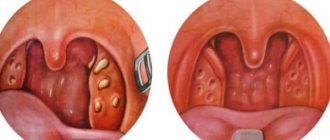
After any surgical intervention, there is a high probability of developing purulent complications. This is due to infection of the wound, as well as the likelihood of an inflammatory process developing in it. This is why antibiotics are prescribed after surgery. These chemicals are used to kill pathogenic pathogens. The result of such an effect is the elimination of the inflammatory process.
The word "antibiotics" translated from ancient Greek means "against life." And this name justifies the action of such means. After all, they are used to suppress the development of living cells.
Antibiotics after surgery are prescribed by the attending physician. Such therapy should be carried out only with his knowledge and in the required dosage.
Composition and release form
Amoxicillin is the active ingredient in all versions of the drug. Presented in trihydrate form. The dosage and composition of auxiliary components depend on the form of release.
The medicine is sold in the form of tablets, capsules and granules.
Amoxicillin capsules
The soft gelatin shell of the capsule facilitates the absorption of the active substance. Antibiotic dosage options: 250 or 500 milligrams. The standard package contains 16 capsules.
Amoxicillin tablets
The tablet form shell promotes the absorption of the active substance in the desired part of the gastrointestinal tract. Dosage options: 250 or 500 milligrams.
Package
Amoxicillin granules
An oral suspension is prepared from the granules. This dosage form is better absorbed in the digestive tract. Standard dosage options: 250 or 500 milligrams.
The antibiotic is approved for use in childhood, but patients under 18 years of age should not take this drug together with metronidazole.
Therapeutic effect
According to the classification, the active substance belongs to semisynthetic antibiotics of the penicillin group. This chemical compound is active against a wide range of pathogens. The base of the active component is made from a mold culture. The mechanism of antimicrobial activity is due to disruption of the formation of an important component of the bacterial cell wall. The effect of the drug is bactericidal, since disruption of the formation of the cell wall leads to the destruction of pathogens.
Activity spectrum
Side effect
During drug therapy, adverse effects sometimes occur due to the action of the active substance on various tissues and organs. The main side effect is considered to be a reaction of increased sensitivity of the immune system to the components of the drug (allergy). To reduce the risk of developing such a complication, it is necessary to exclude in advance an allergy to the chemical compounds included in the granules, tablets or capsules.
Other Adverse Effects:
- Nervous system: agitation, decreased mood, cephalalgia, dizziness, convulsions, sleep disturbance, anxiety, impaired motor activity, behavioral changes, neuropathy, impaired consciousness.
- Abdominal organs: disruption of the intestinal microbiome, deterioration of liver function, pseudomembranous enterocolitis, change in taste, vomiting, loose stools, inflammation of the tongue tissue, inflammation of the oral mucosa, increased levels of liver enzymes.
- Immune system: skin rashes, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Quincke's edema, increased body temperature, redness of the integumentary tissues, inflammation of the conjunctiva and nasal mucosa, anaphylactic shock, arthralgia, increased levels of eosinophils, dermatitis and others.
- Other reactions: decreased leukocyte levels, thrombocytopenic purpura, decreased neutrophils, decreased red blood cells/hemoglobin, respiratory failure, changes in cardiac rhythm, superinfection, secondary infectious diseases.
The severity of side effects depends on the patient's condition, dosage and other factors. Severe complications while taking the drug rarely occur.
Indications for use of Amoxicillin
The drug is used as monotherapy or together with other medications to treat bacterial diseases. Often combined with clavulanic acid to improve antimicrobial activity against infectious agents that secrete beta-lactamase. The drug has a wide spectrum of action, so it is possible to use the antibiotic in the treatment of various pathologies.
The purpose of prescribing the medication is determined by the attending physician. Self-medication is prohibited.
Main indications
- Bacterial damage to the respiratory system: inflammation of the lung tissue, bronchi, throat.
- Bacterial damage to the excretory organs and reproductive system: inflammation of the kidney tissue, urethra, endometrium and other organs.
- Infectious and inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract in combination with metronidazole: Helicobacter pylori infection of the gastric mucosa, gastric ulceration, inflammation of the small intestine.
- Others: gonococcal infection, listeriosis, damage to the skin and soft tissues. Other diseases caused by pathogens sensitive to the drug.
Why are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed?
No comments yet. Be first!
