17.02.2019
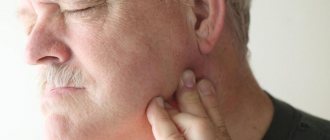
If your lower jaw hurts, then you should consult a dentist, surgeon or neurologist. The fact is that pain in the lower jaw can cause a huge range of reasons, ranging from dental to neurological. If you feel pain in the muscles of the jaw just under your jaw, this is a sufficient reason to contact a specialist, because such pain cannot be tolerated. Self-medicating is not the answer, but you should be aware of what exactly a particular symptom means.
Self-diagnosis
There are a number of signs by which you can determine why your throat hurts under the lower jaw or the jaw itself. This will help you choose the right doctor to see.
Injury
To detect jaw injury, check for bruising and swelling. Also, if you are injured, you will feel pain (strong or not, depending on the type of injury) when you press.
The lower jaw is not so simple.
The pain may be on the right or left, depending on the injury itself. Immediately after an injury, the saliva may contain blood.
Infection
Pain in the lower jaw can cause a dental abscess or, simply put, a tooth abscess, that is, an accumulation of pus in the gum. This abscess is characterized by the presence of a dense swelling on the oral mucosa. When you press on the swelling area, severe sharp pain appears.
Another symptom that often appears is inflammation of the lymph nodes. Hence the pain under the jaw. A dental abscess can be caused, for example, by advanced caries.
The infection can also cause acute osteomyelitis. In this case, it is painful for the patient to open his mouth and swallow (since the muscle usually swells significantly). Pain when swallowing can be concentrated on the right or left.
Actinomycosis (also an infectious disease) affects the right or left corner of the lower jaw. The angle of the jaw is covered with multiple passages with a characteristic greenish-yellow liquid.
Problems with the temporomandibular joint
There can be four such problems:
- dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint (the masticatory muscle spasms, the jaws close tightly);
- rheumatoid arthritis (swelling and pain when pressing in the joint area);
- osteoarthritis (severe swelling, it hurts the patient to open his mouth and chew);
- dislocation of the mandibular joint (the main symptom is the inability to close the mouth).
Lower jaw cyst
Essentially, a jaw cyst is a cavity in the bone filled with fluid. The main problem with such a cyst is that it can be completely asymptomatic for a long time. During inflammation of the cyst, severe pain occurs when chewing, swelling and redness.
Neoplasms
If swelling in the jaw area remains painless for a long time, this may indicate that it was caused by giant cell granuloma, osteogenic sarcoma, or Burkitt's lymphoma.
Each of these neoplasms has its own nuances, for example, with a granuloma, the color of the swelling will be purple with a bluish tint, with sarcoma, the teeth will begin to loosen over time, and lymphoma will develop very rapidly.
Treatment options
If the cause of a unilateral sore throat is cervical osteochondrosis, you need to treat the spine. Therapy should be aimed at relieving pressure from the nerve roots, normalizing blood flow in the cervical spine, and eliminating other symptoms of osteochondrosis. For this purpose, the use of medications, physiotherapy and massage, and physical therapy exercises are prescribed.
The first step is to consult a doctor to determine the exact cause of your sore throat. If this is osteochondrosis, then treatment should be approached comprehensively: NSAIDs, exercises, massage, manual therapy, physiotherapy. Treatment should be carried out by an experienced vertebrologist or neurologist.
Medical therapy
Treatment of sore throat that occurs against the background of cervical osteochondrosis is carried out with local drugs and agents for oral or intramuscular administration.
| Drugs that help eliminate unilateral sore throat with osteochondrosis | Operating principle | |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Nimesulide | Relieves swelling of tissues, inflammation of the roots, helps reduce pain |
| Diclofenac | ||
| Meloxicam | ||
| Nimesulide | ||
| Muscle relaxants | Structum | Eliminate muscle spasms |
| Baclofen | ||
| Sirdalud | ||
| Mydocalm | ||
| Chondroprotectors | Chondroxide | Promote the restoration of cartilage tissue and prevent its further destruction |
| Glucosamine | ||
| Chondrogard | ||
| Stimulating blood circulation | Cinnarizine | Normalize metabolism, blood circulation in the tissues of the brain and cervical region, have an antioxidant effect |
| Piracetam | ||
| Cavinton | ||
For cervical osteochondrosis, accompanied by sore throat on one side, B vitamins are also prescribed. If necessary, antidepressants and sedatives are additionally prescribed.
