Malignant formations in the oral cavity cause the patient not only severe discomfort and acute pain, but also significantly affect his social life. Palate cancer in an advanced stage completely changes articulation, which changes speech and prevents normal communication. A disease of this type is in most cases detected in men over forty years of age and is the result of metastasis of malignant tumors located in the immediate vicinity of the head and neck.
Main varieties
Medicine divides palate cancer depending on its location, which greatly facilitates the process of diagnosing the lesion and helps to obtain more accurate information about the nature of the tumor. Based on their location, all neoplasms are divided into:
- Cancer of the hard palate. This malignant formation is found at the border of the oral cavity and nasopharynx. A tumor of this type spreads through the bone structures and eventually spreads to the mucous membrane.
- Cancer of the soft palate. Oncology is actively developing in the mucous layer and muscles of the oral cavity.
Classification by tissue structure
Based on the structure of malignant neoplasms, they are usually divided into three main types:
- Cylindroma (adenocystic carcinoma) begins to form at the border of the glandular tissue. This type of palate cancer develops very quickly and also spreads uncontrollably, which leads to changes in the structure of tissue cells. In this case, metastases quickly spread to neighboring areas;
- Adenocarcinoma is formed from epithelial cells and can be located on any part of the hard and soft palate.
- Squamous cell carcinoma is a pathology that spreads throughout the mucous membrane. It is usually detected with neoplasms in the oral cavity of a malignant nature.
Reasons for appearance
Palate cancer can occur due to the impact of damaging factors on the human oral cavity, which usually include:
- The irritating effect of consuming aggressive components found in cigarettes, smoking mixtures and alcoholic beverages.
- Regular consumption of hot foods, which burn the mucous membranes and change the structure of cells.
- Chronic injuries to the palate as a result of improperly installed dentures.
- In the presence of leukoplakia or papillomatosis - a precancerous condition of the oral cavity. Formations of this type become malignant, that is, they change to a malignant state (the factors described above only encourage this process).
Palate cancer often takes the form of a secondary disease. These include metastases that appear in the presence of cancer cells in the neck or brain.
Diagnostics
If a neoplasm is present, the doctor examines the oral cavity and identifies some features. If an oncological process is suspected, the following procedures are performed:
- X-ray – visualizes the tumor, showing the location of its formation and spread, as well as its approximate composition.
- Biopsy - a thick needle is used to aspirate and the resulting fluid is examined for the presence of cancer cells.
- CT scan - shows other foci of neoplasms, if any.
A blood test is mandatory, which shows changes in the quantitative and qualitative composition of leukocytes and platelets, and an increased ESR.
Based on the results of the study, the doctor makes a diagnosis, on which further treatment will depend.
CT scan shows metastases, if any
Main signs of damage
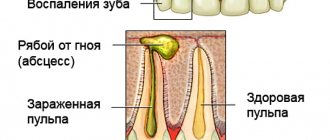
At the initial stage, palate cancer does not provoke any particular discomfort in the patient, but it quickly progresses to a more dangerous form. Sometimes the patient may, when gently touching the palatal area with his tongue, feel a small lump or compaction, around which there is a small cushion.
It is in the presence of such an initial symptom of palate cancer that it is important to see a doctor, otherwise the effect of late diagnosis and treatment will not be high, and the risks of successfully surviving the disease will be low.
As the pathology progresses and malignant cells spread, the tumor increases in size, begins to take control of more and more tissues and goes deeper. In this case, the person already begins to experience characteristic symptoms of palate cancer. When consulting a doctor, many patients complain of:
- pain in the oral cavity (they can move to the ear, temple area and head);
- discomfort when chewing food - a patient with this disease finds it difficult to chew and swallow, his speech apparatus is severely affected;
- a person may constantly feel an unpleasant taste in the mouth (this is usually a foul odor);
- problems with speech – articulation decreases as the tumor spreads, which as a result leads to a change in the mobility of the tongue, while the compaction does not allow the air to move fully;
- increased fatigue, partial or complete lack of appetite, accelerated and causeless weight loss.
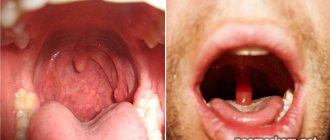
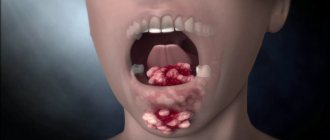
When examining the oral cavity, you can notice compactions, plaques, and ulcers of different sizes and shapes on the soft or hard palate. When neglected, blood comes out of the latter, and the partition between the nose and throat begins to become severely deformed and collapse. This condition causes small pieces of food to enter the nose while eating, as a result of which the patient’s speech becomes increasingly difficult to understand.