General information about drugs
It is worth noting that most old people suffer from many joint diseases, muscle pain, back pain and other ailments, and it is simply necessary to use strong painkillers. For example, painkillers are indispensable for arthrosis, painkillers for back pain, as well as for the development of other “senile” diseases, for the relief of symptoms of which other drugs are ineffective.
All non-steroidal drugs can be divided into 2 groups, taking into account their anti-inflammatory activity and chemical structure. The first group consists of the strongest painkillers that have a pronounced effect. The second group includes drugs that have a weak anti-inflammatory effect, which are called “non-narcotic analgesics.”
New generation NSAIDs
Consider the list of the most common non-steroidal painkillers:
NSAIDs for neuralgia
NSAIDs for intervertebral hernia
Such drugs for the treatment of hernia are produced with different chemical structures and can be used in different forms of release, such as tablets, ointments or suspensions. For example, Aceclofenac and Diclofenac block the production of enzymes that contribute to the occurrence of inflammatory processes. They also help thin the blood and remove toxic substances from it.
NSAIDs for joint pain
Taking these drugs for joint pain can cause allergies, nausea, exacerbation of gastric ulcers, or may not be accompanied by such manifestations at all. Only a doctor can prescribe non-steroidal drugs for joint pain, based on the individual characteristics of the course of the disease, as well as taking into account the patient’s tolerance to a particular drug.
Non-steroidal drugs for joint pain should not be combined with each other. Taking several medications at the same time will not increase their effect, but will increase the likelihood of stomach ulcers.
NSAIDs after surgery
Diclofenac. You can achieve the desired effect within half an hour after taking the medicine. Penetrating into every organ and tissue, the drug is effective in every type of operation. In case of severe pain after surgery, Diclofenac injections are prescribed, gradually switching to tablet form.
Nimesulide. A modern and safer product for use after surgery of various locations. The only drawback of this medicine is that it does not come in an injection form.
Rofecoxib. Both injection and tablet forms are used for use after surgery of various locations. There is no damage to the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, which makes the medicine safe for use for existing stomach ulcers.
Side effects and contraindications
If you take this type of drug for a long time and at the maximum dosage, no matter what disease it is for, you may experience the following side effects:
The main contraindications include:
- individual intolerance to drugs with such an effect;
- stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- other damage to the digestive system;
- impaired functioning of organs such as the liver and kidneys.
To avoid side effects from taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, you must follow all doctor's recommendations for their use.
Contraindications
The product is not suitable for all patients. Some patients are at increased risk of developing serious complications during drug therapy. The main limitation for use is an allergy to the substances contained in the tablets, capsules or granules. Before treatment, you need to study your allergic history.
Prescribed by a doctor
Other contraindications:
- Severe infectious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, manifested by vomiting and loose stools.
- Sensitivity to antibiotics of the penicillin and cephalosporin groups.
- Viral diseases of the respiratory system.
- Benign lymphoblastosis.
- Diathesis of an allergic nature.
- Liver pathologies.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Hay fever.
If the drug is used together with clavulanic acid, it is necessary to exclude liver dysfunction due to such therapy in the past. Use together with metronidazole has additional contraindications: central nervous system pathologies, lymphocytic leukemia, sensitivity to nitroimidazole derivatives.
Instructions for use of Amoxicillin
Any antibiotics are allowed to be used only as prescribed by a doctor. During the appointment, the specialist examines the patient’s complaints, checks the medical history and conducts an initial diagnosis. A safe drug therapy regimen is selected. You can take the product regardless of food intake. It is important to follow the dosage prescribed by your doctor and take the medicine at the same time every day. You should not stop therapy on your own after the symptoms disappear, if the course of treatment prescribed by a specialist has not come to an end.
The dosage regimens listed below are for reference purposes. During therapy, you need to follow the instructions of the attending physician and official instructions.
Application schemes
- For patients over ten years of age: 250 to 500 milligrams at a time. Three times a day. It is possible to increase the dosage to 1000 milligrams at a time as prescribed by a doctor.
- For patients aged five to ten years: 250 milligrams three times a day.
- For patients aged two to five years: 125 milligrams three times a day.
An oral suspension is made by adding granules to drinking water. The interval between doses is eight hours.
additional information
- Interaction with other medications: decreased effectiveness of oral contraception, improved antimicrobial activity in combination with other bactericidal agents and decreased in combination with bacteriostatic drugs, increased effect of anticoagulants and decreased effectiveness of medications that form PABA in the body. There are other interaction features that are indicated in the official instructions.
