Initial signs of hypersalivation
Typically, during normal salivation, about 2 ml of saliva is released every 10 minutes. If this figure in an adult increases to 5 ml, then so-called hypersalivation occurs.
Increased salivation is accompanied by the presence of an excessively large amount of liquid in the oral cavity. This leads to a reflex swallowing or the desire to spit out the accumulated salivary secretions.
In children with excessive salivation, the mouth remains wet all the time, and the clothes around the chest are damp. They may also constantly choke on secretions from the salivary glands in their mouth. After sleep, the presence of saliva stains on the pillow indicates a possible salivation problem. Also, signs of hypersalivation include changes in taste sensitivity, and sometimes nausea and vomiting, but these symptoms are quite rare.
Swallowing saliva from the mouth.
If saliva leaves the mouth (for example, saliva comes out onto the lips) and is then swallowed, the fast is broken, even if it is returned by touching the lips. If you wet a thread or siwak with saliva, and then swallow this moisture that is on it, the fast is broken, but if there was no phlegm, which cannot separate, the fast is not broken.
Those who are engaged in sewing or using a siwak should be very careful in these cases.
Causes
There are many reasons that can cause hypersalivation.
Excessive salivation is a direct indicator of health problems. In addition, drooling flows profusely when it acts as a reaction to certain irritants, or as a consequence of an inflammatory process in the organs (more details in the article: what to do if a child drools profusely at 2 months?). Excessive salivation may be a sign of infection in the body or a symptom of a neurological disease.
In adults - men and women
Among the main causes of excessive drooling in adult men and women are:
Why do children drool?
As for children, up to one year of age, increased drooling is the norm. The main reason for high salivation is unconditioned reflexes. Another natural reason is associated with the eruption of the first milk teeth. Both factors do not require treatment. Also, increased salivation can serve as a protective reaction of the child’s body. Bacteria are removed along with saliva.
However, there are a number of more serious reasons why a child collects a high amount of drool in his mouth:
- Helminthiasis. Small children are more often susceptible to helminth infestations, as they put foreign objects into their mouths and bite their nails.
- False hypersalivation. It occurs in infants due to impaired swallowing, which is caused by paralysis or inflammation in the pharynx. Saliva production remains normal.
- Problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Viral diseases.
In older children, the problem may be related to psychological processes. With the development of higher nervous activity, children are subject to sharp emotional experiences, which contributes to the copious secretion of saliva.
During pregnancy
Most often, hypersalivation occurs in the early stages of pregnancy, as a consequence of toxicosis and frequent vomiting. Trying to stop an attack of vomiting at an early stage, pregnant women involuntarily reduce the frequency of swallowing, which leads to a feeling of excess saliva. The salivary glands work normally.
The second possible cause of increased salivation during pregnancy is called heartburn. The secretion of saliva softens the acid. Another significant factor in impaired salivation during pregnancy is increased sensitivity to all medications.
The main secret: is it true that you can be treated with saliva?
Licking wounds is an instinctive response to trauma not only in animals, but also in our ancestors. According to legend, in 1589, Saint Magdalena de Pazzi cured one of the nuns from ulcers by licking her feet, and the Roman Emperor Vespasian once healed a blind man using his saliva. They did this for a reason; saliva really helped fight inflammation in those days when bactericidal ointments did not exist. “Hungry” or morning saliva was considered especially medicinal - supposedly it was completely cleansed overnight and was saturated with substances that promote healing. Burns, warts and other skin diseases were treated with baby saliva or animal saliva - it was considered quite natural to let a cat or dog lick your wound.
Saliva is a unique fluid secreted by three pairs of salivary glands located under the tongue, under the jaw and near the ears. It consists of 98.5% water, and the rest is various chemicals, which scientists have begun to study quite recently. has been found to contain a unique combination of proteins that can tell the truth about our health, from blood sugar levels to detecting cancer and heart disease. That is why today more and more tests and analyzes in medical laboratories are carried out based on its composition.
Saliva also contains substances that promote blood clotting and protect against infections. The antibacterial enzyme lysozyme attacks the cell walls of many bacteria, and the protein thrombospondin has antiviral properties. Antileukoproteinase present in saliva is both antibacterial and antiviral and also heals wounds. Saliva also contains opiorphin , a powerful analgesic six times more potent than morphine, which was only discovered by scientists in 2006. Thanks to him, we do not feel pain when small wounds appear in the mouth. Well, the main savior protein is histatin . Research conducted in 2008 proved that it not only kills bacteria, but also promotes wound healing within 16 hours.
