, removing the destroyed tooth root, replacing the prosthesis.
Manifestations of the disease
The following clinical symptoms allow you to recognize gum fibromatosis:
- In the initial stages, swelling or enlargement of tissue of a tumor nature.
- On the mucous membrane you can see thickenings that gradually increase.
- Increased gum volume without signs of swelling.
- Filling interdental spaces with soft tissue.
- Overlapping of the teeth with the edges of the gums.
- Injury to overgrown areas during cleaning (this can cause bleeding and inflammation).
- Increasing intensity of tissue color (the gums become bright pink).
If you notice any signs of fibromatosis, you should immediately contact your dentist. If you ignore the problem, unpleasant complications may develop:
- decreased quality of daily hygiene with an increased risk of developing infections;
- pain when eating;
- redistribution of chewing load;
- development of periodontal diseases.
Treatment methods
The treatment regimen is determined by the cause of fibromatosis. Due to the fact that most often the disease is caused by a genetic predisposition, the basis of treatment for the pathology is surgical intervention.
On this topic
- Gum inflammation
Find out why inflammation occurred after tooth extraction
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- September 3, 2020
Oral surgery is performed under local anesthesia. For generalized fibromatosis, general anesthesia is indicated. Removal of overgrown tissue is carried out by:
- carbide boron and turbine nozzle;
- carbon dioxide laser
The latter method of excision is considered the most effective, as it eliminates the formation of bleeding. The duration of the operation is determined by the nature of the lesion. It is often carried out for 15-40 minutes.
In cases where tissue hypertrophy is detected on both jaws, the gums at the top are first excised. Repeated surgery is scheduled after 3 weeks.
During the procedure, the doctor excises the periodontium down to the periosteum. Deeper penetration increases the risk of relapse and is therefore rarely prescribed. Periodontal regrowth is possible 5 or more months after surgery.
If the affected area is not extensive, then surgical removal is completed by applying a bandage of iodomorphic tundra or a silicone membrane to the gum. The last option is considered more preferable. Tundra can lead to oral infection in the future.
After surgery, during the first week, the patient must take anti-inflammatory drugs and multivitamin complexes in the dosage prescribed by the doctor. After the allotted time has passed, the dentist removes the applied bandage. A repeat inspection of the problem area is carried out after a month. By this time, the tissues in the problem area should have fused together.
In cases where diffuse fibromatosis is diagnosed, the operation is performed over several stages. The duration of therapy for this type of lesion is about 80 days.
If during the diagnosis it was determined that the cause of hypertrophy of the gum tissue was the use of certain medications, then therapy for the disease involves stopping the use of the medication and replacing it with another drug with a different composition, but a similar effect.
speed up the recovery process for this type of fibromatosis. During the procedure, plaque is removed from the problem area. In severe cases, the described procedure is supplemented by taking antihistamines.