If there is a feeling of a lump stuck in your throat and it becomes painful to swallow, upon visual examination you may notice that the tongue in the throat is swollen. This condition may be additionally accompanied by increasing pain in the larynx, if you move the tongue and dysfunction of breathing, it becomes heavy and confused.
In the list of diseases, such a pathology is called uvulitis and means acute inflammation of the uvula.
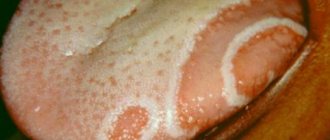
In this case, the uvula changes color from soft pink to intensely purple, becomes covered with a thin whitish film-like coating and becomes noticeably larger (it can hang down to the very root of the tongue).
Sometimes it becomes so deformed that it interferes with the pronunciation of certain sounds and provokes vomiting. The causes of this pathology are different and they all require immediate treatment.
Functions of the uvula: what is the essence of the problem?
The uvula is a distant process that is located in the mouth, on the edge of the soft part of the palate, slightly above the tongue, in a healthy state it is small in size and color, identical to the oral mucosa.
It performs important functions for the body:
- protects the nasopharynx from food entering during swallowing movements;
- separates air flows and warms them;
- is a barrier to infection;
- prevents accidental regurgitation of food;
- provokes a throat spasm, preventing a person from choking;
- participates in the formation of some sounds;
- if necessary, provokes vomiting.
When listing the functions of the uvula, it becomes clear why you need to monitor its condition. Inflammation of this organ leads to a failure in the coordinated functioning of the swallowing, respiratory, protective, resonator, and speech systems and makes the entire body vulnerable.
Principle of operation
Human anatomy in the first stages of its formation forced scientists to ask the question: why does a person need this appendage? Some believed that it was an underdeveloped second language that we inherited from reptiles. Others, on the contrary, were inclined to think that its presence was useless, and in some cases it even interfered. One way or another, with the evolution of medicine, the importance of this pyriform process has been scientifically proven.
The principle of its operation explains all its importance: when food enters the oral cavity and moves further, a spasm of the throat occurs, during which the mechanism of the hyoid muscle is triggered, closing the trachea from food entering them. In addition, the tongue also takes part in the reverse process. That is, when the regurgitation process occurs, he completely controls it, not allowing food to rise into the oral cavity.
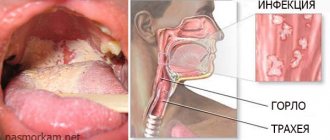
Why the tongue in the throat swells: reasons
If upon examination the soft palate is clean and the uvula is inflamed, the doctor will diagnose uvulitis. Most often, this disease has an acute form, which is characterized by suddenness - pain and swelling appear while eating or even at night during sleep. Reasons include:
- inflammatory pathologies - ENT infections, tonsillitis, advanced dental diseases, abscesses, diphtheria, tuberculosis, sexually transmitted diseases, HIV;
- chemical or thermal damage to the mucous membrane as a result of exposure of the tissue to aggressive compounds (burn with alkali or acid), as well as consumption of hot food and after alcohol;
- allergies – when including foods of an allergic nature in the diet, inhaling allergens (chemicals, natural irritants), taking medications;
- growths and formations in the pharynx - polyps, cysts. In addition to the immediate causes, there are associated factors that influence the enlargement of the tongue in the throat. This:
- a stuck bone in the throat that injures the mucous membrane;
- consumption of low-temperature drinks and foods;
- consequences of instrumental manipulations during examinations of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract, as well as dental procedures;
A tumor of the uvula can appear after vomiting, especially prolonged and repeated attacks, from snoring and in those who smoke a lot.
Fusion of soft tissues
Perhaps the most dangerous and difficult to eliminate is the complete adhesion of the tongue to the tonsil, in which they are observed to articulate into a single organ. The danger of this phenomenon, especially in childhood, is that in the absence of early diagnosis, it is not possible to solve the problem except through surgery.
When tissues grow together, blood supply increases, new vessels and capillaries are formed, of which there are already many in normal condition. It is quite difficult to separate such a plexus, because there is a high probability of open bleeding.
Such processes manifest themselves mainly in those people who have problems with the endocrine system, and are also susceptible to frequent inflammatory processes in the pharynx. Another reason may be neoplasms on the tonsils, increasing their volume, allowing them to come into unhindered contact with the uvula, increasing the area of their contact.
But it is worth noting that such a pathology can be congenital, but, as a rule, it is not hereditary.