- If renal function decreases, the dosage regimen must be adjusted in accordance with creatinine clearance. The correction is carried out by a doctor.
- The antibiotic slightly penetrates the placental barrier. Use during lactation and pregnancy is possible only with the permission of a doctor.
- If you have a history of allergic reactions, the drug should be taken with caution.
- You should not drink alcoholic beverages during therapy.
Full instructions can be found in the packaging.
Amoxicillin for flux
The medication is prescribed when the following symptomatic manifestations are detected:
- when a tumor forms in the gum area, in nearby areas near the problem tooth;
- with purulent discharge from the affected area;
- if enlarged lymph nodes are detected;
- with sudden outbreaks of pain when trying to touch the painful area;
- with an increase in body temperature.
Experts divide pathology into acute and chronic processes. The first has the most striking symptomatic manifestations, the second is formed as a result of a poorly treated tooth.
Simple and effective measures to combat flux include drugs from a subgroup of antibiotics. Most dentists prescribe them to their patients, warning them that they cannot be used independently. Any self-medication for pathology can provoke side effects and the development of complications.
Before prescribing the drug, the specialist sends the patient for laboratory diagnostics - in order to determine the type of pathogenic pathogen that has entered the body. In most cases, the culprit of flux is a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection.
The total duration of therapy does not exceed one calendar week, dosage levels are determined by the attending physician. Attempts at self-treatment in the form of hot compresses or taking Aspirin can provoke further spread of the infection to nearby tissues.
The dosages required by the patient are prescribed on a strictly individual basis, depending on the degree of development of the lesion. Each unit of the drug contains 250 or 500 mg of the active ingredient. For the treatment of the desired pathology, doses of 500 mg are most often used.
Standard antibiotic prescriptions include:
- adult patients and children over 10 years old - three times a day, 500 mg at each dose;
- children from five to ten years old - three times a day, 250 mg;
- for children under two years of age - the volume of medication is prescribed according to the child’s weight - 20 mg of medication per kilogram of body weight.
The drug is taken before and after eating.
Video
Amoxicillin is an effective antibiotic that can eliminate bacterial infection in various organs. Used alone or together with other medications that improve the antimicrobial effect. A doctor's prescription is required to purchase.
Antibiotic drugs are understood as chemical substances, mainly against pathogenic microorganisms.
Often, patients in the postoperative period have doubts about the advisability of taking antibiotics prescribed by specialists.
Doctors say that antibiotic drugs after surgery are a necessity, justified by the possibility of purulent complications due to infection of surgical sites.
Consequences of septoplasty of the nasal septum
Peeling of the skin around the nose
Today, one of the types of this surgical intervention can be used, each of which has a high success rate and is prescribed by the surgeon who will perform the operation, depending on the patient’s health indicators. The main objective of this operation is to eliminate pronounced unevenness of the nasal septum, ensure high-quality nasal breathing and remove excess septal tissue, which impedes the access of air to the nasal cavity.
Therefore, the main consequence of septoplasty, regardless of its type, is the alignment of the nasal septum, ensuring more complete breathing and improving the general condition of the patient. With this operation, you can eliminate frequently occurring ENT diseases, constant nasal congestion, difficulty breathing and frequent nosebleeds.
The rehabilitation period is quite short, and following all the doctor’s recommendations will allow you to avoid possible complications and maintain the positive result for as long as possible.
In this video, the girl will share her experience regarding complications after surgery:
When is it necessary to prescribe antibiotic drugs?
The risk of developing opportunistic infections as a result of reduced immunity should be taken into account. Antibiotic therapy is prescribed after determining the source of the inflammatory process and studying the clinical course of the complication individually.
A course of taking antibiotics is necessary after operations involving extensive interventions against the background of penetrating wounds and injuries, with purulent inflammatory processes affecting the organs of the chest and abdominal cavity.
Antibiotics after abdominal surgery are required to prevent the spread of bacteremia and sepsis (abdominal or general). Surgical intervention is often accompanied by microbial contamination.
The following can enter the body:
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- streptococci;
- enterobacteria;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa and others.