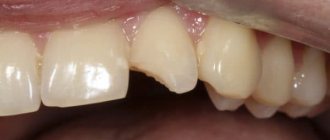
Below is a photo of palate cancer at the initial stage of development. The picture shows obvious changes that the pathology led to.
All signs of cancer of the upper and lower palate only become stronger as the tumor spreads. At the last stage of development of the disease, destruction of all tissues located near the palate occurs.
Oncologist Alexander Zhukovets: 50% of people with oral cancer go to work, but don’t see doctors
Oncologist Alexander Zhukovets: 50% of people with oral cancer go to work, but do not see doctors.
Excessive alcohol consumption and long-term smoking entail an equally dangerous problem - oncology of the oral cavity and larynx. In the early stages, the disease is well treated, but advanced cases are a common cause of disability and rapid death. Oncologist-surgeon Alexander Gennadievich Zhukovets told Komsomolskaya Pravda how to recognize the disease at an early stage, whether a lump in the throat is dangerous and what new trend threatens women’s health.
“There is also a problem with the training of individual doctors. If the doctor missed a tumor in the oral cavity, this is a double disaster, because it cannot be ignored.
Photo: Svyatoslav ZORKY
DOSSIER "KP"
Alexander Gennadievich ZHUKOVETS – Candidate of Medical Sciences, oncologist-surgeon of the highest category. Head of the Department of Oncology of BelMAPO. Member of the Belarusian Society of Oncologists, International Federation of Head and Neck Tumor Specialists (IFHNOS), Russian Partnership of Head and Neck Tumor Specialists (RPHNOS). Author and co-author of more than 300 scientific publications, 16 instructions for use, 15 inventions and patents.
— Alexander Gennadievich, Belarusian men are increasingly afraid of lung cancer, women - of breast cancer. What do they contact you with?
— At the Republican Scientific and Practical Center of Oncology and Medical Radiology named after. Aleksandrov, which is the clinical base of the department, treats all types of tumors. However, if we talk about tumors of the head and neck, these are cancers of the tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, pharynx and larynx.
— If women continue to adopt the bad habits of men, the number of cancers, including those of the oral mucosa, will increase.
Photo: Svyatoslav ZORKY
In 2020 alone, Belarusians received 1,500 cancer diagnoses of these organs, and another 670 cases of laryngeal cancer. Tumors of these organs account for about 5% of the total number of cancer diagnoses.
Unfortunately, stages 1 and 2 - and these are tumors up to two and four centimeters, respectively - in the same 2020 were detected only in 30% of patients, in 70% - stages 3-4. Almost half of the patients have laryngeal cancer at the initial stage - there are more complaints: it is more difficult to breathe, hoarseness develops - this prompts you to consult a doctor earlier. Moreover, examining the oral cavity is easier than examining the larynx.
— Hoarseness prompts you to see a doctor, but a two-centimeter thing in your mouth doesn’t?!
“It’s a matter of the lifestyle of many patients. The incidence of cancer of the oral mucosa is several times higher among smokers and drinkers, who even go to the dentist only if they are very sick.
There is such an indicator - one-year mortality, which means that the patient died in the same year in which he consulted a doctor. In 2015, for patients with cancer of the oral mucosa it was 37%, for patients with laryngeal cancer - 20%.
Women rarely get sick: for every 10 men, there is approximately one woman. Among male patients, 95% are long-term and heavy smokers. Of these, approximately half abuse alcohol. Alcohol itself is not a carcinogen, but it helps the body absorb carcinogens from cigarette smoke.
“Many of those who have developed cancer of the oral mucosa have never sat at a computer in their lives.
Photo: Svyatoslav ZORKY
“There is a problem with the training of individual doctors ”
— The peak incidence occurs at 60-65 years of age, but half of all cases are people of working age. That is, 50% of people with cancer of the oral mucosa go to work, but do not see doctors.
True, there is a problem with the training of individual doctors. If the doctor missed a tumor in the oral cavity, this is a double disaster, because it cannot be ignored.
We hold seminars with dentists and ENT doctors several times a year, there is progress, but the global situation has not yet changed. The Department of Oncology of BelMAPO began to conduct special courses on early diagnosis and treatment of head and neck cancer.