Despite ongoing research into one of the most important secrets of our glands, doctors still do not recommend relying on the disinfecting properties of saliva, because the bacteria it contains can cause harm if they get into the wound, especially if the immune system is weakened. A British medical journal in 2002 described a case in which a man with diabetes cut his finger, decided to lick it, and developed an infection that had to be amputated.
How to stop swallowing with folk remedies?
You can overcome the problem of increased secretion at home using folk remedies. However, it is important to understand that they are only auxiliary. Consultation with a doctor is required. The main folk method is rinsing:
- A decoction of chamomile, nettle, oak bark or sage. Allows you to temporarily reduce symptoms. For 1 tablespoon of herbal mixture you will need half a liter of boiling water. Leave for 40 minutes. Carry out 4-8 rinses per day.
- Tincture of viburnum. Do it 3-5 times a day. Crush 2 tablespoons of viburnum and add 200 ml of water. Let it sit for about 4 hours.
- Tincture of water pepper. For 1 teaspoon of pharmaceutical composition you need to take a glass of water. The minimum course of rinsing is 10 days. Rinse after eating.
- Tincture of shepherd's purse. The proportion is: 25 drops of liquid per 1/3 glass of water. Rinse after every meal.
- Brine cabbage.
- A weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Another effective method is tea or plain water with a few drops of lemon juice. Sometimes vegetable oil is used to combat hypersalivation.
As a preventive measure, it is worth following a number of recommendations that can not only prevent excessive salivation, but also increase the resistance of the immune system and improve overall health. Necessary:
- reduce the presence of salty, spicy and fatty foods in the diet;
- adhere to proper nutrition;
- stop drinking excessive alcohol;
- quit smoking;
- monitor oral hygiene;
- get enough sleep;
- take regular walks in the fresh air;
- eliminate stressful situations and unnecessary worries;
- rinse your mouth with an antiseptic decoction of chamomile or oak bark;
- visit the dentist regularly;
- undergo medical examinations to monitor your health.
Normally, the surface of the human oropharynx and nasopharynx is lined with a mucous membrane, the function of which is to produce mucous secretions. The mucous contents perform a protective function and protect the walls of the nasopharynx and oropharynx from excessive drying out and injury.
If, under the influence of a number of unfavorable factors, excessive mucus production is formed, then this entails a rather unpleasant condition in which a person may feel the presence of a lump in the throat that cannot be swallowed or coughed up, even with effort. In any case, excessive accumulation of mucous contents in the oropharynx is a pathological symptom that indicates the presence of a particular disease.
What are the causes of mucus in the throat, and how to get rid of them once and for all, will be discussed in detail below.
Considering that the production of mucus is one of the manifestations of the body’s protective reaction to irritants (trauma, infection, exposure to allergens), a huge number of provoking factors can be counted.
The most likely causes of excessive mucus production in the oropharynx include:
- Pathologies of the digestive tract. In the first place is gastroesophageal reflux disease, in which there is a reflux of acidic gastric contents into the lumen of the esophagus and then into the pharynx. It is the irritating effect of the acidic contents that causes excessive mucus secretion;
- Deviations from the tracheobronchial tree, both acute and chronic. In this case, hypersecretion of mucus occurs in the lower parts of the respiratory tract, followed by upward displacement.
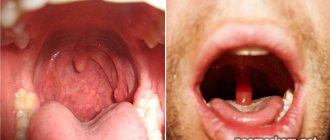
- Diseases or traumatic injuries of the nasopharynx and oropharynx. In this case, hypersecretion of mucous contents can occur directly in the pharynx or flow from the nasal cavity. This group of diseases includes pharyngitis, sinusitis, influenza, ARVI adenoiditis, as well as tonsillitis of various natures. Traumatic injuries to the nose, polyps, and a deviated nasal septum can also lead to a state of hypersecretion of mucous contents.