Physiotherapy, massage
Physiotherapeutic procedures help relax muscles, eliminate lumps and sore throats, and speed up the healing process. Most often prescribed:
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- mud therapy;
- ultrasound therapy.
Massage helps reduce pain, accelerates blood circulation and the flow of nutrients to the spine and tissues of the cervical region, and tones the nervous system. For cervical osteochondrosis, the following massage techniques are allowed: stroking, kneading, rubbing, light tapping, vibration. Intensive effects on muscles are contraindicated.
Physiotherapy
Therapeutic exercises help develop the neck muscles, relieve their spasms and speed up the flow of oxygenated blood to the brain.
For cervical osteochondrosis, it is recommended to perform the following exercises:
- Lie on your back, relax your shoulders. Straining the neck muscles, we raise our head and pull our chin towards our chest. We linger in this position. After 5 seconds we relax. We perform the exercise 10 times.
- We sit down on a chair. Keeping your back straight, tilt your head to the right and left, trying to reach your shoulder with your ear. The number of approaches is 5-10 in each direction.
- Starting position: sitting or standing. Lower and raise your head, slowly rotate it clockwise and back. Repeat 5 times.
A specialist selects a set of exercises based on the stage of osteochondrosis and the severity of its symptoms. You need to perform movements smoothly, without sudden movements or jerks.
Aching pain in the jaw
Aching pain is a special kind of pain, which, it would seem, does not torment as much as acute and sharp pain, but at the same time, does not allow one to forget about itself, especially at night. Why does the right or left side of the lower jaw ache?
The trigeminal nerve is three “processes” that supply our entire face with nerve endings, thereby connecting it with the central nervous system. Inflammation of the mandibular branch of this nerve causes pain in the lower jaw, lip, lower teeth and sometimes in the neck.
Affected by trigeminal neuritis.
Painful attacks due to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve are truly exhausting for patients, because they appear very often and intensify with any movement. Why does this neuritis occur? The reasons for its occurrence are as follows:
- fracture of the lower jaw or base of the skull;
- error during prosthetics or anesthesia;
- infection;
- intoxication;
- nerve injury from a foreign body.
In addition to aching pain, trigeminal neuritis has several other symptoms. Firstly, the mobility and sensitivity of the jaw is impaired (it is difficult to open the mouth, chew, swallow, there is a feeling that the muscle is numb, an unpleasant feeling of numbness in the neck). Secondly, during the examination, slight swelling of the affected area is detected. Thirdly, the skin becomes bluish or marbled in color.
Temporomandibular joint syndrome
Why is the temporomandibular joint so important to us? The fact is that it performs many functions, for example, thanks to it we can open our mouths and chew. Due to the heavy load on this joint, one of the following syndromes may occur:
- aching pain on the left or right in the area of the jaw and ear;
- tension in the lower jaw, a feeling that the muscle is “cramped”;
- difficulty (difficulty) while chewing;
- aching pain in the entire facial area;
- various extraneous sounds during jaw movement (grinding, clicking, etc.);
- malocclusion;
- headache.
Soreness under the jaw
Why it hurts under the jaw is a question to which there is no clear answer. Under the jaw there is a huge number of different anatomical formations, diseases of which can give painful echoes to the right or left corner of the lower jaw, throat, neck.
Gum disease can cause jaw pain.
And yet, returning to the question of why pain occurs under the jaw, we can list a number of main reasons:
- diseases of gums and teeth;
- damage to the facial artery (characterized by burning pain in the lower jaw, moving down to the neck);
- with a fracture of the jaw, the pain can also radiate under the jaw;
- neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve (a specific disease that starts from the root of the tongue, moves to the ear, and then under the jaw to the neck);
- swelling of the larynx (starts with a sensation of a lump in the throat);
- pharyngitis, sore throat, tonsillitis;
- sialolith – the disease is characterized by the fact that the lower jaw swells only on the right or only on the left, the temperature rises and pus is released in the oral cavity;
- sialadenitis - inflammation of the salivary glands, also accompanied by a rise in temperature, lethargy and pain in the neck, under the lower jaw;
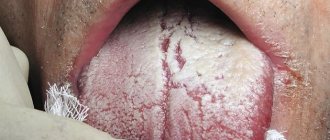
- glossitis or inflammation of the tongue: the tongue becomes bright red, the throat and neck are very sore;
- glossalgia - increased sensitivity of the tongue, pain can also radiate under the jaw. glossalgia is usually provoked by spicy, sour or hot food, prolonged conversation;
- swelling of the submandibular lymph nodes: chronic pain, fever, weakness and weight loss;
- other pathologies of the lymph nodes, in which patients have a sore throat, pain in the neck and general malaise.