— Women suffer from the same head and neck tumors as men, just much less often.
Photo: Svyatoslav ZORKY
“Many people are ringing the bell, claiming that cancer is getting younger.
— As for head and neck tumors, rejuvenation as such does not occur; the bulk of our patients are people over 50 years of age. The reasons for this are well known: smoking, alcohol abuse, and to a lesser extent the human papillomavirus, plus chronic trauma to the mucous membrane from untreated teeth and bad crowns. Although the bacterial infection itself has nothing to do with the development of cancer of the oral mucosa.
— There are those who are afraid of computer radiation...
“All this can be studied, but many of those who developed cancer of the oral mucosa have never sat at a computer in their lives. The highest incidence of this type of cancer is in India, where chewing mixtures with betel leaves, which is classified by WHO as a carcinogenic factor, is common.
Our morbidity-mortality ratio is better than in Russia and Ukraine. Nevertheless, the incidence is growing, and we are slowly entering the group of countries with a high risk of developing cancer of the oral mucosa.
Early diagnosis is very important: no matter how good the operation we perform, if the case is advanced, the chances of recovery are sharply reduced.
I had a case when a guy about 30 years old went to the clinic with a formation on his cheek. They did a biopsy - it was benign. It's growing - we made a second one. His journey to us lasted three months, he arrived when the tumor already occupied his entire cheek, about eight centimeters in size, like an ulcerated mushroom. We removed everything beautifully, microsurgically moved the flap from another part of his body, and performed radiation therapy. And although there were no metastases at the time of his contact with us, a year after the operation the guy died - the tumor turned out to be too large...
— Early diagnosis is very important: no matter how good the operation we perform, if the case is advanced, the chances of recovery are sharply reduced.
Photo: Svyatoslav ZORKY
“Patients often come when they can no longer eat or drink”
— Is it true that plastic surgery is often indicated after such operations?
— If necessary, we perform plastic surgery on all patients. Everything that is done abroad is done here too. We install dentures and reconstruct the lower jaw using donor and own bone.
We also perform organ-preserving operations, when only the affected part of the organ is removed. For example, with a small tumor of the tongue or larynx. The person then talks normally and eats.
If the operation can seriously impair the function of swallowing, chewing and speech, we perform plastic correction of anatomical defects - we move flaps from another part of the patient’s body or use plastic surgery with local tissues.
At the Republican Scientific and Practical Center of Oncology and Medical Radiology named after. Aleksandrov also conducts international research, including on tumors of the oral mucosa. As a rule, these studies are financed by foreign companies, and they are quite satisfied with the level of training of specialists and the available equipment, despite the fact that their requirements for Belarusian doctor-researchers are the same as for American ones.
— Do many patients refuse treatment?
— In 2015, 1.3% of patients with head and neck tumors refused treatment. But if the patient refuses this year, he will still come next year, and what can we do then? Often such patients come when they can no longer eat or drink.
According to the Health Care Law, we must not hide the diagnosis from the patient, because he can sue. In the USSR they spared the psyche, the word cancer was not used in conversations with the patient, while in the USA and Europe they always spoke directly - there a lot is tied to financial and legal issues.
But even now we don’t have to talk directly, we can talk about the tumor, about the danger, about the possibilities of treatment. There are early tumors that can be easily treated without surgery - for example, stage 1-2 laryngeal cancer. These points need to be discussed with the patient so that he is not afraid. But we also need to take into account the psychological characteristics of some of our patients, especially those who abuse alcohol.
“I know a case where a person was told that he had tongue cancer and needed urgent surgery to remove part of it. After it the person will no longer speak?
- Why? They say even after removal of the larynx and tongue. If a person wants to speak, he will be trained during the rehabilitation period, even after removal of the larynx and vocal cords. Yes, the voice is not the same as before, but it allows you to communicate satisfactorily and even talk on the phone.
Now we also install voice prostheses. After removing the larynx, a hole (shunt) is formed between the esophagus and the tracheostomy (respiratory passage - Ed.), where a silicone prosthesis is installed. It allows you to switch air from the lungs to the oropharynx, the patient closes the shunt, the air is directed along the natural path, and the person speaks quickly and clearly.
https://www.fito.by/
“The wound in the mouth does not heal for two weeks after treatment? Run to the oncologist"
— The number of cancer diagnoses is growing, some people find it convenient to believe that cancer is just a chronic disease...