- Contact with specific allergens on the surface of the mucous membrane, which can provoke a hypersensitivity reaction in the body;
- The harmful effects of tobacco smoke, which contains a lot of toxic chemical compounds that have an irritating effect on the surface of the mucous membrane;
- Excessive consumption of alcohol, carbonated drinks, excessively cold or hot food, abuse of spicy foods;
- Hypersecretion of mucus in a child during the neonatal period can be observed due to frequent regurgitation and irritation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa.
How to get rid of an annoying lump in the throat?
The choice of method to combat this condition depends on the frequency of its manifestation. If the sensation of a lump in the throat suddenly occurs, and such sensations have not been observed before, then you can use a number of the following tips:
- Inhalation with the addition of baking soda will facilitate rapid coughing up of the mucus lump. It is necessary to proceed from the calculation of 0.5 teaspoon of soda per 250 ml of boiled water;
- Another effective way to use baking soda is to rinse. The standard dilution is 1 teaspoon of baking soda per 250 ml of boiled warm water;
- Alkaline mineral water like Borjomi can also help cope with such an unpleasant feeling in the throat.
After successful coughing, it is best to spit the mucous contents into a sink or paper napkin. It is extremely undesirable to swallow mucous discharge, as it can cause digestive disorders.
If the mucus in the throat is not swallowed and is putrid in nature, then such symptoms are most typical for an infectious lesion of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and oropharynx (ARVI, sinusitis). In this situation, you should not rely on self-medication. You should seek medical advice from an ENT doctor as soon as possible.
If the accumulation of mucous contents in the oropharynx is permanent, then most likely we are talking about the chronicity of the pathological process, and this is a compelling argument for seeking medical advice.
If excessive mucus production was triggered by exposure to any allergen, then hypersecretion may be accompanied by symptoms such as increased tearing, itching, and a skin reaction in the form of redness.
If medical consultation and diagnosis exclude the influence of pathogenic microflora, as well as the presence of inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system, then you should pay attention to the following circumstances:
- the nature and composition of the daily diet;
- the presence of bad habits, such as smoking and drinking alcohol;
- influence of unfavorable professional factors.
Swallowing less often - with sore throat
Try hot liquids, cold liquids and ice cream. Give a try to some of your favorite sore throat pain relievers that have stood the test of generations—things like chicken soup, hot tea, ice, and frozen ice treats. Cold things can help numb the pain receptors in the throat, and hot things can relieve some of the pain and help get rid of mucus. Having a sore throat can make you feel like repeatedly swallowing in order to temporarily soothe the pain with a coating of saliva. In turn, this can give you dry mouth and even cause stomach upset.
Use warm salt water or throat spray to numb the pain briefly. Stir 3 g (0.11 oz) salt (about ½ teaspoon) into a glass of warm water. Take a big sip, gargle it in the back of your mouth, spit it out and repeat until you run out of glass. Do this as often as every 3 hours to provide some sore throat relief. Alternatively, pump 1 spray the throat numbing spray at the back of the throat, wait 15 seconds, then spit it out. Do this as often as every 2 hours for 2 days. Avoid swallowing salt water or throat numbing spray. Swallowing a small amount will not cause any harm.
Use a humidifier at night to keep the air moist. Dry air dries out your throat as you breathe, forcing your body to produce extra saliva to coat your throat when you swallow. When you have a sore throat, you probably feel most comfortable at a humidity level between 40% and 60%. A humidifier can help during the day and especially at night, when your throat can really dry out and cause you to re-swallow. High levels—above 60% and 70% humidity—can also cause problems. This can lead to additional congestion and more allergens in your home. So, in some cases, you may be better off using a dehumidifier rather than a humidifier.
Call your doctor for severe or prolonged sore throat. Most sore throats are caused by common viruses and resolve within about 3-7 days. If the sore throat is extremely painful or lasts more than 7 days, though, consult a doctor. Also call your doctor if you experience symptoms such as fever, chills, or difficulty breathing. Call your doctor if your child has a sore throat for more than 3 days, or immediately if the sore throat is accompanied by swollen glands or temperature above 38 °C (100 °C). Children 5-15 years of age are most at risk of developing strep throat and similar bacterial infections.
Treatment
The main therapeutic measures in this case are aimed at eliminating not only a person’s subjective sensations, but also at eliminating the very cause of this condition.
Traditional remedies
If hypersecretion of mucus is caused by an inflammatory process against the background of a viral or bacterial infection, then treatment should be aimed at eliminating the causative agent of this disease. Depending on the type of pathogen, the following may be prescribed:
- Antibacterial drugs.