Asks: novel, Stavropol region
Gender: Male
Age: 29
Chronic diseases: Tonsillitis, pharyngitis
Hello, I have a problem. For a month and a half now I have been having problems with my throat, or rather with my left tonsil. It all started with banal tonsillitis, but only on one side, the left tonsil. It hurt when swallowing. I felt an enlarged lymph node on the right. During this time, the pain either went away or returned. I visited 6 ENT doctors. I took blood tests twice - the norm. I treated it with rinses and antibiotics - for the duration of treatment it was better and then it came back again. I took a culture and found nothing. Tested positive for Epstein Barr. An infectious disease specialist began treating me. But the pain in the tonsil on the left side does not go away, especially when swallowing. Now I have added pain on the outside of my neck. There is a painful sensation under the jaw when pressing on the left side and down to the thyroid gland. The last ENT specialist said that he did not see pathologies in the ENT organs and sent me to a neurologist. They seem to be diagnosing infectious neuropathy. But to be honest, the neurologist very much doubts that this is her fault. I had an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and tested for hormones - the norm. Gastroscopy 4 months ago there were problems, treated now, no worries. To be honest, I give up, I don’t know what to do, help if you can
The relationship between sore throat and spinal pathology
The mechanism of sore throat with osteochondrosis is based on compression syndrome. In the cervical region there are arteries that supply the brain and roots that transmit impulses to the muscles of the neck, esophagus, and larynx.
With osteochondrosis, the elasticity and thickness of the intervertebral discs decrease, the vertebrae shift. When moving, they irritate the blood vessels and nerve roots, causing their inflammation: blood flow and transmission of nerve impulses to the brain and cervical region deteriorate. Pain appears, spasm of the neck muscles and larynx occurs, and other symptoms indicate a violation of blood circulation and tissue innervation.
As osteochondrosis progresses, a protrusion forms, and then a herniated disc. Joints, spinal ligaments, and muscles are involved in destructive processes. The altered tissues pinch the vertebral artery and nerve roots: pronounced dysfunctions of the nervous and cardiovascular systems occur.
Sore throat on one side appears when the discs between the 4th and 5th vertebrae are destroyed: in this area there are roots that innervate the tissues of the mouth, lips, eustachian tube, vocal cords, tonsils and pharynx.
Pain and discomfort in the throat are often associated with ENT diseases, but this is not always the case. If pain, burning, and a feeling of a lump in the throat are accompanied without fever, this may indicate cervical osteochondrosis. If you have such a problem, you should contact an ENT specialist to rule out or confirm tonsillitis, sore throat, laryngitis and other similar diseases.
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia and styloid process syndrome
Paroxysmal unilateral pain in the throat, radiating to the ear and lower jaw, is a typical symptom of idiopathic or its secondary form - Eagle syndrome (styloid process). The pain occurs suddenly, can be provoked by eating hard or bitter foods, and goes away spontaneously within a few minutes after the onset. During an attack, patients suffer from a dry throat and cough; after the attack ends, saliva is released in excess.
Styloid process
The causes of idiopathic neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve are unknown; Eagle's syndrome is the result of irritation of the hypoglossal nerve by the elongated styloid process of the temporal bone. Treatment in the first case is selected individually, antiepileptic drugs are used, nerve conduction is carried out, and if there is no effect, they proceed to surgical treatment. In Eagle syndrome, conservative therapy is ineffective; the patient can be relieved of pain by excision of the elongated styloid process.
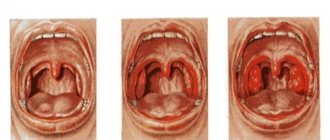
Common diseases when the throat and neck hurt
The most common infections that lead to sore throat and neck are viral, bacterial or fungal. They are manifested by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx. With fungal diseases, a white coating additionally forms on the damaged areas. Neck pain occurs due to inflammation of the lymph nodes. The temperature rises very often. The type of infection is diagnosed using a swab taken from the throat. Based on the test results, a course of treatment is prescribed.