The operation to separate fused organs is usually performed under local anesthesia, sometimes removing part of the tonsils.
In addition to fusions, there is a reverse process in which the tongue can be forked. In most cases, people live with this pathology without resorting to the help of surgeons.
Naturally, the fact that the tongue is stuck to the tonsil should not be ignored, especially for children. In the process of growth and formation of all processes, the child’s body is capable of malfunctioning, causing fusion of soft tissues.
It is necessary to carefully examine the child’s oral cavity, assess the size of the tonsils and uvula. If enlargements or adhesion are detected, it is imperative to consult with an otolaryngologist regarding neoplasms and the possibility of soft tissue fusion. Any pain in the throat should be eliminated, regardless of what nature it is.
Symptoms of inflammation of the uvula in the throat. How does it manifest?
The fact that the tongue in the throat has become enlarged is indicated by painful swallowing of saliva, which occurs immediately after sleep and after a few hours may pass or may remain.
The main symptoms are the same as for sore throat - swelling, redness, pain when swallowing, sensation of a foreign object in the throat. Sometimes unexpected pain may occur when sneezing, coughing or eating.
Particular attention should be paid to complaints of a sore throat in a child - if the uvula is swollen, you should immediately call an ambulance, since even a slight enlargement of the organ significantly narrows the respiratory lumen.
The danger of the disease directly depends on the speed of development of the main symptoms - the faster they are, the more complex the patient’s condition.
Certain symptoms indicate signs of organ inflammation:
1
in case of traumatic injury, the following is observed: difficulty breathing, swallowing, salivation, vomiting, speech and phonation are impaired, the uvula touches the tongue;
2
with an infectious lesion: the body temperature rises, the soft palate swells and turns red, weakness and muscle pain appear, the uvula becomes covered with a white film;
3
for allergies: sensation of a lump in the throat, increased salivation, difficulty pronouncing words, itching and rash all over the body, watery eyes, cough, difficulty breathing.
Due to intolerance to any component in medications, drug-induced uvulitis can develop, which is dangerous due to angioedema (Quincke), causing asphyxia and leading to the death of the patient. In addition to the characteristic symptoms of uvulitis, there are other signs of this disease.
Growth on the tongue in the throat
A visual inspection may reveal growths that have a rough surface. These are papillomas that stand out against the background of the mucous membrane in a lighter color and resemble a mulberry.
Sometimes they can be multiple and creeping in nature and spread throughout the entire oral cavity. In their advanced form, papillomas pose a threat to life, as they significantly narrow the lumen of the airways.
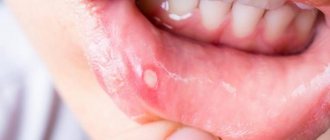
Pimples on the tongue
Pimples may appear on the area of the uvula - pustular formations, which are cysts or polyps, and, as a rule, are of a benign nature.
They need to be treated with antiseptic sprays, but for complete safety, doctors still recommend getting rid of such tumors surgically.
Symptoms of uvulitis
Signs of a disease such as uvulitis can become apparent during meals, after prolonged coughing or sneezing. People whose small tongue has an elongated shape are more predisposed to uvulitis. The disease also develops in the presence of adenoids. If you look into the throat during inflammation, you can see a bright red uvula that has begun to hang down to the root of the tongue. Along with this, the soft palate swells and hurts.
When should you see a doctor? Which one do you need?
If the uvula is very swollen or lengthened, the patient should immediately seek help from a specialized doctor. Such a specialist is an otolaryngologist who will conduct a diagnosis,, if necessary, prescribe additional studies, make a diagnosis and choose a therapeutic tactic.
As a rule, such patients need urgent treatment and can be placed in a hospital, where in case of fulminant asphyxia, qualified medical care will be provided and possible complications of the disease will be prevented.
Most often, the cause of inflammation of the palatine process is an infection, but there are cases when this condition is a symptom of another disease - then the ENT doctor gives the patient a referral to another doctor.
What diagnostics are needed?
When a patient complains that the uvula in the throat has become enlarged, the doctor takes an anamnesis of the disease and conducts a visual examination of the condition of the pharynx - pharyngoscopy.
Using the method of posterior rhinoscopy and oropharyngoscopy, anatomical features, pathologies and defects of the organ are studied, swelling of the uvula is assessed using a spatula and a nasopharyngeal speculum.