- Antiviral drugs.
- Corticosteroid drugs (in especially rare and severe cases).
Each disease that is accompanied by hypersecretion of mucous contents has an individual treatment regimen. The prescription and administration of the above drugs is carried out with extreme caution during pregnancy, as well as during breastfeeding.
If pathology from the gastrointestinal tract is suspected, it is necessary to undergo a full examination, followed by treatment and adherence to an appropriate diet.
Traditional methods
If there are a number of contraindications to traditional methods, then it is possible to treat hypersecretion of mucus with folk remedies with no less success.
Gargling can be done with the following infusion:
It is necessary to mix equal parts (25 g each) of sage grass, chamomile flowers, and eucalyptus leaves. 2 tbsp. the resulting mixture should be poured into 500 ml of boiled water and kept on low heat for 20 minutes, then strained and used 3 times a day to gargle.
Inhalations can be carried out using a decoction of thyme, chamomile, sage, and pine buds.
The following mixture has an excellent effect, which is suitable for treating children and pregnant women:
It is necessary to finely chop 2-3 large aloe leaves and mix with 3 tablespoons of honey. The resulting mixture should be consumed orally, 1 tsp 3 times a day.
Depending on the cause of the development of this condition (mucus in the throat that is not swallowed), not only a detailed consultation with several medical specialists will be required, but also lifestyle adjustments.
When something bothers you in your throat, sometimes unpleasant sensations haunt a person for a long time, for years. A fairly large number of middle-aged people, both men and women (even more women), experience similar feelings. They are described in different ways, from a simple unpleasant feeling to a constant lump in the throat. People go to doctors, change specialists, undergo tests, but no significant improvement occurs, and doctors answer the patient’s questions that everything is normal.
Make sure the discomfort is not a disease
When for a long time the feeling that something is bothering you in your throat does not go away, as if a piece of food is stuck there or it is being squeezed by something, you need to rule out, by taking tests and undergoing examinations, diseases associated with the thyroid gland and other causes that directly indicate about pathology. Let’s assume a situation where tests have been collected and none of the doctors have confirmed the disease. The thyroid gland is normal. There is no tumor, no swelling, nothing interferes with breathing, the feeling of constriction arises and goes away suddenly.
Look at the situation soberly and do not panic
There are no signs of pathology. What can interfere in this case? Most likely, muscle spasm is accompanied by a feeling that there is something in the throat. Observe your condition immediately after waking up. When you have a cold, you feel pain in it in the morning, and when the problem is related to the fear of experiencing a feeling of constriction, your throat does not hurt when you wake up.
This is due to concern and constant anticipation of an unpleasant feeling, control over the act of swallowing and, to a greater extent, a feeling of fear that you will have to experience an unpleasant sensation again. That is, the problem from the physiological area often turns into psychological.
Don't create calluses in your throat
Let's try to figure out the problem when something is bothering you in your throat. Let's consider (gulps). The free tip of the epiglottis (petal), deforming with age, curls into a tube and bends towards the tongue (its root). Hardening and ossification of the epiglottis occurs later in women than in men, so deformation occurs to a greater extent.
The palatine tonsils decrease in volume, and the lingual tonsil increases slightly, which leads to mechanical contact between the root of the tongue and the epiglottis. The most suspicious and emotional people notice this insignificant contact. Constantly focusing on it, checking whether something interferes with swallowing or not, they take sips unnecessarily when there is no need to swallow anything.
Such sips increase mechanical contact. Checking whether the sensation of obstruction in the throat persists, goes away or not, unnecessary sips are taken constantly and thereby contribute to real mechanical contact in the area of the epiglottis. Additional friction is created, which becomes increasingly harsh over time.
There are cases when a person experiences real suffocation at the moment of an “empty” throat; the epiglottis does not deviate, as in a food coma, but bends and blocks the respiratory lumen. In such a situation, when something is bothering the throat, artificially induced vomiting usually helps.
A person becomes fixated on test sips, which are unnecessary and very harmful. There is inflammation, erosion, swelling of the larynx, calluses on the epiglottis, as well as on the lingual tonsil.