In many branches of medicine, be it gynecology, cardiac surgery, urology and others, it may be necessary to destroy the inflammatory processes that have arisen and reduce the possibility of re-infection after operations affecting:
- gastrointestinal organs;
- kidneys;
- pelvic organs;
- lungs;
- liver, bile ducts, bladder;
- blood vessels and heart;
- nervous system.
When prescribing the drug, the following are taken into account:
- location of purulent inflammation;
- the speed of the process;
- characteristics of the infectious pathogen;
- agent resistance to certain antibiotics.
Experts prefer to use fast-acting substances that combine a wide range of effects, low risks of side effects, and satisfactory patient perception of the drug.
When used systemically, various forms of drugs can be used after surgery. For injection and infusion administration, both ready-made ampoule solutions and powders, which include cephalosporins and carbapenems, are used.
After operations, it is acceptable to take antibiotics in tablets and suspensions. The latter are prescribed in cases where the condition is relatively stable and the level of the inflammatory process is low.
The period of taking antibiotics after surgery is strictly regulated and is no more than seven days. Exceptions are possible in case of extensive lesions, bacteremia, sepsis, and it is possible to combine several agents, the interaction of which will provide effective antibacterial treatment.
Review of drugs
It is believed that the most rational way to use antibiotics after surgery is through injections. Let's look at the main methods of administering the most commonly used drugs.
1. Cephalosporins. These antibiotics are administered both by injection and infusion. The doctor calculates the dose based on the existing clinical picture. An antibiotic dose of 0.25 to 0.5 grams is prescribed at eight-hour intervals, and 1 gram at 12-hour intervals. As the patient's condition worsens, the amount of the administered drug is reduced.
2. An antibiotic such as Amikacin is administered intravenously or intramuscularly. Moreover, its daily amount is determined by the attending physician based on the patient’s weight. For one kilogram it is necessary to prescribe 10-15 mg of the drug. The total dose of antibiotic is divided into several doses.
3. A drug such as Amoxiclav is also administered intravenously or by injection. It is injected three times in children under 12 years of age, as well as in adult patients. A single dose is 1-2 grams. When the patient is in the age group from three months to twelve years, the amount of the administered substance is calculated by weight. In this case, 30 mg of the drug must be administered per kilogram.
What medications are prescribed in the postoperative period?
Based on the interaction of pharmaceutical substances and microorganisms, antibiotics are divided into:
Bacteriostatic (does not allow bacteria to multiply, but does not kill pathogens);- Bactericidal (actively fight harmful microorganisms, destroying them).
Treatment of severe infections involves the use of bactericidal agents, especially in cases of weakened immunity.
When bacteriostatic drugs are prescribed and then discontinued, bacterial growth may resume, which leads to relapses and the process becoming chronic.
Antibacterial drugs, according to their chemical structure, are divided into:
- Beta-lactam antibiotics (these include beta-lactamase inhibitors, used exclusively in combination with beta-lactams, as well as penicillins, monobactams, cephalosporins and carbapenems).
- Macrolides.
- Amphenicols.
- Glycopeptides.
Tetracyclines.- Nitrofurans.
- Nitroimidazoles.
- Sulfonamides.
- Lincosamides.
- Aminoglycosides.
- Quinolones.
- Drugs of other groups, the chemical structure of which is different.
- A group of drugs directed against tuberculosis.
- Antifungal drugs.
If we talk about which antibiotics are preferable to prescribe after operations, the list of drugs preferred by specialists includes:
Cephalosporins, which include Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, Cefazolin and others. The action of the drugs is based on the ability to penetrate anaerobic and aerobic agents, thereby changing protein enzymes. As a result, microbial cell division is inhibited.- Drugs belonging to the group of aminoglycosides, in particular Amikacin. The substance cannot invade bacterial cells, but stops their mitosis, destroying protein synthesis. The result is the death of bacteria.
- Amoxiclav belongs to the penicillin group of antibiotics. It contains amoxicillin, clavulanic acid. The first reduces the enzymatic activity of microorganisms and blocks the formation of cell membranes. Acid destroys the bacteria's defenses against antibacterial substances.
Among the drugs belonging to the carbapenem group, the most often prescribed is Meropenem, which destroys protein synthesis, which stops the spread of bacteria. At the same time, the production of toxins by gram-negative microorganisms is suppressed, thereby achieving an additional therapeutic effect.