The doctor and the patient are facing each other, and if necessary (strong gag reflex), before the examination, the area being examined is irrigated with a local anesthetic.
Why the uvula in the throat is swollen, diagnostic measures, which include laboratory tests, will help to find out:
- a general blood test, which helps determine the nature of the disease (in case of infection, the number of leukocytes increases, in case of allergies, eosinophil levels increase);
- conducting an immunogram by collecting blood or saliva if an allergic reaction is suspected;
- throat swab for bacterial culture to determine the causative agent of inflammation and its susceptibility to the main antibacterial drugs.
Additionally, the doctor can send the patient for an X-ray, tomography, or take material for a histological examination for a biopsy to exclude cancer.
What medications are used to treat an inflamed uvula?
When an inflamed tongue swells in the throat, the choice of medications is approached with great caution due to the high risk of complications of the respiratory system. All medicinal tactics are aimed at reducing swelling and relieving inflammation of the uvula.
Complex therapeutic tactics include the use of:
- antiallergic drugs - antihistamines (Lordestin) and glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Triamcinolone);
- decongestant diuretics – Torasemide SZ, Hypothiazide, Furosemide. These medications are considered first aid and prevent the development of asphyxia.
- If the upper uvula is swollen after drinking alcohol, in order to stabilize the condition, Diazolin, Zyrtec or Aleron are prescribed and subsequent alcohol intake is completely avoided.
- When diagnosing a viral or bacterial infection that provoked inflammation of the uvula, antibiotics (Azithromycin, Amoxiclav) or antiviral drugs (Cycloferon, Remantadine, Arbidol) are prescribed.
Complex therapy also includes:
- treatment of the larynx with antiseptic sprays - Hexoral, Kameton;
- taking vitamin complexes (Vitrum, Multi-Tabs and immunomodulators (Immunity, Zdorov).
All medications are taken in a course, in accordance with the doctor’s prescription and under his supervision.
Treatment
Treatment of uvulitis consists of eliminating the underlying disease, which directly caused it. Complex therapy of pathology will help get rid of the main clinical signs and restore the condition of patients.
General recommendations from specialists that should be followed when treating uvulitis:
- Sufficient drinking regimen, restoring water and electrolyte balance,
- Maintaining personal hygiene rules
- Airing the room
- Wet cleaning,
- Air humidification,
- Using separate utensils
- Eliminating foods that irritate the throat from the diet
- Rejection of bad habits.
Traditional medicine
Uvulitis is usually treated by otolaryngologists. The infectious form of the pathology requires a course of antibiotic therapy, as well as local exposure - rinsing the mouth with a decoction of chamomile and sage, and using an antiseptic spray.
Antibiotics are prescribed after analyzing the oral fluid for microflora, determining the type of pathogen and its sensitivity. A positive therapeutic effect is exerted by broad-spectrum drugs from the group of fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, macrolides - Ciprofloxacin, Azithromycin, Ceftazidime.
Treatment of allergic uvulitis involves the use of:
- Antihistamines - “Diazolin”, “Suprastin”, “Cetrin”.
- Diuretics - Furosemide, Veroshpiron, Hypothiazide.
- Glucocorticosteroids for difficulty breathing - Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone, Betamethasone.
Swelling of the uvula and soft palate in advanced cases requires tracheostomy.
Among the most effective physiotherapeutic procedures used to treat uveitis are: UHF therapy, phototherapy, electrophoresis, acupuncture, magnetic therapy, galvanotherapy, ultraviolet irradiation, quartz.
ethnoscience
To treat uvulitis, mouth rinses with decoctions of medicinal herbs, inhalations, and infusions for oral administration are used.
The following products are used to rinse your mouth:
- Viburnum decoction is obtained from dried fruits, which are boiled in a water bath for half an hour.
- Garlic infusion is prepared by chopping garlic and adding boiled water to the resulting mass. Leave the product for 5 hours and use it as directed.
- Raspberry leaves and stems are brewed for half an hour in a glass of boiling water.
- St. John's wort, sage and thyme are infused in vodka for 7 days and taken forty drops orally.
- Pour boiling water over the onion peel and leave for 4 hours, then gargle.
Inhalations are made using essential oils of eucalyptus, cedar, and fir. A decoction of pine buds and thyme infusion are combined, eucalyptus oil is added and inhalation is carried out with the resulting product.
Rosehip infusion has a pronounced diuretic effect. Anise infusion and linden tea are suitable for oral use for uvulitis.