Try to improve your condition on your own
A simple technique allows you to discern how serious the problem is. It is necessary to answer the question: it is difficult to breathe or there is a feeling of an unpleasant lump, but swallowing food or water does not cause pain. If you have a serious illness (neoplastic disease), food or water makes it difficult to swallow, causing pain. And when the problem is in the mechanical contact of the epiglottis and the root of the tongue, then nothing interferes with eating. What recommendations should you remember and apply?
- Understand that this is not a pathology, but “epiglottis syndrome,” and focus less on the problem.
- Stop swallowing in vain, control yourself.
- To help yourself, always have non-carbonated water with you (tea, lemonade, chamomile infusion) and take a sip when the urge to swallow arises.
- Occasionally instill plant oil into your nose (lying on your back) twice (or once a week).
- You can “lubricate” the larynx directly with oil (a quarter teaspoon at a time).
- Do relaxing exercises for the muscles of the neck and larynx. Strengthen your neck muscles with physical exercise.
Increased salivation in adults can become a source of constant discomfort and tension. An increase in the secretion of the salivary glands leads to the need to constantly swallow or spit saliva, to the inability to speak normally and swallow food.
Causes of hypersalivation in adults
Hypersalivation or increased salivation in adults is always a pathology. An increase in the amount of saliva can be caused by diseases of the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, taking certain medications and other reasons. It is not difficult to notice a violation of salivation on your own: the accumulation of saliva in the mouth irritates the patient, makes the patient want to spit it out or swallow it, and also interferes with talking. Another symptom characteristic of increased salivation is nocturnal hypersalivation; during sleep, when a person does not control himself, saliva flows freely from the mouth and streaks or wet marks remain on the patient’s pillow.
Persistent hypersalivation in adults most often occurs due to the following reasons:
1. Irritation of the mucous membrane due to inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity
– stomatitis, gingivitis, tonsillitis and other diseases in which the oral mucosa becomes inflamed, often accompanied by profuse salivation, which occurs due to bacteria that have entered the channels of the salivary glands and caused their inflammation;
2. Digestive disorders
– increased acidity of gastric juice, inflammation and irritation of the gastric mucosa can cause a reflex increase in salivation and constant moderate hypersalivation. With such diseases, increased salivation develops gradually and the patient gets used to the increased amount of saliva, not paying attention to the inconveniences associated with this condition;
3. Foreign bodies in the oral cavity
– incorrectly installed dentures, braces, chewing gum and any other objects that irritate the nerve endings in the oral mucosa can cause reflex salivation;
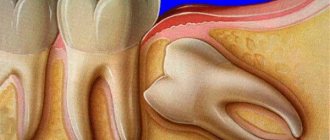
4. Inflammation of the salivary glands or mumps
– an infectious disease characterized by inflammation of the salivary glands. Inflammation of the parotid salivary glands causes the patient's face and neck to swell and increase in size, which is why the disease is called “mumps”;
5. Neurological disorders
– Irritation of the vagus nerve or damage to the central nervous system, which occurs with Parkinson's disease, trigeminal inflammation, head injuries, cerebral palsy and some mental illnesses, leads to an increase in the amount of saliva produced and a loss of control over salivation. Patients with central nervous system diseases may not pay attention to drooling and be unable to control it;
6. Endocrine diseases
– Hormonal imbalance in the body can cause increased secretion of the salivary glands. Increased salivation occurs in people with thyroid pathology, inflammation or tumor of the pancreas, or diabetes;
7. Taking medications
– taking some medications can cause increased salivation, such a side effect is typical for pilocarpine, nitrazepam, muscarine, physostigmine, cardiac glycosides with digitalis alkaloids and some others;
8. Smoking
– active smokers often face a similar problem, due to irritation by nicotine and high temperature of the oral mucosa, the salivary glands reflexively begin to produce more secretion;
9. Pregnancy
– increased salivation is often found in pregnant women. Heartburn, toxicosis and changes in hormonal balance in the body often lead to increased hypersalivation, which during this period is not considered pathological.
Excessive salivation in humans: causes, treatment and prevention
Saliva is one of the most important components of the digestive system. It not only moistens food during eating, but also starts the mechanism of its digestion. In addition, saliva has bactericidal properties, providing reliable protection of the body from various infections.
True, all of the above is relevant only if saliva is produced as much as needed. But if a person has increased salivation, then this becomes a serious problem that needs to be dealt with.