All of these drugs belong to the group of beta-lactam antibiotics. First of all, pharmaceutical preparations of the cephalosporin series are used after operations, which is justified by their increased activity relative to most gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Cephalosporin antibiotics successfully stop infections with minimal risk of negative side effects.
Modern antibiotic drugs
The most successful choice for the treatment of bacterial endometritis, salpingoophoritis and other infectious diseases of the genital area is a combination of protected aminopenicillin (amoxicillin/clavunate) with a macrolide or doxycycline. Such therapy is precisely aimed at suppressing the main aerobic, anaerobic and intracellular microorganisms that are most often isolated during the diagnosis of pelvic infections.
The addition of the substance clavulanic acid to amoxicillin, which became inactive against penicillin-resistant strains of many microorganisms that constantly inhabit the body, led to an increase in the antibiotic effectiveness of the drug and an expansion of its use in gynecological and obstetric practice. This additional substance introduced into the drug protects amoxicillin molecules from the destructive action of bacterial cell enzymes.
Amoxicillin with clavulanic acid is well tolerated with long-term use, but it cannot be used for intramuscular injection. Tablet forms of drugs are also available for intravenous supervised use in a hospital setting.
Due to the fact that there is not a single antibiotic that is immediately active against all microorganisms that cause inflammation of the pelvic organs, combinations of several drugs are used for treatment in medical practice.
Protected amoxicillin for endometritis, inflammation of the appendages and other mixed infections of the pelvic organs is prescribed by a doctor at 1000 mg morning and evening for at least 10 days in combination with ofloxacin tablets 400 mg twice a day for a week. With concomitant thrush, the antifungal drug Fluconazole is introduced into the treatment regimen, 150 mg once or 50 mg for at least 7 days. The tablets should be taken with water during meals, without chewing.
Antibiotics of the group of protected penicillins (Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Panclave) are also used for preventive (preliminary, prophylactic) treatment of infectious complications during gynecological surgical interventions. Thanks to the biochemical properties of the drug, the necessary concentrations of the antibiotic are created in the tissues before contact with possible microbes during surgery, which reduces the risk of complications.
Preference is given to soluble forms of modern antibacterial drugs (solutab) protected amoxicillins. They are distinguished by more complete absorption of the active substance from the gastrointestinal tract, protecting beneficial intestinal microflora and allowing constant therapeutic concentrations to be maintained in the blood to eliminate the pathogen from foci of inflammation. Thus, when treating diseases of the internal genital organs, the frequency of relapses and progression of the infection to a chronic form is reduced.
Video: Live healthy! Women's diseases. Inflammation of the appendages
Do all patients need to take antibiotics after tooth extraction?
Is it necessary to take antibiotics after tooth extraction? Tooth extraction (this is the official name of the removal process) is a surgical operation after which the damaged soft and hard tissues of the jaw require time for rehabilitation. To ensure that the hole formed at the site of the extracted tooth heals without problems, and also to eliminate the risk of infection and the development of complications during this period of time, doctors prescribe antibiotic therapy.
Do you need to have teeth removed during pregnancy and don’t know what to do? Read a detailed article on this topic on our website.
It is not always necessary to take antibiotics after tooth extraction
However, not all patients need to take medications. For example, if the procedure was planned and predictable, the patient is healthy, and the operation itself took place without unnecessary trauma, then the doctor will not prescribe an antibiotic after tooth extraction. Sometimes a specialist assesses the situation over time and may prescribe a course of medication not immediately after the operation, but only after a routine examination. For example, if the patient complains of persistent pain, deterioration in general condition, and the doctor discovers redness and swelling of the mucous membrane, the presence of pus in the socket. That is, in situations where complications arose.
Types of painkillers after surgery
One of the most popular painkillers for terrible pain after surgery is the famous paracetamol.
Penetrating into the source of fire, paracetamol tablets activate the vital processes of the human body, which contributes to the speedy recovery of the affected area of the body.
Painkillers are sold in almost every modern pharmacy and have a relatively low price.
Pain relief from the body after surgery often occurs with the help of Ketone tablets. This type of medicine is not used for chronic diseases and has a number of limitations. For example, the drug should not be taken by: children under 16 years of age, pregnant women, breastfeeding, asthma, diathesis, ulcers, and so on. Thus, under the influence of this drug, pain relief occurs not only after surgery, but also, for example, with osteochondrosis, menstruation, fractures, tissue structure disorders, oncology, abdominal pain and even after the removal of a diseased tooth.