“They are right, but it is important to remember that this is not an infectious disease. Some are educated people! — are still afraid that cancer will be passed on to them or their children. It's crazy to hear that.
— Maybe they are playing it safe, remembering that not everything has been studied yet?
— No, basically we know how a tumor develops, we just can’t always control these processes yet.
Cancer does not appear suddenly, it is a long process. In the beginning, as a rule, there is a pre-tumor background (precancer) - diseases of the mucous membranes, for example, lichen planus, erythroplakia, etc. It is better to immediately get rid of papillomas on the mucous membranes. These are not the same papillomas that are on the skin - cancer does not develop from these, it is rather a cosmetic defect.
There are chronic ulcers. If a wound in the mouth does not heal for two to three weeks after being prescribed by a dentist or ENT doctor, this is a reason to consult an oncologist.
Tumor markers are now popular, but they are mainly used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. In addition, there are no such markers for the oral mucosa. These tumors are classified as tumors of visual localization; they can be seen during examination. It’s difficult not to see a half-centimeter one during a careful examination - and this is an early cancer that can be cured without surgery!
— Women spend their entire lives, some daily, using foams, hairsprays, and hair sprays, inhaling harmful fumes. How dangerous is this?
“It’s difficult to say how much this affects the occurrence and development of the tumor. Genetically determined cancers most often develop at a young age.
Cancer cells are constantly forming in different parts of the body, including in the oral mucosa. The body has specific mechanisms to control them, but as the body ages, so do the mechanisms. Plus, the body is constantly exposed to carcinogenic factors - both physical and chemical, and all this accumulates.
— What do women most often come to you with?
— Women suffer from the same head and neck tumors as men, just much less often. Tumors of the salivary glands occur somewhat more often in women; the causes of their occurrence are not fully understood.
By the way, a new trend has emerged in the United States: men began to smoke less - their rates of lung cancer decreased, but women took up the habit - and the number of lung cancer among the fairer sex is already growing.
If women continue to adopt the bad habits of men, the number of cancers, including those of the oral mucosa, in women will increase.
So, in the past, lip cancer often occurred in men - it was associated not just with smoking, but with smoking unfiltered cigarettes, respectively, with lip burns. We switched to filter cigarettes and today lip cancer is rare. But they didn’t smoke less, so cancer of the oral cavity and larynx increased and continues to increase...
In addition to tumors of the mucous membranes, squamous cell and basal cell cancer often develop on the skin of the head and neck (up to 80% of all cases of this cancer). Fortunately, patients come forward quite quickly: stage 1-2 is diagnosed in more than 90% of cases. It’s not nice to walk around with a non-healing wound or a tight knot on your face.
Squamous cell carcinoma is more aggressive than basal cell carcinoma, which sometimes grows over years and can reach a size of 1-2 centimeters in a year or two. But if left untreated, it can affect the entire face.
— The incidence is growing, we are slowly entering the group of countries with a high risk of developing cancer of the oral mucosa.
Photo: Svyatoslav ZORKY
— And when there is a lump in the throat, are these also your patients?
- Unlikely. A lump in the throat is different: it is a sensation rather than a real thing.
Such patients sometimes come to us, but they rather need consultation with a psychologist or psychotherapist. Sometimes these are neurological symptoms.
On the other hand, if such sensations are not periodic and are not associated with situational anxiety, it is better to play it safe and at least see an ENT doctor.
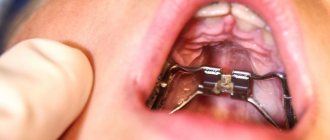
Carrying out diagnostic activities
At an early stage of the development of the disease, it will be very difficult to independently identify it. Only a dentist can accurately diagnose the disease. It is for this reason that you should be examined by this specialist at least several times a year.
At the time when the malignant formation in the oral cavity has already spread over a considerable distance, a preliminary diagnosis can be made after a visual examination.
How to confirm the presence of the disease? To do this, the attending specialist prescribes a number of diagnostic measures to the patient:
- Radiography helps determine all pathological changes in bone structures and tissues located near the oral cavity.
- A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for histological analysis. This procedure is important for determining the changed tumor cells, as well as the stage of its development.
- Blood analysis. This procedure is prescribed to determine the inflammatory process, as well as the symptoms of anemia.
- Radioisotope research, which helps to carefully study the structure of the tumor and its internal structure.
- An ultrasound helps determine cancer metastases and their distance from organs.