- 2 Causes of increased salivation
- 3 Increased salivation in women
- 4 Treatment of increased salivation
- 5 Conclusion
How to understand that everything is normal
The process of salivation is important for the digestion process , maintaining the moist state of the mucous membranes.
Increased secretion of saliva in the mouth occurs in a person when he sees food - this is a normal reaction of the body.
This will be especially noticeable if the person is hungry.
But excessive salivation that occurs during sleep or regardless of the feeling of hunger and other factors may indicate diseases of the thyroid gland and gastrointestinal tract.
It should be taken into account that normally a milliliter of saliva is released every 5-6 minutes.
If it seems that too much of it is accumulating in the mouth, you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe tests and determine the cause of this phenomenon.
The effect of hyaluronic acid on facial skin is discussed in detail in this review. Find out more!
This publication will tell you about the consequences of using Botox for hair.
The main contraindications to hirudotherapy are presented in the current article.
Characteristic symptoms
How do you understand that the glands in the mouth are working more actively than nature intended?
Characteristic features:
- at short intervals there is a desire to spit out the accumulated saliva even in the absence of appetizing dishes nearby;
- after sleep, the patient discovers a spot on the pillow with secretions of the salivary glands;
- In children, it is difficult not to notice profuse drooling: a constantly wet mouth, wet clothes in the chest area.
Learn about the causes and treatment of brown coating on the tongue in adults.
How to remove bad breath? Effective treatment methods are described at this address.
Factors causing hypersalivation
It is normal to produce saliva , but if a person produces too much saliva, it is necessary to determine the cause.
This phenomenon in medicine is called hypersalivation or ptyalism. The main reasons for this are as follows:
- Inflammation in the oral cavity .
Hypersalivation can be a consequence of any disease in which the mucous membrane becomes inflamed. Through the channels, microorganisms enter the salivary glands and provoke sialadenitis. Excessive production of saliva is the body’s protective reaction to pathologies occurring in the mouth. - Mechanical irritants .
Temporary ptyalism can occur due to dental procedures that irritate or damage the gums. Increased secretion is possible in women who use dentures. When adapting, they rub the mucous membrane and provoke reproduction, which leads to copious salivation. - Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Excessive salivation is associated with disorders of the digestive system: gastritis, high acidity, ulcers, neoplasms.
From the gastrointestinal tract, microorganisms can easily enter the oral cavity, where they irritate the salivary glands and gums and provoke the gradual development of hypersalivation.Since it develops slowly, a person does not notice the excess production of saliva.
- Paralysis of the muscular system in the maxillofacial area .
It is a consequence of damage to the facial nerve. The reason is simple: a person cannot normally control the facial muscles, which results in excessive uncontrolled salivation, especially at night and during sleep. - Diseases of the respiratory system and nasopharynx. Many of them lead to abundant formation of salivary secretion. This could be a sore throat, bronchitis, or inflammation of the maxillary sinuses.
In this case, the process of salivation is a protective reaction of the body, since saliva can wash away harmful microorganisms from the oral cavity.If the diseases are cured, hypersalivation disappears along with them.
- Lesions of the central nervous system .
Various mental disorders, brain injuries, cerebral palsy, Parkinson's disease, irritation of the vagus nerve. In this case, increased secretion of the glands is combined with nausea. Patients may have problems with swallowing and nasal breathing that are not under their control. - Medicinal ptyalism .
All medications have side effects, and for many, the list includes increased salivation. This applies to medications with anticholinergic effects. As a rule, after stopping their use, saliva production returns to normal on its own. - Endocrine diseases. When the hormonal balance is disrupted, all functions of the organs and systems of the body are disrupted.
There may also be deviations in the activity of the salivary glands, which produce excessive amounts of fluid.All types of diabetes mellitus, abnormalities of the thyroid gland, and inflammation in the pancreas can lead to this.
- Bad habits. In women who smoke, the inner lining of the oral cavity is constantly damaged.
Every inhalation of smoke, tar and nicotine injures the mucous membrane. And the salivary glands produce more fluid to reduce irritation.Because of this, hypersalivation is common among smokers. If a person quits smoking, salivation returns to normal after a certain time.
They say that pregnancy is often the cause and symptom of increased salivation in women.