It is important to have a medicine such as aspirin. This drug helps to cope with pain in different parts of the human body, as well as at high temperatures. However, like all drugs, aspirin has a number of limitations. For example, the use of the drug is contraindicated for inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, pain during menstruation and for children, including adolescence. Thus, the use of aspirin can cause the development of liver disease in adolescents and even affect the human brain. By the way, aspirin is quite cheap.
One of the controversial painkillers of modern medicine is analgin, which has an effect on the human body. For example, it is much more effective than paracetamol. However, this drug negatively affects the circulatory system, liver, kidneys and lymphatic system. Modern doctors are of the opinion that this device should be used only in case of critical need. For example, when other painkillers did not have the desired effect.
Medicines that have a positive effect after surgery are injections. Typically, the attending physician independently prescribes the required dosage of the medication, which is subsequently used by the nurse.
Who can't do without taking antibiotics?
Antibiotics must be taken during tooth extraction if there is at least one of the following risk factors:
- unscheduled removal due to an acute inflammatory process: it often happens that a patient comes to the dentist with acute pain, but the tooth can no longer be treated or restored (for example, a large cyst has grown on the root),
- “figure eight” extraction: wisdom teeth often have a complex structure (their roots can be branched and tortuous), they can be impacted or dystopic. To remove them from the jawbone, doctors are sometimes forced to cut through the gum, crush the jaw and root, taking it out in parts. Next, stitches are applied. The procedure is complex, therefore, when removing “eights”, antibiotics must be taken,
Mandatory medication is prescribed for complex removal operations
According to statistics, in the case of a complex extraction procedure and without additional drug therapy, complications occur in 38% of patients.
- traumatic removal: for example, a doctor, due to carelessness or lack of professionalism, could severely damage the gum, the wall of the socket, which could cause severe bleeding,
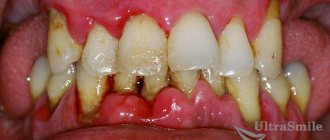
- the presence of untreated teeth in the mouth: when removing a tooth, antibiotics must be taken by all those who have untreated caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, cysts, or periostitis in neighboring units. It is also important to take medications for those who have inflammation of the gums, gingivitis and periodontitis,
- old age: in mature people, the immune system is weakened, and tissue regeneration processes are much slower than in young people,
- the presence of chronic diseases: for example, diabetes, bleeding disorders, hypertension. If hemostasis is impaired, the patient may develop anemia without additional drug support.
What you need to know to properly prepare for anesthesia.
- Operations cannot be performed during acute infectious diseases. Common colds and acute respiratory infections are the most common reasons for postponing surgery
- If you have chronic diseases, then before surgery under general anesthesia they should be in a state of stable remission (without exacerbation).
- The anesthesiologist may prescribe additional studies and consultations that are not included in the mandatory list, as well as reschedule and even cancel surgery for your safety.
- It is necessary to remember in advance (make a list) and inform the anesthesiologist about all existing diseases, operations, allergic reactions and medications that you are taking. In this case, no information can be insignificant or superfluous.
- You must remove all jewelry, piercings and contact lenses. It is advisable to keep your fingernails free of false nails and polish, as this may interfere with the operation of some sensors.
- For surgery, it is recommended to wear underwear made of natural cotton (no synthetics).
- You should not drink or eat before surgery. (6 hours before surgery, you must avoid taking any food or drink). The evening before surgery, prepare yourself a light dinner.
- If you are taking any medications, be sure to inform the anesthesiologist in advance, as some medications must be stopped before surgery.
What happens if a patient refuses to take antibiotics?
If you are interested in the answer to the question of whether you need to take antibiotics after tooth extraction, then you need to have an idea about the negative consequences that can happen if you do not take medications.
The very first thing that can happen is that a protective clot will not form in the hole of the removed unit. For example, this can happen against the background of poor blood clotting, or when the body’s immune forces are weakened. The presence of a “dry” socket in patients is often complicated by alveolitis, when bacteria penetrate into an unprotected wound, and an inflammatory process and suppuration begin in it, accompanied by acute pain, swelling, and a general deterioration of the condition.
Refusal to take medications can lead to inflammation of the socket
Taking antibiotics in dentistry: during tooth extraction, after and during treatment
Antibiotics - their function and role in therapeutic and surgical dentistry.