If necessary, the patient is prescribed additional modern examinations designed specifically to identify malignant tumors.
Probability of disease recurrence
After intensive therapy, the patient is discharged home. He must be observed by an oncologist on an outpatient basis for a year. It is recommended to visit a doctor for a preventive examination every three months. This will allow you to recognize the symptoms of relapse in time and carry out treatment again.
In case of relapse, a cancerous tumor arises either in the same place or in other organs. Distant metastases are difficult to diagnose if the cancer cells are dormant in the organ they entered through the blood or lymphatic system. The period of remission in this case can be long.
Radiation therapy, chemotherapy and surgery
Radiation therapy is the irradiation of a tumor with x-rays. This type of therapy helps stop the spread of malignant cells. If you start treatment at an early stage, then there is a chance to completely get rid of the disease and return to your previous lifestyle, forgetting about the problem forever. Radiation therapy is most often prescribed before and after surgery.
During chemotherapy there is a direct effect of cytostatic drugs on mutated cells. They can be introduced into the patient's body using droppers or prescribed for oral use. The effect of chemotherapy in the fight against cancer can only be achieved when it is combined with radiation treatment and surgery.
Surgery helps remove the tumor formation and nearby infected soft tissue, as well as bone structures. Most often, after removal surgery, a visible defect remains on the face. In order to eliminate it, additional plastic surgery will have to be performed. At a serious stage of the disease, the doctor prescribes complex treatment, consisting of surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
It is important not only to treat the oral cancer itself, but also to identify metastases. The effect of therapeutic therapy will directly depend on the stage of development of the malignant process in the oral cavity.
Treatment methods
When treating tumors of the oral mucosa, doctors use the entire arsenal of available means:
Depending on the stage of the cancer process, both monomethods and combined cancer treatment are used. At stages 1 and 2 of the disease, radiotherapy has a good effect. The advantage of this method is that after it the appearance of cosmetic or functional defects is almost completely eliminated. In addition, it is relatively easy to accept by patients and has minimal side effects. However, at stages 3 and 4 of the disease, the effectiveness of this treatment method is very low.
Surgeries are required for stages 3 and 4 of oral cancer. The volume of the operation depends on the extent of the process. It is important to excise the tumor completely (within healthy tissue) to eliminate the risk of recurrence. Radical surgery often requires excising muscles or resecting bone, which leads to significant cosmetic defects.
After operations to treat tumors of the oral cavity, in some cases plastic surgery is required. If the patient has difficulty breathing, a tracheostomy (hole in the throat) may be placed.
Among all treatment methods, chemotherapy for oral cancer is the least effective, but it can reduce the volume of the tumor by more than 50%, which greatly facilitates surgery. Since chemotherapy cannot cure this type of cancer, it is used only as one stage of complex treatment.
In cases where a patient with advanced cancer has very little time to live due to metastases or cancer intoxication, palliative therapy comes first in treatment. This treatment is aimed at combating associated complications (bleeding, pain) and is to provide a hopeless patient with a normal quality of life. Palliative therapy uses narcotic painkillers.
The use of fairly aggressive methods in treatment (radiation and chemotherapy) affects the patient’s health. During the course of treatment, the following side effects from medications may occur:
- Stool disorder in the form of profuse diarrhea.
- Constant nausea accompanied by vomiting.
- Baldness.
- Development of immunodeficiency (patients should avoid ARVI during chemoradiation treatment).
During treatment of oncopathology of the oral mucosa, patients need to eat well - the diet should be rich in proteins of both animal and plant origin. If oral nutrition (by mouth) is not possible, food can be administered through a pre-installed tube or intravenously (special mixtures for parenteral nutrition are used).
Preventive measures and forecasts
If the patient consults a doctor in a timely manner, undergoes appropriate diagnostic measures and the diagnosis is established correctly, the doctor will prescribe an effective and comprehensive treatment regimen, which 80 percent guarantees a complete cure for the disease. When determining a tumor at a late stage, in almost 70 percent of patients, metastases appear in the first five years after surgery.
You can significantly reduce the risk of cancer of the oral cavity, including the palate, by leading a healthy lifestyle and giving up bad habits: smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages and hot tea. It is better to limit the consumption of too spicy food, but the food should be fortified and healthy.
It is also important to monitor your health by visiting your dentist annually. This reduces the risk of cancer to a minimum.
Prevention
The main preventive value in the fight against cancer of the oral mucosa is giving up bad habits. You should definitely quit smoking, chewing betel nut, and drinking nasvay. It is recommended to give up alcohol.