True, it often occurs in pregnant women .
Its etiology in this case is associated with neuroendocrine disorders that provoke toxicosis in the early or late stages.
This condition is accompanied by excessive salivation, nausea and vomiting. Increased secretion of glands due to heartburn is alkaline and can reduce acidity, improving the condition of the pregnant woman.
Nausea usually occurs in the morning. If we are talking about early toxicosis without pathological abnormalities, there is no need to treat hypersalivation. Over time it will go away on its own.
Another reason for hypersalivation in women is the onset of menopause.
In this case, it is accompanied by severe sweating and frequent flushes of blood. This is a natural process that will gradually disappear.
If you are interested in what diseases plasmaphoresis treats, read our publication.
The technique of lip augmentation with hyaluronic acid is discussed in this material.
Causes
Excessive drooling is associated with diseases of internal organs and oral cavity problems. Certain conditions provoke the problem.
Main reasons:
- violation of metabolic processes;
- dental diseases;
- toxic infections, acute poisoning;
- smoking. Frequent spitting of excess saliva is an unpleasant habit that irritates others;
- problems with the digestive system: most often - stomach ulcers;
- pathological changes in nervous regulation, brain diseases, mental disorders;
- hormonal disruptions in adolescents during puberty;
- pregnancy;
- helminthic infestations;
- pathologies of ENT organs;
- side effect when taking certain medications.
Help yourself
You need to start fighting the problem by finding out the cause and eliminating it. Therefore, you should not take medications or go for procedures without the knowledge of a specialist.
But if you are prone to this problem, then you can reconsider your diet .
It is recommended to limit foods that are high in sugar , as sweets tend to increase the amount of saliva produced.
Try to limit sugary drinks, sweets and baked goods, and dairy desserts. Avoiding acidic foods helps reduce salivation .
Hypersecretion is provoked by citrus fruits, sauerkraut, yoghurts, and products that contain vinegar.
When the functioning of the salivary glands returns to normal, familiar foods can be returned to the diet.
There are foods that cause dry mouth by helping to fight salivation. These are fiber foods: whole grain bread, whole oats, beans and other legumes.
You can rinse your mouth with chamomile decoction, oak bark infusion, and vegetable oils. Unsweetened tea or water with lemon juice helps.
You can rinse your mouth with shepherd's purse infusion, extract or tincture of water pepper, which are sold in pharmacies.
Methods of diagnosis and therapy
If you notice increased salivation, go to your doctor .
If necessary, he will refer you to specialists of a narrower profile. First, the doctor will determine the cause of the pathology and, taking it into account, will choose treatment methods.
The following measures will help cope with the problem of hypersalivation :
- Anticholinergic drugs: Scopolamine and Platiphylline. They help stop salivation, but they have many side effects, including heart and eye problems.
- In extreme cases, a procedure may be necessary to remove part of the glands, which will eliminate the problem of increased salivation.
- Radiation therapy, which involves the destruction of the salivary ducts. But it can lead to damage to tooth enamel.
- For neurological diseases, after a stroke, facial massage may be indicated to normalize salivation.
- In order to block part of the salivary ducts, Botox injections can be used, the duration of which does not exceed 6 months.
- Cryotherapy is sometimes used. After a course of procedures at the reflex level, swallowing saliva will become more frequent.
- Homeopathic medicines can be used to reduce the amount of secretion released.
Thanks to these methods, salivation can be normalized, but a specialist can determine whether they are advisable.
Sometimes such measures are not required , and it will be easier to eliminate the cause of the problem than to force the glands to work normally.
Do you know how often to have your face cleaned by a cosmetologist? Recommendations from experts are in the review article.
Reviews of the removal of moles using the radio wave method are presented in this publication.
Drowsiness
In the first weeks of pregnancy, women are very sleepy. This condition is especially acute for office employees where it is necessary to adhere to work schedules. There is an irresistible feeling of fatigue, “overwhelm,” loss of strength, apathy, and sometimes depression.
Also, many women noticed that sleep becomes restless . I want to sleep early in the evening, and wake up early in the morning. After which it is almost impossible to fall asleep. Despite the fact that the duration of sleep was sufficient for proper rest, pregnant women feel sleep-deprived.
Source: https://PrioritetMed.ru/simptomatika/vydelenie-slyuny-u-cheloveka.html