Sore throat and neck are very common due to allergies. This pathology is characterized by symptoms similar to those of a cold: a sore throat, inflammation of the nasal mucosa and pain when swallowing may occur. The neck hurts due to swelling in various parts of the larynx. Diagnosis is carried out by performing allergy tests.
Intense and constantly increasing pain is characterized by malignant tumor formations. There may be a feeling that there is a foreign body in the neck. For diagnosis, laryngoscopy is initially performed, and if a tumor is detected, MRI and biopsy are mandatory tests. Treatment in any case involves surgery.
Sore throat due to diffuse changes in the thyroid gland. In this case, the pain may occur periodically; it is localized in the area where the thyroid gland is located. An additional sign is a modification of the front side of the neck (the appearance of a goiter). With pathologies of the spine, severe pain usually occurs. They can only go down for a while.
Difficulty erupting and inflammation of wisdom teeth
Difficulty in erupting the third molar of the lower jaw can also cause a sore throat that radiates to the jaw. The rudiment of this tooth is located in close proximity to the medial pterygomaxillary muscle, which borders the peripharyngeal space and is involved in swallowing, opening and closing the mouth - this explains the localization of pain during inflammation of the follicle of the eighth tooth of the lower jaw.
Inflammation of wisdom teeth
To choose the right treatment method, the doctor takes an x-ray of the lower jaw and determines whether there are conditions for the tooth to erupt in the correct position. If there is enough space in the jaw for this, conservative treatment is recommended: antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy, if necessary, parts of the mucous membrane are removed to facilitate tooth eruption. If the position of the germ is incorrect and there is not enough space to place the figure eight in the dental arch, it is removed.
Sore throat when swallowing: a sign of osteochondrosis or other diseases?
Discomfort, burning, feeling of a lump and sore throat on one side are symptoms not only of cervical osteochondrosis, but also of other diseases. Pathologies can be distinguished from each other by additional signs.
| Cause of sore throat when swallowing on one side | Associated symptoms |
| Atypical sore throat | Unilateral enlargement, redness of the tonsils |
| Malaise | |
| Headache | |
| Plaque, ulcers and ulcers on the affected tonsil | |
| Low-grade fever | |
| Inflammation of the pharynx (pharyngitis) | |
| Swelling, redness of the pharynx, palatine arches | |
| Soreness of the cervical lymph nodes | |
| Lymphadenitis | General weakness |
| Fast fatiguability | |
| Chills | |
| Feeling of heaviness in the head | |
| Enlarged lymph nodes | |
| Heat | |
| Decreased (lack of) appetite | |
| Thyroid pathologies | Dry skin |
| Deterioration of hair and nails | |
| Weight loss or gain | |
| Quick mood changes | |
| Changes in body temperature | |
| Diaphragmatic hernia | Pain in the stomach, esophagus, behind the sternum |
| Heartbeat disturbances (extrasystole, tachycardia) | |
| Heartburn | |
| Nausea | |
| Vomiting with blood | |
| Dyspnea | |
| Difficulty swallowing | |
| Hiccups | |
| Sore tongue | |
| Hoarseness of voice | |
| Tumors of the larynx | Constant ear pain |
| Unreasonable weight loss | |
| A lump or swelling in the neck | |
| Hoarseness of voice | |
| Labored breathing |
In addition to sore throat when swallowing, cervical osteochondrosis causes:
- Hearing and visual disorders are the consequences of impaired blood flow in the arteries supplying the posterior parts of the brain. There may be noise and ringing in the ears, decreased vision and hearing, the appearance of black spots and a feeling of a veil before the eyes;
- Pain in the neck and shoulder muscles, their tension. Often combined with headaches in the back of the head, migraine attacks;
- Dizziness – occurs due to disruption of blood and oxygen supply to the tubules of the inner ear, which are responsible for balance;
- Fainting is a consequence of prolonged and severe compression of the vertebral artery and nerve roots;
- Shortness of breath, difficulty with deep breathing is a sign of oxygen deficiency in the posterior parts of the brain;
- Tingling in fingers;
- Tachycardia.
Body temperature does not change with cervical osteochondrosis (only local hyperemia of the skin is noted). There is no redness in the throat or other signs indicating diseases of the pharynx of a viral, bacterial or other nature. But some of the symptoms of spinal pathology can be mistaken for diseases of the ENT organs, endocrine, and digestive systems. It is not possible to correctly determine why a sore throat occurs on one side when swallowing: you need to consult a doctor.