Reducing trauma to the cheeks, tongue, and gums also reduces the risk of tumors in the described localization. All teeth must be treated, installed fillings must be processed. If you need prosthetics, you should select the prosthesis very carefully so that it is easy to use and does not cause discomfort.
Foods with irritating effects should be excluded from the diet, and very hot foods should not be consumed. When the first signs and symptoms of oral cancer appear, you should immediately contact a specialist.
To reduce the likelihood of cancer, people employed in hazardous industries should actively use personal protective equipment - protective clothing, respirators.
Regularly, at least once a year, and if precancerous conditions are detected every quarter, you need to undergo preventive examinations with a dentist and oncologist.
Throat lesions and its structure
Sometimes from the palate, cancer cells can spread further and affect other organs, in particular the throat. This is a very vulnerable part of the human body. To begin with, it is important to determine how the throat itself works. This is the colloquial name for the front part of the neck, which is located in front of the spinal column. It is in this area that the paths are located along which oxygen enters the stomach through the delayed path (food also moves along the same path).
In this area, the common path for air and food is divided into two separate ones - the esophagus and the larynx, which then passes into the trachea. In addition, near the throat there are vessels that supply the brain with blood and nearby important nerve plexuses that affect the functioning of the heart. This area also contains one of the most important endocrine glands – the thyroid gland.
The pharynx is the upper part of the throat, which is located above the larynx. According to its physiological structure, it is divided into three sections. The order from top to bottom is as follows:
- nasopharynx;
- oropharynx;
- hypopharynx.
Soft palate - function
Speech
Speech is a very complex process that involves the tongue, lips and palate. These structures produce speech by directing air flow through the mouth to create specific sounds that form words. If a person has a cleft palate or other soft palate disorder, air may escape through the nose and affect speech. Speech may sound nasal or weak, or the person may miss some sounds.
Breath
The soft palate separates the mouth and nose, acting as a barrier between the digestive and respiratory tracts. This feature allows a person to breathe and eat at the same time. However, people cannot swallow and breathe at the same time.
Swallowing
When people swallow, they move food or liquid from the mouth down the esophagus to the stomach. During swallowing, more than 30 muscles and nerves direct food to the stomach instead of the nose or lungs. When a person swallows food or liquid, the soft palate rises to close the opening of the airway.
What types of diseases are there?
Almost all types of laryngeal cancer are squamous cell. If we consider morphology, cancer can be classified into:
- non-keratinizing;
- keratinizing;
- highly differentiated.
Oncology of the non-keratinizing type spreads rapidly and forms a huge number of metastases, and also quickly grows deep into nearby tissues. This type of disease is diagnosed most often.
Typically, a tumor formation is formed in the upper part of the larynx or in the ventricle of the larynx. Often the tumor moves from one part of the larynx to another. Non-keratinizing cancer provokes a decrease in the existing lumen in the larynx, which leads to loss of voice and severe shortness of breath.
In the photo of the initial stage of palate cancer, the first signs of its manifestation are visible.
The second variety is distinguished by its cells, which become keratinized after some time. This type of tumor progresses slowly compared to others. Metastases almost never occur during the disease. In most cases, the keratinizing type of oncology develops in the area of the vocal cords.
In highly differentiated cancer, the pathological process greatly affects healthy tissue. Treatment of this type of pathology is the longest and most difficult.
Factors leading to the development of the disease are the following:
- inhalation of toxins;
- work with hazardous chemicals (production of paints and varnishes, repairs and construction);
- poor nutrition, with too much salt and few vitamins in the food;
- drinking large amounts of alcohol;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- genetic predisposition;
- development of infectious mononucleosis;
- radiation exposure.
Stages of pathology
The international TNM system distinguishes 4 stages of palate cancer:
- Zero (precancer) – single atypical cells that are capable of forming a tumor are determined. There are no metastases.
- First, the tumor measures up to 1 cm in diameter, there are no metastases.
- The second is accompanied by an increase in the tumor up to 3 cm with possible single metastases in nearby tissues.
- Third, the tumor reaches a large size, metastases are found in regional lymph nodes.
- Fourth, the process of metastasis is active, cancer cells are detected in the bone marrow. The prognosis is the most unfavorable.
Large tumors on the palate are not always an advanced form of cancer. This is how benign neoplasms can appear, which are completely treatable and do not pose a threat to health.